Dipropylene Glycol in Industry: Harnessing Its Versatility
JUL 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DPG Background & Objectives
Dipropylene glycol (DPG) has emerged as a versatile chemical compound with a rich history in industrial applications. Its development can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for efficient solvents and intermediates in various manufacturing processes became increasingly apparent. Over the decades, DPG has evolved from a niche product to a widely used industrial chemical, finding its way into diverse sectors such as cosmetics, plastics, and cleaning agents.
The technological evolution of DPG production has been marked by significant milestones. Initially synthesized through the hydration of propylene oxide, the process has undergone numerous refinements to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. Modern production methods often involve catalytic processes that allow for greater control over the isomeric composition of the final product, tailoring it to specific industrial needs.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods for DPG. This trend aligns with the growing global emphasis on green chemistry and reduced environmental impact. Researchers are exploring bio-based feedstocks and novel catalytic systems to create DPG with a lower carbon footprint, addressing the increasing demand for eco-friendly industrial chemicals.
The primary objective in the field of DPG technology is to further enhance its versatility while minimizing environmental impact. This includes improving production efficiency, expanding its application range, and developing new formulations that leverage DPG's unique properties. Researchers aim to unlock novel uses for DPG in emerging industries, such as advanced materials for energy storage or as a platform chemical for sustainable polymer production.
Another critical goal is to optimize DPG's performance in existing applications. This involves fine-tuning its molecular structure and developing specialized grades for specific industrial processes. For instance, in the personal care industry, there is a push to create DPG variants that offer enhanced moisture retention and improved sensory properties in cosmetic formulations.
The technological trajectory of DPG is also influenced by regulatory trends and consumer preferences. As global regulations become more stringent regarding chemical safety and environmental impact, the DPG industry is adapting by investing in research to ensure compliance and to develop alternatives where necessary. This regulatory landscape is shaping the future direction of DPG technology, driving innovation towards safer and more sustainable variants of this versatile compound.
The technological evolution of DPG production has been marked by significant milestones. Initially synthesized through the hydration of propylene oxide, the process has undergone numerous refinements to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. Modern production methods often involve catalytic processes that allow for greater control over the isomeric composition of the final product, tailoring it to specific industrial needs.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods for DPG. This trend aligns with the growing global emphasis on green chemistry and reduced environmental impact. Researchers are exploring bio-based feedstocks and novel catalytic systems to create DPG with a lower carbon footprint, addressing the increasing demand for eco-friendly industrial chemicals.
The primary objective in the field of DPG technology is to further enhance its versatility while minimizing environmental impact. This includes improving production efficiency, expanding its application range, and developing new formulations that leverage DPG's unique properties. Researchers aim to unlock novel uses for DPG in emerging industries, such as advanced materials for energy storage or as a platform chemical for sustainable polymer production.
Another critical goal is to optimize DPG's performance in existing applications. This involves fine-tuning its molecular structure and developing specialized grades for specific industrial processes. For instance, in the personal care industry, there is a push to create DPG variants that offer enhanced moisture retention and improved sensory properties in cosmetic formulations.
The technological trajectory of DPG is also influenced by regulatory trends and consumer preferences. As global regulations become more stringent regarding chemical safety and environmental impact, the DPG industry is adapting by investing in research to ensure compliance and to develop alternatives where necessary. This regulatory landscape is shaping the future direction of DPG technology, driving innovation towards safer and more sustainable variants of this versatile compound.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) has been steadily increasing across various industries due to its versatile properties and wide range of applications. This chemical compound, known for its excellent solvency, low toxicity, and high boiling point, has become an essential ingredient in numerous products and processes.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, DPG has gained significant traction as a solvent and humectant. Its ability to enhance product stability and improve moisture retention has led to its incorporation in a wide array of skincare products, fragrances, and hair care formulations. The growing consumer preference for long-lasting and effective personal care products has further fueled the demand for DPG in this sector.
The paints and coatings industry has also witnessed a surge in DPG usage. As a coalescent agent, DPG aids in film formation and improves the overall performance of water-based paints and coatings. With the increasing focus on environmentally friendly and low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) products, the demand for DPG as a safer alternative to traditional solvents has risen substantially.
