How Does Isopentane Influence Gas Storage Capabilities
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isopentane Gas Storage Background and Objectives
Isopentane, a branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C5H12, has gained significant attention in the field of gas storage due to its unique properties and potential applications. The evolution of gas storage technologies has been driven by the increasing demand for efficient and safe methods to store and transport various gases, particularly in the energy sector. Isopentane's role in this domain has emerged as a promising area of research and development.
The primary objective of exploring isopentane's influence on gas storage capabilities is to enhance the efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of gas storage systems. This aligns with the broader goals of improving energy security, reducing environmental impact, and meeting the growing global energy demands. By understanding the interactions between isopentane and other gases, researchers aim to develop innovative storage solutions that can overcome the limitations of conventional methods.
Historically, gas storage technologies have progressed from simple pressurized containers to more advanced systems involving adsorbent materials and chemical storage. The introduction of isopentane into this field represents a new frontier in gas storage research, potentially offering advantages in terms of storage capacity, energy density, and operational flexibility.
The technical evolution of isopentane-based gas storage systems has been marked by several key milestones. Initial studies focused on understanding the thermodynamic properties of isopentane and its behavior under various pressure and temperature conditions. This foundational knowledge has led to the exploration of isopentane as a component in gas hydrate formation, which has shown promise for storing gases like methane and carbon dioxide.
Recent technological trends in this area include the development of hybrid storage systems that combine isopentane with other materials to enhance storage performance. These innovations aim to leverage isopentane's unique characteristics, such as its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, to create more efficient and versatile gas storage solutions.
The potential applications of isopentane-influenced gas storage extend across multiple industries, including energy, transportation, and industrial processes. In the energy sector, improved gas storage capabilities could lead to more effective natural gas transportation and storage, potentially reducing reliance on pipeline infrastructure. In the automotive industry, enhanced gas storage systems could contribute to the development of more efficient and compact fuel systems for vehicles.
As research in this field progresses, the overarching goal is to develop a comprehensive understanding of how isopentane influences gas storage capabilities at both the molecular and macroscopic levels. This knowledge will be crucial in designing and optimizing next-generation gas storage technologies that can meet the evolving needs of various industries and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
The primary objective of exploring isopentane's influence on gas storage capabilities is to enhance the efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of gas storage systems. This aligns with the broader goals of improving energy security, reducing environmental impact, and meeting the growing global energy demands. By understanding the interactions between isopentane and other gases, researchers aim to develop innovative storage solutions that can overcome the limitations of conventional methods.
Historically, gas storage technologies have progressed from simple pressurized containers to more advanced systems involving adsorbent materials and chemical storage. The introduction of isopentane into this field represents a new frontier in gas storage research, potentially offering advantages in terms of storage capacity, energy density, and operational flexibility.
The technical evolution of isopentane-based gas storage systems has been marked by several key milestones. Initial studies focused on understanding the thermodynamic properties of isopentane and its behavior under various pressure and temperature conditions. This foundational knowledge has led to the exploration of isopentane as a component in gas hydrate formation, which has shown promise for storing gases like methane and carbon dioxide.
Recent technological trends in this area include the development of hybrid storage systems that combine isopentane with other materials to enhance storage performance. These innovations aim to leverage isopentane's unique characteristics, such as its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, to create more efficient and versatile gas storage solutions.
The potential applications of isopentane-influenced gas storage extend across multiple industries, including energy, transportation, and industrial processes. In the energy sector, improved gas storage capabilities could lead to more effective natural gas transportation and storage, potentially reducing reliance on pipeline infrastructure. In the automotive industry, enhanced gas storage systems could contribute to the development of more efficient and compact fuel systems for vehicles.
As research in this field progresses, the overarching goal is to develop a comprehensive understanding of how isopentane influences gas storage capabilities at both the molecular and macroscopic levels. This knowledge will be crucial in designing and optimizing next-generation gas storage technologies that can meet the evolving needs of various industries and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Market Analysis for Isopentane-Enhanced Gas Storage
The market for isopentane-enhanced gas storage has shown significant growth potential in recent years, driven by increasing demand for efficient energy storage solutions and the push towards cleaner fuel alternatives. Isopentane, a branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C5H12, has emerged as a promising additive for improving gas storage capabilities, particularly in natural gas and hydrogen storage applications.
