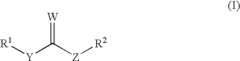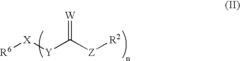Isopentane as a Wax Solvent in Lubricant Formulations
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isopentane Solvent Background and Objectives
Isopentane, a branched alkane with the molecular formula C5H12, has emerged as a promising wax solvent in lubricant formulations. This research aims to explore the potential of isopentane as an effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional solvents used in the lubricant industry. The background of this study is rooted in the growing demand for more efficient and sustainable lubricant solutions across various industrial sectors.
The use of wax solvents in lubricant formulations has been a long-standing practice to improve the low-temperature performance and stability of lubricants. Historically, aromatic solvents and other petroleum-derived compounds have been widely used for this purpose. However, increasing environmental concerns and stricter regulations have necessitated the search for safer and more sustainable alternatives.
Isopentane, also known as 2-methylbutane, has gained attention due to its unique properties that make it suitable for use in lubricant formulations. Its low boiling point, high volatility, and excellent solvency for various organic compounds, including waxes, position it as a potential candidate for replacing conventional solvents. The chemical structure of isopentane, with its branched configuration, contributes to its ability to effectively dissolve and disperse wax molecules within lubricant matrices.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of isopentane as a wax solvent in lubricant formulations. This involves investigating its solvent properties, compatibility with different lubricant base oils, and its impact on the overall performance characteristics of the lubricant. Additionally, the study aims to assess the environmental and safety aspects of using isopentane compared to traditional solvents.
Another key goal is to determine the optimal concentration and blending techniques for incorporating isopentane into various lubricant formulations. This includes examining its effects on viscosity, pour point, cloud point, and other critical parameters that influence lubricant performance across a wide temperature range. The research also seeks to explore potential synergistic effects when isopentane is used in combination with other additives commonly found in lubricant formulations.
Furthermore, this study aims to investigate the long-term stability and durability of lubricants containing isopentane as a wax solvent. This involves accelerated aging tests and performance evaluations under diverse operating conditions to ensure that the benefits of isopentane persist throughout the lubricant's service life.
By addressing these objectives, the research intends to provide valuable insights into the viability of isopentane as an innovative wax solvent solution for the lubricant industry. The findings are expected to contribute to the development of more efficient, environmentally friendly, and high-performance lubricant formulations, potentially revolutionizing the approach to wax management in lubricants.
The use of wax solvents in lubricant formulations has been a long-standing practice to improve the low-temperature performance and stability of lubricants. Historically, aromatic solvents and other petroleum-derived compounds have been widely used for this purpose. However, increasing environmental concerns and stricter regulations have necessitated the search for safer and more sustainable alternatives.
Isopentane, also known as 2-methylbutane, has gained attention due to its unique properties that make it suitable for use in lubricant formulations. Its low boiling point, high volatility, and excellent solvency for various organic compounds, including waxes, position it as a potential candidate for replacing conventional solvents. The chemical structure of isopentane, with its branched configuration, contributes to its ability to effectively dissolve and disperse wax molecules within lubricant matrices.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of isopentane as a wax solvent in lubricant formulations. This involves investigating its solvent properties, compatibility with different lubricant base oils, and its impact on the overall performance characteristics of the lubricant. Additionally, the study aims to assess the environmental and safety aspects of using isopentane compared to traditional solvents.
Another key goal is to determine the optimal concentration and blending techniques for incorporating isopentane into various lubricant formulations. This includes examining its effects on viscosity, pour point, cloud point, and other critical parameters that influence lubricant performance across a wide temperature range. The research also seeks to explore potential synergistic effects when isopentane is used in combination with other additives commonly found in lubricant formulations.
Furthermore, this study aims to investigate the long-term stability and durability of lubricants containing isopentane as a wax solvent. This involves accelerated aging tests and performance evaluations under diverse operating conditions to ensure that the benefits of isopentane persist throughout the lubricant's service life.
