Dipropylene Glycol's Critical Role in Cosmetic Preservation
JUL 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DPG in Cosmetics: Background and Objectives
Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) has emerged as a critical component in cosmetic preservation, marking a significant evolution in the beauty and personal care industry. The journey of DPG in cosmetics began in the mid-20th century when formulators sought alternatives to traditional preservatives that could offer both efficacy and improved safety profiles. As consumer demand for gentler, more natural products grew, the industry faced the challenge of maintaining product integrity while meeting these new expectations.
The primary objective of incorporating DPG into cosmetic formulations is to enhance the preservation system's effectiveness while minimizing potential irritation and allergic reactions associated with conventional preservatives. DPG acts as a multifunctional ingredient, serving not only as a preservative booster but also as a solvent and humectant. This versatility has made it an invaluable tool for cosmetic chemists striving to create stable, long-lasting products that meet stringent safety standards.
The technical evolution of DPG in cosmetics has been driven by several factors, including regulatory changes, advancements in microbiology, and a deeper understanding of skin-product interactions. Initially used primarily as a solvent, researchers discovered its synergistic effects with traditional preservatives, leading to its widespread adoption as a preservation enhancer. This discovery allowed formulators to reduce the concentration of more aggressive preservatives while maintaining product safety and stability.
As the cosmetic industry continues to innovate, the role of DPG has expanded beyond mere preservation. Its ability to improve the solubility of active ingredients and enhance product texture has made it a key component in a wide range of cosmetic products, from skincare to color cosmetics. The ongoing research into DPG's properties and interactions with other ingredients aims to further optimize its use, potentially leading to even more effective and consumer-friendly formulations.
The technical goals associated with DPG in cosmetic preservation are multifaceted. Researchers and formulators are working to:
1. Enhance the synergistic effects between DPG and other preservatives to create more robust preservation systems.
2. Develop methodologies for incorporating DPG into challenging formulations, such as natural and organic products.
3. Investigate the potential of DPG to replace certain controversial preservatives entirely, without compromising product safety or efficacy.
4. Explore the long-term effects of DPG on product stability and shelf life across various cosmetic categories.
As we look to the future, the role of DPG in cosmetic preservation is expected to evolve further. With increasing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly formulations, research is likely to focus on optimizing DPG usage to minimize environmental impact while maximizing its preservative efficacy. This ongoing evolution underscores the critical importance of DPG in shaping the future of cosmetic preservation technologies.
The primary objective of incorporating DPG into cosmetic formulations is to enhance the preservation system's effectiveness while minimizing potential irritation and allergic reactions associated with conventional preservatives. DPG acts as a multifunctional ingredient, serving not only as a preservative booster but also as a solvent and humectant. This versatility has made it an invaluable tool for cosmetic chemists striving to create stable, long-lasting products that meet stringent safety standards.
The technical evolution of DPG in cosmetics has been driven by several factors, including regulatory changes, advancements in microbiology, and a deeper understanding of skin-product interactions. Initially used primarily as a solvent, researchers discovered its synergistic effects with traditional preservatives, leading to its widespread adoption as a preservation enhancer. This discovery allowed formulators to reduce the concentration of more aggressive preservatives while maintaining product safety and stability.
As the cosmetic industry continues to innovate, the role of DPG has expanded beyond mere preservation. Its ability to improve the solubility of active ingredients and enhance product texture has made it a key component in a wide range of cosmetic products, from skincare to color cosmetics. The ongoing research into DPG's properties and interactions with other ingredients aims to further optimize its use, potentially leading to even more effective and consumer-friendly formulations.
The technical goals associated with DPG in cosmetic preservation are multifaceted. Researchers and formulators are working to:
1. Enhance the synergistic effects between DPG and other preservatives to create more robust preservation systems.
2. Develop methodologies for incorporating DPG into challenging formulations, such as natural and organic products.
3. Investigate the potential of DPG to replace certain controversial preservatives entirely, without compromising product safety or efficacy.
