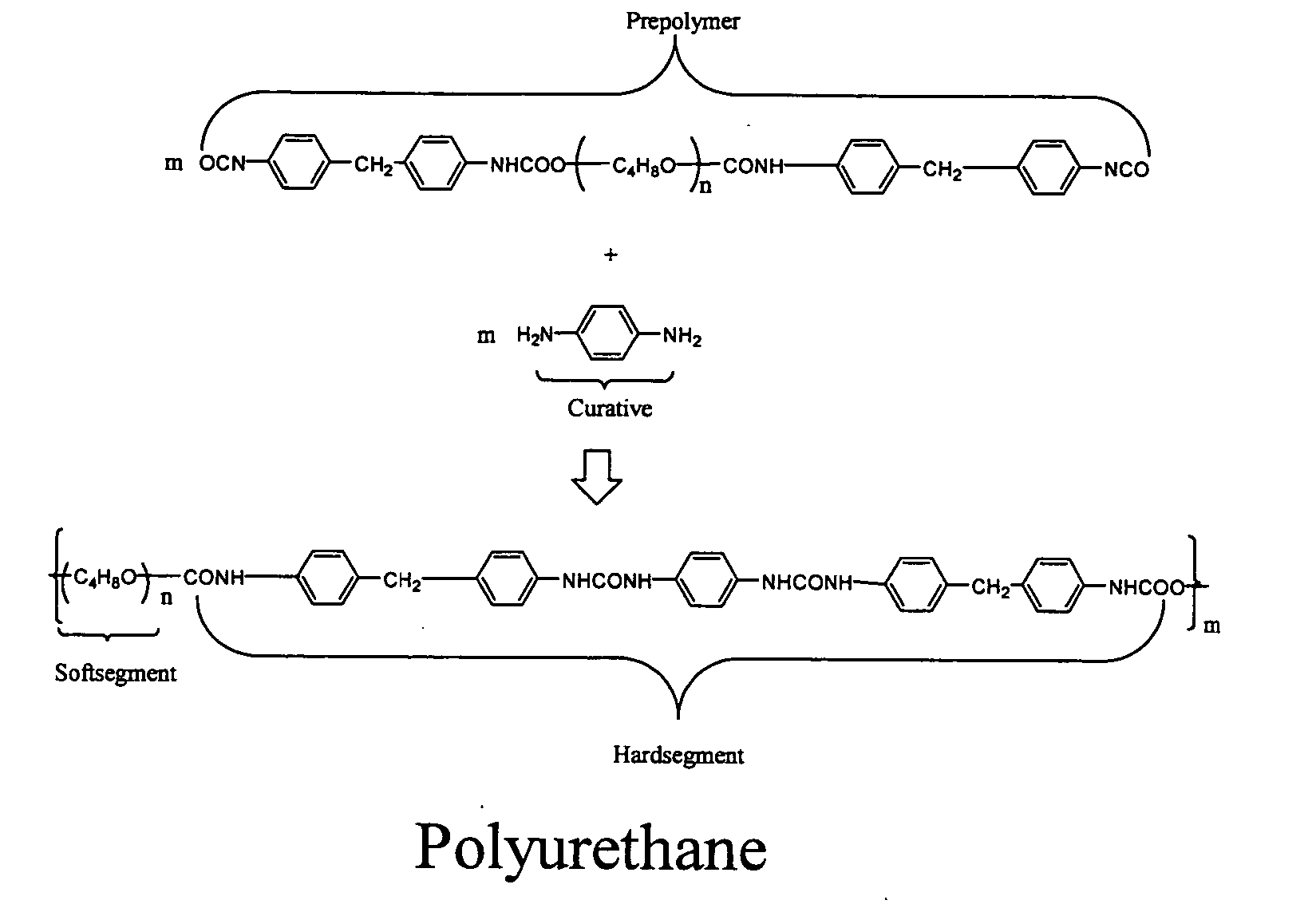
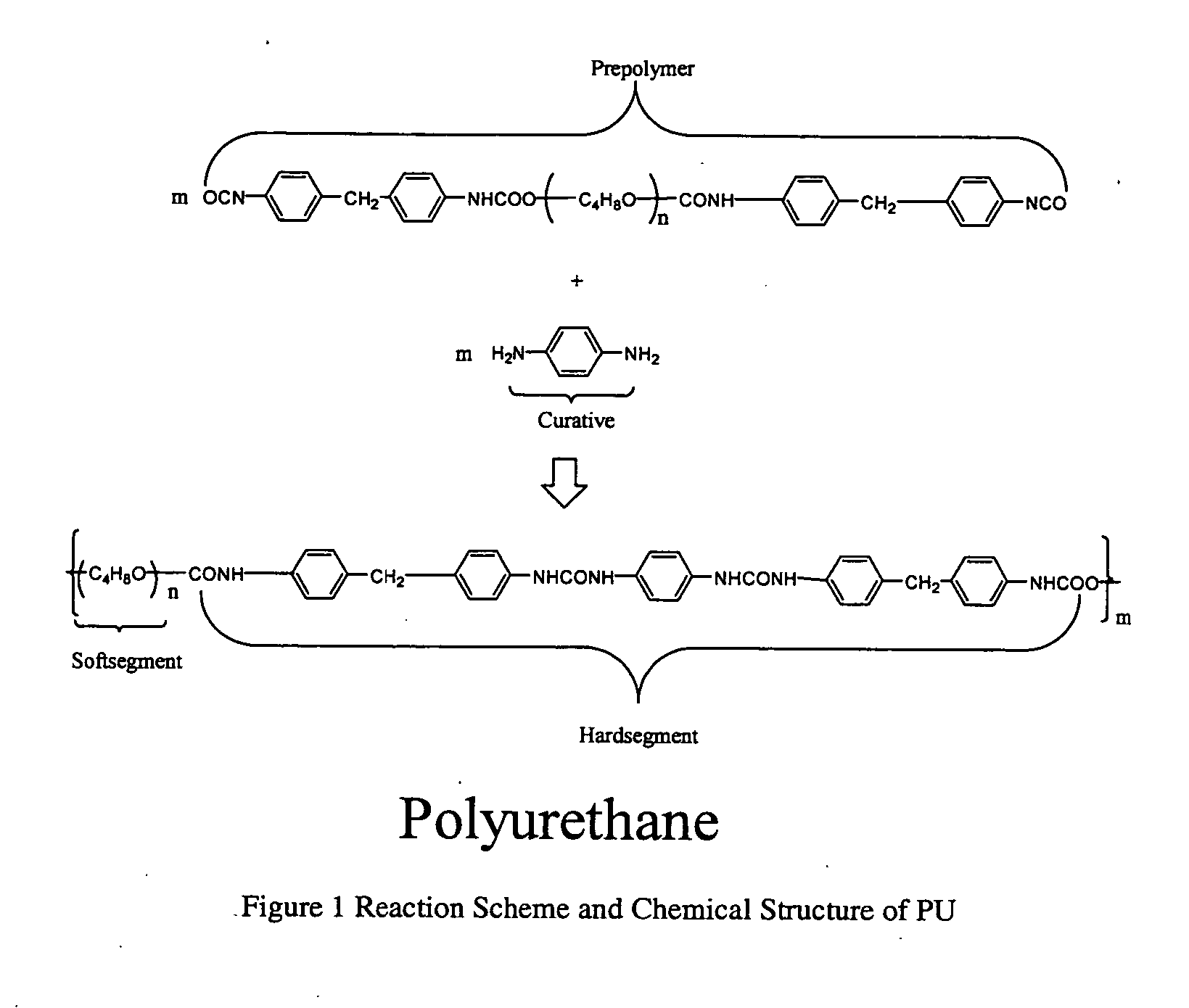
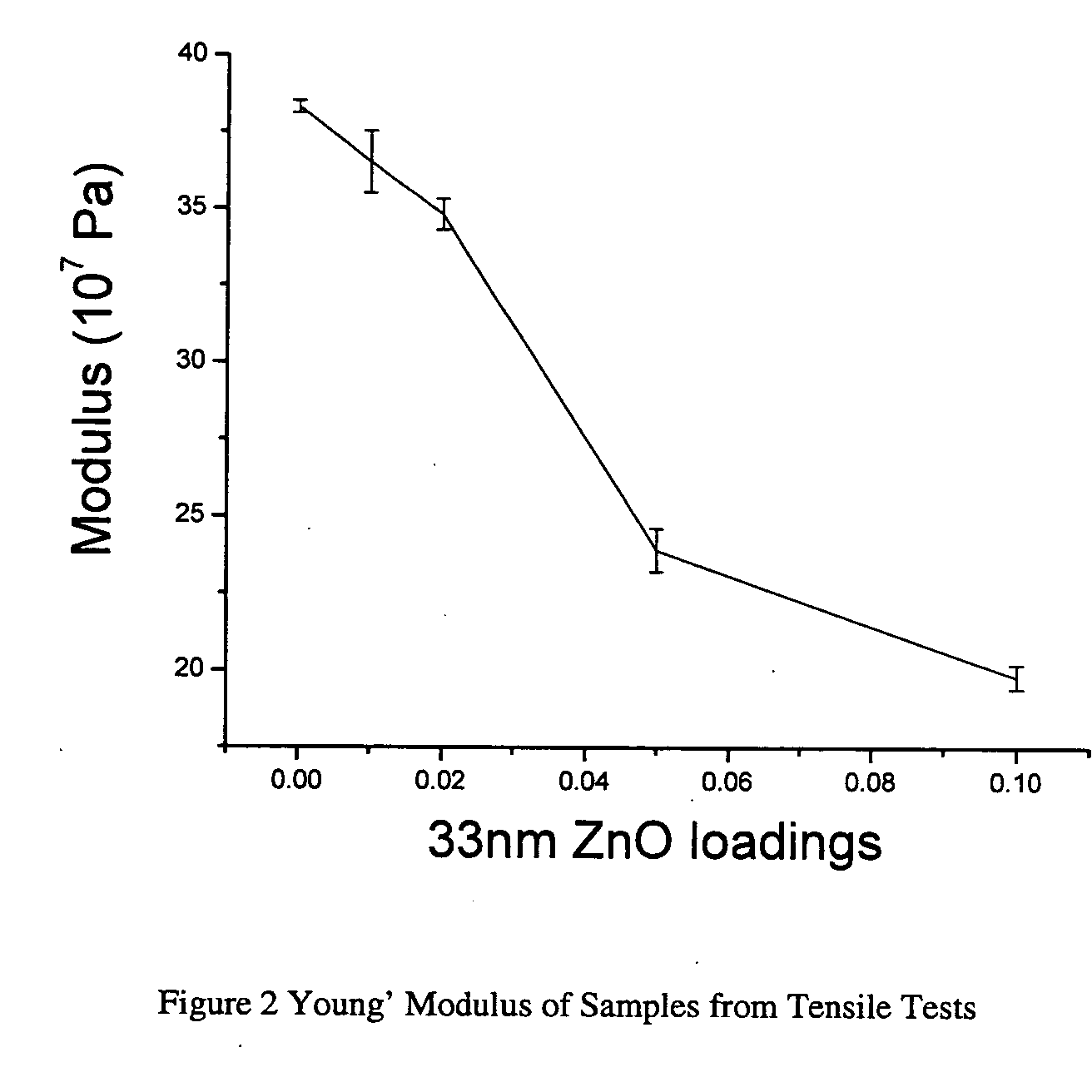
How Has PU Magnetic Nanoparticle Integration Improved Actuation?
JUN 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PU-MNP Actuation Background and Objectives
The integration of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) into polyurethane (PU) matrices has emerged as a groundbreaking approach in the field of smart materials and actuation technologies. This fusion of polymer science and nanotechnology has opened up new avenues for developing responsive and adaptive systems with enhanced performance characteristics.
The journey of PU-MNP actuation began with the recognition of polyurethane's versatile properties, including its elasticity, durability, and ease of processing. Concurrently, the unique magnetic properties of nanoparticles, particularly their ability to respond to external magnetic fields, presented an opportunity to create materials with controllable and reversible deformation capabilities.
