How Decane Blends Influence Jet Fuel Performance Parameters
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Decane Blends in Jet Fuel: Background and Objectives
Decane blends have emerged as a crucial area of study in the field of jet fuel performance optimization. The aviation industry's continuous pursuit of enhanced fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved overall performance has led to an increased focus on understanding the influence of various fuel components, particularly decane blends, on jet fuel characteristics.
The historical development of jet fuels has been marked by a series of advancements aimed at meeting the evolving demands of aircraft engines and environmental regulations. Initially, kerosene-based fuels were the standard, but as engine technology progressed, the need for fuels with specific performance attributes became apparent. This led to the exploration of various hydrocarbon blends, with decane and its isomers gaining prominence due to their favorable properties.
Decane, a straight-chain alkane with ten carbon atoms, and its branched isomers have been identified as key components in jet fuel formulations. Their presence can significantly impact critical fuel parameters such as energy density, freezing point, and combustion characteristics. The study of decane blends is driven by the potential to fine-tune these properties, thereby enhancing overall jet fuel performance.
The primary objective of investigating decane blends in jet fuel is to establish a comprehensive understanding of how varying concentrations and combinations of decane isomers affect fuel performance parameters. This includes examining the influence on fuel density, viscosity, thermal stability, and combustion efficiency. Additionally, researchers aim to determine the optimal blend ratios that can maximize energy content while maintaining other essential fuel properties within acceptable ranges.
Another critical goal is to assess the environmental impact of decane-enriched jet fuels. With increasing global emphasis on reducing aviation's carbon footprint, there is a pressing need to develop fuel blends that can contribute to lower emissions without compromising engine performance or safety standards. The study of decane blends aligns with this objective, as it may lead to the formulation of cleaner-burning fuels.
Furthermore, the research into decane blends seeks to address the challenges associated with fuel stability and storage. As the aviation industry explores the use of alternative and sustainable fuel sources, understanding how decane blends interact with these new components becomes crucial. This knowledge will be instrumental in developing robust fuel formulations that can maintain their performance characteristics under various operational conditions and storage durations.
The historical development of jet fuels has been marked by a series of advancements aimed at meeting the evolving demands of aircraft engines and environmental regulations. Initially, kerosene-based fuels were the standard, but as engine technology progressed, the need for fuels with specific performance attributes became apparent. This led to the exploration of various hydrocarbon blends, with decane and its isomers gaining prominence due to their favorable properties.
Decane, a straight-chain alkane with ten carbon atoms, and its branched isomers have been identified as key components in jet fuel formulations. Their presence can significantly impact critical fuel parameters such as energy density, freezing point, and combustion characteristics. The study of decane blends is driven by the potential to fine-tune these properties, thereby enhancing overall jet fuel performance.
The primary objective of investigating decane blends in jet fuel is to establish a comprehensive understanding of how varying concentrations and combinations of decane isomers affect fuel performance parameters. This includes examining the influence on fuel density, viscosity, thermal stability, and combustion efficiency. Additionally, researchers aim to determine the optimal blend ratios that can maximize energy content while maintaining other essential fuel properties within acceptable ranges.
Another critical goal is to assess the environmental impact of decane-enriched jet fuels. With increasing global emphasis on reducing aviation's carbon footprint, there is a pressing need to develop fuel blends that can contribute to lower emissions without compromising engine performance or safety standards. The study of decane blends aligns with this objective, as it may lead to the formulation of cleaner-burning fuels.
Furthermore, the research into decane blends seeks to address the challenges associated with fuel stability and storage. As the aviation industry explores the use of alternative and sustainable fuel sources, understanding how decane blends interact with these new components becomes crucial. This knowledge will be instrumental in developing robust fuel formulations that can maintain their performance characteristics under various operational conditions and storage durations.
Market Demand Analysis for Enhanced Jet Fuel Performance
The global aviation industry's demand for enhanced jet fuel performance has been steadily increasing, driven by the need for improved efficiency, reduced emissions, and better overall aircraft performance. The market for advanced jet fuels, particularly those incorporating decane blends, is experiencing significant growth as airlines and aircraft manufacturers seek to optimize fuel consumption and meet stringent environmental regulations.
