Dynamics of HEV Market Adoption in Developing Regions
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HEV Technology Evolution and Objectives
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) have emerged as a pivotal technology in the automotive industry's transition towards more sustainable transportation solutions. The evolution of HEV technology can be traced back to the late 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the past two decades. This progression has been driven by the growing need for fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles, particularly in developing regions where concerns about air pollution and energy security are increasingly prominent.
The primary objective of HEV technology is to combine the benefits of internal combustion engines with electric propulsion systems, thereby reducing fuel consumption and emissions while maintaining or improving vehicle performance. In developing regions, the adoption of HEVs faces unique challenges and opportunities, necessitating a tailored approach to technology development and market penetration.
One of the key trends in HEV technology evolution is the continuous improvement in battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries have become the standard, offering higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to earlier nickel-metal hydride batteries. This advancement has led to increased electric-only driving range and overall system efficiency, making HEVs more attractive to consumers in developing markets where fuel costs can be a significant concern.
Another important aspect of HEV technology evolution is the development of more sophisticated power management systems. These systems optimize the interplay between the electric motor and the internal combustion engine, maximizing efficiency across various driving conditions. This is particularly relevant in developing regions, where diverse road conditions and driving patterns necessitate adaptive and robust powertrain solutions.
The miniaturization and cost reduction of electric components have also played a crucial role in HEV technology advancement. This trend has made HEVs more accessible to a broader range of consumers in developing markets, where price sensitivity is often a critical factor in vehicle purchasing decisions.
Looking forward, the objectives for HEV technology in developing regions are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a push towards developing more affordable HEV models that can compete with conventional vehicles on initial purchase price. This involves optimizing manufacturing processes and localizing production to reduce costs.
Secondly, there is a focus on adapting HEV technology to suit the specific needs and conditions of developing markets. This includes designing systems that can withstand extreme temperatures, poor road conditions, and varying fuel quality. Additionally, there is an emphasis on developing HEVs that are compatible with the existing infrastructure in these regions, considering factors such as charging capabilities and maintenance requirements.
Lastly, a key objective is to enhance the overall value proposition of HEVs in developing markets. This involves not only improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions but also incorporating features that address local preferences and needs, such as enhanced durability, lower maintenance costs, and improved resale value. By aligning HEV technology with these objectives, manufacturers aim to accelerate market adoption and contribute to sustainable transportation solutions in developing regions.
The primary objective of HEV technology is to combine the benefits of internal combustion engines with electric propulsion systems, thereby reducing fuel consumption and emissions while maintaining or improving vehicle performance. In developing regions, the adoption of HEVs faces unique challenges and opportunities, necessitating a tailored approach to technology development and market penetration.
One of the key trends in HEV technology evolution is the continuous improvement in battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries have become the standard, offering higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to earlier nickel-metal hydride batteries. This advancement has led to increased electric-only driving range and overall system efficiency, making HEVs more attractive to consumers in developing markets where fuel costs can be a significant concern.
Another important aspect of HEV technology evolution is the development of more sophisticated power management systems. These systems optimize the interplay between the electric motor and the internal combustion engine, maximizing efficiency across various driving conditions. This is particularly relevant in developing regions, where diverse road conditions and driving patterns necessitate adaptive and robust powertrain solutions.
The miniaturization and cost reduction of electric components have also played a crucial role in HEV technology advancement. This trend has made HEVs more accessible to a broader range of consumers in developing markets, where price sensitivity is often a critical factor in vehicle purchasing decisions.
Looking forward, the objectives for HEV technology in developing regions are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a push towards developing more affordable HEV models that can compete with conventional vehicles on initial purchase price. This involves optimizing manufacturing processes and localizing production to reduce costs.
Secondly, there is a focus on adapting HEV technology to suit the specific needs and conditions of developing markets. This includes designing systems that can withstand extreme temperatures, poor road conditions, and varying fuel quality. Additionally, there is an emphasis on developing HEVs that are compatible with the existing infrastructure in these regions, considering factors such as charging capabilities and maintenance requirements.
Lastly, a key objective is to enhance the overall value proposition of HEVs in developing markets. This involves not only improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions but also incorporating features that address local preferences and needs, such as enhanced durability, lower maintenance costs, and improved resale value. By aligning HEV technology with these objectives, manufacturers aim to accelerate market adoption and contribute to sustainable transportation solutions in developing regions.