By addressing these objectives, the research intends to provide valuable insights into the viability of isopentane as an innovative wax solvent solution for the lubricant industry. The findings are expected to contribute to the development of more efficient, environmentally friendly, and high-performance lubricant formulations, potentially revolutionizing the approach to wax management in lubricants.
Market Analysis for Isopentane-based Lubricants
The market for isopentane-based lubricants is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance lubricants in various industries. The global lubricants market is projected to reach $166.25 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% from 2021 to 2026. Within this market, isopentane-based lubricants are gaining traction due to their superior properties and environmental benefits.
The automotive sector represents the largest market segment for isopentane-based lubricants, accounting for approximately 40% of the total market share. This is primarily due to the growing automotive industry, particularly in emerging economies, and the increasing focus on fuel efficiency and emission reduction. The industrial sector, including manufacturing and heavy machinery, is the second-largest consumer of isopentane-based lubricants, with a market share of around 30%.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the isopentane-based lubricants market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the rapid industrialization, growing automotive production, and increasing disposable income in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with market shares of approximately 25% and 20%, respectively.
The demand for environmentally friendly lubricants is a key driver for the isopentane-based lubricants market. Stringent environmental regulations and growing awareness of sustainability are pushing industries to adopt more eco-friendly solutions. Isopentane-based lubricants offer lower volatility and reduced emissions compared to traditional mineral oil-based lubricants, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Another significant trend in the market is the increasing focus on energy efficiency. Isopentane-based lubricants have demonstrated superior performance in reducing friction and wear, leading to improved energy efficiency in various applications. This property is particularly valuable in the automotive and industrial sectors, where even small improvements in efficiency can result in significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
The market for isopentane-based lubricants is highly competitive, with major players investing heavily in research and development to improve product performance and expand their product portfolios. Key market players include ExxonMobil, Shell, BP, Chevron, and Total, among others. These companies are focusing on developing advanced formulations that offer enhanced performance, longer service life, and improved environmental compatibility.
The automotive sector represents the largest market segment for isopentane-based lubricants, accounting for approximately 40% of the total market share. This is primarily due to the growing automotive industry, particularly in emerging economies, and the increasing focus on fuel efficiency and emission reduction. The industrial sector, including manufacturing and heavy machinery, is the second-largest consumer of isopentane-based lubricants, with a market share of around 30%.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the isopentane-based lubricants market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the rapid industrialization, growing automotive production, and increasing disposable income in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with market shares of approximately 25% and 20%, respectively.
The demand for environmentally friendly lubricants is a key driver for the isopentane-based lubricants market. Stringent environmental regulations and growing awareness of sustainability are pushing industries to adopt more eco-friendly solutions. Isopentane-based lubricants offer lower volatility and reduced emissions compared to traditional mineral oil-based lubricants, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Another significant trend in the market is the increasing focus on energy efficiency. Isopentane-based lubricants have demonstrated superior performance in reducing friction and wear, leading to improved energy efficiency in various applications. This property is particularly valuable in the automotive and industrial sectors, where even small improvements in efficiency can result in significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
The market for isopentane-based lubricants is highly competitive, with major players investing heavily in research and development to improve product performance and expand their product portfolios. Key market players include ExxonMobil, Shell, BP, Chevron, and Total, among others. These companies are focusing on developing advanced formulations that offer enhanced performance, longer service life, and improved environmental compatibility.
Current Challenges in Isopentane Wax Dissolution
The use of isopentane as a wax solvent in lubricant formulations faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary issues is the volatility of isopentane, which can lead to rapid evaporation at elevated temperatures. This characteristic poses difficulties in maintaining consistent lubricant properties over extended periods, particularly in high-temperature applications such as automotive engines or industrial machinery.
Another challenge lies in the limited solubility of certain types of waxes in isopentane. While isopentane demonstrates good solvency for some wax varieties, it may struggle to effectively dissolve others, especially those with higher molecular weights or more complex structures. This selective solubility can result in incomplete wax dissolution, potentially leading to the formation of precipitates or gel-like structures within the lubricant formulation.