As research in this area progressed, scientists and engineers focused on overcoming the challenges of uniform dispersion of MNPs within the PU matrix and optimizing the interaction between the two components. The goal was to develop materials that could exhibit significant shape changes or force generation in response to applied magnetic fields, while maintaining the desirable mechanical properties of polyurethane.
The evolution of PU-MNP actuation technology has been driven by the increasing demand for smart materials in various sectors, including biomedical engineering, soft robotics, and adaptive structures. The ability to remotely control the shape and behavior of materials has far-reaching implications for developing minimally invasive medical devices, self-adjusting components, and energy-efficient actuators.
Key objectives in the development of PU-MNP actuators have included enhancing the magnitude of actuation, improving response times, and achieving precise control over the actuation behavior. Researchers have explored various types of magnetic nanoparticles, such as iron oxide and nickel, and investigated different synthesis methods to optimize the composite's performance.
Another critical aspect of PU-MNP actuation research has been the development of mathematical models and simulation techniques to predict and design the behavior of these composite materials under different conditions. This theoretical foundation has been essential in guiding experimental work and accelerating the development of practical applications.
The integration of MNPs into PU matrices has not only improved actuation capabilities but has also led to the discovery of additional functionalities, such as self-healing properties and enhanced thermal conductivity. These multifunctional characteristics have further expanded the potential applications of PU-MNP composites across diverse fields.
As the technology continues to mature, researchers are now focusing on scaling up production processes, improving long-term stability, and developing more sophisticated control mechanisms. The ultimate goal is to transition PU-MNP actuators from laboratory curiosities to widely adopted technological solutions that can address real-world challenges in various industries.