4. Explore the long-term effects of DPG on product stability and shelf life across various cosmetic categories.
As we look to the future, the role of DPG in cosmetic preservation is expected to evolve further. With increasing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly formulations, research is likely to focus on optimizing DPG usage to minimize environmental impact while maximizing its preservative efficacy. This ongoing evolution underscores the critical importance of DPG in shaping the future of cosmetic preservation technologies.
Market Analysis for DPG-based Preservatives
The market for DPG-based preservatives in cosmetics has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for safer and more effective personal care products. Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) has emerged as a critical component in cosmetic preservation due to its multifunctional properties and compatibility with a wide range of formulations.
The global cosmetic preservatives market, which includes DPG-based solutions, was valued at approximately $1.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.8 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.5%. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising awareness of product safety and the need for extended shelf life in cosmetic and personal care products.
DPG-based preservatives have gained traction in the market due to their effectiveness against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds. They offer excellent stability in various pH ranges and are compatible with most cosmetic ingredients, making them versatile for use in a wide array of products such as skincare, haircare, and color cosmetics.
The market demand for DPG-based preservatives is particularly strong in regions with stringent regulations on cosmetic ingredients, such as the European Union and North America. These regions have implemented strict guidelines on the use of traditional preservatives, leading formulators to seek alternative solutions like DPG-based systems.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market for DPG-based preservatives, driven by the booming cosmetics industry in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. The increasing disposable income and changing consumer preferences in these regions are fueling the demand for premium and natural-inspired cosmetic products, which often rely on advanced preservation systems.
The clean beauty trend has also contributed to the growing market for DPG-based preservatives. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with minimal synthetic ingredients, and DPG's ability to enhance the efficacy of natural preservatives aligns well with this trend. This has led to a surge in demand for DPG in formulations marketed as "clean" or "natural-inspired."
Key players in the DPG-based preservatives market include major chemical companies and specialized cosmetic ingredient suppliers. These companies are investing in research and development to create innovative preservation systems that leverage DPG's properties while meeting evolving regulatory requirements and consumer preferences.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as the potential for skin sensitization in some individuals and the push for completely natural preservation systems may impact the growth of DPG-based preservatives. However, ongoing research into optimizing DPG formulations and combining them with other natural ingredients is expected to address these concerns and further expand market opportunities.
The global cosmetic preservatives market, which includes DPG-based solutions, was valued at approximately $1.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.8 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.5%. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising awareness of product safety and the need for extended shelf life in cosmetic and personal care products.
DPG-based preservatives have gained traction in the market due to their effectiveness against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds. They offer excellent stability in various pH ranges and are compatible with most cosmetic ingredients, making them versatile for use in a wide array of products such as skincare, haircare, and color cosmetics.
The market demand for DPG-based preservatives is particularly strong in regions with stringent regulations on cosmetic ingredients, such as the European Union and North America. These regions have implemented strict guidelines on the use of traditional preservatives, leading formulators to seek alternative solutions like DPG-based systems.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market for DPG-based preservatives, driven by the booming cosmetics industry in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. The increasing disposable income and changing consumer preferences in these regions are fueling the demand for premium and natural-inspired cosmetic products, which often rely on advanced preservation systems.
The clean beauty trend has also contributed to the growing market for DPG-based preservatives. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with minimal synthetic ingredients, and DPG's ability to enhance the efficacy of natural preservatives aligns well with this trend. This has led to a surge in demand for DPG in formulations marketed as "clean" or "natural-inspired."
Key players in the DPG-based preservatives market include major chemical companies and specialized cosmetic ingredient suppliers. These companies are investing in research and development to create innovative preservation systems that leverage DPG's properties while meeting evolving regulatory requirements and consumer preferences.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as the potential for skin sensitization in some individuals and the push for completely natural preservation systems may impact the growth of DPG-based preservatives. However, ongoing research into optimizing DPG formulations and combining them with other natural ingredients is expected to address these concerns and further expand market opportunities.
Current Challenges in Cosmetic Preservation
The cosmetics industry faces several significant challenges in preserving products effectively while meeting consumer demands for safety and sustainability. One of the primary concerns is the increasing resistance of microorganisms to traditional preservatives. As bacteria and fungi evolve, they develop mechanisms to withstand commonly used preservatives, necessitating higher concentrations or new formulations to maintain product integrity.