The commercial aviation sector, which accounts for the largest share of jet fuel consumption, is a key driver of this demand. With the number of air passengers projected to double by 2037, according to the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the need for high-performance jet fuels is expected to surge. This growth is further amplified by the increasing focus on sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) and the industry's commitment to reducing carbon emissions.
Military aviation represents another substantial market segment for enhanced jet fuels. Defense departments worldwide are investing in research and development of advanced propulsion systems that require high-performance fuels. The demand in this sector is driven by the need for increased range, improved thrust-to-weight ratios, and enhanced operational capabilities of military aircraft.
The market for decane-blended jet fuels is particularly promising due to their potential to improve several critical performance parameters. These include increased energy density, better low-temperature properties, and reduced particulate emissions. As a result, major oil companies and specialty fuel producers are investing heavily in research and development of decane-based fuel formulations.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market demand for enhanced jet fuels, owing to their large commercial and military aviation sectors. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, driven by rapidly expanding air travel markets in countries like China and India.
The push for cleaner and more efficient aviation is also creating new market opportunities. Regulatory initiatives, such as the International Civil Aviation Organization's (ICAO) Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA), are incentivizing the adoption of high-performance, low-emission fuels. This regulatory landscape is expected to further boost the demand for advanced jet fuels, including those utilizing decane blends.
In conclusion, the market demand for enhanced jet fuel performance, particularly through the use of decane blends, is robust and growing. The convergence of factors such as increasing air traffic, environmental concerns, and technological advancements is creating a favorable environment for innovation in jet fuel formulations. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the market for high-performance fuels is poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
The commercial aviation sector, which accounts for the largest share of jet fuel consumption, is a key driver of this demand. With the number of air passengers projected to double by 2037, according to the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the need for high-performance jet fuels is expected to surge. This growth is further amplified by the increasing focus on sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) and the industry's commitment to reducing carbon emissions.
Military aviation represents another substantial market segment for enhanced jet fuels. Defense departments worldwide are investing in research and development of advanced propulsion systems that require high-performance fuels. The demand in this sector is driven by the need for increased range, improved thrust-to-weight ratios, and enhanced operational capabilities of military aircraft.
The market for decane-blended jet fuels is particularly promising due to their potential to improve several critical performance parameters. These include increased energy density, better low-temperature properties, and reduced particulate emissions. As a result, major oil companies and specialty fuel producers are investing heavily in research and development of decane-based fuel formulations.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market demand for enhanced jet fuels, owing to their large commercial and military aviation sectors. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, driven by rapidly expanding air travel markets in countries like China and India.
The push for cleaner and more efficient aviation is also creating new market opportunities. Regulatory initiatives, such as the International Civil Aviation Organization's (ICAO) Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA), are incentivizing the adoption of high-performance, low-emission fuels. This regulatory landscape is expected to further boost the demand for advanced jet fuels, including those utilizing decane blends.
In conclusion, the market demand for enhanced jet fuel performance, particularly through the use of decane blends, is robust and growing. The convergence of factors such as increasing air traffic, environmental concerns, and technological advancements is creating a favorable environment for innovation in jet fuel formulations. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the market for high-performance fuels is poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
Current State and Challenges in Jet Fuel Formulation
The current state of jet fuel formulation is characterized by a complex interplay of performance requirements, environmental considerations, and technological advancements. Conventional jet fuels, primarily derived from petroleum, have been the industry standard for decades. However, the aviation sector faces increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and enhance fuel efficiency, driving research into alternative formulations and additives.
One of the primary challenges in jet fuel formulation is balancing the need for high energy density with stringent safety and performance standards. Jet fuels must maintain their properties across a wide range of temperatures and pressures encountered during flight. The inclusion of decane blends in jet fuel formulations has garnered significant attention due to their potential to improve certain performance parameters.
Decane, a straight-chain alkane with ten carbon atoms, is known for its high energy content and favorable combustion characteristics. When blended with conventional jet fuels, decane can potentially enhance the fuel's energy density, leading to improved range and fuel efficiency. However, the integration of decane blends presents several challenges that researchers and fuel formulators must address.
