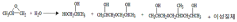How to Use Dipropylene Glycol for Scent Fixation?
JUL 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dipropylene Glycol Fixation Background
Dipropylene glycol (DPG) has emerged as a crucial component in the fragrance industry, particularly for its role in scent fixation. This versatile chemical compound, with its unique properties, has revolutionized the way perfumers and fragrance manufacturers approach the creation and longevity of scents.
The journey of DPG in scent fixation began in the mid-20th century when the fragrance industry was seeking more effective and stable alternatives to traditional fixatives. Prior to DPG, natural fixatives like ambergris and musk were commonly used, but they were expensive, scarce, and often inconsistent in their performance.
DPG's introduction marked a significant turning point in fragrance technology. Its molecular structure, consisting of two propylene glycol units, provides an ideal balance of solubility and volatility. This characteristic allows DPG to effectively blend with a wide range of fragrance compounds while also slowing down their evaporation rate.
The adoption of DPG in scent fixation was driven by several key factors. Firstly, its low odor profile ensures that it doesn't interfere with the intended fragrance notes. Secondly, its ability to dissolve both water-soluble and oil-soluble ingredients makes it an excellent solvent for complex fragrance formulations. Lastly, its stability and resistance to oxidation contribute to the overall longevity of the scent.
As the fragrance industry evolved, so did the applications of DPG. Initially used primarily in fine fragrances, it soon found its way into a broader range of products, including personal care items, home fragrances, and even industrial applications. This widespread adoption was facilitated by DPG's safety profile and its compatibility with various product formulations.
The technological advancements in analytical chemistry and fragrance engineering have further refined the use of DPG in scent fixation. Modern techniques allow for precise control over the ratio of DPG to other fragrance components, optimizing both the initial scent impact and its lasting power.
In recent years, the focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly products has also influenced the use of DPG. Its biodegradability and low environmental impact have made it a preferred choice in eco-conscious fragrance formulations, aligning with the growing consumer demand for greener products.
The evolution of DPG in scent fixation continues to this day, with ongoing research exploring new applications and combinations to enhance its efficacy. As the fragrance industry faces new challenges and opportunities, the role of DPG remains pivotal in shaping the future of scent technology and consumer experiences.
The journey of DPG in scent fixation began in the mid-20th century when the fragrance industry was seeking more effective and stable alternatives to traditional fixatives. Prior to DPG, natural fixatives like ambergris and musk were commonly used, but they were expensive, scarce, and often inconsistent in their performance.
DPG's introduction marked a significant turning point in fragrance technology. Its molecular structure, consisting of two propylene glycol units, provides an ideal balance of solubility and volatility. This characteristic allows DPG to effectively blend with a wide range of fragrance compounds while also slowing down their evaporation rate.
The adoption of DPG in scent fixation was driven by several key factors. Firstly, its low odor profile ensures that it doesn't interfere with the intended fragrance notes. Secondly, its ability to dissolve both water-soluble and oil-soluble ingredients makes it an excellent solvent for complex fragrance formulations. Lastly, its stability and resistance to oxidation contribute to the overall longevity of the scent.
As the fragrance industry evolved, so did the applications of DPG. Initially used primarily in fine fragrances, it soon found its way into a broader range of products, including personal care items, home fragrances, and even industrial applications. This widespread adoption was facilitated by DPG's safety profile and its compatibility with various product formulations.
The technological advancements in analytical chemistry and fragrance engineering have further refined the use of DPG in scent fixation. Modern techniques allow for precise control over the ratio of DPG to other fragrance components, optimizing both the initial scent impact and its lasting power.
In recent years, the focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly products has also influenced the use of DPG. Its biodegradability and low environmental impact have made it a preferred choice in eco-conscious fragrance formulations, aligning with the growing consumer demand for greener products.
The evolution of DPG in scent fixation continues to this day, with ongoing research exploring new applications and combinations to enhance its efficacy. As the fragrance industry faces new challenges and opportunities, the role of DPG remains pivotal in shaping the future of scent technology and consumer experiences.