Another challenge is the growing consumer preference for "natural" and "clean" beauty products. This trend has led to a demand for preservative systems that are perceived as more natural, despite the fact that many synthetic preservatives have proven safety records. Formulators must balance efficacy with consumer perception, often leading to compromises in preservation strategies.
Regulatory pressures also pose significant challenges. Different regions have varying regulations on permissible preservatives and their concentrations. For instance, the European Union's stringent regulations on preservatives like parabens have forced manufacturers to reformulate products for global markets, increasing complexity and costs.
The quest for multifunctional ingredients has intensified, with formulators seeking preservatives that not only protect against microbial growth but also offer additional benefits such as moisturization or antioxidant properties. This demand for dual-purpose ingredients complicates the preservation process, as these compounds may not be as effective as dedicated preservatives.
Water activity in cosmetic formulations presents another challenge. Many modern cosmetic products aim for high water content to provide hydration benefits, but this increases the risk of microbial contamination. Balancing water content with effective preservation becomes a delicate task for formulators.
The rise of waterless and anhydrous formulations, while potentially reducing the need for preservatives, introduces new challenges in ensuring product stability and preventing oxidation. These formulations often require different preservation strategies and may be more susceptible to certain types of degradation.
Lastly, the challenge of preserving natural and organic cosmetics is particularly acute. These products often contain botanical ingredients that can introduce additional microbial contaminants and provide nutrients for microbial growth. Finding preservative systems that are both effective and compatible with natural and organic certifications remains an ongoing challenge for the industry.
Another challenge is the growing consumer preference for "natural" and "clean" beauty products. This trend has led to a demand for preservative systems that are perceived as more natural, despite the fact that many synthetic preservatives have proven safety records. Formulators must balance efficacy with consumer perception, often leading to compromises in preservation strategies.
Regulatory pressures also pose significant challenges. Different regions have varying regulations on permissible preservatives and their concentrations. For instance, the European Union's stringent regulations on preservatives like parabens have forced manufacturers to reformulate products for global markets, increasing complexity and costs.
The quest for multifunctional ingredients has intensified, with formulators seeking preservatives that not only protect against microbial growth but also offer additional benefits such as moisturization or antioxidant properties. This demand for dual-purpose ingredients complicates the preservation process, as these compounds may not be as effective as dedicated preservatives.
Water activity in cosmetic formulations presents another challenge. Many modern cosmetic products aim for high water content to provide hydration benefits, but this increases the risk of microbial contamination. Balancing water content with effective preservation becomes a delicate task for formulators.
The rise of waterless and anhydrous formulations, while potentially reducing the need for preservatives, introduces new challenges in ensuring product stability and preventing oxidation. These formulations often require different preservation strategies and may be more susceptible to certain types of degradation.
Lastly, the challenge of preserving natural and organic cosmetics is particularly acute. These products often contain botanical ingredients that can introduce additional microbial contaminants and provide nutrients for microbial growth. Finding preservative systems that are both effective and compatible with natural and organic certifications remains an ongoing challenge for the industry.
DPG-based Preservation Solutions
01 Use of dipropylene glycol as a preservative
Dipropylene glycol is utilized as a preservative in various formulations due to its antimicrobial properties. It helps extend the shelf life of products by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. This compound is particularly useful in cosmetics, personal care products, and industrial applications.- Use of dipropylene glycol as a preservative: Dipropylene glycol is utilized as a preservative in various formulations due to its antimicrobial properties. It helps extend the shelf life of products by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. This compound is particularly effective in water-based formulations and is often used in cosmetics, personal care products, and industrial applications.
- Combination with other preservatives: Dipropylene glycol is frequently combined with other preservatives to enhance its effectiveness and broaden the spectrum of antimicrobial activity. This synergistic approach allows for lower concentrations of individual preservatives while maintaining optimal preservation. Common combinations include parabens, phenoxyethanol, and organic acids.