The environmental impact of isopentane usage also presents a significant concern. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), isopentane contributes to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. Stringent regulations on VOC emissions in many jurisdictions create barriers to the widespread use of isopentane in lubricant formulations, necessitating the development of alternative solutions or improved containment methods.
Safety considerations pose another challenge in the application of isopentane as a wax solvent. Its high flammability and low flash point require specialized handling, storage, and transportation procedures. These safety requirements can increase operational costs and complexity for lubricant manufacturers and end-users alike.
Furthermore, the interaction between isopentane and other lubricant additives remains a complex issue. The presence of isopentane may affect the performance of critical additives such as anti-wear agents, antioxidants, or viscosity modifiers. Understanding and mitigating these potential interactions is crucial for maintaining the overall effectiveness of the lubricant formulation.
The long-term stability of lubricant formulations containing isopentane is another area of concern. Continuous exposure to varying temperatures and pressures in real-world applications may lead to changes in the solvent-wax equilibrium, potentially causing wax recrystallization or separation over time. This instability can compromise the lubricant's performance and longevity.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of using isopentane as a wax solvent presents a challenge for widespread industrial adoption. While isopentane offers certain advantages, its price volatility and the potential need for higher concentrations to achieve desired results may impact the economic viability of its use in large-scale lubricant production.
Another challenge lies in the limited solubility of certain types of waxes in isopentane. While isopentane demonstrates good solvency for some wax varieties, it may struggle to effectively dissolve others, especially those with higher molecular weights or more complex structures. This selective solubility can result in incomplete wax dissolution, potentially leading to the formation of precipitates or gel-like structures within the lubricant formulation.
The environmental impact of isopentane usage also presents a significant concern. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), isopentane contributes to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. Stringent regulations on VOC emissions in many jurisdictions create barriers to the widespread use of isopentane in lubricant formulations, necessitating the development of alternative solutions or improved containment methods.
Safety considerations pose another challenge in the application of isopentane as a wax solvent. Its high flammability and low flash point require specialized handling, storage, and transportation procedures. These safety requirements can increase operational costs and complexity for lubricant manufacturers and end-users alike.
Furthermore, the interaction between isopentane and other lubricant additives remains a complex issue. The presence of isopentane may affect the performance of critical additives such as anti-wear agents, antioxidants, or viscosity modifiers. Understanding and mitigating these potential interactions is crucial for maintaining the overall effectiveness of the lubricant formulation.
The long-term stability of lubricant formulations containing isopentane is another area of concern. Continuous exposure to varying temperatures and pressures in real-world applications may lead to changes in the solvent-wax equilibrium, potentially causing wax recrystallization or separation over time. This instability can compromise the lubricant's performance and longevity.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of using isopentane as a wax solvent presents a challenge for widespread industrial adoption. While isopentane offers certain advantages, its price volatility and the potential need for higher concentrations to achieve desired results may impact the economic viability of its use in large-scale lubricant production.
Existing Isopentane Solvent Formulations
01 Use of isopentane as a wax solvent
Isopentane is utilized as an effective solvent for waxes in various applications. Its low boiling point and high volatility make it suitable for dissolving and removing wax residues. This property is particularly useful in industrial processes where wax removal or modification is required.- Use of isopentane as a wax solvent: Isopentane is utilized as an effective solvent for waxes in various applications. Its low boiling point and high volatility make it suitable for dissolving and removing wax residues. This property is particularly useful in industrial processes where wax removal or manipulation is required.
- Isopentane in dewaxing processes: Isopentane plays a crucial role in dewaxing processes, particularly in the petroleum industry. It is used to separate waxes from oils and other hydrocarbons, improving the quality and properties of the final products. This process is essential in the production of lubricating oils and other refined petroleum products.
- Isopentane as a component in wax-based formulations: Isopentane is incorporated into various wax-based formulations to enhance their properties. It can improve the spreadability, consistency, and performance of wax products. This application is relevant in industries such as cosmetics, personal care, and industrial coatings.
