Ensuring Safe Isopentane Transport in Bulk Shipments
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isopentane Transport Safety Overview
Isopentane, a highly volatile and flammable hydrocarbon, presents significant safety challenges during bulk transportation. This overview examines the critical aspects of ensuring safe isopentane transport, addressing the potential risks and necessary precautions.
The primary concern in isopentane transport is its low boiling point of approximately 28°C (82°F), which makes it prone to vaporization at ambient temperatures. This characteristic increases the risk of fire and explosion, particularly during loading, unloading, and transit operations. Additionally, isopentane's high vapor pressure contributes to the formation of potentially explosive atmospheres in confined spaces.
To mitigate these risks, stringent safety measures are essential throughout the transportation process. Proper container selection is crucial, with pressure vessels or specialized tankers designed to withstand the vapor pressure of isopentane being the preferred choice. These containers must be equipped with pressure relief valves and vapor recovery systems to manage internal pressure and prevent the release of flammable vapors.
Temperature control during transport is another critical factor. Insulated containers and temperature monitoring systems are employed to maintain isopentane below its boiling point, reducing the risk of vapor formation. In regions with high ambient temperatures, additional cooling mechanisms may be necessary to ensure safe transportation.
Grounding and bonding procedures are vital to prevent the accumulation of static electricity, which could potentially ignite isopentane vapors. All equipment used in handling and transporting isopentane must be properly grounded, and personnel must follow strict protocols to dissipate static charges.
Emergency response planning is an integral part of isopentane transport safety. This includes developing comprehensive spill containment strategies, training personnel in firefighting techniques specific to hydrocarbon fires, and establishing clear communication protocols with local emergency services along transportation routes.
Regulatory compliance plays a significant role in ensuring safe isopentane transport. Various international and national regulations govern the handling and transportation of hazardous materials, including isopentane. These regulations typically cover aspects such as container specifications, labeling requirements, documentation, and driver qualifications.
The use of advanced monitoring technologies has become increasingly important in enhancing isopentane transport safety. Real-time tracking systems, pressure sensors, and leak detection devices provide continuous oversight of shipment conditions, allowing for prompt intervention in case of anomalies.
In conclusion, safe isopentane transport in bulk shipments requires a multifaceted approach that combines engineering controls, operational procedures, regulatory compliance, and advanced technologies. By addressing the unique properties and risks associated with isopentane, stakeholders can significantly reduce the potential for accidents and ensure the safe delivery of this valuable but hazardous material.
The primary concern in isopentane transport is its low boiling point of approximately 28°C (82°F), which makes it prone to vaporization at ambient temperatures. This characteristic increases the risk of fire and explosion, particularly during loading, unloading, and transit operations. Additionally, isopentane's high vapor pressure contributes to the formation of potentially explosive atmospheres in confined spaces.
To mitigate these risks, stringent safety measures are essential throughout the transportation process. Proper container selection is crucial, with pressure vessels or specialized tankers designed to withstand the vapor pressure of isopentane being the preferred choice. These containers must be equipped with pressure relief valves and vapor recovery systems to manage internal pressure and prevent the release of flammable vapors.
Temperature control during transport is another critical factor. Insulated containers and temperature monitoring systems are employed to maintain isopentane below its boiling point, reducing the risk of vapor formation. In regions with high ambient temperatures, additional cooling mechanisms may be necessary to ensure safe transportation.
Grounding and bonding procedures are vital to prevent the accumulation of static electricity, which could potentially ignite isopentane vapors. All equipment used in handling and transporting isopentane must be properly grounded, and personnel must follow strict protocols to dissipate static charges.
Emergency response planning is an integral part of isopentane transport safety. This includes developing comprehensive spill containment strategies, training personnel in firefighting techniques specific to hydrocarbon fires, and establishing clear communication protocols with local emergency services along transportation routes.
Regulatory compliance plays a significant role in ensuring safe isopentane transport. Various international and national regulations govern the handling and transportation of hazardous materials, including isopentane. These regulations typically cover aspects such as container specifications, labeling requirements, documentation, and driver qualifications.
The use of advanced monitoring technologies has become increasingly important in enhancing isopentane transport safety. Real-time tracking systems, pressure sensors, and leak detection devices provide continuous oversight of shipment conditions, allowing for prompt intervention in case of anomalies.
