Dolby Vision’s Role in Enhancing Broadcast Journalism
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dolby Vision Evolution
Dolby Vision has undergone a remarkable evolution since its inception, transforming the landscape of visual technology in broadcast journalism. Initially introduced in 2014, Dolby Vision was primarily focused on enhancing the viewing experience for cinema and high-end home entertainment systems. However, its potential for improving broadcast quality quickly became apparent, leading to its adoption in the broadcasting industry.
The early stages of Dolby Vision's evolution in broadcast journalism were characterized by limited implementation due to hardware constraints and the need for specialized equipment. As technology advanced, Dolby Vision began to find its way into professional-grade cameras and production tools, allowing for capture and processing of high dynamic range (HDR) content directly at the source.
A significant milestone in Dolby Vision's evolution was the development of real-time encoding capabilities. This breakthrough enabled live broadcast of Dolby Vision content, a crucial feature for news and sports coverage. The ability to deliver HDR content in real-time opened up new possibilities for enhancing the visual quality of breaking news, live events, and on-location reporting.
As Dolby Vision matured, it began to address the challenges specific to broadcast journalism. The technology was refined to handle diverse lighting conditions encountered in news gathering, from bright outdoor scenes to dimly lit indoor environments. This adaptability proved invaluable for journalists working in varied and often unpredictable settings.
The evolution of Dolby Vision also saw the development of more efficient compression techniques. These advancements allowed for the transmission of high-quality HDR content over existing broadcast infrastructure without significantly increasing bandwidth requirements. This was particularly important for news organizations operating within the constraints of traditional broadcast channels.
In recent years, Dolby Vision has expanded its reach beyond traditional broadcast mediums. The technology has been optimized for streaming platforms, enabling news organizations to deliver HDR content across a wide range of devices, from smart TVs to mobile phones. This multi-platform compatibility has become increasingly important as news consumption habits shift towards digital and on-demand formats.
The latest iterations of Dolby Vision have also focused on improving workflow integration within broadcast environments. Software-based solutions and cloud processing capabilities have made it easier for news organizations to incorporate Dolby Vision into their existing production pipelines without extensive hardware overhauls.
As Dolby Vision continues to evolve, its role in broadcast journalism is expected to grow further. Future developments may include enhanced AI-driven scene analysis for optimal HDR rendering, improved compatibility with emerging display technologies, and even more efficient encoding methods to support ultra-high-resolution broadcasts.
The early stages of Dolby Vision's evolution in broadcast journalism were characterized by limited implementation due to hardware constraints and the need for specialized equipment. As technology advanced, Dolby Vision began to find its way into professional-grade cameras and production tools, allowing for capture and processing of high dynamic range (HDR) content directly at the source.
A significant milestone in Dolby Vision's evolution was the development of real-time encoding capabilities. This breakthrough enabled live broadcast of Dolby Vision content, a crucial feature for news and sports coverage. The ability to deliver HDR content in real-time opened up new possibilities for enhancing the visual quality of breaking news, live events, and on-location reporting.
As Dolby Vision matured, it began to address the challenges specific to broadcast journalism. The technology was refined to handle diverse lighting conditions encountered in news gathering, from bright outdoor scenes to dimly lit indoor environments. This adaptability proved invaluable for journalists working in varied and often unpredictable settings.
The evolution of Dolby Vision also saw the development of more efficient compression techniques. These advancements allowed for the transmission of high-quality HDR content over existing broadcast infrastructure without significantly increasing bandwidth requirements. This was particularly important for news organizations operating within the constraints of traditional broadcast channels.
In recent years, Dolby Vision has expanded its reach beyond traditional broadcast mediums. The technology has been optimized for streaming platforms, enabling news organizations to deliver HDR content across a wide range of devices, from smart TVs to mobile phones. This multi-platform compatibility has become increasingly important as news consumption habits shift towards digital and on-demand formats.
The latest iterations of Dolby Vision have also focused on improving workflow integration within broadcast environments. Software-based solutions and cloud processing capabilities have made it easier for news organizations to incorporate Dolby Vision into their existing production pipelines without extensive hardware overhauls.