In the industrial cleaning and degreasing sector, DPG has emerged as a preferred choice due to its excellent solvency and low volatility. Its effectiveness in removing stubborn stains and grease, coupled with its relatively low environmental impact, has led to its widespread adoption in industrial cleaning formulations and processes.
The plastics industry has also recognized the benefits of DPG as a plasticizer and processing aid. Its compatibility with various polymers and its ability to improve flexibility and durability have made it an important component in the production of plastics and resins. The growing demand for high-performance plastics in automotive, construction, and consumer goods sectors has consequently driven the market for DPG.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry has shown increased interest in DPG as a solvent and stabilizer in drug formulations. Its low toxicity and ability to enhance drug solubility and stability have made it a valuable ingredient in various pharmaceutical products, including oral medications and topical preparations.
The global market for DPG is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by expanding applications and increasing demand from emerging economies. As industries continue to seek sustainable and versatile chemical solutions, DPG's market potential is likely to expand further, with new applications and formulations being developed to harness its unique properties.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, DPG has gained significant traction as a solvent and humectant. Its ability to enhance product stability and improve moisture retention has led to its incorporation in a wide array of skincare products, fragrances, and hair care formulations. The growing consumer preference for long-lasting and effective personal care products has further fueled the demand for DPG in this sector.
The paints and coatings industry has also witnessed a surge in DPG usage. As a coalescent agent, DPG aids in film formation and improves the overall performance of water-based paints and coatings. With the increasing focus on environmentally friendly and low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) products, the demand for DPG as a safer alternative to traditional solvents has risen substantially.
In the industrial cleaning and degreasing sector, DPG has emerged as a preferred choice due to its excellent solvency and low volatility. Its effectiveness in removing stubborn stains and grease, coupled with its relatively low environmental impact, has led to its widespread adoption in industrial cleaning formulations and processes.
The plastics industry has also recognized the benefits of DPG as a plasticizer and processing aid. Its compatibility with various polymers and its ability to improve flexibility and durability have made it an important component in the production of plastics and resins. The growing demand for high-performance plastics in automotive, construction, and consumer goods sectors has consequently driven the market for DPG.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry has shown increased interest in DPG as a solvent and stabilizer in drug formulations. Its low toxicity and ability to enhance drug solubility and stability have made it a valuable ingredient in various pharmaceutical products, including oral medications and topical preparations.
The global market for DPG is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by expanding applications and increasing demand from emerging economies. As industries continue to seek sustainable and versatile chemical solutions, DPG's market potential is likely to expand further, with new applications and formulations being developed to harness its unique properties.
DPG Technical Challenges
Dipropylene glycol (DPG) faces several technical challenges in its industrial applications, despite its versatility. One of the primary issues is its hygroscopic nature, which can lead to moisture absorption during storage and transportation. This property can affect the quality and performance of DPG in various applications, particularly in industries where moisture sensitivity is critical, such as in the production of polyurethanes or as a solvent in personal care products.
Another significant challenge is the potential for thermal degradation at high temperatures. While DPG has a relatively high boiling point, prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures can lead to decomposition, resulting in the formation of unwanted byproducts. This limitation can be particularly problematic in industrial processes that require high-temperature operations, such as in certain coating applications or as a heat transfer fluid.
The purity of DPG is also a concern in many industrial applications. The presence of impurities, even in small quantities, can significantly impact the performance and reliability of products incorporating DPG. Achieving and maintaining high purity levels during production and throughout the supply chain remains a technical challenge, especially as industry standards become increasingly stringent.
Compatibility issues with certain materials pose another technical hurdle. DPG can interact with some plastics and elastomers, potentially causing swelling or degradation of these materials. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration in the selection of storage containers, processing equipment, and end-use applications, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace where material integrity is crucial.
Environmental and health concerns associated with DPG usage present ongoing challenges. While generally considered to have low toxicity, there are still concerns about potential long-term effects of exposure, especially in occupational settings. Additionally, the environmental impact of DPG production and disposal requires continuous monitoring and improvement in manufacturing processes to align with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Lastly, the optimization of DPG production processes remains an area of technical focus. Current methods often involve energy-intensive steps and the use of catalysts that may have environmental implications. Developing more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly production techniques is an ongoing challenge for the industry, particularly as demand for DPG continues to grow across various sectors.