- Isopentane in wax extraction and purification: Isopentane is employed in the extraction and purification of waxes from natural sources. Its selective solvent properties allow for efficient separation of waxes from other components. This technique is valuable in the production of high-purity waxes for specialized applications.
- Safety and environmental considerations of isopentane use: The use of isopentane as a wax solvent requires careful consideration of safety and environmental factors. Its high volatility and flammability necessitate proper handling and storage procedures. Additionally, efforts are made to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives or to optimize processes to reduce isopentane consumption and emissions.
02 Isopentane in dewaxing processes
Isopentane is employed in dewaxing processes, particularly in the petroleum industry. It is used to separate waxes from oils, improving the quality and properties of the final product. The solvent's ability to selectively dissolve certain components makes it valuable in refining operations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isopentane as a component in wax-based formulations
Isopentane is incorporated into various wax-based formulations to modify their properties. It can be used to adjust the consistency, melting point, or application characteristics of wax products. This is particularly useful in industries such as cosmetics, coatings, and adhesives.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isopentane in extraction and separation processes
The solvent properties of isopentane are utilized in extraction and separation processes involving waxes. It can be used to selectively extract certain wax components or to separate waxes from other materials. This application is relevant in industries such as food processing and chemical manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and environmental considerations of isopentane use
When using isopentane as a wax solvent, safety and environmental factors must be considered. Its high volatility and flammability require proper handling and storage procedures. Additionally, efforts are made to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives or to optimize processes to reduce isopentane consumption and emissions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isopentane and Lubricant Production
The research on isopentane as a wax solvent in lubricant formulations is in a developing stage, with growing market potential due to increasing demand for high-performance lubricants. The global lubricant additives market, which includes wax solvents, is expected to reach significant growth in the coming years. Major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., BASF Corp., and Chevron Oronite Co. LLC are actively involved in research and development in this field. These companies, along with others such as The Lubrizol Corp. and ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co., are at various stages of technological maturity, ranging from early-stage research to advanced formulation development and commercialization efforts.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has conducted extensive research on isopentane as a wax solvent in lubricant formulations. Their approach involves utilizing isopentane's low boiling point (28°C) and excellent solvency to effectively dissolve and disperse wax particles in lubricants[1]. Sinopec's method incorporates isopentane at concentrations ranging from 5-15% by weight, which has been shown to significantly improve the low-temperature fluidity of lubricants[2]. The company has also developed a proprietary blending process that ensures uniform distribution of isopentane throughout the lubricant matrix, enhancing its wax-dissolving capabilities[3]. Additionally, Sinopec has explored synergistic effects between isopentane and other additives, such as pour point depressants, to further optimize lubricant performance in cold conditions[4].
Strengths: Excellent low-temperature performance, improved wax dissolution, and enhanced lubricant fluidity. Weaknesses: Potential volatility issues due to isopentane's low boiling point, and possible environmental concerns related to VOC emissions.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed an innovative approach to using isopentane as a wax solvent in lubricant formulations. Their research focuses on creating a stable microemulsion system that incorporates isopentane, allowing for improved wax solubility and dispersion[1]. BASF's technology utilizes a carefully designed surfactant package that enables the formation of nanoscale isopentane droplets within the lubricant matrix[2]. This approach has been shown to enhance the wax-dissolving capacity of the lubricant while minimizing the amount of isopentane required, typically ranging from 2-8% by weight[3]. The company has also investigated the use of isopentane in combination with synthetic base oils to further improve low-temperature performance and extend the operating temperature range of lubricants[4]. BASF's research has demonstrated that their isopentane-based formulations can achieve pour points as low as -45°C, significantly outperforming conventional lubricants[5].
Strengths: Enhanced wax solubility, improved low-temperature performance, and efficient use of isopentane. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in formulation and manufacturing processes, and possible increased production costs.