As Dolby Vision continues to evolve, its role in broadcast journalism is expected to grow further. Future developments may include enhanced AI-driven scene analysis for optimal HDR rendering, improved compatibility with emerging display technologies, and even more efficient encoding methods to support ultra-high-resolution broadcasts.
Broadcast Market Demand
The broadcast market has witnessed a significant shift towards high-quality content delivery, driven by the increasing demand for immersive viewing experiences. Dolby Vision, with its advanced HDR technology, has emerged as a key player in meeting this demand, particularly in the realm of broadcast journalism. The market for enhanced visual experiences in news and current affairs programming has grown substantially, as viewers seek more engaging and lifelike representations of world events.
Research indicates that broadcasters adopting Dolby Vision technology have seen a notable increase in viewer engagement and retention. This trend is particularly pronounced in news segments featuring complex visual elements, such as weather reports, data visualizations, and on-location coverage. The technology's ability to render a wider range of colors and contrast levels has proven especially valuable in accurately depicting challenging lighting conditions often encountered in field reporting.
Consumer surveys reveal a growing preference for news channels that offer superior picture quality, with many viewers citing enhanced visual clarity as a factor in their choice of news sources. This preference has led to a competitive advantage for broadcasters who have invested in Dolby Vision-enabled equipment and infrastructure. The technology's impact is not limited to traditional television broadcasts; streaming platforms offering news content have also seen increased subscriber interest in Dolby Vision-enabled programming.
The demand for Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism extends beyond consumer preferences, influencing production workflows and equipment choices within the industry. News organizations are increasingly investing in cameras, editing suites, and transmission equipment compatible with Dolby Vision, recognizing the technology's potential to elevate the quality of their output. This shift has created a ripple effect in the broadcast equipment market, with manufacturers racing to integrate Dolby Vision capabilities into their product lines.
Furthermore, the adoption of Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism has opened new avenues for storytelling and information presentation. The technology's enhanced dynamic range allows for more nuanced visual narratives, particularly in documentaries and investigative reports where atmospheric elements play a crucial role in conveying the story's context. This has led to a reevaluation of visual storytelling techniques within the journalism community, with many professionals exploring innovative ways to leverage the technology's capabilities.
As the broadcast market continues to evolve, the demand for Dolby Vision in journalism is expected to grow further. Industry analysts project an increase in Dolby Vision-enabled content across various news formats, from breaking news coverage to in-depth analytical programs. This trend is likely to drive further investment in compatible infrastructure and talent development, shaping the future landscape of broadcast journalism.
Research indicates that broadcasters adopting Dolby Vision technology have seen a notable increase in viewer engagement and retention. This trend is particularly pronounced in news segments featuring complex visual elements, such as weather reports, data visualizations, and on-location coverage. The technology's ability to render a wider range of colors and contrast levels has proven especially valuable in accurately depicting challenging lighting conditions often encountered in field reporting.
Consumer surveys reveal a growing preference for news channels that offer superior picture quality, with many viewers citing enhanced visual clarity as a factor in their choice of news sources. This preference has led to a competitive advantage for broadcasters who have invested in Dolby Vision-enabled equipment and infrastructure. The technology's impact is not limited to traditional television broadcasts; streaming platforms offering news content have also seen increased subscriber interest in Dolby Vision-enabled programming.
The demand for Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism extends beyond consumer preferences, influencing production workflows and equipment choices within the industry. News organizations are increasingly investing in cameras, editing suites, and transmission equipment compatible with Dolby Vision, recognizing the technology's potential to elevate the quality of their output. This shift has created a ripple effect in the broadcast equipment market, with manufacturers racing to integrate Dolby Vision capabilities into their product lines.
Furthermore, the adoption of Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism has opened new avenues for storytelling and information presentation. The technology's enhanced dynamic range allows for more nuanced visual narratives, particularly in documentaries and investigative reports where atmospheric elements play a crucial role in conveying the story's context. This has led to a reevaluation of visual storytelling techniques within the journalism community, with many professionals exploring innovative ways to leverage the technology's capabilities.
As the broadcast market continues to evolve, the demand for Dolby Vision in journalism is expected to grow further. Industry analysts project an increase in Dolby Vision-enabled content across various news formats, from breaking news coverage to in-depth analytical programs. This trend is likely to drive further investment in compatible infrastructure and talent development, shaping the future landscape of broadcast journalism.