Another significant challenge is the potential for thermal degradation at high temperatures. While DPG has a relatively high boiling point, prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures can lead to decomposition, resulting in the formation of unwanted byproducts. This limitation can be particularly problematic in industrial processes that require high-temperature operations, such as in certain coating applications or as a heat transfer fluid.
The purity of DPG is also a concern in many industrial applications. The presence of impurities, even in small quantities, can significantly impact the performance and reliability of products incorporating DPG. Achieving and maintaining high purity levels during production and throughout the supply chain remains a technical challenge, especially as industry standards become increasingly stringent.
Compatibility issues with certain materials pose another technical hurdle. DPG can interact with some plastics and elastomers, potentially causing swelling or degradation of these materials. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration in the selection of storage containers, processing equipment, and end-use applications, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace where material integrity is crucial.
Environmental and health concerns associated with DPG usage present ongoing challenges. While generally considered to have low toxicity, there are still concerns about potential long-term effects of exposure, especially in occupational settings. Additionally, the environmental impact of DPG production and disposal requires continuous monitoring and improvement in manufacturing processes to align with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Lastly, the optimization of DPG production processes remains an area of technical focus. Current methods often involve energy-intensive steps and the use of catalysts that may have environmental implications. Developing more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly production techniques is an ongoing challenge for the industry, particularly as demand for DPG continues to grow across various sectors.
Current DPG Applications
01 Solvent and carrier in various formulations
Dipropylene glycol is widely used as a solvent and carrier in various formulations due to its excellent solvency properties. It can dissolve a wide range of substances, making it versatile in applications such as cosmetics, personal care products, and industrial formulations. Its ability to blend with both water and oil-based ingredients enhances its utility in creating stable and effective products.- Solvent and carrier in personal care products: Dipropylene glycol is widely used as a solvent and carrier in various personal care products such as cosmetics, fragrances, and skincare formulations. Its versatility lies in its ability to dissolve both water-soluble and oil-soluble ingredients, making it an excellent choice for creating stable and effective product formulations.
- Humectant and moisturizing agent: Dipropylene glycol serves as an effective humectant and moisturizing agent in various applications. It helps to attract and retain moisture, making it valuable in skincare products, hair care formulations, and industrial applications where moisture control is crucial.
- Industrial applications and chemical synthesis: The versatility of dipropylene glycol extends to industrial applications and chemical synthesis. It is used as a raw material in the production of polyurethanes, resins, and other polymers. Additionally, it serves as a reaction medium and intermediate in various chemical processes.
- Cooling and heat transfer applications: Dipropylene glycol is utilized in cooling and heat transfer applications due to its thermal properties. It is employed in antifreeze formulations, hydraulic fluids, and heat transfer fluids, providing efficient temperature control in various industrial and automotive systems.
- Plasticizer and softening agent: The compound acts as a plasticizer and softening agent in various materials. It is used to improve the flexibility and workability of plastics, resins, and other polymeric materials. This property makes it valuable in the production of films, coatings, and other flexible products.