- Application in personal care and cosmetic products: Dipropylene glycol is widely used as a preservative in personal care and cosmetic products. Its low toxicity and skin-friendly properties make it suitable for use in lotions, creams, shampoos, and other beauty products. It helps maintain product integrity and prevents contamination during use and storage.
- Preservation of industrial and household products: Dipropylene glycol is employed as a preservative in various industrial and household products. It is effective in preventing microbial growth in paints, cleaning solutions, and other water-based formulations. This helps maintain product quality and extends the usable life of these products.
- Formulation considerations and stability: When using dipropylene glycol as a preservative, formulators must consider factors such as pH, temperature stability, and compatibility with other ingredients. Proper formulation ensures optimal preservative efficacy and product stability. Additionally, the concentration of dipropylene glycol must be carefully controlled to meet regulatory requirements and ensure product safety.
02 Combination with other preservatives
Dipropylene glycol is often combined with other preservatives to enhance its effectiveness and broaden the spectrum of antimicrobial activity. This synergistic approach allows for lower concentrations of individual preservatives while maintaining optimal preservation. Common combinations include parabens, phenoxyethanol, and organic acids.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in personal care and cosmetic products
Dipropylene glycol is widely used in personal care and cosmetic products as a preservative and solvent. It helps maintain product stability, prevents microbial contamination, and enhances the solubility of other ingredients. This compound is found in various formulations such as lotions, creams, shampoos, and makeup products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial and pharmaceutical applications
Beyond personal care products, dipropylene glycol is utilized as a preservative in industrial and pharmaceutical applications. It helps prevent microbial growth in various formulations, including lubricants, paints, and medications. The compound's low toxicity and broad compatibility make it suitable for diverse preservation needs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The use of dipropylene glycol as a preservative is subject to environmental and safety regulations. Research focuses on optimizing its concentration to ensure effective preservation while minimizing potential risks. Studies evaluate its biodegradability, toxicity profile, and potential for skin irritation to ensure safe and sustainable use in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cosmetic Preservation
The competitive landscape for Dipropylene Glycol's role in cosmetic preservation is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing innovation. The global cosmetics industry, valued at over $380 billion, drives demand for effective preservatives. Major companies like L'Oréal, Shiseido, and Beiersdorf are investing in research and development to enhance preservation techniques. Emerging players such as ActivOn and Plant Advanced Technologies are focusing on natural and alternative preservation methods. The technology's maturity is evident in widespread adoption, but there's a trend towards more sustainable and skin-friendly solutions, pushing companies to innovate continuously in this space.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed advanced formulations incorporating Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) as a key ingredient in their cosmetic preservation systems. Their approach involves using DPG in combination with other preservatives to create synergistic effects, enhancing the overall preservation efficacy while minimizing the concentration of individual components. L'Oréal's research has shown that DPG can act as a solvent and enhance the penetration of other preservatives, allowing for a more uniform distribution throughout the product[1]. Additionally, they have explored the use of DPG in water-in-oil emulsions, where its hygroscopic properties help maintain product stability and prevent microbial growth in the aqueous phase[3].
Strengths: Synergistic preservation system, enhanced efficacy with lower concentrations of individual preservatives. Weaknesses: May require careful formulation to balance preservation and sensory properties.
Shiseido Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shiseido has pioneered the use of Dipropylene Glycol in their cosmetic formulations, focusing on its multifunctional properties. Their approach leverages DPG's ability to act as both a humectant and a solvent, contributing to product stability and sensory qualities while supporting preservation. Shiseido's research has demonstrated that DPG can enhance the solubility of certain active ingredients, improving their efficacy and stability in complex formulations[2]. They have also developed techniques to use DPG in conjunction with natural preservatives, aligning with the growing consumer demand for "clean" beauty products. Shiseido's formulations often incorporate DPG at concentrations ranging from 3-5%, which they have found to be optimal for balancing preservation needs with product performance[4].
Strengths: Multifunctional use of DPG, improved product stability and ingredient solubility. Weaknesses: May face challenges in marketing products with synthetic ingredients to "clean beauty" consumers.