HDR Challenges in News
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology presents significant challenges in the realm of news broadcasting, particularly when implementing Dolby Vision. The fast-paced nature of news production and live broadcasting creates unique hurdles for HDR implementation.
One of the primary challenges is the need for real-time HDR processing. News content often requires immediate transmission, leaving little time for extensive post-production color grading. This necessitates the development of efficient, automated HDR workflows that can deliver high-quality results without introducing delays in the broadcasting pipeline.
Another critical issue is the variability of lighting conditions in news environments. Unlike controlled studio settings, field reporting often occurs in unpredictable lighting situations. This can lead to extreme contrasts and exposure variations, which HDR systems must accurately capture and reproduce. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata capabilities can potentially address this challenge, but implementing these features in live broadcasting scenarios remains complex.
The integration of HDR technology with existing Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) infrastructure also poses significant challenges. Many news organizations operate with a mix of HDR and SDR equipment, necessitating seamless conversion between the two formats. This requirement for backward compatibility adds another layer of complexity to the implementation of Dolby Vision in news broadcasting.
Furthermore, the diverse range of display devices used by viewers presents additional challenges. News content must be optimized for viewing on everything from high-end HDR televisions to standard mobile devices. Ensuring consistent quality and accurate color representation across this spectrum of devices is a formidable task.
The cost of upgrading to HDR-capable equipment is another significant barrier for many news organizations. Implementing Dolby Vision requires substantial investments in cameras, production equipment, and transmission infrastructure. This financial burden can be particularly challenging for smaller news outlets or those in developing markets.
Lastly, there is the challenge of training and adapting workflows. News production teams need to be educated on HDR technology, color grading techniques, and the specific requirements of Dolby Vision. This learning curve can initially slow down production processes and requires a significant investment in staff training and development.
One of the primary challenges is the need for real-time HDR processing. News content often requires immediate transmission, leaving little time for extensive post-production color grading. This necessitates the development of efficient, automated HDR workflows that can deliver high-quality results without introducing delays in the broadcasting pipeline.
Another critical issue is the variability of lighting conditions in news environments. Unlike controlled studio settings, field reporting often occurs in unpredictable lighting situations. This can lead to extreme contrasts and exposure variations, which HDR systems must accurately capture and reproduce. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata capabilities can potentially address this challenge, but implementing these features in live broadcasting scenarios remains complex.
The integration of HDR technology with existing Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) infrastructure also poses significant challenges. Many news organizations operate with a mix of HDR and SDR equipment, necessitating seamless conversion between the two formats. This requirement for backward compatibility adds another layer of complexity to the implementation of Dolby Vision in news broadcasting.
Furthermore, the diverse range of display devices used by viewers presents additional challenges. News content must be optimized for viewing on everything from high-end HDR televisions to standard mobile devices. Ensuring consistent quality and accurate color representation across this spectrum of devices is a formidable task.
The cost of upgrading to HDR-capable equipment is another significant barrier for many news organizations. Implementing Dolby Vision requires substantial investments in cameras, production equipment, and transmission infrastructure. This financial burden can be particularly challenging for smaller news outlets or those in developing markets.
Lastly, there is the challenge of training and adapting workflows. News production teams need to be educated on HDR technology, color grading techniques, and the specific requirements of Dolby Vision. This learning curve can initially slow down production processes and requires a significant investment in staff training and development.
Current Dolby Solutions
01 High Dynamic Range (HDR) and Wide Color Gamut
Dolby Vision technology enhances image quality by implementing HDR and wide color gamut capabilities. This allows for a broader range of colors and improved contrast, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images with greater detail in both bright and dark areas.- High Dynamic Range (HDR) Technology: Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance image quality by expanding the range of both contrast and color. This results in brighter highlights, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut, providing a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience.
- Dynamic Metadata Processing: Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata processing to optimize image quality on a frame-by-frame or scene-by-scene basis. This allows for precise control over brightness, contrast, and color, ensuring that each frame is displayed at its best possible quality.
- Color Mapping and Gamut Expansion: The technology incorporates advanced color mapping and gamut expansion techniques to reproduce a wider range of colors more accurately. This results in more vibrant and true-to-life images, with smoother color gradients and reduced banding artifacts.