In conclusion, safe isopentane transport in bulk shipments requires a multifaceted approach that combines engineering controls, operational procedures, regulatory compliance, and advanced technologies. By addressing the unique properties and risks associated with isopentane, stakeholders can significantly reduce the potential for accidents and ensure the safe delivery of this valuable but hazardous material.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for safe isopentane transport in bulk shipments has been steadily increasing due to the growing applications of isopentane in various industries. Isopentane, a highly volatile and flammable hydrocarbon, is widely used in the production of polystyrene foam, refrigerants, and as a blowing agent in the manufacture of insulation materials. The expanding construction and automotive sectors have significantly contributed to the rising demand for isopentane.
The global isopentane market size was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient insulation materials in the construction industry and the rising adoption of eco-friendly refrigerants in the HVAC sector.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the isopentane market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India, leading to a surge in construction activities and automotive production. North America and Europe follow closely, with significant demand from the aerospace and electronics industries.
The need for safe transport of isopentane in bulk shipments has become paramount due to its hazardous nature. Stringent regulations imposed by environmental agencies and transportation authorities have further emphasized the importance of ensuring safe handling and transportation of isopentane. This has created a substantial market for specialized transportation equipment and safety systems designed specifically for isopentane and other volatile hydrocarbons.
The market for safe isopentane transport solutions is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is driven by the increasing focus on worker safety, environmental protection, and the need to comply with evolving regulatory standards. Companies involved in the production, distribution, and use of isopentane are investing heavily in advanced transportation technologies and safety measures to mitigate risks associated with bulk shipments.
The demand for innovative solutions in isopentane transport has led to the development of new technologies such as advanced monitoring systems, improved tank designs, and enhanced safety protocols. These advancements not only ensure safer transportation but also contribute to operational efficiency and cost reduction in the long run.
As sustainability becomes a key focus across industries, there is a growing trend towards the use of bio-based isopentane alternatives. This shift is expected to impact the market dynamics for isopentane transport, potentially leading to the development of new safety standards and transportation methods tailored to these eco-friendly alternatives.
The global isopentane market size was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient insulation materials in the construction industry and the rising adoption of eco-friendly refrigerants in the HVAC sector.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the isopentane market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India, leading to a surge in construction activities and automotive production. North America and Europe follow closely, with significant demand from the aerospace and electronics industries.
The need for safe transport of isopentane in bulk shipments has become paramount due to its hazardous nature. Stringent regulations imposed by environmental agencies and transportation authorities have further emphasized the importance of ensuring safe handling and transportation of isopentane. This has created a substantial market for specialized transportation equipment and safety systems designed specifically for isopentane and other volatile hydrocarbons.
The market for safe isopentane transport solutions is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is driven by the increasing focus on worker safety, environmental protection, and the need to comply with evolving regulatory standards. Companies involved in the production, distribution, and use of isopentane are investing heavily in advanced transportation technologies and safety measures to mitigate risks associated with bulk shipments.
The demand for innovative solutions in isopentane transport has led to the development of new technologies such as advanced monitoring systems, improved tank designs, and enhanced safety protocols. These advancements not only ensure safer transportation but also contribute to operational efficiency and cost reduction in the long run.
As sustainability becomes a key focus across industries, there is a growing trend towards the use of bio-based isopentane alternatives. This shift is expected to impact the market dynamics for isopentane transport, potentially leading to the development of new safety standards and transportation methods tailored to these eco-friendly alternatives.
Current Challenges in Bulk Isopentane Shipping
The bulk shipping of isopentane presents several significant challenges that require careful consideration and management. One of the primary concerns is the highly flammable nature of isopentane, which has a low flash point and can easily form explosive vapor-air mixtures. This characteristic necessitates stringent safety measures throughout the transportation process, from loading to unloading and storage.
Temperature control is another critical challenge in bulk isopentane shipping. Isopentane has a low boiling point, making it susceptible to expansion and vaporization during transport, especially in warm climates or when exposed to direct sunlight. This can lead to pressure build-up within containers, increasing the risk of leaks or ruptures. Implementing effective temperature regulation systems and selecting appropriate shipping containers are essential to mitigate these risks.
The potential for static electricity accumulation poses an additional hazard during the handling and transfer of isopentane. Static charges can generate sparks, potentially igniting the flammable vapors. This necessitates the implementation of proper grounding and bonding procedures, as well as the use of specialized equipment designed to minimize static build-up.
