Hirudoid in Dermatology: A Comprehensive Review
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hirudoid Background and Objectives
Hirudoid, a topical heparin-containing gel, has been a significant player in dermatological treatments for several decades. Its development can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring the potential of heparin in topical applications. The primary objective of Hirudoid was to harness the anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic properties of heparin for dermatological use, particularly in treating superficial thrombophlebitis and hematomas.
The evolution of Hirudoid has been closely tied to advancements in our understanding of skin physiology and the mechanisms of wound healing. Initially, the focus was on its ability to reduce inflammation and promote the dissolution of blood clots. However, as research progressed, its potential applications expanded to include the treatment of various skin conditions, such as bruises, scars, and certain types of dermatitis.
One of the key technological challenges in the development of Hirudoid was creating a formulation that could effectively deliver heparin through the skin barrier. This required innovative approaches in pharmaceutical technology to ensure that the active ingredient could penetrate the epidermis and reach the target tissues. The resulting gel formulation represented a significant breakthrough in topical drug delivery systems.
Over time, the objectives of Hirudoid research and development have evolved. While the initial goal was to provide an effective treatment for superficial vein thrombosis, current research aims to explore its potential in broader dermatological applications. These include its use in cosmetic dermatology for improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of scars and wrinkles.
The technological trajectory of Hirudoid has also been influenced by changing regulatory landscapes and increasing demands for evidence-based medicine. This has led to more rigorous clinical trials and studies to validate its efficacy and safety across various dermatological conditions. The ongoing research aims to not only expand its therapeutic applications but also to optimize its formulation for enhanced efficacy and patient compliance.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create more comprehensive dermatological solutions. This trend reflects the broader shift in the pharmaceutical industry towards combination therapies and personalized medicine. The future objectives for Hirudoid research include exploring these synergistic combinations and developing novel delivery systems to improve its efficacy and expand its range of applications in dermatology.
The evolution of Hirudoid has been closely tied to advancements in our understanding of skin physiology and the mechanisms of wound healing. Initially, the focus was on its ability to reduce inflammation and promote the dissolution of blood clots. However, as research progressed, its potential applications expanded to include the treatment of various skin conditions, such as bruises, scars, and certain types of dermatitis.
One of the key technological challenges in the development of Hirudoid was creating a formulation that could effectively deliver heparin through the skin barrier. This required innovative approaches in pharmaceutical technology to ensure that the active ingredient could penetrate the epidermis and reach the target tissues. The resulting gel formulation represented a significant breakthrough in topical drug delivery systems.
Over time, the objectives of Hirudoid research and development have evolved. While the initial goal was to provide an effective treatment for superficial vein thrombosis, current research aims to explore its potential in broader dermatological applications. These include its use in cosmetic dermatology for improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of scars and wrinkles.
The technological trajectory of Hirudoid has also been influenced by changing regulatory landscapes and increasing demands for evidence-based medicine. This has led to more rigorous clinical trials and studies to validate its efficacy and safety across various dermatological conditions. The ongoing research aims to not only expand its therapeutic applications but also to optimize its formulation for enhanced efficacy and patient compliance.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create more comprehensive dermatological solutions. This trend reflects the broader shift in the pharmaceutical industry towards combination therapies and personalized medicine. The future objectives for Hirudoid research include exploring these synergistic combinations and developing novel delivery systems to improve its efficacy and expand its range of applications in dermatology.
Dermatological Market Analysis
The dermatological market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing skin disorders, growing awareness of skin health, and advancements in treatment options. The global dermatology market was valued at approximately $20 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $33 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% during the forecast period.
Hirudoid, a topical heparinoid-based product, has carved out a niche within this expanding market. Its primary applications include the treatment of superficial thrombophlebitis, bruises, and localized swelling. The demand for Hirudoid and similar products is expected to grow due to the rising incidence of venous disorders and an aging population more prone to bruising and skin injuries.
Within the dermatology market, topical medications like Hirudoid represent a substantial segment. Topical drugs accounted for over 40% of the global dermatology market share in 2020, highlighting the importance of such products in skin treatment regimens. The ease of application and reduced systemic side effects associated with topical treatments contribute to their popularity among both patients and healthcare providers.