- Display-Specific Optimization: Dolby Vision adapts its output to the specific capabilities of each display device, ensuring optimal image quality across a wide range of screens. This includes adjusting brightness, contrast, and color to match the display's peak luminance and color gamut capabilities.
- Content Creation and Mastering Tools: The technology provides content creators with specialized tools for mastering and grading content in Dolby Vision. These tools enable precise control over the final image quality, ensuring that the creator's intent is preserved across different viewing devices and environments.
02 Dynamic Metadata Processing
Dolby Vision utilizes dynamic metadata to optimize image quality on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis. This adaptive approach ensures that each image is displayed with the best possible contrast, brightness, and color settings, enhancing overall visual quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Display Calibration and Optimization
The technology incorporates advanced display calibration and optimization techniques to ensure consistent image quality across different devices and viewing environments. This includes adjusting for ambient light conditions and display capabilities to maintain the intended visual experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 Content Mapping and Tone Mapping
Dolby Vision employs sophisticated content mapping and tone mapping algorithms to adapt the original content to various display capabilities. This ensures optimal image quality on a wide range of devices, from high-end TVs to mobile screens, while preserving the creator's intent.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enhanced Color Bit Depth
The technology supports higher color bit depths, typically up to 12 bits per color channel. This increased color precision allows for smoother color gradients and reduces banding artifacts, contributing to overall improved image quality and more accurate color reproduction.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism is evolving rapidly, with the market still in its growth phase. As the demand for high-quality visual experiences in news broadcasting increases, the market size is expected to expand significantly. Major players like LG Electronics, Samsung Electronics, and Sony Group are at the forefront of implementing Dolby Vision technology in their broadcast equipment and displays. These companies, along with others like Toshiba and Philips, are investing heavily in R&D to enhance their Dolby Vision capabilities. The technology's maturity is advancing, with Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp. continuously refining and expanding its applications in the broadcast sector, potentially reshaping the future of television news presentation.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG has embraced Dolby Vision technology in its broadcast-related products, particularly in its OLED and NanoCell TV lineups. These TVs support Dolby Vision IQ, an advanced version of the technology that adjusts HDR performance based on ambient light conditions[6]. For broadcast journalism, this means that news content can be viewed optimally in various lighting environments, from bright living rooms to dimly lit bedrooms. LG has also incorporated Dolby Vision into its professional monitors used in broadcast studios, ensuring that news producers can accurately assess and edit HDR content[7].
Strengths: Wide range of consumer and professional products supporting Dolby Vision, enhancing both production and viewing experiences. Weaknesses: Heavy reliance on OLED technology, which may have limitations in very bright viewing environments.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: While Samsung has not adopted Dolby Vision, it has developed its own HDR10+ technology, which competes with Dolby Vision in the broadcast and consumer electronics space. HDR10+ uses dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision, allowing for frame-by-frame optimization of brightness and color[8]. For broadcast journalism, HDR10+ enables high-quality HDR content delivery without the licensing fees associated with Dolby Vision. Samsung has implemented this technology across its QLED TV lineup and has partnered with various content creators and broadcasters to promote HDR10+ adoption[9].
Strengths: Proprietary HDR technology with no licensing fees, wide adoption in Samsung's product ecosystem. Weaknesses: Less widespread adoption compared to Dolby Vision, potentially limiting compatibility with some broadcast equipment.