Environmental concerns also present challenges in bulk isopentane shipping. Accidental spills or leaks can have severe ecological consequences, contaminating soil and water sources. The volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with isopentane can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to workers and communities near shipping routes or storage facilities.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to bulk isopentane transport. Different countries and regions have varying regulations governing the shipment of hazardous materials, requiring shippers to navigate a complex web of legal requirements, documentation, and safety protocols. This often necessitates specialized training for personnel involved in handling and transporting isopentane.
The selection of appropriate transportation modes and routes presents logistical challenges. While sea transport is often preferred for large volumes, it introduces additional risks related to maritime conditions and potential accidents at sea. Land transport, on the other hand, must contend with varying road conditions, traffic, and the proximity to populated areas.
Lastly, emergency response preparedness is a crucial aspect of bulk isopentane shipping. Developing comprehensive contingency plans, training personnel in emergency procedures, and coordinating with local authorities along shipping routes are essential but challenging tasks. These measures must account for various scenarios, including spills, fires, and other potential accidents specific to isopentane's properties.
Temperature control is another critical challenge in bulk isopentane shipping. Isopentane has a low boiling point, making it susceptible to expansion and vaporization during transport, especially in warm climates or when exposed to direct sunlight. This can lead to pressure build-up within containers, increasing the risk of leaks or ruptures. Implementing effective temperature regulation systems and selecting appropriate shipping containers are essential to mitigate these risks.
The potential for static electricity accumulation poses an additional hazard during the handling and transfer of isopentane. Static charges can generate sparks, potentially igniting the flammable vapors. This necessitates the implementation of proper grounding and bonding procedures, as well as the use of specialized equipment designed to minimize static build-up.
Environmental concerns also present challenges in bulk isopentane shipping. Accidental spills or leaks can have severe ecological consequences, contaminating soil and water sources. The volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with isopentane can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to workers and communities near shipping routes or storage facilities.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to bulk isopentane transport. Different countries and regions have varying regulations governing the shipment of hazardous materials, requiring shippers to navigate a complex web of legal requirements, documentation, and safety protocols. This often necessitates specialized training for personnel involved in handling and transporting isopentane.
The selection of appropriate transportation modes and routes presents logistical challenges. While sea transport is often preferred for large volumes, it introduces additional risks related to maritime conditions and potential accidents at sea. Land transport, on the other hand, must contend with varying road conditions, traffic, and the proximity to populated areas.
Lastly, emergency response preparedness is a crucial aspect of bulk isopentane shipping. Developing comprehensive contingency plans, training personnel in emergency procedures, and coordinating with local authorities along shipping routes are essential but challenging tasks. These measures must account for various scenarios, including spills, fires, and other potential accidents specific to isopentane's properties.
Existing Safety Protocols and Solutions
01 Safety measures in handling and storage
Isopentane requires specific safety measures for handling and storage due to its flammable nature. Proper ventilation, grounding of equipment, and use of explosion-proof electrical systems are essential. Storage should be in cool, well-ventilated areas away from sources of ignition. Personal protective equipment such as gloves and goggles should be used when handling isopentane.- Safety measures in isopentane handling and storage: Proper handling and storage of isopentane are crucial for safety. This includes using appropriate containment systems, implementing safety protocols, and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent the accumulation of flammable vapors. Safety measures also involve the use of specialized equipment and procedures to minimize the risk of fire or explosion during storage and transportation.
- Isopentane in chemical processes and reactions: Isopentane is used in various chemical processes and reactions. Safety considerations in these applications include controlling reaction conditions, using appropriate catalysts, and implementing process safety management systems. Proper design of reaction vessels and control systems is essential to prevent runaway reactions or uncontrolled releases of isopentane.
- Environmental and health impacts of isopentane: The environmental and health impacts of isopentane are important safety considerations. This includes assessing its potential for air and water pollution, as well as its effects on human health through inhalation or skin contact. Proper risk assessment and mitigation strategies are necessary to minimize environmental and health hazards associated with isopentane use and production.
- Isopentane in refrigeration and heat transfer applications: Isopentane is used in refrigeration and heat transfer applications due to its thermodynamic properties. Safety considerations in these applications include proper system design to prevent leaks, ensuring adequate ventilation in enclosed spaces, and implementing appropriate maintenance procedures to detect and address potential safety issues.