HEV Market Demand Analysis in Developing Regions
The market demand for Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) in developing regions is experiencing a significant upward trend, driven by a combination of factors that are reshaping the automotive landscape. As urbanization accelerates and environmental concerns grow, governments in these regions are implementing stricter emissions regulations and offering incentives for cleaner vehicle technologies. This regulatory push, coupled with rising fuel prices and increasing consumer awareness about environmental issues, is creating a fertile ground for HEV adoption.
In many developing countries, the middle class is expanding rapidly, leading to increased vehicle ownership. However, this growth is accompanied by a heightened sensitivity to fuel costs and a desire for more economical transportation options. HEVs, with their improved fuel efficiency and lower operating costs, are well-positioned to meet this demand. The potential for long-term savings on fuel expenses is a particularly attractive proposition for cost-conscious consumers in these markets.
The infrastructure challenges that have historically hindered electric vehicle adoption in developing regions are less of a barrier for HEVs. Unlike fully electric vehicles, HEVs do not require an extensive charging network, making them a more practical choice for areas with limited electrical infrastructure. This advantage allows HEVs to serve as a bridge technology, paving the way for future electrification while providing immediate benefits in terms of reduced emissions and fuel consumption.
Market research indicates that consumer preferences in developing regions are shifting towards vehicles that offer a balance of performance, efficiency, and affordability. HEVs are increasingly seen as a premium option that delivers on these criteria without the range anxiety associated with fully electric vehicles. As more HEV models become available at various price points, the technology is becoming accessible to a broader segment of the population.
The commercial sector in developing regions is also showing interest in HEVs, particularly for fleet operations. Taxi companies, ride-sharing services, and delivery businesses are recognizing the potential for operational cost savings and improved corporate image through the adoption of hybrid technology. This B2B demand is expected to contribute significantly to overall HEV market growth in these regions.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain. The higher upfront costs of HEVs compared to conventional vehicles continue to be a barrier for some consumers. Additionally, the lack of local manufacturing capabilities in many developing countries results in import duties that can inflate prices further. However, as production scales up and more automakers enter the market, prices are expected to become more competitive, potentially accelerating adoption rates.
In many developing countries, the middle class is expanding rapidly, leading to increased vehicle ownership. However, this growth is accompanied by a heightened sensitivity to fuel costs and a desire for more economical transportation options. HEVs, with their improved fuel efficiency and lower operating costs, are well-positioned to meet this demand. The potential for long-term savings on fuel expenses is a particularly attractive proposition for cost-conscious consumers in these markets.
The infrastructure challenges that have historically hindered electric vehicle adoption in developing regions are less of a barrier for HEVs. Unlike fully electric vehicles, HEVs do not require an extensive charging network, making them a more practical choice for areas with limited electrical infrastructure. This advantage allows HEVs to serve as a bridge technology, paving the way for future electrification while providing immediate benefits in terms of reduced emissions and fuel consumption.
Market research indicates that consumer preferences in developing regions are shifting towards vehicles that offer a balance of performance, efficiency, and affordability. HEVs are increasingly seen as a premium option that delivers on these criteria without the range anxiety associated with fully electric vehicles. As more HEV models become available at various price points, the technology is becoming accessible to a broader segment of the population.
The commercial sector in developing regions is also showing interest in HEVs, particularly for fleet operations. Taxi companies, ride-sharing services, and delivery businesses are recognizing the potential for operational cost savings and improved corporate image through the adoption of hybrid technology. This B2B demand is expected to contribute significantly to overall HEV market growth in these regions.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain. The higher upfront costs of HEVs compared to conventional vehicles continue to be a barrier for some consumers. Additionally, the lack of local manufacturing capabilities in many developing countries results in import duties that can inflate prices further. However, as production scales up and more automakers enter the market, prices are expected to become more competitive, potentially accelerating adoption rates.
HEV Adoption Challenges in Emerging Markets
The adoption of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) in developing regions faces unique challenges that differ significantly from those in mature markets. These obstacles stem from a combination of economic, infrastructural, and socio-cultural factors that are characteristic of emerging economies.
One of the primary hurdles is the higher initial cost of HEVs compared to conventional vehicles. In developing countries, where disposable income is generally lower, the price premium associated with hybrid technology can be a significant deterrent for potential buyers. This cost barrier is further exacerbated by limited access to financing options and higher interest rates, making it difficult for consumers to justify the long-term savings of HEVs against the upfront investment.
Infrastructure limitations also play a crucial role in impeding HEV adoption. Many developing regions lack the necessary charging infrastructure to support widespread use of electric and hybrid vehicles. The absence of a reliable power grid in some areas further compounds this issue, raising concerns about the practicality of owning an HEV.