Core Dolby Patents
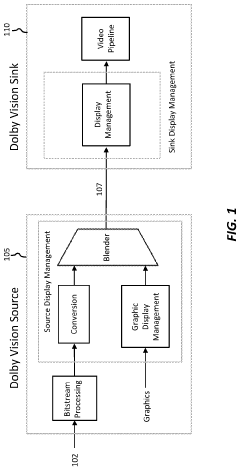
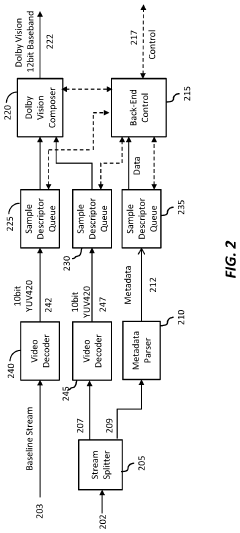
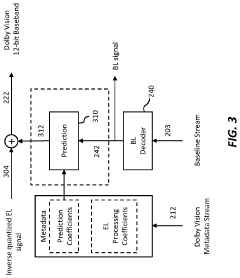
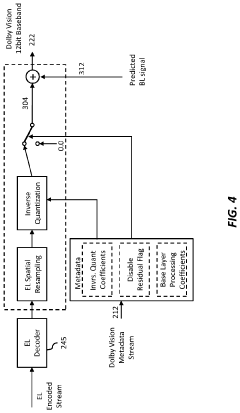
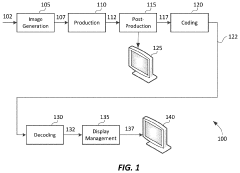
Layered representation and delivery of high dynamic range video
PatentActiveUS20190373290A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a layered representation and delivery system for HDR video, utilizing Dolby Vision technology, which includes a base layer and enhancement layer, along with metadata processing to reconstruct HDR signals, ensuring seamless playback on compatible displays.
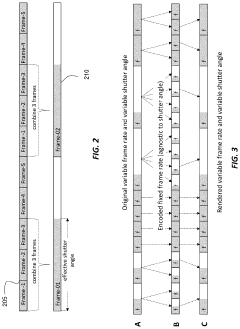
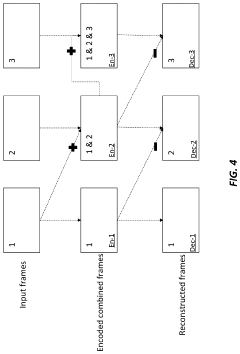
Frame-rate scalable video coding
PatentActiveUS11936888B1
Innovation
- The development of frame-rate scalable video coding techniques that allow for the encoding and decoding of video content at various frame rates and shutter angles, enabling the creation of a single version of HDR content that can be rendered compatible with a range of devices by combining and duplicating frames, while signaling metadata for efficient processing.
Regulatory Compliance
The implementation of Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism must adhere to a complex web of regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) plays a crucial role in setting standards for broadcast technologies. While the FCC has not yet established specific regulations for HDR content, broadcasters utilizing Dolby Vision must ensure compliance with existing rules regarding signal quality, closed captioning, and accessibility features.
In the European Union, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has developed standards for HDR and Wide Color Gamut (WCG) technologies, including Dolby Vision. Broadcasters must align their implementations with these standards to ensure interoperability and maintain consistent quality across different devices and platforms.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has also published recommendations for HDR systems in broadcast and broadband television production. These guidelines, such as ITU-R BT.2100, provide a framework for implementing HDR technologies like Dolby Vision in a standardized manner across international markets.
Content creators and broadcasters must navigate copyright and licensing issues when incorporating Dolby Vision into their workflows. This includes obtaining proper licenses from Dolby Laboratories and ensuring that all content displayed using the technology complies with relevant intellectual property laws.
Data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, may also come into play when Dolby Vision-enabled devices collect and process viewer data for content optimization or personalization purposes. Broadcasters and device manufacturers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard user privacy and comply with these regulations.
As the adoption of Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism continues to grow, industry stakeholders must remain vigilant about evolving regulatory landscapes. This includes monitoring proposed changes to broadcast standards, participating in public consultations, and adapting their technologies and practices to meet new requirements as they emerge.
Broadcasters should also consider voluntary industry standards and best practices, such as those developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) in North America, to ensure that their Dolby Vision implementations align with broader industry trends and expectations.
In the European Union, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has developed standards for HDR and Wide Color Gamut (WCG) technologies, including Dolby Vision. Broadcasters must align their implementations with these standards to ensure interoperability and maintain consistent quality across different devices and platforms.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has also published recommendations for HDR systems in broadcast and broadband television production. These guidelines, such as ITU-R BT.2100, provide a framework for implementing HDR technologies like Dolby Vision in a standardized manner across international markets.
Content creators and broadcasters must navigate copyright and licensing issues when incorporating Dolby Vision into their workflows. This includes obtaining proper licenses from Dolby Laboratories and ensuring that all content displayed using the technology complies with relevant intellectual property laws.
Data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, may also come into play when Dolby Vision-enabled devices collect and process viewer data for content optimization or personalization purposes. Broadcasters and device manufacturers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard user privacy and comply with these regulations.
