How Isopentane Enhances Chemical Vapor Deposition Coatings
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isopentane in CVD: Background and Objectives
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a widely used technique in the semiconductor and materials science industries for depositing thin films of various materials onto substrates. The process involves the reaction of gaseous precursors on a heated substrate surface to form a solid film. Over the years, researchers and engineers have been continuously seeking ways to enhance the efficiency and quality of CVD coatings.
Isopentane, a branched alkane with the molecular formula C5H12, has emerged as a promising additive in CVD processes. Its unique properties, including low boiling point, high vapor pressure, and chemical stability, make it an attractive candidate for improving CVD coating performance. The integration of isopentane into CVD processes aims to address several key challenges in the field, such as improving film uniformity, increasing deposition rates, and enhancing the overall quality of the deposited layers.
The evolution of CVD technology has been driven by the ever-increasing demands of the semiconductor industry for more precise and efficient coating methods. Traditional CVD processes often face limitations in terms of deposition rate, film quality, and process control. The introduction of isopentane as a process enhancer represents a significant step forward in addressing these challenges and pushing the boundaries of CVD capabilities.
The primary objective of incorporating isopentane into CVD processes is to optimize the coating performance across various applications. This includes improving the uniformity of film thickness, enhancing the conformality of coatings on complex geometries, and increasing the overall deposition rate without compromising film quality. Additionally, researchers aim to explore the potential of isopentane in enabling the deposition of novel materials or achieving unique film properties that were previously difficult to attain with conventional CVD methods.
As the demand for advanced materials and high-performance coatings continues to grow across industries such as electronics, optics, and energy, the role of isopentane in CVD processes is expected to gain increasing attention. The technology's potential to address critical challenges in thin film deposition positions it as a key area of research and development in the field of materials science and engineering.
Understanding the mechanisms by which isopentane enhances CVD coatings is crucial for optimizing process parameters and expanding the range of applications. This involves investigating the interaction between isopentane and various precursor gases, studying its impact on gas-phase and surface reactions, and exploring its influence on film nucleation and growth kinetics. By elucidating these fundamental aspects, researchers aim to develop more efficient and versatile CVD processes that can meet the evolving needs of advanced manufacturing and materials engineering.
Isopentane, a branched alkane with the molecular formula C5H12, has emerged as a promising additive in CVD processes. Its unique properties, including low boiling point, high vapor pressure, and chemical stability, make it an attractive candidate for improving CVD coating performance. The integration of isopentane into CVD processes aims to address several key challenges in the field, such as improving film uniformity, increasing deposition rates, and enhancing the overall quality of the deposited layers.
The evolution of CVD technology has been driven by the ever-increasing demands of the semiconductor industry for more precise and efficient coating methods. Traditional CVD processes often face limitations in terms of deposition rate, film quality, and process control. The introduction of isopentane as a process enhancer represents a significant step forward in addressing these challenges and pushing the boundaries of CVD capabilities.
The primary objective of incorporating isopentane into CVD processes is to optimize the coating performance across various applications. This includes improving the uniformity of film thickness, enhancing the conformality of coatings on complex geometries, and increasing the overall deposition rate without compromising film quality. Additionally, researchers aim to explore the potential of isopentane in enabling the deposition of novel materials or achieving unique film properties that were previously difficult to attain with conventional CVD methods.
As the demand for advanced materials and high-performance coatings continues to grow across industries such as electronics, optics, and energy, the role of isopentane in CVD processes is expected to gain increasing attention. The technology's potential to address critical challenges in thin film deposition positions it as a key area of research and development in the field of materials science and engineering.
Understanding the mechanisms by which isopentane enhances CVD coatings is crucial for optimizing process parameters and expanding the range of applications. This involves investigating the interaction between isopentane and various precursor gases, studying its impact on gas-phase and surface reactions, and exploring its influence on film nucleation and growth kinetics. By elucidating these fundamental aspects, researchers aim to develop more efficient and versatile CVD processes that can meet the evolving needs of advanced manufacturing and materials engineering.