In the natural gas sector, the use of isopentane as an additive has gained traction due to its ability to enhance the energy density of stored gas. This property allows for increased storage capacity in existing infrastructure, potentially reducing the need for costly expansions of storage facilities. The market for isopentane in this application is expected to grow as countries seek to bolster their natural gas reserves and improve energy security.
The hydrogen storage market represents another significant opportunity for isopentane-enhanced solutions. As the global focus on hydrogen as a clean energy carrier intensifies, the need for efficient storage methods becomes paramount. Isopentane's potential to improve the volumetric energy density of hydrogen storage systems has attracted attention from both research institutions and industry players.
The automotive sector has shown particular interest in isopentane-enhanced gas storage technologies. With the rise of natural gas and hydrogen-powered vehicles, there is a growing demand for compact, high-capacity fuel storage systems. Isopentane's ability to increase storage efficiency could lead to extended driving ranges and reduced refueling frequency, addressing key consumer concerns in the alternative fuel vehicle market.
In the industrial gas sector, isopentane-enhanced storage solutions are being explored for applications in manufacturing processes that require large volumes of gases. The potential for increased storage capacity could lead to operational efficiencies and cost savings for industrial users, driving adoption in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently leading the market for isopentane-enhanced gas storage technologies, with significant research and development activities underway. However, rapid industrialization and increasing energy demands in Asia-Pacific regions, particularly China and India, are expected to create substantial market opportunities in the coming years.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as safety concerns related to the flammability of isopentane and the need for specialized handling and storage equipment. Regulatory frameworks governing the use of isopentane in gas storage applications are still evolving, which could impact market growth rates in certain regions.
In the natural gas sector, the use of isopentane as an additive has gained traction due to its ability to enhance the energy density of stored gas. This property allows for increased storage capacity in existing infrastructure, potentially reducing the need for costly expansions of storage facilities. The market for isopentane in this application is expected to grow as countries seek to bolster their natural gas reserves and improve energy security.
The hydrogen storage market represents another significant opportunity for isopentane-enhanced solutions. As the global focus on hydrogen as a clean energy carrier intensifies, the need for efficient storage methods becomes paramount. Isopentane's potential to improve the volumetric energy density of hydrogen storage systems has attracted attention from both research institutions and industry players.
The automotive sector has shown particular interest in isopentane-enhanced gas storage technologies. With the rise of natural gas and hydrogen-powered vehicles, there is a growing demand for compact, high-capacity fuel storage systems. Isopentane's ability to increase storage efficiency could lead to extended driving ranges and reduced refueling frequency, addressing key consumer concerns in the alternative fuel vehicle market.
In the industrial gas sector, isopentane-enhanced storage solutions are being explored for applications in manufacturing processes that require large volumes of gases. The potential for increased storage capacity could lead to operational efficiencies and cost savings for industrial users, driving adoption in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently leading the market for isopentane-enhanced gas storage technologies, with significant research and development activities underway. However, rapid industrialization and increasing energy demands in Asia-Pacific regions, particularly China and India, are expected to create substantial market opportunities in the coming years.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as safety concerns related to the flammability of isopentane and the need for specialized handling and storage equipment. Regulatory frameworks governing the use of isopentane in gas storage applications are still evolving, which could impact market growth rates in certain regions.
Current Challenges in Isopentane-Based Gas Storage
The current challenges in isopentane-based gas storage primarily revolve around efficiency, safety, and environmental concerns. One of the main obstacles is the optimization of storage capacity while maintaining the stability of the gas-isopentane mixture. Isopentane, being a highly volatile hydrocarbon, presents unique challenges in terms of containment and pressure management.
Researchers are grappling with the issue of isopentane's low boiling point, which can lead to increased vapor pressure within storage systems. This heightened pressure poses risks of leakage and potential explosions, necessitating the development of more robust containment solutions. Additionally, the interaction between isopentane and various gases under different temperature and pressure conditions is not fully understood, making it difficult to predict long-term storage behavior accurately.