One key challenge is maintaining the fuel's low-temperature performance. Jet fuels must remain fluid at extremely low temperatures encountered at high altitudes. The addition of decane, which has a higher freezing point than some other jet fuel components, can potentially compromise the fuel's cold flow properties. This necessitates careful balancing of the blend composition to ensure compliance with freezing point specifications.
Another significant challenge lies in ensuring the stability and compatibility of decane blends with existing aircraft fuel systems. The introduction of new fuel components can potentially affect seals, gaskets, and other fuel system components, requiring extensive testing and validation to prevent unintended consequences.
Furthermore, the impact of decane blends on combustion characteristics and emissions profiles must be thoroughly evaluated. While decane has the potential to improve combustion efficiency, its effects on particulate matter and other emissions must be carefully assessed to ensure compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
The aviation industry's shift towards sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) adds another layer of complexity to jet fuel formulation. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate decane blends derived from renewable sources, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals. However, this introduces additional challenges in terms of production scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ensuring drop-in compatibility with existing aircraft and infrastructure.
As the aviation sector continues to evolve, addressing these challenges in jet fuel formulation remains crucial for enhancing performance, reducing environmental impact, and meeting future regulatory requirements. The ongoing research into decane blends and other innovative fuel components represents a critical step towards more efficient and sustainable aviation propulsion systems.
One of the primary challenges in jet fuel formulation is balancing the need for high energy density with stringent safety and performance standards. Jet fuels must maintain their properties across a wide range of temperatures and pressures encountered during flight. The inclusion of decane blends in jet fuel formulations has garnered significant attention due to their potential to improve certain performance parameters.
Decane, a straight-chain alkane with ten carbon atoms, is known for its high energy content and favorable combustion characteristics. When blended with conventional jet fuels, decane can potentially enhance the fuel's energy density, leading to improved range and fuel efficiency. However, the integration of decane blends presents several challenges that researchers and fuel formulators must address.
One key challenge is maintaining the fuel's low-temperature performance. Jet fuels must remain fluid at extremely low temperatures encountered at high altitudes. The addition of decane, which has a higher freezing point than some other jet fuel components, can potentially compromise the fuel's cold flow properties. This necessitates careful balancing of the blend composition to ensure compliance with freezing point specifications.
Another significant challenge lies in ensuring the stability and compatibility of decane blends with existing aircraft fuel systems. The introduction of new fuel components can potentially affect seals, gaskets, and other fuel system components, requiring extensive testing and validation to prevent unintended consequences.
Furthermore, the impact of decane blends on combustion characteristics and emissions profiles must be thoroughly evaluated. While decane has the potential to improve combustion efficiency, its effects on particulate matter and other emissions must be carefully assessed to ensure compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
The aviation industry's shift towards sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) adds another layer of complexity to jet fuel formulation. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate decane blends derived from renewable sources, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals. However, this introduces additional challenges in terms of production scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ensuring drop-in compatibility with existing aircraft and infrastructure.
As the aviation sector continues to evolve, addressing these challenges in jet fuel formulation remains crucial for enhancing performance, reducing environmental impact, and meeting future regulatory requirements. The ongoing research into decane blends and other innovative fuel components represents a critical step towards more efficient and sustainable aviation propulsion systems.
Existing Decane Blend Solutions for Jet Fuel
01 Performance optimization of decane blends in fuel systems
Decane blends are optimized for use in fuel systems, focusing on improving performance parameters such as combustion efficiency, emissions reduction, and overall engine performance. This involves analyzing and adjusting the composition of decane blends to achieve optimal results in various operating conditions.- Performance optimization of decane blends in fuel systems: Decane blends are optimized for use in fuel systems, focusing on improving performance parameters such as combustion efficiency, emissions reduction, and overall engine performance. This involves analyzing and adjusting the composition of decane blends to achieve optimal results in various operating conditions.