02 Humectant and moisturizing agent
Dipropylene glycol acts as an effective humectant and moisturizing agent in various products. It has the ability to attract and retain moisture, making it valuable in skincare, haircare, and other personal care formulations. This property helps to improve product texture, prevent drying, and enhance the overall efficacy of moisturizing products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Plasticizer in polymer applications
In polymer applications, dipropylene glycol serves as a plasticizer, improving the flexibility and workability of various materials. It can enhance the properties of plastics, resins, and other polymeric substances, making them more pliable and easier to process. This versatility extends to applications in construction materials, automotive parts, and consumer goods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Heat transfer fluid and antifreeze component
Dipropylene glycol is utilized as a heat transfer fluid and antifreeze component in various industrial and automotive applications. Its thermal stability and low freezing point make it suitable for use in cooling systems, heat exchangers, and other temperature control applications. It helps prevent freezing and improves the overall efficiency of thermal management systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Fragrance and flavor carrier
In the fragrance and flavor industry, dipropylene glycol serves as an excellent carrier for various aromatic compounds. Its ability to dissolve and stabilize fragrances and flavors makes it valuable in perfumes, air fresheners, and food additives. It helps to enhance the longevity and dispersion of scents and flavors in different product formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The dipropylene glycol industry is in a mature stage, with a stable global market size estimated at over $1 billion. The technology is well-established, with major players like Dow Chemical, BASF, and LyondellBasell dominating production. China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and GS Caltex are also significant producers in Asia. The market is characterized by incremental innovations in production processes and applications rather than disruptive breakthroughs. Key areas of focus include improving purity levels, developing bio-based alternatives, and expanding into emerging applications like personal care products and pharmaceuticals. Companies like Colgate-Palmolive, Procter & Gamble, and Unilever are driving demand through product formulations.