Market Analysis for Enhanced CVD Coatings
The market for enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) coatings has been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance materials in various industries. The use of isopentane as an enhancing agent in CVD processes has opened up new possibilities for coating applications, particularly in sectors such as semiconductors, aerospace, and automotive.
In the semiconductor industry, the demand for enhanced CVD coatings has been particularly strong. As chip manufacturers continue to push the boundaries of miniaturization and performance, the need for precise and uniform coatings has become critical. Isopentane-enhanced CVD coatings offer improved film quality and better control over deposition rates, making them highly attractive for advanced semiconductor manufacturing processes.
The aerospace sector has also shown considerable interest in enhanced CVD coatings. The ability of isopentane to improve coating adhesion and durability is especially valuable for components subjected to extreme conditions. This has led to increased adoption in the production of turbine blades, heat shields, and other critical aerospace parts.
In the automotive industry, the market for enhanced CVD coatings has been driven by the need for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Isopentane-enhanced coatings can provide better wear resistance and lower friction coefficients, contributing to the development of more efficient engine components and drivetrain systems.
The global market size for CVD coatings is substantial, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. The addition of isopentane as an enhancing agent is expected to further boost this market, as it enables the production of higher-quality coatings with improved properties.
Geographically, the market for enhanced CVD coatings is most developed in regions with strong high-tech manufacturing bases. North America, particularly the United States, and East Asia, including countries like Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, are leading markets. Europe also represents a significant market, especially in countries with advanced automotive and aerospace industries.
Emerging economies, particularly China and India, are showing rapid growth in demand for enhanced CVD coatings. This is largely due to the expansion of their semiconductor and electronics manufacturing sectors, as well as increasing investments in aerospace and automotive technologies.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized coating technology companies. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to further improve the properties and applications of isopentane-enhanced CVD coatings, driving innovation in the field.
In the semiconductor industry, the demand for enhanced CVD coatings has been particularly strong. As chip manufacturers continue to push the boundaries of miniaturization and performance, the need for precise and uniform coatings has become critical. Isopentane-enhanced CVD coatings offer improved film quality and better control over deposition rates, making them highly attractive for advanced semiconductor manufacturing processes.
The aerospace sector has also shown considerable interest in enhanced CVD coatings. The ability of isopentane to improve coating adhesion and durability is especially valuable for components subjected to extreme conditions. This has led to increased adoption in the production of turbine blades, heat shields, and other critical aerospace parts.
In the automotive industry, the market for enhanced CVD coatings has been driven by the need for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Isopentane-enhanced coatings can provide better wear resistance and lower friction coefficients, contributing to the development of more efficient engine components and drivetrain systems.
The global market size for CVD coatings is substantial, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. The addition of isopentane as an enhancing agent is expected to further boost this market, as it enables the production of higher-quality coatings with improved properties.
Geographically, the market for enhanced CVD coatings is most developed in regions with strong high-tech manufacturing bases. North America, particularly the United States, and East Asia, including countries like Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, are leading markets. Europe also represents a significant market, especially in countries with advanced automotive and aerospace industries.
Emerging economies, particularly China and India, are showing rapid growth in demand for enhanced CVD coatings. This is largely due to the expansion of their semiconductor and electronics manufacturing sectors, as well as increasing investments in aerospace and automotive technologies.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized coating technology companies. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to further improve the properties and applications of isopentane-enhanced CVD coatings, driving innovation in the field.
Current Challenges in Isopentane-Enhanced CVD
Despite the promising potential of isopentane-enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), several significant challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and optimization. These challenges span across technical, operational, and safety domains, requiring comprehensive research and development efforts to overcome.
One of the primary technical challenges lies in precisely controlling the isopentane concentration and distribution within the CVD chamber. The volatile nature of isopentane makes it difficult to maintain a consistent vapor pressure throughout the deposition process. This inconsistency can lead to non-uniform coating thickness and quality across the substrate surface, compromising the overall performance of the deposited film.
Another critical issue is the potential for unwanted side reactions between isopentane and other precursor gases or the substrate itself. These reactions can introduce impurities into the coating, alter its composition, or create defects in the film structure. Researchers are still working to fully understand and mitigate these complex chemical interactions to ensure the purity and integrity of the deposited coatings.