- Fire and explosion prevention in isopentane-related processes: Due to its high flammability, fire and explosion prevention is critical in isopentane-related processes. This includes implementing proper grounding and bonding procedures, using explosion-proof electrical equipment, and installing appropriate fire suppression systems. Regular safety audits and employee training are essential to maintain a safe working environment when handling isopentane.
02 Fire and explosion prevention
Isopentane is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Fire prevention measures include using appropriate fire suppression systems, implementing strict no-smoking policies, and avoiding static electricity buildup. In case of fire, suitable extinguishing agents should be used, and the area should be evacuated immediately.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental and health considerations
Isopentane can have environmental impacts if released into the atmosphere or water systems. It may contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. Inhalation of isopentane vapors can cause respiratory irritation and central nervous system depression. Proper containment and disposal methods should be employed to minimize environmental and health risks.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial applications and safety protocols
Isopentane is used in various industrial applications, including as a blowing agent in foam production and as a refrigerant. Safety protocols for these applications include regular equipment maintenance, leak detection systems, and employee training on proper handling procedures. Closed-loop systems and recovery methods can help minimize exposure and emissions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Transportation and emergency response
Safe transportation of isopentane requires compliance with hazardous materials regulations. Proper labeling, packaging, and documentation are essential. Emergency response plans should be in place, including spill containment procedures and evacuation protocols. First responders should be trained in handling isopentane-related incidents.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Chemical Logistics
The market for safe isopentane transport in bulk shipments is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for petrochemicals and stringent safety regulations. The global market size is expanding, with key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., PetroChina Co., Ltd., and Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. leading the way. These companies are investing in advanced technologies and safety measures to ensure secure transportation. The technology for safe isopentane transport is relatively mature, with ongoing innovations focused on improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Companies like SABIC Global Technologies BV and Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing are at the forefront of developing new solutions, indicating a competitive landscape with a mix of established players and innovative newcomers.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a comprehensive approach to ensuring safe isopentane transport in bulk shipments. Their method involves using advanced double-walled insulated tanks with inert gas blanketing systems to maintain a stable pressure and temperature environment[1]. The company has implemented a real-time monitoring system that tracks key parameters such as pressure, temperature, and vapor concentration throughout the transport process[2]. Additionally, Sinopec has developed proprietary safety valves and emergency release systems specifically designed for isopentane's unique properties, reducing the risk of overpressurization and potential leaks[3]. The company also employs specialized loading and unloading procedures, including the use of grounding equipment to prevent static electricity buildup, which is crucial for handling volatile substances like isopentane[4].
Strengths: Comprehensive safety measures, advanced monitoring systems, and specialized equipment tailored for isopentane. Weaknesses: Potentially higher costs associated with specialized equipment and procedures, which may impact competitiveness in price-sensitive markets.
Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd.
Technical Solution: Mitsui O.S.K. Lines (MOL) has developed a state-of-the-art bulk carrier design specifically for transporting volatile organic compounds like isopentane. Their ships feature an innovative cargo containment system that incorporates multi-layer membranes and a full secondary barrier to prevent leakage[5]. MOL's vessels are equipped with an advanced gas detection system that continuously monitors the cargo hold and surrounding spaces for any potential leaks[6]. The company has also implemented a proprietary vapor handling system that manages cargo boil-off, reducing pressure build-up and minimizing the risk of over-pressurization during transport[7]. Furthermore, MOL has developed specialized crew training programs focused on the safe handling and emergency response procedures for isopentane and similar volatile cargoes[8].
Strengths: Specialized ship design for volatile cargoes, advanced leak detection and vapor handling systems, and comprehensive crew training. Weaknesses: Limited to maritime transport, potentially higher operational costs due to specialized equipment and training requirements.