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced processes for the production of dipropylene glycol (DPG) as a byproduct of propylene oxide synthesis. Their technology utilizes a proprietary catalyst system that enhances selectivity towards DPG formation, achieving yields of up to 10% by weight[1]. The company has also implemented an innovative purification process that employs multi-stage distillation and extraction techniques to obtain high-purity DPG (>99.5%)[2]. Additionally, Sinopec has integrated DPG production into their existing petrochemical complexes, leveraging synergies in raw material supply and utility systems to improve overall efficiency[3].
Strengths: Integrated production system, high-purity product, cost-effective. Weaknesses: Byproduct-dependent production, limited flexibility in output volumes.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies has pioneered a direct synthesis route for dipropylene glycol production, bypassing the traditional propylene oxide intermediate. Their process involves the catalytic oxidation of propylene using a novel heterogeneous catalyst system, achieving DPG selectivity of up to 85%[4]. The company has also developed a continuous flow reactor design that enhances heat transfer and reaction control, resulting in improved product consistency and reduced energy consumption[5]. Furthermore, Dow has implemented advanced process control systems utilizing machine learning algorithms to optimize reaction conditions in real-time, leading to a 15% increase in overall process efficiency[6].
Strengths: Direct synthesis route, high selectivity, advanced process control. Weaknesses: Higher initial capital investment, potential catalyst deactivation issues.
DPG Innovations Review
Methods for converting glycerol to propanol
PatentWO2010074841A2
Innovation
- A hydrogenolysis process that includes pretreatment, blending with a base to adjust pH, reaction with specific catalysts (Ni/Re or Co/Pd/Re) under controlled conditions, followed by separation and purification steps to produce high-purity propylene glycol, allowing for efficient conversion of crude glycerol into propylene glycol.
Process for the conversion of glycerol to propylene glycol and amino alcohols