Innovative Isopentane-Wax Interaction Mechanisms
Carbonyl, thiocarbonyl or imine containing compounds as asphaltene dispersants in crude oil
PatentInactiveUS20040235676A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising 0.001% to 20% of compounds with carbonyl-, thiocarbonyl-, or imine-containing functional groups and polar groups, specifically designed to disperse asphaltenes in petroleum products, where the carbonyl group is an amide or ester and the polar group is other than a keto or hydroxy group, particularly with alkyl substituents having at least 15 carbon atoms.
Wax formulations and their use for maintaining and preserving surfaces
PatentInactiveUS20040110887A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a high molecular mass isobutene polymer in combination with conventional waxes and silicone oils, along with other components like finely divided powders and abrasives, to create a formulation that enhances detergent stability and luster.
Environmental Impact of Isopentane-based Lubricants
The environmental impact of isopentane-based lubricants is a critical consideration in the development and application of these formulations. Isopentane, as a volatile organic compound (VOC), presents both advantages and challenges from an environmental perspective.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isopentane-based lubricants is their potential contribution to air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, isopentane can react with other pollutants to form ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems in urban areas where air quality is already compromised.
However, compared to some traditional solvents used in lubricant formulations, isopentane has a lower global warming potential and ozone depletion potential. This makes it a potentially more environmentally friendly option in terms of long-term atmospheric impacts.
The volatility of isopentane also raises concerns about its persistence in the environment. While this property can be advantageous in certain applications, it may lead to increased evaporative emissions during storage, handling, and use of isopentane-based lubricants. This necessitates careful consideration of containment and handling procedures to minimize environmental release.
In aquatic environments, isopentane poses a potential threat due to its low water solubility and tendency to form a surface film. This can impact aquatic organisms and ecosystems if the lubricant is improperly disposed of or accidentally released into water bodies. However, its rapid evaporation rate may mitigate some of these impacts in open water systems.
From a waste management perspective, the use of isopentane in lubricant formulations presents both challenges and opportunities. Its volatility can complicate recycling processes, potentially requiring specialized equipment to capture and reuse the solvent. On the other hand, this same property could facilitate easier separation of the solvent from other components during recycling, potentially improving the overall recyclability of the lubricant.
The production of isopentane itself also has environmental implications. While it can be derived from natural gas processing, which is generally considered less environmentally impactful than petroleum refining, the extraction and processing of natural gas still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental concerns.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, the use of isopentane in lubricant formulations may face scrutiny. Manufacturers and users of these lubricants may need to implement additional control measures to comply with VOC emission limits and other environmental standards.
In conclusion, while isopentane offers certain environmental advantages over some traditional solvents, its use in lubricant formulations requires careful consideration of its potential environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle. Balancing its performance benefits with environmental concerns will be crucial for the sustainable development and application of isopentane-based lubricants.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isopentane-based lubricants is their potential contribution to air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, isopentane can react with other pollutants to form ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems in urban areas where air quality is already compromised.
However, compared to some traditional solvents used in lubricant formulations, isopentane has a lower global warming potential and ozone depletion potential. This makes it a potentially more environmentally friendly option in terms of long-term atmospheric impacts.
The volatility of isopentane also raises concerns about its persistence in the environment. While this property can be advantageous in certain applications, it may lead to increased evaporative emissions during storage, handling, and use of isopentane-based lubricants. This necessitates careful consideration of containment and handling procedures to minimize environmental release.
In aquatic environments, isopentane poses a potential threat due to its low water solubility and tendency to form a surface film. This can impact aquatic organisms and ecosystems if the lubricant is improperly disposed of or accidentally released into water bodies. However, its rapid evaporation rate may mitigate some of these impacts in open water systems.
From a waste management perspective, the use of isopentane in lubricant formulations presents both challenges and opportunities. Its volatility can complicate recycling processes, potentially requiring specialized equipment to capture and reuse the solvent. On the other hand, this same property could facilitate easier separation of the solvent from other components during recycling, potentially improving the overall recyclability of the lubricant.