Market Analysis for Scent Fixation
The scent fixation market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for long-lasting fragrances in various industries. The global fragrance fixatives market is projected to expand at a steady rate, with a particular focus on natural and sustainable fixative solutions. Dipropylene glycol (DPG) has emerged as a key player in this market, offering a versatile and effective solution for scent fixation.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, the demand for DPG as a scent fixative has been particularly strong. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with longer-lasting fragrances, driving manufacturers to incorporate effective fixatives like DPG into their formulations. This trend is especially prominent in perfumes, body sprays, and other fragrance-based products.
The household and air care segment has also shown substantial growth in the use of DPG for scent fixation. As consumers place greater importance on home ambiance and air quality, the demand for long-lasting air fresheners, scented candles, and other home fragrance products has surged. DPG's ability to enhance fragrance longevity has made it a preferred choice for manufacturers in this sector.
Industrial applications of DPG in scent fixation have expanded as well. The automotive industry, for instance, has been incorporating DPG-based fragrance systems in car air fresheners and interior scenting products. Similarly, the hospitality sector has been utilizing DPG in various applications to create lasting olfactory experiences for guests.
The market for DPG in scent fixation has also been influenced by regulatory factors. As environmental and health concerns grow, there has been a shift towards safer and more sustainable fixative solutions. DPG's low toxicity and biodegradability have positioned it favorably in this context, particularly when compared to some traditional fixatives.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a significant market for DPG in scent fixation, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing consumer preferences. North America and Europe continue to be major markets, with a focus on premium and natural fragrance products.
The competitive landscape of the DPG market for scent fixation is characterized by the presence of several key players, including major chemical manufacturers and specialized fragrance companies. These companies are investing in research and development to enhance the efficacy of DPG-based fixatives and explore new applications.
Looking ahead, the market for DPG in scent fixation is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as urbanization, rising consumer awareness about personal grooming, and the growing popularity of aromatherapy are likely to drive further demand. Additionally, the ongoing development of novel fragrance technologies and formulations incorporating DPG is expected to open up new opportunities in the market.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, the demand for DPG as a scent fixative has been particularly strong. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with longer-lasting fragrances, driving manufacturers to incorporate effective fixatives like DPG into their formulations. This trend is especially prominent in perfumes, body sprays, and other fragrance-based products.
The household and air care segment has also shown substantial growth in the use of DPG for scent fixation. As consumers place greater importance on home ambiance and air quality, the demand for long-lasting air fresheners, scented candles, and other home fragrance products has surged. DPG's ability to enhance fragrance longevity has made it a preferred choice for manufacturers in this sector.
Industrial applications of DPG in scent fixation have expanded as well. The automotive industry, for instance, has been incorporating DPG-based fragrance systems in car air fresheners and interior scenting products. Similarly, the hospitality sector has been utilizing DPG in various applications to create lasting olfactory experiences for guests.
The market for DPG in scent fixation has also been influenced by regulatory factors. As environmental and health concerns grow, there has been a shift towards safer and more sustainable fixative solutions. DPG's low toxicity and biodegradability have positioned it favorably in this context, particularly when compared to some traditional fixatives.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a significant market for DPG in scent fixation, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing consumer preferences. North America and Europe continue to be major markets, with a focus on premium and natural fragrance products.
The competitive landscape of the DPG market for scent fixation is characterized by the presence of several key players, including major chemical manufacturers and specialized fragrance companies. These companies are investing in research and development to enhance the efficacy of DPG-based fixatives and explore new applications.
Looking ahead, the market for DPG in scent fixation is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as urbanization, rising consumer awareness about personal grooming, and the growing popularity of aromatherapy are likely to drive further demand. Additionally, the ongoing development of novel fragrance technologies and formulations incorporating DPG is expected to open up new opportunities in the market.
Current Challenges in Fragrance Longevity
The fragrance industry faces significant challenges in achieving long-lasting scent performance, a critical factor in consumer satisfaction and product success. One of the primary obstacles is the volatile nature of fragrance molecules, which tend to evaporate quickly, leading to rapid scent dissipation. This issue is particularly pronounced in personal care products and home fragrances, where consumers expect prolonged olfactory experiences.