PatentActiveUS20070287865A1
Innovation
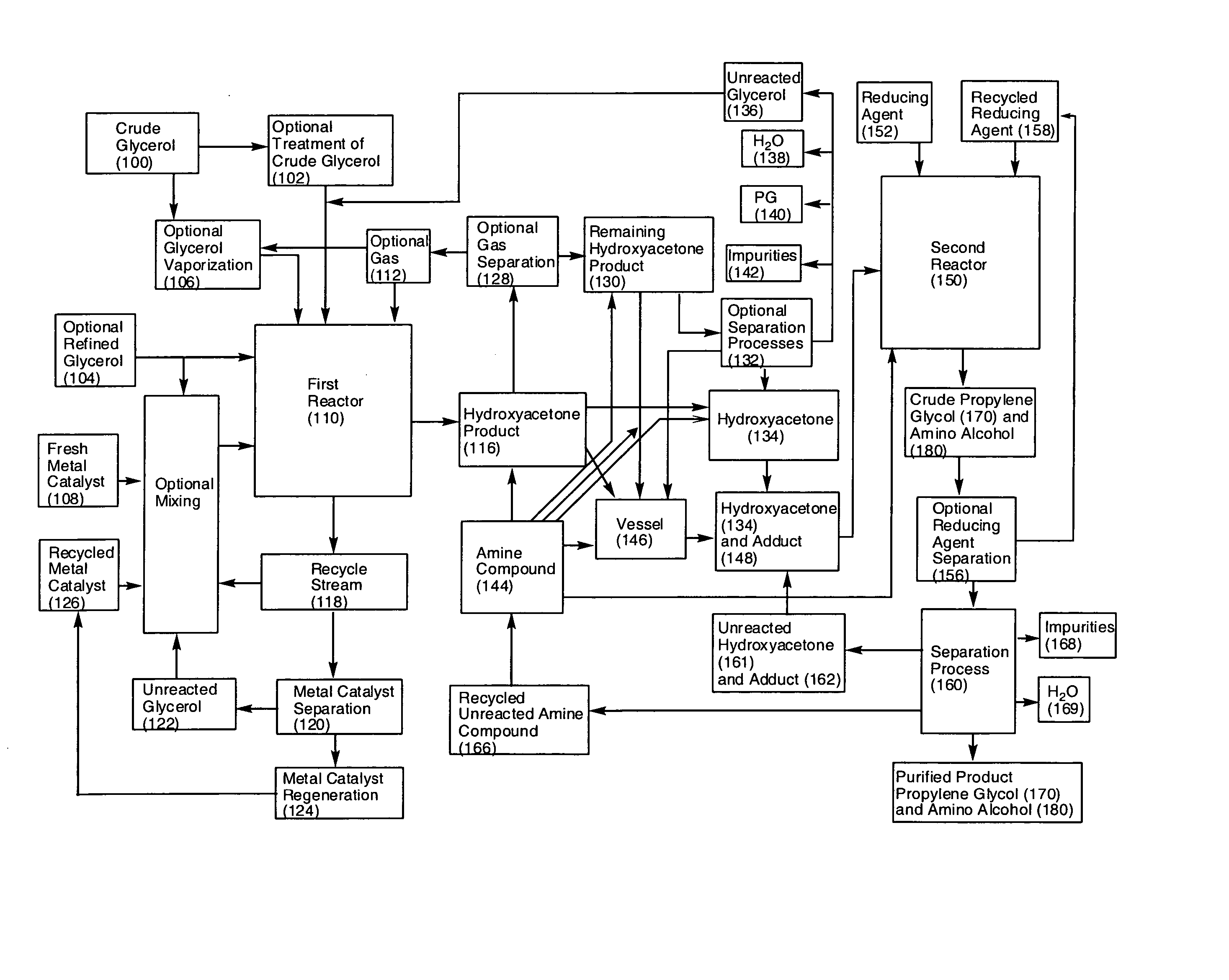
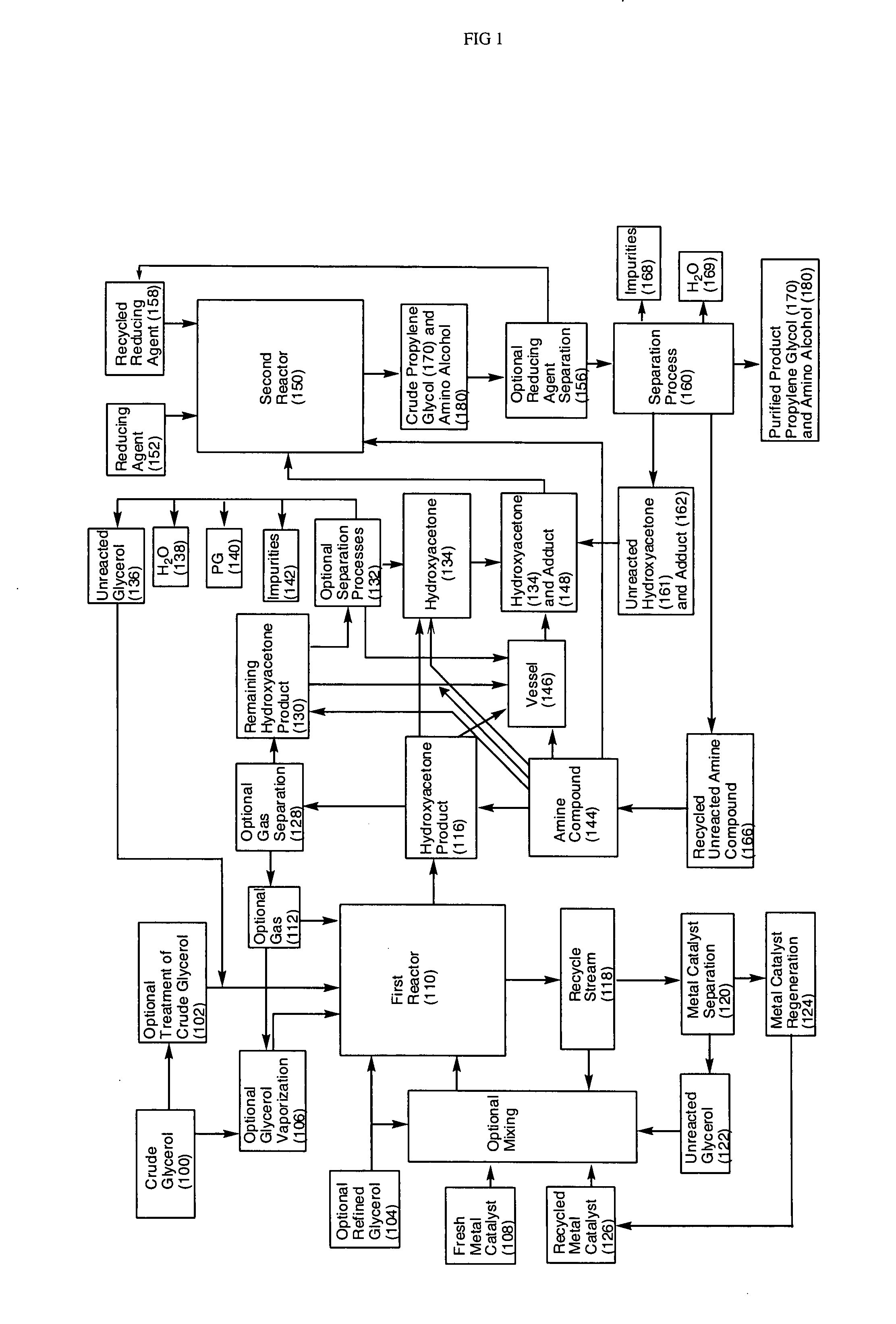
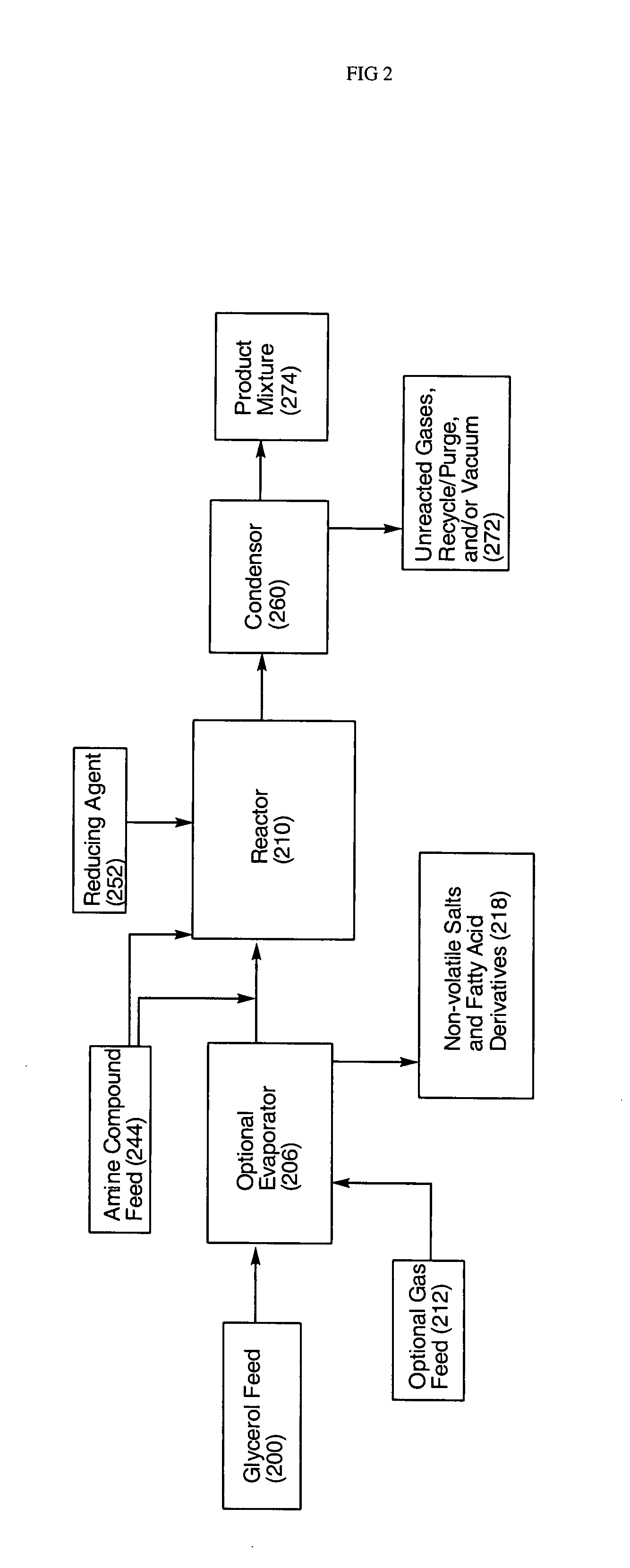
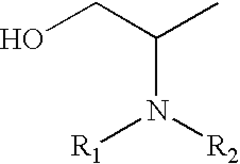
- A process involving the reaction of glycerol with a metal catalyst to produce hydroxyacetone, which is then reduced or reacted with an amine compound to yield a product mixture comprising propylene glycol and an amino alcohol, utilizing a reducing agent to achieve high yields and reduce byproduct formation, allowing for the use of renewable feedstocks.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of dipropylene glycol (DPG) in industrial applications is a crucial consideration for sustainable development. DPG, while versatile and widely used, presents both challenges and opportunities in terms of its ecological footprint. One of the primary environmental concerns associated with DPG is its potential for water pollution. When released into aquatic ecosystems, DPG can contribute to the depletion of dissolved oxygen, potentially harming aquatic life. However, its relatively low toxicity compared to other glycols mitigates some of these risks.
In terms of air quality, DPG has a low vapor pressure, which reduces its potential for atmospheric emissions. This characteristic makes it a preferable choice in many industrial applications where volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are a concern. Nevertheless, the production process of DPG, which typically involves the hydration of propylene oxide, can have significant energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
The biodegradability of DPG is another important environmental factor. Studies have shown that DPG is inherently biodegradable under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. This property ensures that, when released into the environment, DPG does not persist for extended periods, reducing long-term ecological impacts. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, and high concentrations may still pose temporary risks to ecosystems.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental impact of DPG extends beyond its use phase. The production of propylene oxide, a key precursor in DPG synthesis, often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of chlorine-based chemicals, which can have their own environmental implications. Efforts to develop more sustainable production methods, such as the use of renewable feedstocks or more efficient catalytic processes, are ongoing in the industry.