Innovative Containment Technologies
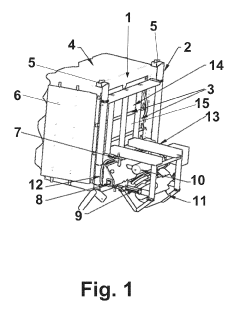
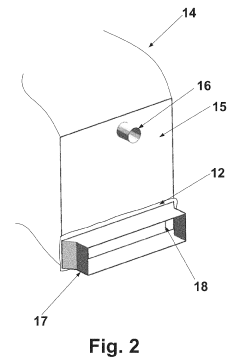
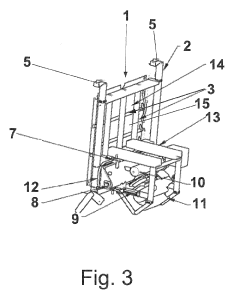
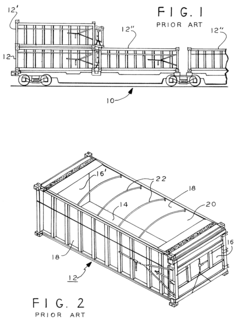
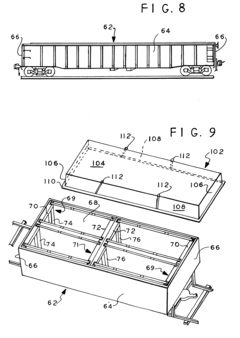
Unloading system for bulk material from a transport vessel, in particular a container
PatentInactiveUS10322891B2
Innovation
- An unloading system featuring a basic frame with a horizontally shiftable and lockable screw trough, a pressurizable dust seal, a dosing device, and transport brackets for forklift trucks, which forms a dual gasket with the container liner to ensure contamination-free and emission-free unloading, using a flexible discharge device and pressure compensation to improve flow characteristics and secure complete unloading.
Bulk material transport system
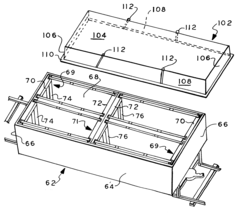
PatentInactiveUS6523482B2
Innovation
- A lightweight, low-cost bulk material transport system featuring a carrier supporting frame secured to vehicles and a flexible high-density polyethylene sling, allowing secure attachment to both rail cars and trucks, with features like tubular supports and U-shaped pocket members to prevent horizontal displacement and facilitate easy lifting.
Regulatory Framework for Hazardous Cargo
The regulatory framework for hazardous cargo transport, particularly for substances like isopentane, is a complex and multi-layered system designed to ensure safety and environmental protection. At the international level, the United Nations' Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods serve as the foundation for many national and regional regulations. These recommendations provide a classification system for dangerous goods and outline general provisions for their safe transport.
In the context of maritime transport, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, developed by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), provides detailed guidelines for the safe transportation of hazardous materials by sea. The IMDG Code classifies isopentane as a Class 3 flammable liquid and specifies requirements for its packaging, labeling, and stowage on vessels.
For land transport, different regions have their own regulatory frameworks. In Europe, the Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) governs the transportation of hazardous materials by road. The United States relies on the Department of Transportation's (DOT) Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR), which provide comprehensive guidelines for the safe transport of dangerous goods across all modes of transportation.
These regulations typically mandate specific requirements for bulk shipments of flammable liquids like isopentane. These include the use of approved containers, proper labeling and placarding, documentation requirements, and specific handling procedures. Additionally, they often stipulate training requirements for personnel involved in the transportation process.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in the transport of hazardous materials. In many jurisdictions, regulations require measures to prevent spills and leaks, as well as procedures for responding to incidents. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), for instance, enforces regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) that apply to the transportation of hazardous waste.
Compliance with these regulations is typically enforced through a system of inspections, audits, and penalties for non-compliance. Many countries have established specialized agencies, such as the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) in the United States, to oversee the implementation of these regulations.
It's important to note that regulations are continually evolving in response to new technologies, emerging risks, and lessons learned from incidents. Companies involved in the transport of hazardous materials like isopentane must stay informed about these changes and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
In the context of maritime transport, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, developed by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), provides detailed guidelines for the safe transportation of hazardous materials by sea. The IMDG Code classifies isopentane as a Class 3 flammable liquid and specifies requirements for its packaging, labeling, and stowage on vessels.
For land transport, different regions have their own regulatory frameworks. In Europe, the Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) governs the transportation of hazardous materials by road. The United States relies on the Department of Transportation's (DOT) Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR), which provide comprehensive guidelines for the safe transport of dangerous goods across all modes of transportation.