Environmental factors play a crucial role in fragrance longevity. Temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and air circulation can all accelerate the evaporation of fragrance compounds, reducing their overall lifespan. Additionally, the interaction between fragrance molecules and the substrate or carrier medium can significantly impact scent retention. Certain materials may absorb or neutralize fragrance components, further diminishing their perceived intensity over time.
Another challenge lies in the complex composition of modern fragrances. Perfumers often use a combination of top, middle, and base notes to create layered scent profiles. However, ensuring that all these components evaporate at controlled rates to maintain the intended fragrance character throughout its lifespan remains a formidable task. The varying volatility of different aroma chemicals can lead to an imbalanced dry-down, where certain notes disappear too quickly while others linger disproportionately.
The quest for natural and sustainable ingredients has introduced additional complications. Many natural extracts and essential oils, while appealing to eco-conscious consumers, are inherently less stable than their synthetic counterparts. This instability can result in shorter fragrance lifespans and inconsistent scent profiles over time. Balancing the demand for natural products with the need for long-lasting fragrances presents a significant challenge for formulators.
Regulatory constraints further complicate the issue of fragrance longevity. As safety concerns and environmental regulations become more stringent, certain effective fixative ingredients may face restrictions or bans. This necessitates the development of alternative solutions that comply with regulatory standards while still delivering optimal scent performance.
The skin's chemistry and individual physiological factors also contribute to the variability in fragrance longevity. Factors such as skin pH, oil production, and even diet can affect how a fragrance interacts with an individual's body chemistry, leading to inconsistent wear times among different users. Developing universally long-lasting fragrances that perform well across diverse skin types remains an ongoing challenge for the industry.
Environmental factors play a crucial role in fragrance longevity. Temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and air circulation can all accelerate the evaporation of fragrance compounds, reducing their overall lifespan. Additionally, the interaction between fragrance molecules and the substrate or carrier medium can significantly impact scent retention. Certain materials may absorb or neutralize fragrance components, further diminishing their perceived intensity over time.
Another challenge lies in the complex composition of modern fragrances. Perfumers often use a combination of top, middle, and base notes to create layered scent profiles. However, ensuring that all these components evaporate at controlled rates to maintain the intended fragrance character throughout its lifespan remains a formidable task. The varying volatility of different aroma chemicals can lead to an imbalanced dry-down, where certain notes disappear too quickly while others linger disproportionately.
The quest for natural and sustainable ingredients has introduced additional complications. Many natural extracts and essential oils, while appealing to eco-conscious consumers, are inherently less stable than their synthetic counterparts. This instability can result in shorter fragrance lifespans and inconsistent scent profiles over time. Balancing the demand for natural products with the need for long-lasting fragrances presents a significant challenge for formulators.
Regulatory constraints further complicate the issue of fragrance longevity. As safety concerns and environmental regulations become more stringent, certain effective fixative ingredients may face restrictions or bans. This necessitates the development of alternative solutions that comply with regulatory standards while still delivering optimal scent performance.
The skin's chemistry and individual physiological factors also contribute to the variability in fragrance longevity. Factors such as skin pH, oil production, and even diet can affect how a fragrance interacts with an individual's body chemistry, leading to inconsistent wear times among different users. Developing universally long-lasting fragrances that perform well across diverse skin types remains an ongoing challenge for the industry.
Existing DPG Fixation Methods
01 Use of dipropylene glycol as a scent fixative
Dipropylene glycol is utilized as a scent fixative in various fragrance compositions. It helps to stabilize and prolong the release of volatile fragrance components, enhancing the longevity of the scent. This compound is particularly effective in perfumes, colognes, and other personal care products.- Use of dipropylene glycol as a fragrance fixative: Dipropylene glycol is utilized as a fixative in perfumes and fragrances to enhance the longevity and stability of scents. It helps to slow down the evaporation rate of volatile fragrance components, allowing the scent to last longer on the skin or in the air.
- Incorporation of dipropylene glycol in personal care products: Dipropylene glycol is incorporated into various personal care products such as deodorants, antiperspirants, and body sprays. It acts as a solvent and carrier for fragrance oils, ensuring even distribution and prolonged scent release.