The production of isopentane itself also has environmental implications. While it can be derived from natural gas processing, which is generally considered less environmentally impactful than petroleum refining, the extraction and processing of natural gas still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental concerns.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, the use of isopentane in lubricant formulations may face scrutiny. Manufacturers and users of these lubricants may need to implement additional control measures to comply with VOC emission limits and other environmental standards.
In conclusion, while isopentane offers certain environmental advantages over some traditional solvents, its use in lubricant formulations requires careful consideration of its potential environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle. Balancing its performance benefits with environmental concerns will be crucial for the sustainable development and application of isopentane-based lubricants.
Regulatory Framework for Solvent Use in Lubricants
The regulatory framework for solvent use in lubricants is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the research and development of isopentane as a wax solvent in lubricant formulations. This framework is primarily governed by environmental, health, and safety regulations at both national and international levels.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating solvents used in lubricants. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), the EPA has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemical substances, including solvents like isopentane. The agency also maintains the TSCA Inventory, which lists all existing chemical substances manufactured or processed in the U.S.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace exposure limits to solvents, including isopentane. These standards are crucial for ensuring worker safety during the production and handling of lubricants containing this solvent.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation is the primary framework governing the use of chemical substances, including solvents in lubricants. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety information, which is particularly relevant for the use of isopentane in lubricant formulations.
The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation in the EU complements REACH by ensuring that the hazards of chemicals are clearly communicated to workers and consumers through classification and labeling requirements. This regulation directly affects how isopentane-containing lubricants are packaged and marketed.
Globally, the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Many countries, including the U.S. and EU member states, have adopted GHS principles, which impacts the labeling and safety data sheets for lubricants containing isopentane.
Environmental regulations, such as the Clean Air Act in the U.S. and similar legislation in other countries, also play a role in regulating volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions. As isopentane is a VOC, its use in lubricants may be subject to restrictions or reporting requirements in certain jurisdictions.
Industry-specific regulations, such as those governing the automotive or aerospace sectors, may impose additional requirements on lubricant formulations. These regulations often focus on performance standards and compatibility with specific materials, which can influence the choice of solvents like isopentane in lubricant formulations.
As environmental concerns grow, many regions are implementing or considering stricter regulations on the use of petroleum-derived solvents. This trend may impact the future use of isopentane in lubricants and drive research towards more sustainable alternatives or improved formulation techniques to minimize solvent use.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating solvents used in lubricants. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), the EPA has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemical substances, including solvents like isopentane. The agency also maintains the TSCA Inventory, which lists all existing chemical substances manufactured or processed in the U.S.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace exposure limits to solvents, including isopentane. These standards are crucial for ensuring worker safety during the production and handling of lubricants containing this solvent.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation is the primary framework governing the use of chemical substances, including solvents in lubricants. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety information, which is particularly relevant for the use of isopentane in lubricant formulations.
The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation in the EU complements REACH by ensuring that the hazards of chemicals are clearly communicated to workers and consumers through classification and labeling requirements. This regulation directly affects how isopentane-containing lubricants are packaged and marketed.
Globally, the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Many countries, including the U.S. and EU member states, have adopted GHS principles, which impacts the labeling and safety data sheets for lubricants containing isopentane.
Environmental regulations, such as the Clean Air Act in the U.S. and similar legislation in other countries, also play a role in regulating volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions. As isopentane is a VOC, its use in lubricants may be subject to restrictions or reporting requirements in certain jurisdictions.
Industry-specific regulations, such as those governing the automotive or aerospace sectors, may impose additional requirements on lubricant formulations. These regulations often focus on performance standards and compatibility with specific materials, which can influence the choice of solvents like isopentane in lubricant formulations.
As environmental concerns grow, many regions are implementing or considering stricter regulations on the use of petroleum-derived solvents. This trend may impact the future use of isopentane in lubricants and drive research towards more sustainable alternatives or improved formulation techniques to minimize solvent use.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!