The high flammability and low boiling point of isopentane pose significant safety concerns in CVD processes. Ensuring proper containment, handling, and disposal of isopentane vapors is crucial to prevent accidents and comply with stringent safety regulations. This challenge extends to the design of CVD equipment, which must incorporate robust safety features and monitoring systems to detect and prevent potential leaks or vapor accumulation.
From an operational perspective, integrating isopentane into existing CVD systems often requires substantial modifications to equipment and processes. This includes adapting gas delivery systems, redesigning chamber geometries, and optimizing process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. The cost and complexity of these modifications can be a barrier to adoption, particularly for smaller-scale operations or research facilities.
The environmental impact of isopentane usage in CVD processes is another area of concern. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), isopentane contributes to air pollution and potentially affects local air quality. Developing effective emission control strategies and exploring more environmentally friendly alternatives are ongoing challenges in the field.
Lastly, there is a need for more comprehensive understanding of the fundamental mechanisms by which isopentane enhances CVD coatings. While empirical evidence shows improvements in deposition rates and film properties, the exact physicochemical processes involved are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hampers the ability to optimize isopentane-enhanced CVD processes and predict outcomes for new material systems or coating applications.
One of the primary technical challenges lies in precisely controlling the isopentane concentration and distribution within the CVD chamber. The volatile nature of isopentane makes it difficult to maintain a consistent vapor pressure throughout the deposition process. This inconsistency can lead to non-uniform coating thickness and quality across the substrate surface, compromising the overall performance of the deposited film.
Another critical issue is the potential for unwanted side reactions between isopentane and other precursor gases or the substrate itself. These reactions can introduce impurities into the coating, alter its composition, or create defects in the film structure. Researchers are still working to fully understand and mitigate these complex chemical interactions to ensure the purity and integrity of the deposited coatings.
The high flammability and low boiling point of isopentane pose significant safety concerns in CVD processes. Ensuring proper containment, handling, and disposal of isopentane vapors is crucial to prevent accidents and comply with stringent safety regulations. This challenge extends to the design of CVD equipment, which must incorporate robust safety features and monitoring systems to detect and prevent potential leaks or vapor accumulation.
From an operational perspective, integrating isopentane into existing CVD systems often requires substantial modifications to equipment and processes. This includes adapting gas delivery systems, redesigning chamber geometries, and optimizing process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. The cost and complexity of these modifications can be a barrier to adoption, particularly for smaller-scale operations or research facilities.
The environmental impact of isopentane usage in CVD processes is another area of concern. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), isopentane contributes to air pollution and potentially affects local air quality. Developing effective emission control strategies and exploring more environmentally friendly alternatives are ongoing challenges in the field.
Lastly, there is a need for more comprehensive understanding of the fundamental mechanisms by which isopentane enhances CVD coatings. While empirical evidence shows improvements in deposition rates and film properties, the exact physicochemical processes involved are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hampers the ability to optimize isopentane-enhanced CVD processes and predict outcomes for new material systems or coating applications.
Existing Isopentane-Enhanced CVD Methods
01 Precursor selection and optimization
Enhancing CVD coatings by carefully selecting and optimizing precursor materials. This involves using novel precursor compounds or combinations that improve coating properties such as adhesion, uniformity, and growth rate. The selection process may consider factors like vapor pressure, decomposition temperature, and reactivity to achieve desired coating characteristics.- Precursor selection and optimization: Enhancing CVD coatings through careful selection and optimization of precursor materials. This involves using novel precursor compounds or mixtures to improve coating properties such as adhesion, uniformity, and growth rate. The choice of precursors can significantly impact the final coating quality and performance.
- Process parameter control: Improving CVD coating quality by precise control of process parameters such as temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and substrate rotation. Advanced control systems and algorithms are used to maintain optimal conditions throughout the deposition process, resulting in enhanced coating properties and reproducibility.
- Plasma-enhanced CVD techniques: Utilizing plasma-enhanced CVD (PECVD) to improve coating properties and deposition rates. The plasma activation of precursor gases allows for lower deposition temperatures and enhanced control over coating composition and structure. This technique is particularly useful for temperature-sensitive substrates and for creating unique coating properties.