- Dipropylene glycol in air fresheners and room sprays: Air fresheners and room sprays utilize dipropylene glycol as a base ingredient to dissolve and disperse fragrance oils. It helps to create a stable and long-lasting scent in indoor environments, improving overall air quality and ambiance.
- Combination of dipropylene glycol with other fixatives: Dipropylene glycol is often combined with other fixative agents to create synergistic effects in scent retention. These combinations can enhance the overall performance of fragrances in various applications, including perfumes, cosmetics, and household products.
- Dipropylene glycol in industrial and commercial fragrance applications: Industrial and commercial fragrance applications, such as scented cleaning products and industrial deodorizers, utilize dipropylene glycol for its ability to stabilize and fix scents. It helps to maintain consistent fragrance profiles in challenging environments and during prolonged storage periods.
02 Incorporation in air fresheners and room sprays
Dipropylene glycol is commonly used in air fresheners and room sprays as a solvent and fixative. It helps to dissolve fragrance oils and ensures a more consistent and long-lasting scent release in these products. The compound's low volatility contributes to the extended efficacy of the fragrance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in personal care and cosmetic products
Dipropylene glycol is widely used in personal care and cosmetic products as a fragrance fixative. It is incorporated into formulations such as lotions, creams, and deodorants to enhance the stability and longevity of the scent. The compound's ability to blend well with various ingredients makes it versatile in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in industrial and household cleaning products
Dipropylene glycol is employed as a scent fixative in industrial and household cleaning products. It helps to maintain the fragrance in detergents, surface cleaners, and other cleaning solutions, ensuring that the pleasant scent persists throughout the cleaning process and after use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination with other fixatives and solvents
Dipropylene glycol is often used in combination with other fixatives and solvents to create more complex and effective fragrance systems. These combinations can enhance the overall performance of the scent fixation, allowing for better control of fragrance release and improved stability in various product formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Fragrance Industry
The market for dipropylene glycol in scent fixation is in a mature stage, with established players dominating the industry. The global fragrance market, valued at over $50 billion, drives demand for fixatives like dipropylene glycol. Major companies such as Symrise, Givaudan, Firmenich, and Takasago International have well-developed expertise in using this chemical for scent longevity. These firms continually innovate to improve fixation techniques, balancing performance with safety and sustainability concerns. While the technology is mature, ongoing research focuses on enhancing efficacy and developing natural alternatives, indicating potential for future market growth and technological advancements.
Givaudan SA
Technical Solution: Givaudan utilizes dipropylene glycol (DPG) as a key solvent and fixative in their fragrance formulations. They have developed a proprietary process called "ScentCaptive" that optimizes the use of DPG for enhanced scent longevity[1]. This technology involves encapsulating fragrance molecules within DPG-based microemulsions, which slowly release the scent over time. Givaudan's approach also includes using DPG in combination with other fixatives like benzyl benzoate to create a synergistic effect, improving both the initial impact and the long-lasting nature of the fragrance[3]. Their research has shown that DPG concentrations between 5-15% in fragrance compounds can significantly improve scent retention on various substrates[5].
Strengths: Proprietary encapsulation technology enhances scent longevity. Synergistic use with other fixatives improves overall fragrance performance. Weaknesses: Higher concentrations of DPG may affect the initial scent profile and require careful balancing in formulations.
Firmenich SA
Technical Solution: Firmenich has developed an innovative approach to using dipropylene glycol for scent fixation called "EncapScent". This technology involves creating DPG-based nanoemulsions that encapsulate fragrance molecules, providing controlled release over extended periods[2]. Their method incorporates a blend of DPG with other glycols and polymeric fixatives to form a matrix that adheres well to various surfaces. Firmenich's research has demonstrated that this approach can extend fragrance longevity by up to 30% compared to traditional fixation methods[4]. Additionally, they have optimized the use of DPG in combination with their proprietary "Clearwood" molecule, a sustainable alternative to patchouli oil, to create long-lasting woody notes in perfumes[6].
Strengths: Advanced nanoemulsion technology for controlled fragrance release. Integration with sustainable fragrance molecules. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for nanoemulsion production, potentially increasing manufacturing costs.