Government policies and incentives, which have been key drivers of HEV adoption in developed markets, are often lacking or inconsistent in emerging economies. Without strong regulatory support and financial incentives, consumers and manufacturers alike have less motivation to embrace hybrid technology.
Consumer awareness and perception present another significant challenge. In many developing regions, there is a lack of understanding about HEV technology and its benefits. This knowledge gap, combined with cultural preferences for traditional combustion engines and concerns about the reliability of new technology, creates resistance to change among potential buyers.
The automotive market structure in developing countries also poses challenges. Many of these markets are dominated by low-cost, locally manufactured vehicles or imported used cars. The introduction of HEVs disrupts this established ecosystem, requiring significant changes in manufacturing, distribution, and after-sales service networks.
Technical expertise for maintenance and repair of HEVs is often scarce in developing regions. This shortage of skilled technicians can lead to higher maintenance costs and longer downtimes, further deterring potential adopters who prioritize reliability and low operating costs.
Environmental concerns, while growing, often take a backseat to more immediate economic considerations in developing countries. The long-term benefits of reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency may not be as compelling to consumers facing more pressing financial constraints.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that considers the unique economic, social, and infrastructural contexts of developing regions. Strategies must be tailored to overcome cost barriers, improve infrastructure, enhance consumer education, and align with local market dynamics to successfully drive HEV adoption in these emerging markets.
One of the primary hurdles is the higher initial cost of HEVs compared to conventional vehicles. In developing countries, where disposable income is generally lower, the price premium associated with hybrid technology can be a significant deterrent for potential buyers. This cost barrier is further exacerbated by limited access to financing options and higher interest rates, making it difficult for consumers to justify the long-term savings of HEVs against the upfront investment.
Infrastructure limitations also play a crucial role in impeding HEV adoption. Many developing regions lack the necessary charging infrastructure to support widespread use of electric and hybrid vehicles. The absence of a reliable power grid in some areas further compounds this issue, raising concerns about the practicality of owning an HEV.
Government policies and incentives, which have been key drivers of HEV adoption in developed markets, are often lacking or inconsistent in emerging economies. Without strong regulatory support and financial incentives, consumers and manufacturers alike have less motivation to embrace hybrid technology.
Consumer awareness and perception present another significant challenge. In many developing regions, there is a lack of understanding about HEV technology and its benefits. This knowledge gap, combined with cultural preferences for traditional combustion engines and concerns about the reliability of new technology, creates resistance to change among potential buyers.
The automotive market structure in developing countries also poses challenges. Many of these markets are dominated by low-cost, locally manufactured vehicles or imported used cars. The introduction of HEVs disrupts this established ecosystem, requiring significant changes in manufacturing, distribution, and after-sales service networks.
Technical expertise for maintenance and repair of HEVs is often scarce in developing regions. This shortage of skilled technicians can lead to higher maintenance costs and longer downtimes, further deterring potential adopters who prioritize reliability and low operating costs.
Environmental concerns, while growing, often take a backseat to more immediate economic considerations in developing countries. The long-term benefits of reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency may not be as compelling to consumers facing more pressing financial constraints.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that considers the unique economic, social, and infrastructural contexts of developing regions. Strategies must be tailored to overcome cost barriers, improve infrastructure, enhance consumer education, and align with local market dynamics to successfully drive HEV adoption in these emerging markets.
Current HEV Solutions for Developing Markets
01 Charging infrastructure development
The adoption of HEVs is closely tied to the development of charging infrastructure. This includes the installation of charging stations in public spaces, workplaces, and residential areas. Improved charging infrastructure reduces range anxiety and makes HEVs more practical for everyday use, thereby increasing market adoption.- Charging infrastructure development: The adoption of HEVs is closely tied to the development of charging infrastructure. This includes the installation of charging stations in public spaces, workplaces, and residential areas. Improved charging infrastructure reduces range anxiety and makes HEVs more practical for everyday use, thereby increasing market adoption.
- Battery technology advancements: Advancements in battery technology are crucial for HEV market adoption. This includes improvements in energy density, charging speed, and overall battery life. Enhanced battery performance leads to increased driving range and reduced charging times, making HEVs more attractive to consumers.
- Government incentives and regulations: Government policies play a significant role in HEV market adoption. This includes financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies for HEV purchases. Additionally, regulations on emissions standards and fuel efficiency requirements encourage automakers to produce more HEVs, driving market growth.