In industrial applications, the use of DPG can contribute to environmental sustainability in several ways. Its effectiveness as a solvent and coupling agent in water-based formulations can reduce the need for more environmentally harmful organic solvents. Additionally, its role in improving the efficiency of heat transfer fluids can lead to energy savings in various industrial processes, indirectly reducing carbon emissions.
The disposal of DPG-containing products and waste streams requires careful management to minimize environmental impact. While DPG itself is not classified as hazardous waste in many jurisdictions, improper disposal can still lead to soil and groundwater contamination. Industrial users are increasingly implementing closed-loop systems and recycling processes to minimize DPG waste and reduce the overall environmental footprint of their operations.
In terms of air quality, DPG has a low vapor pressure, which reduces its potential for atmospheric emissions. This characteristic makes it a preferable choice in many industrial applications where volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are a concern. Nevertheless, the production process of DPG, which typically involves the hydration of propylene oxide, can have significant energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
The biodegradability of DPG is another important environmental factor. Studies have shown that DPG is inherently biodegradable under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. This property ensures that, when released into the environment, DPG does not persist for extended periods, reducing long-term ecological impacts. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, and high concentrations may still pose temporary risks to ecosystems.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental impact of DPG extends beyond its use phase. The production of propylene oxide, a key precursor in DPG synthesis, often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of chlorine-based chemicals, which can have their own environmental implications. Efforts to develop more sustainable production methods, such as the use of renewable feedstocks or more efficient catalytic processes, are ongoing in the industry.