Another significant challenge lies in the environmental impact of isopentane-based gas storage. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), isopentane can contribute to air pollution and ozone depletion if released into the atmosphere. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a push for more environmentally friendly alternatives or improved containment methods.
The energy efficiency of isopentane-based gas storage systems is also a concern. While isopentane can enhance the storage capacity of certain gases, the energy required for compression and cooling in these systems can be substantial. Researchers are working on developing more energy-efficient processes to make isopentane-based storage economically viable on a larger scale.
Material compatibility is another hurdle facing the industry. Isopentane can degrade certain materials commonly used in gas storage infrastructure, leading to potential leaks and reduced system lifespan. This necessitates the development and testing of new materials that can withstand prolonged exposure to isopentane without compromising their structural integrity.
Furthermore, the scalability of isopentane-based gas storage technologies presents challenges. While promising results have been achieved in laboratory settings, translating these successes to industrial-scale applications requires overcoming significant engineering and logistical hurdles. This includes designing large-scale storage facilities that can safely handle the increased volumes of isopentane and gas mixtures.
Lastly, there is a need for more comprehensive safety protocols and risk assessment methodologies specific to isopentane-based gas storage. The unique properties of isopentane, combined with various gases, create complex safety scenarios that are not fully addressed by existing industry standards. Developing these protocols is crucial for the widespread adoption of this technology in commercial and industrial applications.
Researchers are grappling with the issue of isopentane's low boiling point, which can lead to increased vapor pressure within storage systems. This heightened pressure poses risks of leakage and potential explosions, necessitating the development of more robust containment solutions. Additionally, the interaction between isopentane and various gases under different temperature and pressure conditions is not fully understood, making it difficult to predict long-term storage behavior accurately.
Another significant challenge lies in the environmental impact of isopentane-based gas storage. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), isopentane can contribute to air pollution and ozone depletion if released into the atmosphere. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a push for more environmentally friendly alternatives or improved containment methods.
The energy efficiency of isopentane-based gas storage systems is also a concern. While isopentane can enhance the storage capacity of certain gases, the energy required for compression and cooling in these systems can be substantial. Researchers are working on developing more energy-efficient processes to make isopentane-based storage economically viable on a larger scale.
Material compatibility is another hurdle facing the industry. Isopentane can degrade certain materials commonly used in gas storage infrastructure, leading to potential leaks and reduced system lifespan. This necessitates the development and testing of new materials that can withstand prolonged exposure to isopentane without compromising their structural integrity.
Furthermore, the scalability of isopentane-based gas storage technologies presents challenges. While promising results have been achieved in laboratory settings, translating these successes to industrial-scale applications requires overcoming significant engineering and logistical hurdles. This includes designing large-scale storage facilities that can safely handle the increased volumes of isopentane and gas mixtures.
Lastly, there is a need for more comprehensive safety protocols and risk assessment methodologies specific to isopentane-based gas storage. The unique properties of isopentane, combined with various gases, create complex safety scenarios that are not fully addressed by existing industry standards. Developing these protocols is crucial for the widespread adoption of this technology in commercial and industrial applications.