- Integration of smart technologies: The incorporation of smart technologies in HEVs enhances their appeal and market adoption. This includes features like advanced driver assistance systems, connectivity solutions, and energy management systems. These technologies improve the overall driving experience and efficiency of HEVs.
- Manufacturing and supply chain optimization: Optimizing manufacturing processes and supply chains is essential for increasing HEV production and reducing costs. This includes developing more efficient production methods, improving supply chain management, and localizing component production. These efforts help make HEVs more affordable and accessible to a wider range of consumers.
02 Battery technology advancements
Advancements in battery technology are crucial for HEV market adoption. This includes improvements in energy density, charging speed, and overall battery life. Enhanced battery performance leads to increased driving range and reduced charging times, making HEVs more attractive to consumers.Expand Specific Solutions03 Government incentives and regulations
Government policies play a significant role in HEV market adoption. This includes financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies for HEV purchases. Additionally, regulations on emissions standards and fuel efficiency requirements encourage automakers to produce more HEVs, driving market growth.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of smart technologies
The integration of smart technologies in HEVs enhances their appeal and market adoption. This includes features such as advanced driver assistance systems, connectivity solutions, and energy management systems. These technologies improve the overall driving experience and efficiency of HEVs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing and supply chain optimization
Optimizing manufacturing processes and supply chains is crucial for increasing HEV production and reducing costs. This includes developing more efficient production techniques, improving supply chain management, and localizing component production. These efforts help make HEVs more affordable and accessible to a wider range of consumers.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HEV Manufacturers and Market Competitors
The HEV market adoption in developing regions is in a growth phase, characterized by increasing demand and expanding market size. The technology is maturing, with major players like Toyota, Hyundai, and Volkswagen leading the way. These companies are leveraging their global experience to adapt HEV technology for emerging markets. Local manufacturers such as Chery Automobile and Great Wall Motor are also entering the space, indicating growing domestic capabilities. The market is seeing a mix of established global brands and emerging local players, suggesting a competitive and dynamic landscape. As infrastructure and consumer awareness improve, the HEV market in developing regions is poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has been at the forefront of HEV market adoption in developing regions, leveraging its extensive experience with the Prius model. The company has implemented a localized approach, adapting its hybrid technology to suit specific market needs. In India, Toyota introduced the Urban Cruiser Hyryder, a locally manufactured hybrid SUV, to cater to the growing demand for fuel-efficient vehicles[1]. The company has also established partnerships with local manufacturers in countries like Brazil and Thailand to produce hybrid vehicles, reducing costs and increasing accessibility[2]. Toyota's strategy includes offering a range of hybrid options across different vehicle segments, from compact cars to SUVs, to appeal to diverse consumer preferences in developing markets[3].
Strengths: Established hybrid technology, strong brand recognition, and extensive manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher initial costs compared to conventional vehicles, potential challenges in establishing charging infrastructure in some developing regions.
Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hyundai has been actively expanding its HEV presence in developing regions, focusing on a strategy that combines affordability with advanced technology. The company has introduced models like the Ioniq Hybrid and Sonata Hybrid in markets such as India, Brazil, and Southeast Asian countries. Hyundai's approach includes localizing production to reduce costs and adapting vehicle specifications to meet local preferences and regulations[4]. The company has also invested in developing hybrid powertrains specifically designed for emerging markets, balancing performance with fuel efficiency. In countries like Indonesia, Hyundai has partnered with local entities to establish manufacturing facilities for hybrid vehicles, aiming to capture a significant market share in the growing HEV segment[5].
Strengths: Competitive pricing, diverse product range, and strong focus on localization. Weaknesses: Relatively newer entrant in the HEV market compared to some competitors, potential challenges in brand perception for premium hybrid models.
Innovative HEV Technologies for Emerging Economies
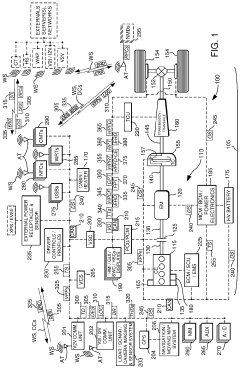
Hybrid electrical vehicle and method for controlling same
PatentActiveUS20160221571A1
Innovation
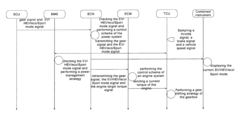
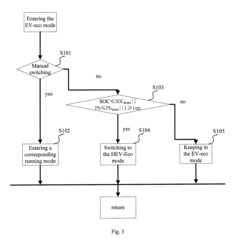
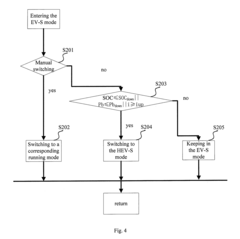
- A control system and method for a hybrid electrical vehicle that allows switching between EV and HEV modes based on battery power and slope conditions, enabling parallel connection of engine and motor power subsystems to improve energy utilization and reduce complex transmission requirements.