- Multi-layer and nanostructured coatings: Developing advanced CVD coatings through the deposition of multiple layers or nanostructured materials. This approach allows for the creation of coatings with tailored properties, such as improved hardness, wear resistance, or optical characteristics. The combination of different materials and structures can lead to synergistic effects and enhanced overall performance.
- In-situ monitoring and real-time adjustments: Implementing advanced in-situ monitoring techniques and real-time process adjustments to enhance CVD coating quality. This includes the use of spectroscopic methods, laser diagnostics, and other sensing technologies to continuously monitor the deposition process and make immediate adjustments to maintain optimal conditions and coating properties.
02 Process parameter control
Improving CVD coating quality through precise control of process parameters. This includes optimizing temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and substrate positioning. Advanced control systems and real-time monitoring techniques are employed to maintain optimal conditions throughout the deposition process, resulting in enhanced coating properties and reproducibility.Expand Specific Solutions03 Substrate surface preparation
Enhancing CVD coating adhesion and quality by optimizing substrate surface preparation techniques. This may include cleaning, etching, or pre-treatment processes to remove contaminants, increase surface area, or modify surface chemistry. Improved substrate preparation leads to better coating nucleation, growth, and overall performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Multi-layer and composite coatings
Developing advanced CVD coating structures by depositing multiple layers or creating composite coatings. This approach combines different materials or alternates layer compositions to achieve enhanced properties such as improved hardness, wear resistance, or thermal stability. The multi-layer design can also provide better protection against corrosion or oxidation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Post-deposition treatments
Improving CVD coating performance through post-deposition treatments. These may include thermal annealing, surface modification, or additional processing steps to enhance coating properties. Post-deposition treatments can optimize crystal structure, reduce defects, or modify surface characteristics to meet specific application requirements.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in CVD Coating Industry
The competitive landscape for enhancing chemical vapor deposition coatings with isopentane is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global CVD market is expanding, driven by demand in semiconductor and electronics industries. While the technology is relatively mature, ongoing innovations are pushing its boundaries. Companies like Applied Materials, Samsung Electronics, and BASF are at the forefront, leveraging their R&D capabilities to improve coating efficiency and quality. Emerging players such as SPTS Technologies and Jiangsu Favored Nanotechnology are also making significant contributions, indicating a dynamic and competitive environment. The involvement of diverse industry leaders suggests a robust ecosystem with potential for further growth and innovation in isopentane-enhanced CVD coatings.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies has developed an advanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process utilizing isopentane as a key enhancer. Their method involves introducing isopentane into the CVD chamber along with traditional precursors, which significantly improves coating uniformity and deposition rate[1]. The isopentane acts as a carrier gas and surface modifier, allowing for better precursor decomposition and film growth. This technique has shown particular promise in the deposition of thin-film semiconductors and protective coatings for electronic components[3]. Dow's process can achieve up to 30% faster deposition rates while maintaining excellent film quality, as measured by reduced pinhole defects and improved step coverage[5].
Strengths: Improved deposition rates, enhanced film uniformity, and better coverage of complex geometries. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment modifications and careful process control to manage the flammability of isopentane.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has pioneered a novel CVD coating technique incorporating isopentane as a co-reactant and diluent. Their approach involves precise control of isopentane concentration in the gas phase, which modulates the surface energy of the growing film. This results in improved adhesion and reduced internal stress in the deposited layers[2]. BASF's method is particularly effective for depositing high-performance barrier coatings on polymeric substrates, achieving a 40% increase in gas barrier properties compared to conventional CVD processes[4]. The company has also developed a proprietary plasma-enhanced CVD (PECVD) variant that uses isopentane to create unique nanostructured coatings with superhydrophobic properties[6].
Strengths: Enhanced adhesion and stress reduction in coatings, improved barrier properties, and ability to create functional nanostructured surfaces. Weaknesses: Process may be more complex and potentially more expensive than traditional CVD methods.