As the adoption of Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism continues to grow, industry stakeholders must remain vigilant about evolving regulatory landscapes. This includes monitoring proposed changes to broadcast standards, participating in public consultations, and adapting their technologies and practices to meet new requirements as they emerge.
Broadcasters should also consider voluntary industry standards and best practices, such as those developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) in North America, to ensure that their Dolby Vision implementations align with broader industry trends and expectations.
Viewer Experience Impact
Dolby Vision's implementation in broadcast journalism has significantly transformed the viewer experience, elevating it to unprecedented levels of immersion and realism. This advanced HDR technology enhances the visual quality of news broadcasts, documentaries, and live reporting, allowing viewers to perceive a wider range of colors and contrast that more closely resembles real-world scenes.
The impact on viewer engagement is profound. With Dolby Vision, news footage of natural disasters, for instance, conveys the intensity and scale of events with greater fidelity. Viewers can discern subtle details in both bright and dark areas of the image, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the situation. This enhanced visual information aids in creating a stronger emotional connection to the news story, potentially increasing viewer empathy and awareness.
In studio settings, Dolby Vision's capabilities shine through improved color accuracy and depth. News anchors and interview subjects appear more lifelike, with skin tones rendered more naturally across various lighting conditions. This heightened realism can foster a sense of trust and authenticity, crucial elements in broadcast journalism.
For investigative journalism and documentary work, Dolby Vision's expanded dynamic range allows for better preservation of visual evidence. Footage captured in challenging lighting conditions, such as dimly lit interiors or high-contrast outdoor scenes, retains more detail. This can be particularly valuable when presenting visual information that is critical to understanding complex stories or uncovering hidden truths.
Live sports broadcasting also benefits significantly from Dolby Vision. The technology's ability to handle fast-moving action while maintaining clarity and color accuracy enhances the viewing experience of sporting events. Viewers can better appreciate the nuances of play, from the texture of the playing field to the expressions on athletes' faces, even in varying lighting conditions throughout a game.
The implementation of Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism also has implications for archival purposes. News footage captured and stored in this format preserves a higher quality visual record, which may prove invaluable for future historical analysis and documentation.
However, it's important to note that the full impact of Dolby Vision on viewer experience is contingent upon the availability of compatible display devices in viewers' homes. As the adoption of HDR-capable televisions and mobile devices increases, the potential for Dolby Vision to revolutionize broadcast journalism's visual storytelling capabilities continues to grow.
The impact on viewer engagement is profound. With Dolby Vision, news footage of natural disasters, for instance, conveys the intensity and scale of events with greater fidelity. Viewers can discern subtle details in both bright and dark areas of the image, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the situation. This enhanced visual information aids in creating a stronger emotional connection to the news story, potentially increasing viewer empathy and awareness.
In studio settings, Dolby Vision's capabilities shine through improved color accuracy and depth. News anchors and interview subjects appear more lifelike, with skin tones rendered more naturally across various lighting conditions. This heightened realism can foster a sense of trust and authenticity, crucial elements in broadcast journalism.
For investigative journalism and documentary work, Dolby Vision's expanded dynamic range allows for better preservation of visual evidence. Footage captured in challenging lighting conditions, such as dimly lit interiors or high-contrast outdoor scenes, retains more detail. This can be particularly valuable when presenting visual information that is critical to understanding complex stories or uncovering hidden truths.
Live sports broadcasting also benefits significantly from Dolby Vision. The technology's ability to handle fast-moving action while maintaining clarity and color accuracy enhances the viewing experience of sporting events. Viewers can better appreciate the nuances of play, from the texture of the playing field to the expressions on athletes' faces, even in varying lighting conditions throughout a game.
The implementation of Dolby Vision in broadcast journalism also has implications for archival purposes. News footage captured and stored in this format preserves a higher quality visual record, which may prove invaluable for future historical analysis and documentation.
However, it's important to note that the full impact of Dolby Vision on viewer experience is contingent upon the availability of compatible display devices in viewers' homes. As the adoption of HDR-capable televisions and mobile devices increases, the potential for Dolby Vision to revolutionize broadcast journalism's visual storytelling capabilities continues to grow.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!