These regulations typically mandate specific requirements for bulk shipments of flammable liquids like isopentane. These include the use of approved containers, proper labeling and placarding, documentation requirements, and specific handling procedures. Additionally, they often stipulate training requirements for personnel involved in the transportation process.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in the transport of hazardous materials. In many jurisdictions, regulations require measures to prevent spills and leaks, as well as procedures for responding to incidents. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), for instance, enforces regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) that apply to the transportation of hazardous waste.
Compliance with these regulations is typically enforced through a system of inspections, audits, and penalties for non-compliance. Many countries have established specialized agencies, such as the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) in the United States, to oversee the implementation of these regulations.
It's important to note that regulations are continually evolving in response to new technologies, emerging risks, and lessons learned from incidents. Companies involved in the transport of hazardous materials like isopentane must stay informed about these changes and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of isopentane transport in bulk shipments is a critical aspect of ensuring safe and sustainable practices. Isopentane, a highly volatile organic compound, poses significant environmental risks if not properly managed during transportation. The primary environmental concerns associated with isopentane transport include air pollution, water contamination, and soil degradation.
Air pollution is a major consideration, as isopentane readily evaporates at room temperature. During bulk shipments, there is a risk of fugitive emissions through leaks, spills, or improper handling. These emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, which can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. Additionally, isopentane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide. Therefore, minimizing emissions during transport is crucial for mitigating climate change impacts.
Water contamination is another significant environmental risk associated with isopentane transport. In the event of a spill or leak, isopentane can quickly spread across water surfaces, forming a thin film that impedes oxygen transfer and harms aquatic ecosystems. The low water solubility of isopentane means it can persist in water bodies for extended periods, potentially causing long-term ecological damage. Groundwater contamination is also a concern, particularly in areas with shallow water tables or porous soil structures.
Soil degradation can occur if isopentane is released onto land during transport accidents or improper handling. The compound can penetrate soil layers, affecting soil microorganisms and potentially contaminating underground water sources. This can lead to reduced soil fertility and long-term environmental damage in affected areas.
To mitigate these environmental risks, stringent safety measures and best practices must be implemented throughout the isopentane transport process. This includes using specialized containment systems designed to prevent leaks and spills, implementing robust monitoring and detection systems, and ensuring proper training for all personnel involved in handling and transporting isopentane. Additionally, route planning should consider environmentally sensitive areas, avoiding regions with high ecological value or vulnerable water resources whenever possible.
Regular environmental impact assessments and risk analyses should be conducted to identify potential hazards and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. These assessments should consider factors such as local climate conditions, proximity to populated areas, and the presence of sensitive ecosystems along transport routes. By proactively addressing environmental concerns and implementing comprehensive safety measures, the risks associated with isopentane transport can be significantly reduced, ensuring both environmental protection and operational efficiency.
Air pollution is a major consideration, as isopentane readily evaporates at room temperature. During bulk shipments, there is a risk of fugitive emissions through leaks, spills, or improper handling. These emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, which can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. Additionally, isopentane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide. Therefore, minimizing emissions during transport is crucial for mitigating climate change impacts.
Water contamination is another significant environmental risk associated with isopentane transport. In the event of a spill or leak, isopentane can quickly spread across water surfaces, forming a thin film that impedes oxygen transfer and harms aquatic ecosystems. The low water solubility of isopentane means it can persist in water bodies for extended periods, potentially causing long-term ecological damage. Groundwater contamination is also a concern, particularly in areas with shallow water tables or porous soil structures.
Soil degradation can occur if isopentane is released onto land during transport accidents or improper handling. The compound can penetrate soil layers, affecting soil microorganisms and potentially contaminating underground water sources. This can lead to reduced soil fertility and long-term environmental damage in affected areas.
To mitigate these environmental risks, stringent safety measures and best practices must be implemented throughout the isopentane transport process. This includes using specialized containment systems designed to prevent leaks and spills, implementing robust monitoring and detection systems, and ensuring proper training for all personnel involved in handling and transporting isopentane. Additionally, route planning should consider environmentally sensitive areas, avoiding regions with high ecological value or vulnerable water resources whenever possible.
Regular environmental impact assessments and risk analyses should be conducted to identify potential hazards and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. These assessments should consider factors such as local climate conditions, proximity to populated areas, and the presence of sensitive ecosystems along transport routes. By proactively addressing environmental concerns and implementing comprehensive safety measures, the risks associated with isopentane transport can be significantly reduced, ensuring both environmental protection and operational efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!