Existing Isopentane Gas Storage Solutions
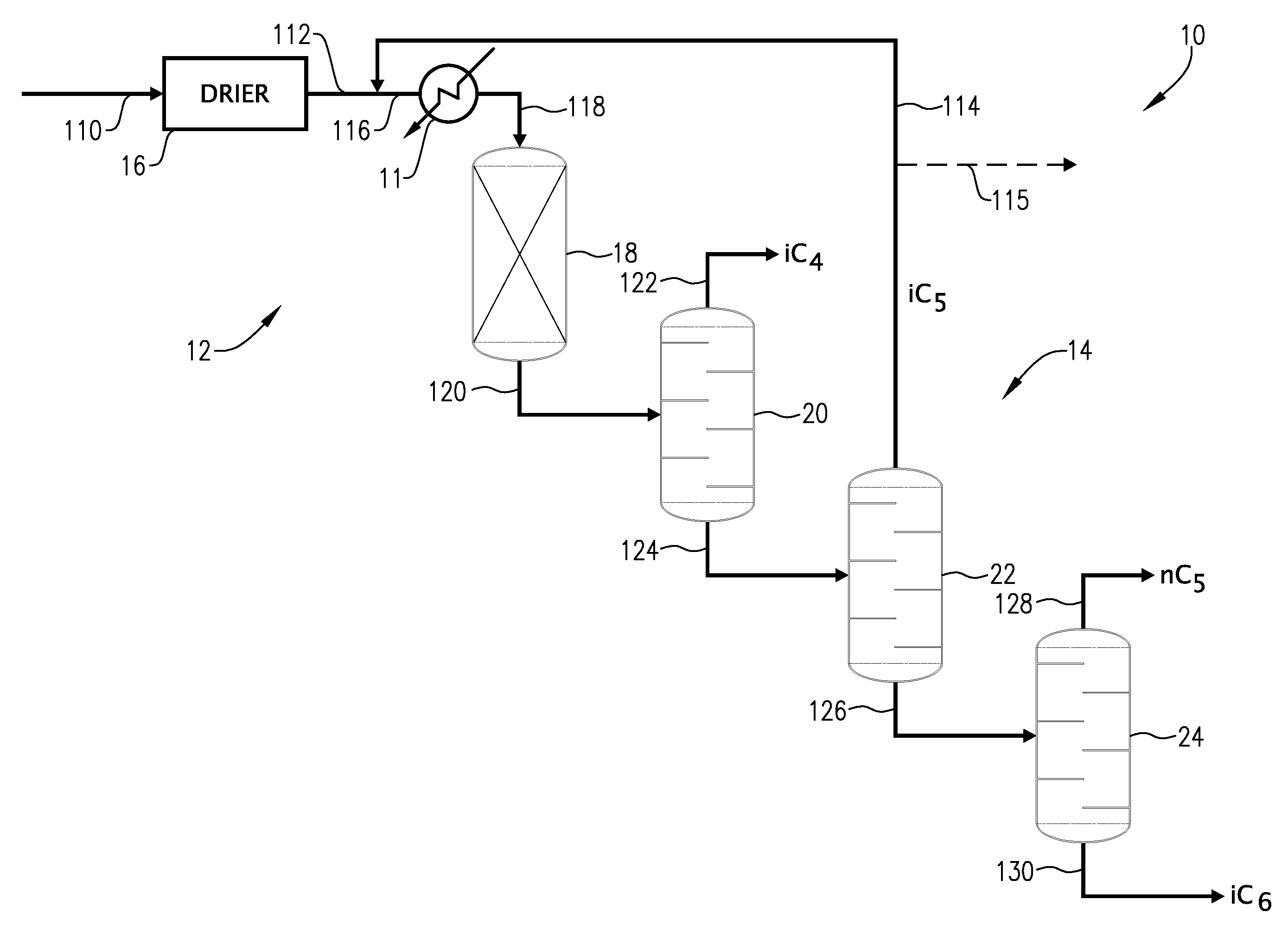
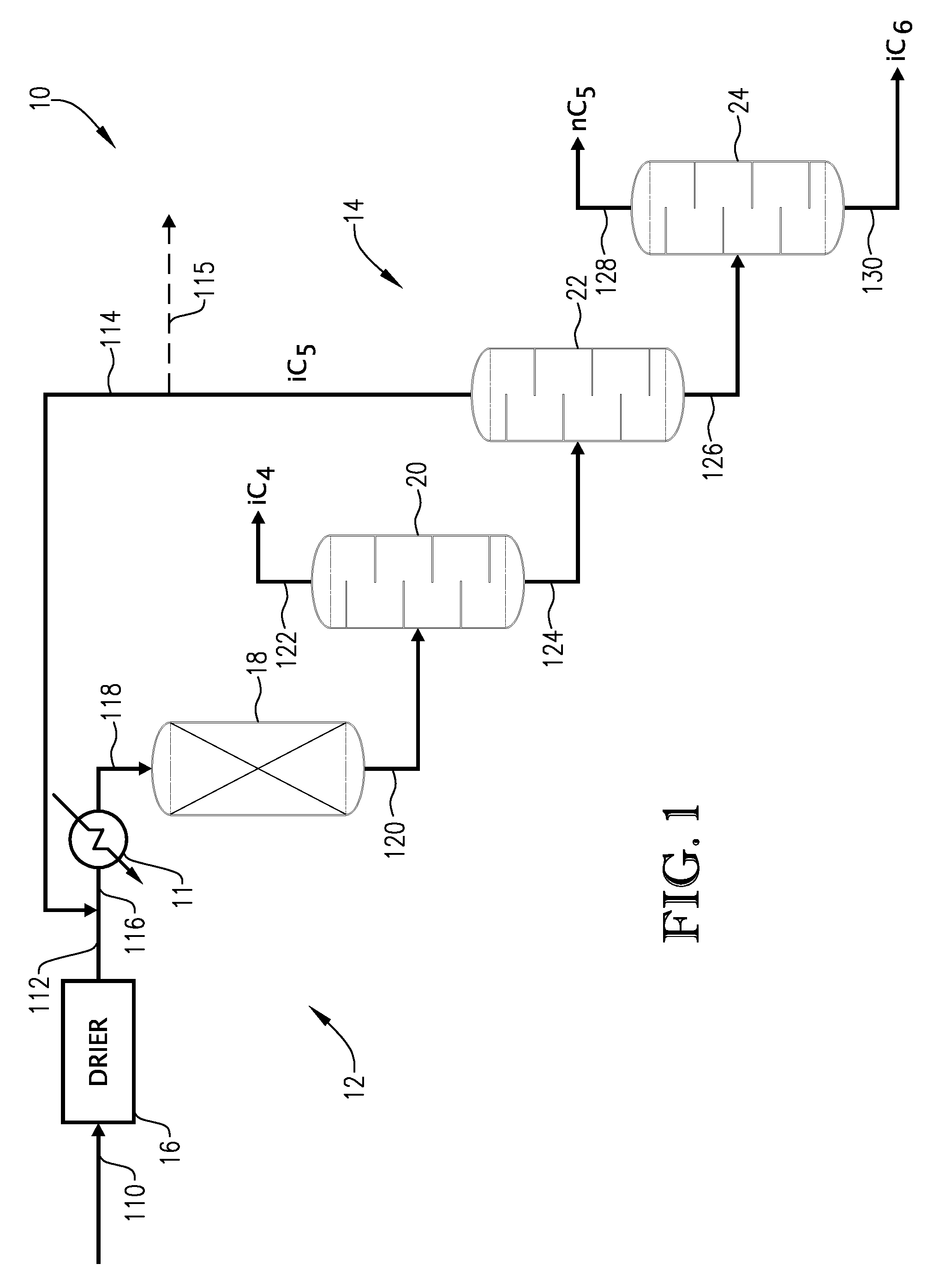
01 Storage containers for isopentane gas
Various specialized containers and vessels are designed for the safe storage of isopentane gas. These containers are engineered to withstand the pressure and temperature requirements of isopentane, ensuring proper containment and preventing leaks. The designs may include features such as pressure relief valves, insulation, and corrosion-resistant materials to maintain the integrity of the stored gas.- Storage containers for isopentane gas: Various specialized containers and vessels are designed for storing isopentane gas safely. These storage solutions often incorporate pressure-resistant materials and safety features to prevent leaks and maintain the gas in its liquid state under pressure.
- Cryogenic storage of isopentane: Cryogenic storage methods are employed to maintain isopentane in a liquid state at very low temperatures. This approach involves specialized insulation techniques and temperature control systems to minimize boil-off and ensure safe long-term storage.
- Adsorption-based storage systems: Adsorption-based storage systems utilize porous materials to increase the storage capacity of isopentane gas. These systems can store a larger volume of gas at lower pressures, improving safety and efficiency in storage and transportation.
- Isopentane storage in chemical processes: In various chemical processes, isopentane is stored as an intermediate or product. Specialized storage solutions are designed to integrate with production facilities, ensuring safe containment and easy access for further processing or distribution.