Geographically, North America dominates the dermatology market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness the highest growth rates in the coming years. This growth is attributed to improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness of skin health in these regions.
The competitive landscape of the dermatology market is characterized by the presence of both large pharmaceutical companies and specialized dermatology firms. Key players include Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, AbbVie, and LEO Pharma. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and expand their market share.
In the context of Hirudoid and similar heparinoid-based products, the market is relatively concentrated, with a few established brands dominating the segment. However, there is potential for new entrants, especially those offering improved formulations or novel delivery systems.
The future of the dermatology market, including products like Hirudoid, is likely to be shaped by several trends. These include the increasing adoption of combination therapies, the rise of personalized medicine in dermatology, and the growing importance of cosmeceuticals. Additionally, the integration of digital technologies in skin health management and diagnosis is expected to create new opportunities and change the landscape of dermatological care.
Hirudoid, a topical heparinoid-based product, has carved out a niche within this expanding market. Its primary applications include the treatment of superficial thrombophlebitis, bruises, and localized swelling. The demand for Hirudoid and similar products is expected to grow due to the rising incidence of venous disorders and an aging population more prone to bruising and skin injuries.
Within the dermatology market, topical medications like Hirudoid represent a substantial segment. Topical drugs accounted for over 40% of the global dermatology market share in 2020, highlighting the importance of such products in skin treatment regimens. The ease of application and reduced systemic side effects associated with topical treatments contribute to their popularity among both patients and healthcare providers.
Geographically, North America dominates the dermatology market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness the highest growth rates in the coming years. This growth is attributed to improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness of skin health in these regions.
The competitive landscape of the dermatology market is characterized by the presence of both large pharmaceutical companies and specialized dermatology firms. Key players include Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, AbbVie, and LEO Pharma. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and expand their market share.
In the context of Hirudoid and similar heparinoid-based products, the market is relatively concentrated, with a few established brands dominating the segment. However, there is potential for new entrants, especially those offering improved formulations or novel delivery systems.
The future of the dermatology market, including products like Hirudoid, is likely to be shaped by several trends. These include the increasing adoption of combination therapies, the rise of personalized medicine in dermatology, and the growing importance of cosmeceuticals. Additionally, the integration of digital technologies in skin health management and diagnosis is expected to create new opportunities and change the landscape of dermatological care.
Current Hirudoid Applications
Hirudoid, a topical heparinoid, has gained significant traction in dermatology for its versatile applications. Currently, it is widely used in the treatment of various skin conditions, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory, anti-coagulant, and anti-thrombotic properties. One of the most common applications of Hirudoid is in the management of superficial thrombophlebitis, where it helps reduce inflammation and pain associated with varicose veins and other venous disorders.
In the realm of wound healing, Hirudoid has shown promising results. It is frequently employed to accelerate the healing process of minor cuts, abrasions, and burns. The heparin-like compound in Hirudoid promotes tissue repair by enhancing blood flow to the affected area and stimulating the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. This property makes it particularly useful in the treatment of slow-healing wounds and ulcers, especially in patients with compromised circulation.
Hirudoid has also found application in the treatment of bruises and hematomas. Its ability to improve local blood circulation helps in the rapid absorption of blood extravasations, thereby reducing the appearance of bruises and speeding up the healing process. This makes it a popular choice among dermatologists for post-procedural care, particularly after minor surgical interventions or cosmetic procedures.
In the field of aesthetic dermatology, Hirudoid is increasingly being used to address various cosmetic concerns. It has shown efficacy in reducing the appearance of scars, including hypertrophic and keloid scars. The product's ability to soften scar tissue and improve skin elasticity makes it a valuable tool in scar management protocols. Additionally, some practitioners have reported success in using Hirudoid for the treatment of dark under-eye circles, leveraging its capacity to improve microcirculation in the delicate periorbital area.