- Computational modeling of decane blend properties: Advanced computational techniques are employed to model and predict the performance parameters of decane blends. These models take into account various factors such as molecular structure, thermodynamic properties, and reaction kinetics to simulate the behavior of decane blends under different conditions.
- Experimental analysis of decane blend performance: Experimental methods are used to evaluate the performance parameters of decane blends. This includes conducting laboratory tests and field trials to measure factors such as energy content, volatility, and stability. The results are used to validate computational models and inform blend optimization strategies.
- Integration of decane blends in multi-component fuel systems: Decane blends are integrated into multi-component fuel systems, considering their interactions with other fuel components and system elements. This involves analyzing the performance parameters of the entire fuel system and optimizing the decane blend composition to enhance overall system efficiency and reliability.
- Environmental impact assessment of decane blend usage: The environmental impact of using decane blends is assessed, focusing on performance parameters related to emissions, biodegradability, and overall ecological footprint. This includes analyzing the life cycle of decane blends and their effects on air and water quality when used in various applications.
02 Computational modeling of decane blend properties
Advanced computational techniques are employed to model and predict the performance parameters of decane blends. These models consider factors such as molecular structure, thermodynamic properties, and reaction kinetics to simulate blend behavior under different conditions, aiding in the development of improved formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Experimental analysis of decane blend performance
Experimental methods are used to evaluate the performance parameters of decane blends in real-world applications. This includes testing in engines, combustion chambers, and other relevant systems to measure factors such as power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions levels, providing empirical data to validate computational models and guide blend optimization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of decane blends in multi-component fuel systems
Decane blends are incorporated into multi-component fuel systems, where their performance parameters are evaluated in conjunction with other fuel components. This approach aims to create synergistic effects that enhance overall system performance, considering factors such as blend stability, energy density, and compatibility with existing infrastructure.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental impact assessment of decane blend usage
The environmental implications of using decane blends are assessed, focusing on performance parameters related to emissions, biodegradability, and overall ecological footprint. This evaluation helps in developing more sustainable fuel formulations that meet both performance requirements and environmental regulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Aviation Fuel Industry
The jet fuel performance enhancement through decane blends is in a mature stage of development, with a significant market size driven by the aviation industry's demand for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. The technology's maturity is evident from the involvement of major players like ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co., TotalEnergies OneTech SAS, and Saudi Arabian Oil Co., who possess extensive research capabilities and industry experience. The competitive landscape is diverse, including established oil and gas companies, specialized aviation firms like General Aviation Modifications, Inc., and academic institutions such as Tianjin University and Xi'an Jiaotong University, indicating a blend of industry expertise and cutting-edge research in this field.
ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed advanced blending techniques for decane in jet fuel, focusing on optimizing the balance between performance and environmental impact. Their approach involves precise control of decane isomer ratios to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The company utilizes proprietary catalytic processes to selectively produce specific decane isomers that contribute to improved combustion characteristics[1]. ExxonMobil's research has shown that carefully tailored decane blends can increase the energy density of jet fuel by up to 3%, resulting in extended flight ranges and reduced fuel consumption[2]. Additionally, their blending strategy incorporates advanced additives that work synergistically with decane to enhance low-temperature performance and reduce the risk of fuel system icing[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, proprietary catalytic processes, and a holistic approach to fuel optimization. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs and the need for specialized blending facilities.
TotalEnergies OneTech SAS
Technical Solution: TotalEnergies OneTech has developed a novel approach to decane blending in jet fuel, focusing on the integration of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) components. Their method involves carefully balancing decane isomers with bio-derived hydrocarbons to create a high-performance, low-carbon fuel. The company's research has demonstrated that specific decane blends can enhance the miscibility of SAF components, allowing for higher percentages of sustainable content without compromising fuel properties[4]. TotalEnergies' blending strategy also incorporates advanced molecular modeling to predict and optimize fuel performance across a wide range of operating conditions. Their studies have shown that optimized decane-SAF blends can maintain thermal stability at temperatures up to 5°C higher than conventional jet fuel, potentially improving engine efficiency and reducing maintenance requirements[5].