In industrial applications, the use of DPG can contribute to environmental sustainability in several ways. Its effectiveness as a solvent and coupling agent in water-based formulations can reduce the need for more environmentally harmful organic solvents. Additionally, its role in improving the efficiency of heat transfer fluids can lead to energy savings in various industrial processes, indirectly reducing carbon emissions.
The disposal of DPG-containing products and waste streams requires careful management to minimize environmental impact. While DPG itself is not classified as hazardous waste in many jurisdictions, improper disposal can still lead to soil and groundwater contamination. Industrial users are increasingly implementing closed-loop systems and recycling processes to minimize DPG waste and reduce the overall environmental footprint of their operations.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of the industrial use of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG). As a widely used chemical compound, DPG is subject to various regulations and standards across different regions and industries. Understanding and adhering to these regulatory requirements is essential for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users of DPG.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates DPG under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The compound is listed on the TSCA inventory, which means it has been assessed for potential risks to human health and the environment. Companies dealing with DPG must comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements as specified by the EPA.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a role in regulating DPG, particularly in its use in food contact materials and cosmetics. The FDA has approved DPG as an indirect food additive and as a component in certain food packaging materials. For cosmetic applications, DPG must be listed as an ingredient on product labels in accordance with FDA regulations.
In the European Union, DPG falls under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Manufacturers and importers of DPG in quantities of one tonne or more per year are required to register the substance with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). This registration process involves providing detailed information on the properties, uses, and potential risks of DPG.
The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation in the EU also applies to DPG. This regulation ensures that the hazards presented by chemicals are clearly communicated to workers and consumers through classification and labeling. Manufacturers and importers must classify, label, and package DPG according to the harmonized system established by the CLP Regulation.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, also impact the use of DPG in industrial settings. These regulations set permissible exposure limits and require employers to implement appropriate safety measures, including proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and employee training.
Transportation of DPG is subject to regulations governing the shipment of hazardous materials. In the US, the Department of Transportation (DOT) classifies DPG as a Class 9 miscellaneous hazardous material. Shippers must comply with specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements when transporting DPG.
Globally, the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Many countries have adopted GHS standards, which affect the classification, labeling, and safety data sheets for DPG.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations surrounding the disposal and environmental impact of DPG are becoming increasingly stringent. Companies must be aware of local, national, and international regulations regarding waste management and environmental protection when handling and disposing of DPG.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates DPG under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The compound is listed on the TSCA inventory, which means it has been assessed for potential risks to human health and the environment. Companies dealing with DPG must comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements as specified by the EPA.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a role in regulating DPG, particularly in its use in food contact materials and cosmetics. The FDA has approved DPG as an indirect food additive and as a component in certain food packaging materials. For cosmetic applications, DPG must be listed as an ingredient on product labels in accordance with FDA regulations.
In the European Union, DPG falls under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Manufacturers and importers of DPG in quantities of one tonne or more per year are required to register the substance with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). This registration process involves providing detailed information on the properties, uses, and potential risks of DPG.
The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation in the EU also applies to DPG. This regulation ensures that the hazards presented by chemicals are clearly communicated to workers and consumers through classification and labeling. Manufacturers and importers must classify, label, and package DPG according to the harmonized system established by the CLP Regulation.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, also impact the use of DPG in industrial settings. These regulations set permissible exposure limits and require employers to implement appropriate safety measures, including proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and employee training.
Transportation of DPG is subject to regulations governing the shipment of hazardous materials. In the US, the Department of Transportation (DOT) classifies DPG as a Class 9 miscellaneous hazardous material. Shippers must comply with specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements when transporting DPG.
Globally, the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Many countries have adopted GHS standards, which affect the classification, labeling, and safety data sheets for DPG.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations surrounding the disposal and environmental impact of DPG are becoming increasingly stringent. Companies must be aware of local, national, and international regulations regarding waste management and environmental protection when handling and disposing of DPG.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!