- Safety measures for isopentane storage: Given the flammable nature of isopentane, storage facilities incorporate multiple safety measures. These include pressure relief systems, fire suppression equipment, leak detection technologies, and proper ventilation to mitigate risks associated with gas storage.
02 Cryogenic storage of isopentane
Cryogenic storage methods are employed for isopentane gas, involving the use of low-temperature systems to maintain the gas in a liquid state. This approach allows for more efficient storage and transportation of larger volumes of isopentane. Specialized cryogenic tanks and insulation techniques are utilized to minimize heat transfer and maintain the required low temperatures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Adsorption-based storage systems
Adsorption-based storage systems utilize porous materials to increase the storage capacity of isopentane gas. These systems exploit the high surface area of adsorbents to store a larger amount of gas at lower pressures compared to conventional compression methods. Various adsorbent materials and their modifications are explored to optimize the storage efficiency and safety of isopentane gas.Expand Specific Solutions04 Underground storage of isopentane
Underground storage facilities are developed for large-scale storage of isopentane gas. These may include caverns, depleted oil and gas reservoirs, or specially constructed underground chambers. The natural insulation provided by the earth helps maintain stable temperatures and pressures, while specialized monitoring and safety systems ensure the integrity of the stored gas.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isopentane storage in chemical processes
In various chemical processes, isopentane gas is stored as an intermediate or product. Specialized storage systems are integrated into process plants to handle isopentane safely and efficiently. These systems may include buffer tanks, pressure-swing adsorption units, or membrane separation technologies to manage the flow and purity of isopentane gas within the production cycle.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isopentane and Gas Storage Industry
The competition landscape for isopentane's influence on gas storage capabilities is in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by rising demand for energy storage solutions. The technology is moderately mature, with ongoing research to enhance efficiency. Key players like BASF Corp., Air Liquide SA, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are investing in R&D to improve isopentane-based storage systems. Emerging companies such as SustainX, Inc. and Hydrostor, Inc. are developing innovative compressed air energy storage technologies that may incorporate isopentane. Academic institutions like Kyoto University and University of Michigan are contributing to fundamental research, potentially leading to breakthroughs in gas storage applications.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced gas storage solutions incorporating isopentane as a key component. Their technology utilizes isopentane's unique properties to enhance gas storage capabilities in various applications. BASF's approach involves creating specialized adsorbent materials that interact favorably with isopentane, leading to increased storage capacity and improved efficiency. The company has conducted extensive research on the molecular interactions between isopentane and different gas species, optimizing the storage system's performance[1]. BASF's solution also addresses safety concerns associated with isopentane's flammability by implementing innovative containment and handling protocols[3].
Strengths: Expertise in chemical engineering, extensive R&D capabilities, and a global presence. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges and the need for significant infrastructure investments.
Air Liquide SA
Technical Solution: Air Liquide has pioneered a novel gas storage technology that leverages isopentane's properties to enhance storage efficiency and capacity. Their approach involves a multi-phase system where isopentane acts as a buffer medium, allowing for higher gas compression ratios without significant temperature increases. This technology utilizes isopentane's low boiling point and high vapor pressure to create a more stable storage environment[2]. Air Liquide's system also incorporates advanced heat exchange mechanisms to manage the thermal effects of gas compression and expansion, further improving overall efficiency[4]. The company has successfully demonstrated this technology in pilot projects, showing potential for both industrial and transportation applications.
Strengths: Strong expertise in gas handling and storage, extensive global infrastructure. Weaknesses: High initial implementation costs and potential challenges in scaling up the technology.
Core Innovations in Isopentane-Based Storage
Systems for isomerization and catalytic activation of pentane-enriched hydrocarbon mixtures
PatentActiveUS20200339888A1
Innovation
- A system that separates a hydrocarbon feed stream into fractions based on vapor pressure, followed by isomerization and catalytic activation in reactors to convert n-pentane to isopentane and produce olefins and aromatics, minimizing the production of C1-C4 paraffins, and further upgrading through oligomerization or alkylation to produce larger hydrocarbons suitable for transportation fuels.