Strengths: Integration of sustainable components, advanced molecular modeling capabilities, and focus on future-proof fuel solutions. Weaknesses: Dependence on the availability of sustainable feedstocks and potential regulatory hurdles for novel fuel blends.
Core Innovations in Decane-based Fuel Formulations
Jet fuel composition and method for producing a jet fuel composition
PatentActiveUS20230313061A1
Innovation
- A jet fuel composition is created by mixing a petroleum-derived jet fuel component with 1 to 50 vol% of a renewable component consisting of hydroprocessed esters and fatty acids, which includes a specific normal paraffins content, resulting in a freezing point of −40° C. or below, and a content of C9-C12 normal paraffins from 17 wt% to 30 wt%, thereby lowering the freezing point below the theoretical linear relation.
Process for producing renewable jet fuel compositions
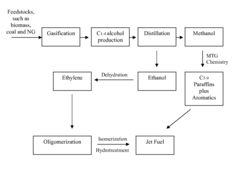
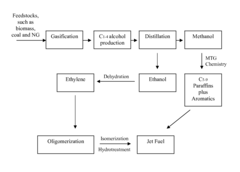
PatentActiveUS9422494B2
Innovation
- A process that generates syngas from biomass or other carbon-containing feedstocks, converts it into methanol and ethanol using an alcohol-synthesis catalyst, then converts methanol to dimethyl ether and ethanol to jet fuel range hydrocarbons using zeolite catalysts, with optional dehydration and oligomerization steps to produce paraffins and aromatics.
Environmental Impact of Decane Blends in Aviation Fuel
The environmental impact of decane blends in aviation fuel is a critical consideration as the aviation industry seeks to reduce its carbon footprint and meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Decane, a hydrocarbon compound, is a key component in jet fuel blends, and its influence on environmental parameters is significant.
When used in aviation fuel blends, decane contributes to the overall emissions profile of aircraft engines. The combustion of decane-rich fuel mixtures typically results in the production of carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and other greenhouse gases. These emissions contribute to global warming and climate change, which are major concerns for the aviation sector and environmental regulators worldwide.
However, the specific environmental impact of decane blends can vary depending on the precise composition and ratio of components in the fuel mixture. Some decane blends may offer improved combustion efficiency, potentially reducing overall fuel consumption and, consequently, lowering emissions per flight. This efficiency gain could lead to a net positive environmental impact when considered across the entire fleet of aircraft using such fuel blends.
Particulate matter emissions are another important environmental consideration. Decane blends can influence the formation and characteristics of particulates produced during combustion. Depending on the blend composition, there may be potential to reduce the number and size of particulates emitted, which could have positive implications for local air quality around airports and in flight corridors.
The production and transportation of decane-based aviation fuels also have environmental implications. The extraction, refining, and distribution processes associated with these fuels contribute to the overall lifecycle emissions. As such, any assessment of the environmental impact must consider not only the combustion phase but also the entire supply chain.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of decane blends in aviation fuel include research into bio-derived decane alternatives. These sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) aim to reduce the carbon intensity of flight by utilizing renewable sources for decane production. While promising, the scalability and economic viability of these alternatives remain challenges to widespread adoption.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of decane blends in aviation fuel is multifaceted, encompassing both direct emissions from combustion and indirect effects from production and distribution. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, understanding and optimizing the environmental performance of decane blends will be crucial in developing more sustainable air travel solutions.
When used in aviation fuel blends, decane contributes to the overall emissions profile of aircraft engines. The combustion of decane-rich fuel mixtures typically results in the production of carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and other greenhouse gases. These emissions contribute to global warming and climate change, which are major concerns for the aviation sector and environmental regulators worldwide.
However, the specific environmental impact of decane blends can vary depending on the precise composition and ratio of components in the fuel mixture. Some decane blends may offer improved combustion efficiency, potentially reducing overall fuel consumption and, consequently, lowering emissions per flight. This efficiency gain could lead to a net positive environmental impact when considered across the entire fleet of aircraft using such fuel blends.
Particulate matter emissions are another important environmental consideration. Decane blends can influence the formation and characteristics of particulates produced during combustion. Depending on the blend composition, there may be potential to reduce the number and size of particulates emitted, which could have positive implications for local air quality around airports and in flight corridors.