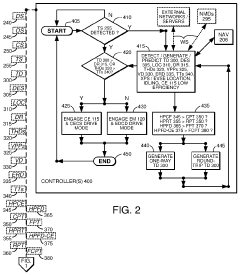
Hybrid electric vehicle fuel conservation system
PatentActiveUS10793135B2
Innovation
- The implementation of advanced controller systems that estimate trip distances, detect thermal demands, and adjust drive modes based on real-time data from navigation systems, sensors, and historical probabilities to optimize the engagement of electric drive modes and combustion engine modes, ensuring efficient energy use and minimizing fuel consumption.
Government Policies and Incentives for HEV Adoption
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in shaping the adoption of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) in developing regions. These measures are designed to overcome barriers to entry and accelerate market penetration of environmentally friendly transportation options.
Many developing countries have implemented tax incentives to make HEVs more affordable for consumers. These often include reduced import duties, lower sales taxes, or income tax credits for HEV purchases. For example, in India, the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme offers subsidies to buyers, effectively lowering the purchase price of HEVs.
Infrastructure development is another key area of government focus. Policies that support the expansion of charging networks and service facilities are essential for increasing consumer confidence in HEV technology. Countries like China have made significant investments in charging infrastructure, which has contributed to the rapid growth of their electric vehicle market, including HEVs.
Regulatory frameworks also play a significant role in HEV adoption. Stricter emissions standards and fuel efficiency requirements incentivize automakers to produce more HEVs and consumers to choose them. For instance, Brazil's Inovar-Auto program rewards manufacturers for producing more fuel-efficient vehicles, indirectly promoting HEV technology.
Some governments in developing regions have implemented preferential policies for HEVs in urban areas. These may include exemptions from traffic restrictions, reduced tolls, or free parking. Such measures not only provide immediate benefits to HEV owners but also raise awareness about the technology among the general public.
Public procurement policies can significantly impact HEV adoption. By mandating the inclusion of HEVs in government fleets or public transportation systems, governments create a stable demand for these vehicles and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable transportation. This approach has been successfully implemented in countries like Thailand and Malaysia.
Education and awareness campaigns are often overlooked but are crucial components of government strategies to promote HEV adoption. These initiatives help to address misconceptions about HEV technology and highlight the environmental and economic benefits of these vehicles.
However, the effectiveness of these policies varies across different developing regions due to factors such as economic conditions, existing infrastructure, and cultural attitudes towards new technologies. Successful implementation requires a holistic approach that addresses multiple aspects of the HEV ecosystem simultaneously.
Many developing countries have implemented tax incentives to make HEVs more affordable for consumers. These often include reduced import duties, lower sales taxes, or income tax credits for HEV purchases. For example, in India, the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme offers subsidies to buyers, effectively lowering the purchase price of HEVs.
Infrastructure development is another key area of government focus. Policies that support the expansion of charging networks and service facilities are essential for increasing consumer confidence in HEV technology. Countries like China have made significant investments in charging infrastructure, which has contributed to the rapid growth of their electric vehicle market, including HEVs.
Regulatory frameworks also play a significant role in HEV adoption. Stricter emissions standards and fuel efficiency requirements incentivize automakers to produce more HEVs and consumers to choose them. For instance, Brazil's Inovar-Auto program rewards manufacturers for producing more fuel-efficient vehicles, indirectly promoting HEV technology.
Some governments in developing regions have implemented preferential policies for HEVs in urban areas. These may include exemptions from traffic restrictions, reduced tolls, or free parking. Such measures not only provide immediate benefits to HEV owners but also raise awareness about the technology among the general public.
Public procurement policies can significantly impact HEV adoption. By mandating the inclusion of HEVs in government fleets or public transportation systems, governments create a stable demand for these vehicles and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable transportation. This approach has been successfully implemented in countries like Thailand and Malaysia.
Education and awareness campaigns are often overlooked but are crucial components of government strategies to promote HEV adoption. These initiatives help to address misconceptions about HEV technology and highlight the environmental and economic benefits of these vehicles.