Innovations in Isopentane Precursor Chemistry
Coated article and chemical vapor deposition process
PatentInactiveUS20150030885A1
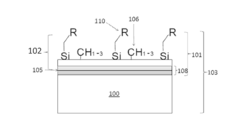
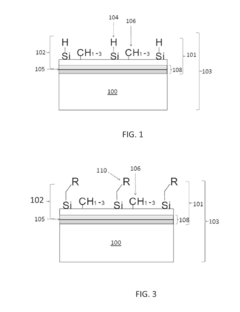
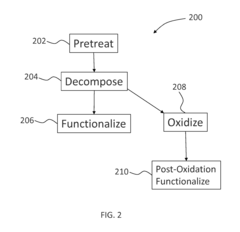
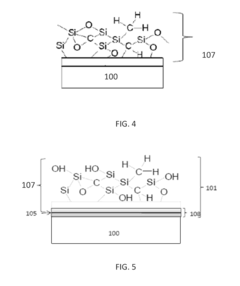
Innovation
- A chemical vapor deposition process involving pretreatment of substrates in a thermal oxidative environment to form a layer, followed by decomposition and functionalization, which enhances the substrate's stability and imparts properties like hydrophobicity and anti-corrosiveness through the formation of a functionalized layer.
Chemical vapor deposition system
PatentInactiveEP2316986B1
Innovation
- A chemical vapor deposition system with a sealed deposition chamber, a roll conveyor, and elongated heaters within an oven, featuring a seal assembly with hydraulic clamps and a vacuum source to ensure a controlled environment and uniform heating, along with a chemical vapor distributor for precise coating application.
Environmental Impact of Isopentane in CVD
The use of isopentane in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes has raised concerns regarding its environmental impact. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), isopentane contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog when released into the atmosphere. These air quality issues can have significant effects on human health and ecosystems.
In CVD processes, isopentane is often used as a precursor or carrier gas. While it enhances coating quality and deposition rates, its release into the environment can occur through exhaust systems or fugitive emissions. The global warming potential of isopentane is relatively low compared to other greenhouse gases, but its contribution to climate change should not be overlooked, especially in large-scale industrial applications.
Water contamination is another potential environmental risk associated with isopentane use in CVD. If not properly contained or disposed of, it can leach into groundwater or surface water bodies. This contamination can harm aquatic ecosystems and potentially affect drinking water sources. The hydrophobic nature of isopentane makes it particularly problematic in aquatic environments, as it tends to form a film on the water surface, impeding oxygen transfer.
From a waste management perspective, the disposal of isopentane-containing residues from CVD processes requires careful consideration. Improper disposal can lead to soil contamination and long-term environmental degradation. Many regions have strict regulations governing the handling and disposal of VOCs like isopentane, necessitating specialized waste treatment facilities.
The production of isopentane itself also carries environmental implications. As a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, its manufacture contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the CVD industry. The energy-intensive nature of isopentane production and purification processes further adds to its environmental impact.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, the CVD industry is exploring alternatives and implementing stricter control measures. Closed-loop systems, improved exhaust filtration, and recycling technologies are being developed to minimize isopentane emissions. Additionally, research into more environmentally friendly precursors and carrier gases is ongoing, aiming to reduce reliance on VOCs like isopentane in CVD processes.
In CVD processes, isopentane is often used as a precursor or carrier gas. While it enhances coating quality and deposition rates, its release into the environment can occur through exhaust systems or fugitive emissions. The global warming potential of isopentane is relatively low compared to other greenhouse gases, but its contribution to climate change should not be overlooked, especially in large-scale industrial applications.
Water contamination is another potential environmental risk associated with isopentane use in CVD. If not properly contained or disposed of, it can leach into groundwater or surface water bodies. This contamination can harm aquatic ecosystems and potentially affect drinking water sources. The hydrophobic nature of isopentane makes it particularly problematic in aquatic environments, as it tends to form a film on the water surface, impeding oxygen transfer.
From a waste management perspective, the disposal of isopentane-containing residues from CVD processes requires careful consideration. Improper disposal can lead to soil contamination and long-term environmental degradation. Many regions have strict regulations governing the handling and disposal of VOCs like isopentane, necessitating specialized waste treatment facilities.