Another emerging application of Hirudoid is in the management of skin aging. Its moisturizing properties and ability to improve skin texture have led to its inclusion in anti-aging skincare regimens. Some studies suggest that regular application of Hirudoid may help in reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, although more research is needed to fully substantiate these claims.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential of Hirudoid in treating more severe dermatological conditions. Preliminary studies have explored its use in managing symptoms of psoriasis and eczema, with some promising results in reducing inflammation and itching. However, these applications are still considered off-label and require further clinical investigation to establish their efficacy and safety profiles.
In the realm of wound healing, Hirudoid has shown promising results. It is frequently employed to accelerate the healing process of minor cuts, abrasions, and burns. The heparin-like compound in Hirudoid promotes tissue repair by enhancing blood flow to the affected area and stimulating the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. This property makes it particularly useful in the treatment of slow-healing wounds and ulcers, especially in patients with compromised circulation.
Hirudoid has also found application in the treatment of bruises and hematomas. Its ability to improve local blood circulation helps in the rapid absorption of blood extravasations, thereby reducing the appearance of bruises and speeding up the healing process. This makes it a popular choice among dermatologists for post-procedural care, particularly after minor surgical interventions or cosmetic procedures.
In the field of aesthetic dermatology, Hirudoid is increasingly being used to address various cosmetic concerns. It has shown efficacy in reducing the appearance of scars, including hypertrophic and keloid scars. The product's ability to soften scar tissue and improve skin elasticity makes it a valuable tool in scar management protocols. Additionally, some practitioners have reported success in using Hirudoid for the treatment of dark under-eye circles, leveraging its capacity to improve microcirculation in the delicate periorbital area.
Another emerging application of Hirudoid is in the management of skin aging. Its moisturizing properties and ability to improve skin texture have led to its inclusion in anti-aging skincare regimens. Some studies suggest that regular application of Hirudoid may help in reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, although more research is needed to fully substantiate these claims.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential of Hirudoid in treating more severe dermatological conditions. Preliminary studies have explored its use in managing symptoms of psoriasis and eczema, with some promising results in reducing inflammation and itching. However, these applications are still considered off-label and require further clinical investigation to establish their efficacy and safety profiles.
Key Pharmaceutical Companies
The market for Hirudoid in dermatology is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced skincare solutions. The global dermatology market is expanding, with a projected size of $145 billion by 2028. Technologically, Hirudoid's application in dermatology is evolving, with companies like Bayer HealthCare, L'Oréal SA, and Galderma Research & Development SNC leading innovation. These firms are investing in research to enhance Hirudoid's efficacy and explore new applications. Emerging players such as Almirall SA and Lesley Cosmetics AB are also contributing to the competitive landscape, focusing on niche dermatological solutions. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing clinical trials and product developments indicating potential for further advancements in dermatological treatments.
Bayer HealthCare
Technical Solution: Bayer HealthCare has developed a proprietary formulation of Hirudoid for dermatological applications. Their approach involves enhancing the penetration and efficacy of mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS) through advanced delivery systems. The company has conducted extensive clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of Hirudoid in various skin conditions, including bruising, superficial thrombophlebitis, and scar management. Bayer's formulation aims to improve the absorption of MPS into the skin, potentially leading to faster healing and reduced inflammation.
Strengths: Established brand recognition, extensive clinical research, and global distribution network. Weaknesses: Potential for generic competition and the need for continuous innovation to maintain market leadership.
Galderma Research & Development SNC
Technical Solution: Galderma has focused on developing novel applications of Hirudoid in combination with other active ingredients for enhanced dermatological benefits. Their research explores the synergistic effects of Hirudoid with retinoids and antioxidants for anti-aging and skin repair treatments. Galderma's approach involves microencapsulation technology to improve the stability and controlled release of Hirudoid in topical formulations. They have also investigated the potential of Hirudoid in treating rosacea and other inflammatory skin conditions, leveraging its anti-inflammatory and vascular protective properties.
Strengths: Strong focus on dermatology, innovative formulation techniques, and a diverse product pipeline. Weaknesses: Limited to prescription markets in some regions and potential regulatory challenges for new combination products.