Innovations in DPG Formulations
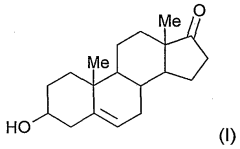
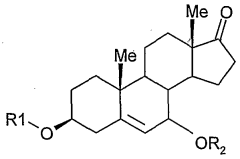
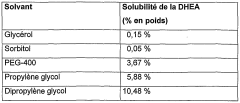
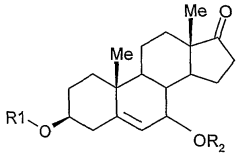
Composition containing a steroid and a glycol
PatentWO2003011244A1
Innovation
- Incorporating dipropylene glycol as a solubilizer for DHEA and its derivatives, which can be mixed at various temperatures to prevent recrystallization and enhance solubility, allowing for stable and effective topical formulations without compromising cosmetic properties.
Viscous Cosmetic Item
PatentInactiveUS20090162130A1
Innovation
- A viscous cosmetic item with a container featuring an elastic application part, an inclined application face, and a cylinder-shaped supply pipe with a diameter of 1.7 to 2.2 mm, along with a viscous cosmetic material having viscosities of 19000 mPa·s or greater at rest and 11000 mPa·s or less at higher shear rates, and incorporating 0.2 wt % or more of dipropylene glycol as an antiseptic agent to prevent contamination.
Regulatory Framework for Cosmetic Preservatives
The regulatory framework for cosmetic preservatives, including Dipropylene Glycol (DPG), is a complex and evolving landscape that varies across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees cosmetic regulations under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and the Fair Packaging and Labeling Act. While the FDA does not specifically approve preservatives for use in cosmetics, it requires that products be safe for consumers under customary conditions of use.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework is more stringent. The EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 governs the use of preservatives in cosmetic products. This regulation includes a positive list of approved preservatives in Annex V, which specifies the maximum concentrations and conditions of use. Although DPG is not listed as a preservative in Annex V, it is often used as a solvent and humectant in cosmetic formulations.
Japan's regulatory system for cosmetics is governed by the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare maintains a list of approved ingredients, including preservatives, for use in cosmetic products. Similar to the EU, Japan has specific regulations on the types and concentrations of preservatives allowed in cosmetics.
International organizations also play a role in shaping the regulatory landscape. The International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) is a voluntary group of cosmetic regulatory authorities from the United States, Japan, the European Union, and Canada. This group works towards aligning regulatory policies and promoting global harmonization in cosmetic regulations.
The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR), an independent expert panel, evaluates the safety of cosmetic ingredients used in the United States. While not a regulatory body, its findings are often considered by the FDA and industry professionals. The CIR has reviewed the safety of DPG and concluded that it is safe for use in cosmetic products at current concentrations.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the concept of "preservation systems" rather than individual preservatives. This approach recognizes that ingredients like DPG, while not classified as preservatives, can contribute to the overall preservation of a product. This shift in perspective is influencing how regulations are developed and applied to cosmetic formulations.
As concerns about certain preservatives grow, there is a trend towards stricter regulations and increased transparency in ingredient labeling. Many regulatory bodies are requiring more detailed information on product labels, including the disclosure of preservatives and their concentrations. This trend is likely to continue, potentially impacting the use and regulation of ingredients like DPG in cosmetic preservation systems.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework is more stringent. The EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 governs the use of preservatives in cosmetic products. This regulation includes a positive list of approved preservatives in Annex V, which specifies the maximum concentrations and conditions of use. Although DPG is not listed as a preservative in Annex V, it is often used as a solvent and humectant in cosmetic formulations.
Japan's regulatory system for cosmetics is governed by the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare maintains a list of approved ingredients, including preservatives, for use in cosmetic products. Similar to the EU, Japan has specific regulations on the types and concentrations of preservatives allowed in cosmetics.
International organizations also play a role in shaping the regulatory landscape. The International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) is a voluntary group of cosmetic regulatory authorities from the United States, Japan, the European Union, and Canada. This group works towards aligning regulatory policies and promoting global harmonization in cosmetic regulations.