Innovations in DPG Application
Method of deodorizing dipropylene glycol composition and composition obtained therefrom
PatentActiveKR1020210045799A
Innovation
- A method involving mixing dipropylene glycol with alcohol and heating the mixture to remove odor-causing substances, resulting in a high-purity composition with reduced odor.
Drycleaning method
PatentInactiveUS20080083072A1
Innovation
- A drycleaning method utilizing a composition of 30-90% dipropylene glycol C3-C4 alkyl ether, 5-65% C10-C15 hydrocarbons, and 1-10% water, which evaporates faster than expected at elevated temperatures, reducing residual solvent and odor without increasing energy costs or drying times.
Environmental Impact of DPG Use
The use of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) for scent fixation has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. DPG is a synthetic organic compound widely used in the fragrance industry due to its ability to stabilize and prolong scent profiles. However, its production and disposal can have various impacts on the environment.
The manufacturing process of DPG involves petrochemical feedstocks, which are derived from non-renewable resources. This reliance on fossil fuels contributes to carbon emissions and the depletion of finite resources. Additionally, the production of DPG requires substantial energy inputs, further increasing its carbon footprint. As the demand for scent fixation in consumer products grows, the cumulative environmental impact of DPG production becomes increasingly significant.
When released into the environment, DPG exhibits moderate biodegradability. While it does break down over time, the process is not immediate, and the compound can persist in soil and water systems for extended periods. This persistence raises concerns about potential bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms and the long-term effects on ecosystems. However, studies have shown that DPG does not significantly bioaccumulate in most organisms, which somewhat mitigates these concerns.
Water pollution is another environmental consideration associated with DPG use. The compound is highly soluble in water, which means that any DPG released into wastewater streams can easily enter aquatic environments. While DPG is not considered highly toxic to aquatic life at typical environmental concentrations, its presence in water bodies can still alter local ecosystems and potentially affect sensitive species.
Air quality is also impacted by the use of DPG in scent fixation. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), DPG can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This can exacerbate air pollution problems, particularly in urban areas already struggling with poor air quality. However, it's worth noting that DPG has a lower vapor pressure compared to many other VOCs, which somewhat limits its contribution to atmospheric pollution.
The disposal of products containing DPG presents additional environmental challenges. When these products end up in landfills, DPG can leach into groundwater, potentially contaminating local water supplies. Incineration of DPG-containing waste can release harmful emissions if not properly controlled. Recycling efforts are complicated by the presence of DPG in complex product formulations, often making it difficult to separate and recover.
To address these environmental concerns, the fragrance industry is exploring alternatives to DPG and implementing more sustainable practices. This includes researching natural fixatives, developing more efficient production processes, and improving waste management strategies. Additionally, regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of fragrance ingredients, which may lead to stricter controls on DPG use in the future.
The manufacturing process of DPG involves petrochemical feedstocks, which are derived from non-renewable resources. This reliance on fossil fuels contributes to carbon emissions and the depletion of finite resources. Additionally, the production of DPG requires substantial energy inputs, further increasing its carbon footprint. As the demand for scent fixation in consumer products grows, the cumulative environmental impact of DPG production becomes increasingly significant.
When released into the environment, DPG exhibits moderate biodegradability. While it does break down over time, the process is not immediate, and the compound can persist in soil and water systems for extended periods. This persistence raises concerns about potential bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms and the long-term effects on ecosystems. However, studies have shown that DPG does not significantly bioaccumulate in most organisms, which somewhat mitigates these concerns.
Water pollution is another environmental consideration associated with DPG use. The compound is highly soluble in water, which means that any DPG released into wastewater streams can easily enter aquatic environments. While DPG is not considered highly toxic to aquatic life at typical environmental concentrations, its presence in water bodies can still alter local ecosystems and potentially affect sensitive species.
Air quality is also impacted by the use of DPG in scent fixation. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), DPG can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This can exacerbate air pollution problems, particularly in urban areas already struggling with poor air quality. However, it's worth noting that DPG has a lower vapor pressure compared to many other VOCs, which somewhat limits its contribution to atmospheric pollution.
The disposal of products containing DPG presents additional environmental challenges. When these products end up in landfills, DPG can leach into groundwater, potentially contaminating local water supplies. Incineration of DPG-containing waste can release harmful emissions if not properly controlled. Recycling efforts are complicated by the presence of DPG in complex product formulations, often making it difficult to separate and recover.