Disproportionation of isopentane
PatentActiveUS20080021254A1
Innovation
- A process for disproportionating isopentane into isobutane and isohexanes using a catalyst composition comprising at least 80 weight percent aluminum halide on a support, which allows for the conversion of isopentane into lower RVP products that can be more easily blended into motor fuels, thereby addressing the excess inventory issue.
Environmental Impact of Isopentane in Gas Storage
The environmental impact of isopentane in gas storage is a critical consideration for the energy industry. Isopentane, a volatile organic compound, plays a significant role in enhancing gas storage capabilities but also poses potential risks to the environment.
When used in gas storage facilities, isopentane acts as a cushion gas, improving the overall efficiency of natural gas storage. However, its release into the atmosphere can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. This is particularly concerning in urban areas where air quality is already compromised.
Isopentane's high vapor pressure increases the risk of leaks and emissions during storage and transportation. These emissions can lead to the formation of photochemical smog, which has adverse effects on human health and vegetation. Additionally, isopentane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period.
Water contamination is another environmental concern associated with isopentane in gas storage. Accidental spills or leaks can result in the infiltration of isopentane into groundwater and surface water bodies. This contamination can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems and potentially impact drinking water sources.
The production and use of isopentane in gas storage also contribute to resource depletion. As a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, its extraction and purification require energy and resources, further adding to the overall environmental footprint of gas storage operations.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, the industry has been developing and implementing various strategies. These include improved leak detection and repair programs, advanced sealing technologies, and the use of vapor recovery systems to capture and recycle isopentane emissions. Some facilities are exploring alternatives to isopentane, such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, as cushion gases to reduce the reliance on volatile organic compounds.
Regulatory bodies have also responded to the environmental concerns surrounding isopentane use in gas storage. Stricter emission standards and monitoring requirements have been implemented in many jurisdictions to minimize the release of isopentane into the environment. Environmental impact assessments are now commonly required for new gas storage projects, with a focus on potential isopentane-related risks.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, balancing the benefits of isopentane in gas storage with its environmental impact remains a challenge. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on finding more sustainable solutions that can maintain or improve gas storage capabilities while reducing the environmental footprint associated with isopentane use.
When used in gas storage facilities, isopentane acts as a cushion gas, improving the overall efficiency of natural gas storage. However, its release into the atmosphere can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. This is particularly concerning in urban areas where air quality is already compromised.
Isopentane's high vapor pressure increases the risk of leaks and emissions during storage and transportation. These emissions can lead to the formation of photochemical smog, which has adverse effects on human health and vegetation. Additionally, isopentane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period.
Water contamination is another environmental concern associated with isopentane in gas storage. Accidental spills or leaks can result in the infiltration of isopentane into groundwater and surface water bodies. This contamination can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems and potentially impact drinking water sources.
The production and use of isopentane in gas storage also contribute to resource depletion. As a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, its extraction and purification require energy and resources, further adding to the overall environmental footprint of gas storage operations.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, the industry has been developing and implementing various strategies. These include improved leak detection and repair programs, advanced sealing technologies, and the use of vapor recovery systems to capture and recycle isopentane emissions. Some facilities are exploring alternatives to isopentane, such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, as cushion gases to reduce the reliance on volatile organic compounds.
Regulatory bodies have also responded to the environmental concerns surrounding isopentane use in gas storage. Stricter emission standards and monitoring requirements have been implemented in many jurisdictions to minimize the release of isopentane into the environment. Environmental impact assessments are now commonly required for new gas storage projects, with a focus on potential isopentane-related risks.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, balancing the benefits of isopentane in gas storage with its environmental impact remains a challenge. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on finding more sustainable solutions that can maintain or improve gas storage capabilities while reducing the environmental footprint associated with isopentane use.
Safety Regulations for Isopentane Storage Systems
Safety regulations for isopentane storage systems are critical due to the compound's high flammability and volatility. These regulations typically encompass several key areas to ensure the safe handling, storage, and use of isopentane in gas storage applications.