The production and transportation of decane-based aviation fuels also have environmental implications. The extraction, refining, and distribution processes associated with these fuels contribute to the overall lifecycle emissions. As such, any assessment of the environmental impact must consider not only the combustion phase but also the entire supply chain.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of decane blends in aviation fuel include research into bio-derived decane alternatives. These sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) aim to reduce the carbon intensity of flight by utilizing renewable sources for decane production. While promising, the scalability and economic viability of these alternatives remain challenges to widespread adoption.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of decane blends in aviation fuel is multifaceted, encompassing both direct emissions from combustion and indirect effects from production and distribution. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, understanding and optimizing the environmental performance of decane blends will be crucial in developing more sustainable air travel solutions.
Regulatory Framework for Alternative Jet Fuel Blends
The regulatory framework for alternative jet fuel blends plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, performance, and environmental sustainability of aviation fuels. This framework is primarily governed by international organizations such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and national aviation authorities like the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States.
ASTM International, a global standards organization, has developed the ASTM D7566 specification, which sets the standards for aviation turbine fuel containing synthesized hydrocarbons. This specification allows for the approval of new alternative jet fuel production pathways and provides a framework for blending these fuels with conventional petroleum-based jet fuel.
The approval process for new alternative jet fuel blends involves rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure compatibility with existing aircraft systems and infrastructure. This process typically includes extensive laboratory testing, engine testing, and flight demonstrations. The fuel must meet or exceed the performance characteristics of conventional jet fuel in areas such as energy content, freezing point, thermal stability, and lubricity.
Environmental considerations are also a key component of the regulatory framework. The Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA), implemented by ICAO, aims to address CO2 emissions from international aviation. This scheme encourages the use of sustainable aviation fuels that meet specific sustainability criteria.
National and regional regulations also play a significant role in shaping the adoption of alternative jet fuel blends. For example, the European Union's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) sets targets for renewable energy use in transport, including aviation. Similarly, the United States Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program provides incentives for the production and use of renewable fuels in aviation.
The regulatory framework also addresses the certification of fuel production facilities and the traceability of alternative jet fuels throughout the supply chain. This ensures that the fuels meet the required specifications and sustainability criteria from production to use.
As the aviation industry continues to evolve and new alternative fuel technologies emerge, the regulatory framework must adapt to accommodate these changes while maintaining the highest standards of safety and performance. This requires ongoing collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and research institutions to develop and refine standards and approval processes for innovative fuel blends.
ASTM International, a global standards organization, has developed the ASTM D7566 specification, which sets the standards for aviation turbine fuel containing synthesized hydrocarbons. This specification allows for the approval of new alternative jet fuel production pathways and provides a framework for blending these fuels with conventional petroleum-based jet fuel.
The approval process for new alternative jet fuel blends involves rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure compatibility with existing aircraft systems and infrastructure. This process typically includes extensive laboratory testing, engine testing, and flight demonstrations. The fuel must meet or exceed the performance characteristics of conventional jet fuel in areas such as energy content, freezing point, thermal stability, and lubricity.
Environmental considerations are also a key component of the regulatory framework. The Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA), implemented by ICAO, aims to address CO2 emissions from international aviation. This scheme encourages the use of sustainable aviation fuels that meet specific sustainability criteria.
National and regional regulations also play a significant role in shaping the adoption of alternative jet fuel blends. For example, the European Union's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) sets targets for renewable energy use in transport, including aviation. Similarly, the United States Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program provides incentives for the production and use of renewable fuels in aviation.
The regulatory framework also addresses the certification of fuel production facilities and the traceability of alternative jet fuels throughout the supply chain. This ensures that the fuels meet the required specifications and sustainability criteria from production to use.
As the aviation industry continues to evolve and new alternative fuel technologies emerge, the regulatory framework must adapt to accommodate these changes while maintaining the highest standards of safety and performance. This requires ongoing collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and research institutions to develop and refine standards and approval processes for innovative fuel blends.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!