The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR), an independent expert panel, evaluates the safety of cosmetic ingredients used in the United States. While not a regulatory body, its findings are often considered by the FDA and industry professionals. The CIR has reviewed the safety of DPG and concluded that it is safe for use in cosmetic products at current concentrations.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the concept of "preservation systems" rather than individual preservatives. This approach recognizes that ingredients like DPG, while not classified as preservatives, can contribute to the overall preservation of a product. This shift in perspective is influencing how regulations are developed and applied to cosmetic formulations.
As concerns about certain preservatives grow, there is a trend towards stricter regulations and increased transparency in ingredient labeling. Many regulatory bodies are requiring more detailed information on product labels, including the disclosure of preservatives and their concentrations. This trend is likely to continue, potentially impacting the use and regulation of ingredients like DPG in cosmetic preservation systems.
Environmental Impact of DPG Usage
The environmental impact of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) usage in cosmetic preservation is a critical consideration for the beauty industry. As a widely used solvent and preservative, DPG's environmental footprint extends from its production to its disposal, affecting various ecological systems.
DPG production primarily relies on petrochemical processes, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing of DPG involves the reaction of propylene oxide with water, a process that requires significant energy input and may result in the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled.
In terms of biodegradability, DPG demonstrates relatively favorable characteristics compared to some other synthetic preservatives. Studies have shown that DPG can be biodegraded by microorganisms in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, albeit at varying rates depending on environmental factors. This biodegradability reduces the long-term accumulation of DPG in ecosystems, mitigating potential chronic environmental impacts.
Water pollution is another concern associated with DPG usage. When cosmetic products containing DPG are washed off or disposed of, they can enter wastewater systems and potentially reach natural water bodies. While DPG is generally considered to have low aquatic toxicity, high concentrations in water can still affect aquatic organisms and disrupt ecosystem balance.
The persistence of DPG in the environment is relatively low due to its biodegradability and volatility. However, its widespread use in cosmetics and other industries means that there is a constant influx of DPG into the environment, which may lead to localized accumulation in areas with high cosmetic product usage or manufacturing facilities.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of DPG include improving production efficiency to reduce energy consumption and emissions, implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste, and developing more sustainable alternatives. Some companies are exploring bio-based sources for DPG production, which could potentially reduce its carbon footprint.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of cosmetic ingredients, including preservatives like DPG. This has led to more stringent requirements for environmental risk assessments and encouraged the development of greener preservation methods. The cosmetic industry is responding by investing in research for eco-friendly alternatives and optimizing formulations to minimize DPG usage while maintaining product efficacy and safety.
DPG production primarily relies on petrochemical processes, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing of DPG involves the reaction of propylene oxide with water, a process that requires significant energy input and may result in the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled.
In terms of biodegradability, DPG demonstrates relatively favorable characteristics compared to some other synthetic preservatives. Studies have shown that DPG can be biodegraded by microorganisms in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, albeit at varying rates depending on environmental factors. This biodegradability reduces the long-term accumulation of DPG in ecosystems, mitigating potential chronic environmental impacts.
Water pollution is another concern associated with DPG usage. When cosmetic products containing DPG are washed off or disposed of, they can enter wastewater systems and potentially reach natural water bodies. While DPG is generally considered to have low aquatic toxicity, high concentrations in water can still affect aquatic organisms and disrupt ecosystem balance.
The persistence of DPG in the environment is relatively low due to its biodegradability and volatility. However, its widespread use in cosmetics and other industries means that there is a constant influx of DPG into the environment, which may lead to localized accumulation in areas with high cosmetic product usage or manufacturing facilities.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of DPG include improving production efficiency to reduce energy consumption and emissions, implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste, and developing more sustainable alternatives. Some companies are exploring bio-based sources for DPG production, which could potentially reduce its carbon footprint.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of cosmetic ingredients, including preservatives like DPG. This has led to more stringent requirements for environmental risk assessments and encouraged the development of greener preservation methods. The cosmetic industry is responding by investing in research for eco-friendly alternatives and optimizing formulations to minimize DPG usage while maintaining product efficacy and safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!