Storage tank design and construction standards form a fundamental aspect of these regulations. Tanks must be built to withstand the pressure exerted by isopentane vapor and resist corrosion. Double-walled tanks with leak detection systems are often mandated to prevent accidental releases. Pressure relief valves and emergency venting systems are required to manage potential overpressure situations.
Ventilation requirements are stringent for isopentane storage areas. Adequate air circulation is essential to prevent the accumulation of flammable vapors. Explosion-proof electrical equipment and lighting fixtures are mandatory in storage zones to eliminate ignition sources. Grounding and bonding procedures are strictly enforced to prevent static electricity buildup, which could potentially ignite isopentane vapors.
Fire protection systems are a crucial component of safety regulations. Automatic fire detection and suppression systems, such as foam or dry chemical extinguishing agents, must be installed. Fire-resistant barriers and containment areas are required to isolate storage tanks and limit the spread of potential fires.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) regulations for workers handling isopentane are comprehensive. This includes requirements for chemical-resistant gloves, protective eyewear, and flame-resistant clothing. Respiratory protection may be necessary in certain situations, particularly during maintenance or in the event of a leak.
Emergency response planning is a key element of safety regulations. Facilities must develop and regularly update detailed procedures for handling spills, leaks, and fires involving isopentane. This includes evacuation plans, communication protocols, and coordination with local emergency services.
Training requirements for personnel working with isopentane storage systems are typically rigorous. Workers must be educated on the properties of isopentane, safe handling procedures, emergency response protocols, and the proper use of safety equipment. Regular refresher courses and safety drills are often mandated to maintain preparedness.
Monitoring and inspection protocols are essential components of safety regulations. Regular checks of storage tanks, piping systems, and safety equipment are required to ensure integrity and proper functioning. This may include pressure testing, leak detection surveys, and non-destructive testing of tank walls.
Documentation and record-keeping requirements are typically extensive. Facilities must maintain detailed logs of inspections, maintenance activities, safety incidents, and personnel training. These records are subject to review by regulatory authorities to ensure ongoing compliance with safety standards.
Storage tank design and construction standards form a fundamental aspect of these regulations. Tanks must be built to withstand the pressure exerted by isopentane vapor and resist corrosion. Double-walled tanks with leak detection systems are often mandated to prevent accidental releases. Pressure relief valves and emergency venting systems are required to manage potential overpressure situations.
Ventilation requirements are stringent for isopentane storage areas. Adequate air circulation is essential to prevent the accumulation of flammable vapors. Explosion-proof electrical equipment and lighting fixtures are mandatory in storage zones to eliminate ignition sources. Grounding and bonding procedures are strictly enforced to prevent static electricity buildup, which could potentially ignite isopentane vapors.
Fire protection systems are a crucial component of safety regulations. Automatic fire detection and suppression systems, such as foam or dry chemical extinguishing agents, must be installed. Fire-resistant barriers and containment areas are required to isolate storage tanks and limit the spread of potential fires.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) regulations for workers handling isopentane are comprehensive. This includes requirements for chemical-resistant gloves, protective eyewear, and flame-resistant clothing. Respiratory protection may be necessary in certain situations, particularly during maintenance or in the event of a leak.
Emergency response planning is a key element of safety regulations. Facilities must develop and regularly update detailed procedures for handling spills, leaks, and fires involving isopentane. This includes evacuation plans, communication protocols, and coordination with local emergency services.
Training requirements for personnel working with isopentane storage systems are typically rigorous. Workers must be educated on the properties of isopentane, safe handling procedures, emergency response protocols, and the proper use of safety equipment. Regular refresher courses and safety drills are often mandated to maintain preparedness.
Monitoring and inspection protocols are essential components of safety regulations. Regular checks of storage tanks, piping systems, and safety equipment are required to ensure integrity and proper functioning. This may include pressure testing, leak detection surveys, and non-destructive testing of tank walls.
Documentation and record-keeping requirements are typically extensive. Facilities must maintain detailed logs of inspections, maintenance activities, safety incidents, and personnel training. These records are subject to review by regulatory authorities to ensure ongoing compliance with safety standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!