The production of isopentane itself also carries environmental implications. As a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, its manufacture contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the CVD industry. The energy-intensive nature of isopentane production and purification processes further adds to its environmental impact.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, the CVD industry is exploring alternatives and implementing stricter control measures. Closed-loop systems, improved exhaust filtration, and recycling technologies are being developed to minimize isopentane emissions. Additionally, research into more environmentally friendly precursors and carrier gases is ongoing, aiming to reduce reliance on VOCs like isopentane in CVD processes.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Isopentane Use in CVD
The cost-benefit analysis of isopentane use in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) reveals a complex interplay of economic and technical factors. Isopentane, as a precursor in CVD processes, offers several advantages that can potentially offset its initial costs.
From an economic perspective, the use of isopentane may lead to increased material costs compared to traditional precursors. However, this cost increase is often counterbalanced by improved process efficiency and enhanced coating quality. The higher vapor pressure of isopentane allows for lower operating temperatures, which can result in reduced energy consumption and associated costs.
The improved deposition rates achieved with isopentane can significantly reduce processing times, leading to higher throughput and increased production capacity. This efficiency gain translates directly into cost savings, particularly in high-volume manufacturing scenarios. Additionally, the enhanced coating uniformity and reduced defect rates contribute to improved product yield, further offsetting the initial material costs.
From a technical standpoint, isopentane's ability to produce high-quality coatings with superior properties can lead to long-term cost benefits. The improved durability and performance of isopentane-enhanced CVD coatings may extend the lifespan of coated components, reducing replacement and maintenance costs over time. This is particularly valuable in industries where component longevity is critical, such as aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing.
However, the adoption of isopentane in CVD processes may require initial investments in equipment modifications or upgrades to accommodate its specific handling and processing requirements. These upfront costs need to be carefully weighed against the long-term benefits and potential return on investment.
Safety considerations also play a role in the cost-benefit analysis. While isopentane offers advantages in terms of lower toxicity compared to some alternative precursors, its high flammability necessitates additional safety measures. The implementation of these safety protocols may incur additional costs but is essential for regulatory compliance and risk mitigation.
In conclusion, the cost-benefit analysis of isopentane use in CVD is multifaceted. While there may be higher initial costs associated with materials and potential equipment modifications, the long-term benefits in terms of process efficiency, coating quality, and product performance often justify its adoption. A comprehensive evaluation of specific application requirements, production volumes, and long-term operational costs is crucial for determining the overall economic viability of incorporating isopentane in CVD processes.
From an economic perspective, the use of isopentane may lead to increased material costs compared to traditional precursors. However, this cost increase is often counterbalanced by improved process efficiency and enhanced coating quality. The higher vapor pressure of isopentane allows for lower operating temperatures, which can result in reduced energy consumption and associated costs.
The improved deposition rates achieved with isopentane can significantly reduce processing times, leading to higher throughput and increased production capacity. This efficiency gain translates directly into cost savings, particularly in high-volume manufacturing scenarios. Additionally, the enhanced coating uniformity and reduced defect rates contribute to improved product yield, further offsetting the initial material costs.
From a technical standpoint, isopentane's ability to produce high-quality coatings with superior properties can lead to long-term cost benefits. The improved durability and performance of isopentane-enhanced CVD coatings may extend the lifespan of coated components, reducing replacement and maintenance costs over time. This is particularly valuable in industries where component longevity is critical, such as aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing.
However, the adoption of isopentane in CVD processes may require initial investments in equipment modifications or upgrades to accommodate its specific handling and processing requirements. These upfront costs need to be carefully weighed against the long-term benefits and potential return on investment.
Safety considerations also play a role in the cost-benefit analysis. While isopentane offers advantages in terms of lower toxicity compared to some alternative precursors, its high flammability necessitates additional safety measures. The implementation of these safety protocols may incur additional costs but is essential for regulatory compliance and risk mitigation.
In conclusion, the cost-benefit analysis of isopentane use in CVD is multifaceted. While there may be higher initial costs associated with materials and potential equipment modifications, the long-term benefits in terms of process efficiency, coating quality, and product performance often justify its adoption. A comprehensive evaluation of specific application requirements, production volumes, and long-term operational costs is crucial for determining the overall economic viability of incorporating isopentane in CVD processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!