However, the effectiveness of these policies varies across different developing regions due to factors such as economic conditions, existing infrastructure, and cultural attitudes towards new technologies. Successful implementation requires a holistic approach that addresses multiple aspects of the HEV ecosystem simultaneously.
Infrastructure Development for HEV Support
The development of infrastructure to support Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) in developing regions is a critical factor in the adoption and growth of this market. As these regions seek to balance economic growth with environmental concerns, the establishment of a robust HEV support infrastructure becomes paramount.
One of the primary challenges in developing regions is the creation of an adequate charging network. Unlike developed countries with extensive electrical grids, many developing areas face limitations in power distribution. To address this, governments and private entities are investing in the expansion of charging stations, particularly in urban centers and along major highways. These efforts often involve partnerships between automotive manufacturers, energy companies, and local authorities to ensure strategic placement and efficient operation of charging points.
Another crucial aspect of infrastructure development is the upgrade of existing power grids. Many developing regions are grappling with unreliable electricity supply, which poses a significant barrier to HEV adoption. Investments in smart grid technologies and renewable energy sources are being made to enhance grid stability and capacity. This not only supports HEV charging but also contributes to overall energy security and sustainability in these regions.
Maintenance and service infrastructure for HEVs is equally important. As the technology is relatively new in many developing markets, there is a pressing need for skilled technicians and specialized service centers. Automotive companies are establishing training programs and partnerships with local educational institutions to build a workforce capable of servicing and maintaining HEVs. This not only supports the growth of the HEV market but also creates new employment opportunities in the automotive sector.
The development of supportive policies and regulations is another critical infrastructure component. Governments in developing regions are implementing incentives such as tax breaks, subsidies, and preferential parking to encourage HEV adoption. Additionally, they are working on standardizing charging protocols and safety regulations to ensure interoperability and consumer confidence in HEV technology.
Public awareness and education form an essential part of the infrastructure ecosystem. Many developing regions are launching campaigns to inform consumers about the benefits of HEVs and dispel misconceptions. These efforts include demonstration projects, public exhibitions, and collaboration with media outlets to showcase HEV technology and its advantages in local contexts.
Lastly, the integration of HEVs into public transportation systems is emerging as a key strategy in infrastructure development. Cities in developing regions are piloting HEV buses and taxis, which not only reduces emissions but also serves as a visible demonstration of the technology's viability. This approach helps in building public trust and familiarity with HEVs, potentially accelerating broader market adoption.
One of the primary challenges in developing regions is the creation of an adequate charging network. Unlike developed countries with extensive electrical grids, many developing areas face limitations in power distribution. To address this, governments and private entities are investing in the expansion of charging stations, particularly in urban centers and along major highways. These efforts often involve partnerships between automotive manufacturers, energy companies, and local authorities to ensure strategic placement and efficient operation of charging points.
Another crucial aspect of infrastructure development is the upgrade of existing power grids. Many developing regions are grappling with unreliable electricity supply, which poses a significant barrier to HEV adoption. Investments in smart grid technologies and renewable energy sources are being made to enhance grid stability and capacity. This not only supports HEV charging but also contributes to overall energy security and sustainability in these regions.
Maintenance and service infrastructure for HEVs is equally important. As the technology is relatively new in many developing markets, there is a pressing need for skilled technicians and specialized service centers. Automotive companies are establishing training programs and partnerships with local educational institutions to build a workforce capable of servicing and maintaining HEVs. This not only supports the growth of the HEV market but also creates new employment opportunities in the automotive sector.
The development of supportive policies and regulations is another critical infrastructure component. Governments in developing regions are implementing incentives such as tax breaks, subsidies, and preferential parking to encourage HEV adoption. Additionally, they are working on standardizing charging protocols and safety regulations to ensure interoperability and consumer confidence in HEV technology.
Public awareness and education form an essential part of the infrastructure ecosystem. Many developing regions are launching campaigns to inform consumers about the benefits of HEVs and dispel misconceptions. These efforts include demonstration projects, public exhibitions, and collaboration with media outlets to showcase HEV technology and its advantages in local contexts.
Lastly, the integration of HEVs into public transportation systems is emerging as a key strategy in infrastructure development. Cities in developing regions are piloting HEV buses and taxis, which not only reduces emissions but also serves as a visible demonstration of the technology's viability. This approach helps in building public trust and familiarity with HEVs, potentially accelerating broader market adoption.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!