Hirudoid Mechanism of Action
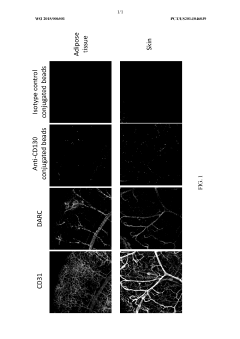
Microvessel endothelial cell surface markers and uses thereof
PatentWO2015006501A2
Innovation
- A method of delivering a microvessel endothelial cell targeting agent that binds to specific proteins on the surface of microvessel endothelial cells, allowing for targeted action on these cells or adjacent tissues, using agents such as small molecules, peptides, or nucleic acids, which can be internalized or transported across endothelial cells to accumulate in microvessels without affecting non-target tissues.
Compositions and methods for treating skin disorders
PatentWO2024197144A1
Innovation
- A composition combining a retinoid with an amphiregulin inhibitor, such as Paeonia suffructicosa root extract, and an anti-inflammatory agent, like Centipeda cunninghammii, formulated for topical administration, which increases retinoid efficacy while reducing side effects.
Regulatory Framework for Topical Medications
The regulatory framework for topical medications, including Hirudoid, is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of dermatological products. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing topical medications. The FDA classifies topical products into different categories, such as drugs, cosmetics, or medical devices, depending on their intended use and claims.
For topical drugs like Hirudoid, manufacturers must follow the New Drug Application (NDA) process or the Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) for generic versions. This process involves extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The FDA also requires adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides centralized authorization for certain medications, while national regulatory agencies handle others. The EU's regulatory framework includes the Clinical Trials Regulation and the Medicinal Products Directive, which set standards for clinical research and marketing authorization.
Pharmacovigilance is a critical component of the regulatory framework for topical medications. Manufacturers are required to monitor and report adverse events associated with their products, even after market approval. This ongoing surveillance helps identify potential safety issues and informs regulatory decisions.
Labeling and packaging regulations are particularly important for topical medications. Clear instructions for use, warnings, and ingredient lists are mandatory to ensure proper application and minimize risks. In many jurisdictions, certain active ingredients in topical products may be subject to specific restrictions or require prescription-only status.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the environmental impact of topical medications. Many countries have implemented regulations concerning the disposal of pharmaceutical products and their potential effects on ecosystems.
As the field of dermatology advances, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate new technologies and formulations. For instance, the emergence of nanotechnology in topical drug delivery has prompted regulatory bodies to develop specific guidelines for these novel products.
International harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different regions. These initiatives facilitate global development and marketing of topical medications while maintaining high standards of safety and efficacy.
For topical drugs like Hirudoid, manufacturers must follow the New Drug Application (NDA) process or the Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) for generic versions. This process involves extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The FDA also requires adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides centralized authorization for certain medications, while national regulatory agencies handle others. The EU's regulatory framework includes the Clinical Trials Regulation and the Medicinal Products Directive, which set standards for clinical research and marketing authorization.
Pharmacovigilance is a critical component of the regulatory framework for topical medications. Manufacturers are required to monitor and report adverse events associated with their products, even after market approval. This ongoing surveillance helps identify potential safety issues and informs regulatory decisions.
Labeling and packaging regulations are particularly important for topical medications. Clear instructions for use, warnings, and ingredient lists are mandatory to ensure proper application and minimize risks. In many jurisdictions, certain active ingredients in topical products may be subject to specific restrictions or require prescription-only status.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the environmental impact of topical medications. Many countries have implemented regulations concerning the disposal of pharmaceutical products and their potential effects on ecosystems.
As the field of dermatology advances, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate new technologies and formulations. For instance, the emergence of nanotechnology in topical drug delivery has prompted regulatory bodies to develop specific guidelines for these novel products.
International harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different regions. These initiatives facilitate global development and marketing of topical medications while maintaining high standards of safety and efficacy.
Safety and Efficacy Profile
The safety and efficacy profile of Hirudoid in dermatology has been extensively studied and documented. Clinical trials and long-term use have demonstrated that Hirudoid, containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), is generally well-tolerated and effective for various dermatological conditions.