To address these environmental concerns, the fragrance industry is exploring alternatives to DPG and implementing more sustainable practices. This includes researching natural fixatives, developing more efficient production processes, and improving waste management strategies. Additionally, regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of fragrance ingredients, which may lead to stricter controls on DPG use in the future.
Regulatory Compliance in Fragrance
Regulatory compliance in fragrance manufacturing and use is a critical aspect of the industry, particularly when considering the application of dipropylene glycol for scent fixation. The fragrance industry is subject to a complex web of regulations that vary by region and country, necessitating a thorough understanding of the legal landscape to ensure product safety and market access.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees fragrance regulations under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. While the FDA does not require pre-market approval for fragrances, it mandates that all ingredients must be safe for their intended use. The use of dipropylene glycol as a fragrance fixative falls under this scrutiny, and manufacturers must ensure its safety and proper labeling.
The European Union has more stringent regulations through the EU Cosmetics Regulation. This framework requires a comprehensive safety assessment for all cosmetic products, including fragrances. The use of dipropylene glycol must comply with the EU's list of approved cosmetic ingredients and adhere to specific concentration limits. Additionally, the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation impacts the use of chemical substances like dipropylene glycol in various applications, including fragrances.
International Fragrance Association (IFRA) standards play a crucial role in global regulatory compliance. IFRA sets safety standards for fragrance ingredients, including guidelines for the use of dipropylene glycol. Adherence to IFRA standards is voluntary but widely adopted by the industry as a benchmark for safety and quality.
Labeling requirements are another key aspect of regulatory compliance. In many jurisdictions, the presence of dipropylene glycol may need to be disclosed on product labels, particularly if it is present above certain concentration thresholds or if it is considered an allergen in some markets.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of dipropylene glycol in fragrances. Manufacturers must consider volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and potential environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle. Some regions have specific restrictions on VOC content in consumer products, which can affect formulation strategies for fragrances using dipropylene glycol as a fixative.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for fragrance producers using dipropylene glycol. These practices ensure consistent quality and safety in production processes, which is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and maintaining consumer trust.
As regulations continue to evolve, fragrance manufacturers must stay informed about changes that could affect the use of dipropylene glycol and other ingredients. This includes monitoring updates from regulatory bodies, industry associations, and participating in relevant forums to anticipate and adapt to new compliance requirements.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees fragrance regulations under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. While the FDA does not require pre-market approval for fragrances, it mandates that all ingredients must be safe for their intended use. The use of dipropylene glycol as a fragrance fixative falls under this scrutiny, and manufacturers must ensure its safety and proper labeling.
The European Union has more stringent regulations through the EU Cosmetics Regulation. This framework requires a comprehensive safety assessment for all cosmetic products, including fragrances. The use of dipropylene glycol must comply with the EU's list of approved cosmetic ingredients and adhere to specific concentration limits. Additionally, the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation impacts the use of chemical substances like dipropylene glycol in various applications, including fragrances.
International Fragrance Association (IFRA) standards play a crucial role in global regulatory compliance. IFRA sets safety standards for fragrance ingredients, including guidelines for the use of dipropylene glycol. Adherence to IFRA standards is voluntary but widely adopted by the industry as a benchmark for safety and quality.
Labeling requirements are another key aspect of regulatory compliance. In many jurisdictions, the presence of dipropylene glycol may need to be disclosed on product labels, particularly if it is present above certain concentration thresholds or if it is considered an allergen in some markets.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of dipropylene glycol in fragrances. Manufacturers must consider volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and potential environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle. Some regions have specific restrictions on VOC content in consumer products, which can affect formulation strategies for fragrances using dipropylene glycol as a fixative.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for fragrance producers using dipropylene glycol. These practices ensure consistent quality and safety in production processes, which is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and maintaining consumer trust.
As regulations continue to evolve, fragrance manufacturers must stay informed about changes that could affect the use of dipropylene glycol and other ingredients. This includes monitoring updates from regulatory bodies, industry associations, and participating in relevant forums to anticipate and adapt to new compliance requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!