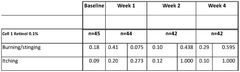
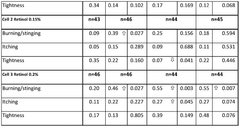
In terms of safety, Hirudoid has shown a favorable profile with minimal adverse effects. The most commonly reported side effects are mild and transient, including local skin irritation, redness, or itching at the application site. These reactions typically subside without intervention and do not necessitate discontinuation of treatment. Allergic reactions are rare but have been reported in some cases, emphasizing the importance of patch testing for sensitive individuals.
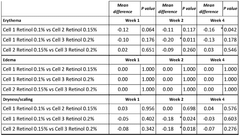
Efficacy studies have shown promising results across several dermatological applications. In the treatment of superficial thrombophlebitis, Hirudoid has demonstrated significant reduction in pain, erythema, and edema compared to placebo. The anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous properties of MPS contribute to faster resolution of symptoms and improved patient comfort.
For bruising and hematoma management, Hirudoid has been shown to accelerate the resolution of ecchymosis and reduce associated pain. Clinical trials have reported faster resorption of hematomas and improved tissue healing when Hirudoid is applied topically. This makes it particularly useful in post-surgical care and for patients prone to easy bruising.
In the context of scar management, Hirudoid has shown efficacy in improving the appearance and texture of hypertrophic and keloid scars. Studies have reported increased scar pliability, reduced itching, and improved overall cosmetic outcomes. The mechanism is thought to involve modulation of collagen synthesis and organization within the scar tissue.
Hirudoid's efficacy extends to the treatment of venous insufficiency symptoms. Clinical trials have demonstrated improvements in leg heaviness, pain, and edema associated with chronic venous disorders. The product's ability to enhance microcirculation and reduce capillary permeability contributes to these beneficial effects.
Long-term safety data from post-marketing surveillance further supports the favorable risk-benefit profile of Hirudoid. No significant systemic adverse effects have been reported with prolonged use, and the product maintains its efficacy over extended treatment periods.
While the overall safety and efficacy profile is positive, it's important to note that individual responses may vary. Factors such as the specific dermatological condition, severity of symptoms, and concurrent treatments can influence outcomes. As with any medical intervention, proper patient selection and adherence to recommended usage guidelines are crucial for optimal results.
In terms of safety, Hirudoid has shown a favorable profile with minimal adverse effects. The most commonly reported side effects are mild and transient, including local skin irritation, redness, or itching at the application site. These reactions typically subside without intervention and do not necessitate discontinuation of treatment. Allergic reactions are rare but have been reported in some cases, emphasizing the importance of patch testing for sensitive individuals.
Efficacy studies have shown promising results across several dermatological applications. In the treatment of superficial thrombophlebitis, Hirudoid has demonstrated significant reduction in pain, erythema, and edema compared to placebo. The anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous properties of MPS contribute to faster resolution of symptoms and improved patient comfort.
For bruising and hematoma management, Hirudoid has been shown to accelerate the resolution of ecchymosis and reduce associated pain. Clinical trials have reported faster resorption of hematomas and improved tissue healing when Hirudoid is applied topically. This makes it particularly useful in post-surgical care and for patients prone to easy bruising.
In the context of scar management, Hirudoid has shown efficacy in improving the appearance and texture of hypertrophic and keloid scars. Studies have reported increased scar pliability, reduced itching, and improved overall cosmetic outcomes. The mechanism is thought to involve modulation of collagen synthesis and organization within the scar tissue.
Hirudoid's efficacy extends to the treatment of venous insufficiency symptoms. Clinical trials have demonstrated improvements in leg heaviness, pain, and edema associated with chronic venous disorders. The product's ability to enhance microcirculation and reduce capillary permeability contributes to these beneficial effects.
Long-term safety data from post-marketing surveillance further supports the favorable risk-benefit profile of Hirudoid. No significant systemic adverse effects have been reported with prolonged use, and the product maintains its efficacy over extended treatment periods.
While the overall safety and efficacy profile is positive, it's important to note that individual responses may vary. Factors such as the specific dermatological condition, severity of symptoms, and concurrent treatments can influence outcomes. As with any medical intervention, proper patient selection and adherence to recommended usage guidelines are crucial for optimal results.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!