The journey of PU-MNP actuation began with the recognition of polyurethane's versatile properties, including its elasticity, durability, and ease of processing. Concurrently, the unique magnetic properties of nanoparticles, particularly their ability to respond to external magnetic fields, presented an opportunity to create materials with controllable and reversible deformation capabilities.
As research in this area progressed, scientists and engineers focused on overcoming the challenges of uniform dispersion of MNPs within the PU matrix and optimizing the interaction between the two components. The goal was to develop materials that could exhibit significant shape changes or force generation in response to applied magnetic fields, while maintaining the desirable mechanical properties of polyurethane.
The evolution of PU-MNP actuation technology has been driven by the increasing demand for smart materials in various sectors, including biomedical engineering, soft robotics, and adaptive structures. The ability to remotely control the shape and behavior of materials has far-reaching implications for developing minimally invasive medical devices, self-adjusting components, and energy-efficient actuators.
Key objectives in the development of PU-MNP actuators have included enhancing the magnitude of actuation, improving response times, and achieving precise control over the actuation behavior. Researchers have explored various types of magnetic nanoparticles, such as iron oxide and nickel, and investigated different synthesis methods to optimize the composite's performance.
Another critical aspect of PU-MNP actuation research has been the development of mathematical models and simulation techniques to predict and design the behavior of these composite materials under different conditions. This theoretical foundation has been essential in guiding experimental work and accelerating the development of practical applications.
The integration of MNPs into PU matrices has not only improved actuation capabilities but has also led to the discovery of additional functionalities, such as self-healing properties and enhanced thermal conductivity. These multifunctional characteristics have further expanded the potential applications of PU-MNP composites across diverse fields.
As the technology continues to mature, researchers are now focusing on scaling up production processes, improving long-term stability, and developing more sophisticated control mechanisms. The ultimate goal is to transition PU-MNP actuators from laboratory curiosities to widely adopted technological solutions that can address real-world challenges in various industries.
Market Demand Analysis for Smart Actuators
The integration of PU magnetic nanoparticles into smart actuators has sparked significant market interest and demand across various industries. This innovative technology has opened up new possibilities for precise and responsive actuation systems, driving growth in the smart actuator market.
The automotive sector has emerged as a key driver of demand for smart actuators incorporating PU magnetic nanoparticles. These advanced actuators offer improved performance in vehicle suspension systems, engine management, and adaptive aerodynamics. The push towards autonomous vehicles has further amplified the need for highly responsive and reliable actuation systems, positioning PU magnetic nanoparticle-based actuators as a critical component in next-generation automotive design.
In the aerospace industry, there is a growing demand for lightweight and efficient actuation solutions. PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators provide an excellent balance of power density and weight reduction, making them ideal for applications in aircraft control surfaces, landing gear systems, and satellite positioning mechanisms. The increasing focus on fuel efficiency and electrification in aviation is expected to further boost the adoption of these advanced actuators.
The robotics and automation sector represents another significant market for smart actuators enhanced with PU magnetic nanoparticles. These actuators enable more precise and responsive movements in robotic arms, exoskeletons, and automated manufacturing equipment. As industries continue to embrace Industry 4.0 principles, the demand for high-performance actuators capable of supporting complex automation tasks is projected to rise steadily.
In the medical field, PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators are gaining traction for their potential in minimally invasive surgical tools, prosthetics, and drug delivery systems. The ability to achieve fine control and adaptability in medical devices is driving research and development efforts, with market analysts predicting substantial growth in this segment over the coming years.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also exploring the integration of PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators in devices such as smartphones, wearables, and haptic feedback systems. The compact size and energy efficiency of these actuators make them attractive for enhancing user experience and device functionality.
Market research indicates that the global smart actuator market, including those utilizing PU magnetic nanoparticles, is experiencing robust growth. Factors such as increasing automation across industries, the need for energy-efficient solutions, and the push for miniaturization in various applications are fueling this expansion. While specific market size figures vary among different research reports, there is a consensus on the strong upward trajectory of the smart actuator market, with compound annual growth rates projected to remain in the high single digits or low double digits for the foreseeable future.
The automotive sector has emerged as a key driver of demand for smart actuators incorporating PU magnetic nanoparticles. These advanced actuators offer improved performance in vehicle suspension systems, engine management, and adaptive aerodynamics. The push towards autonomous vehicles has further amplified the need for highly responsive and reliable actuation systems, positioning PU magnetic nanoparticle-based actuators as a critical component in next-generation automotive design.
In the aerospace industry, there is a growing demand for lightweight and efficient actuation solutions. PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators provide an excellent balance of power density and weight reduction, making them ideal for applications in aircraft control surfaces, landing gear systems, and satellite positioning mechanisms. The increasing focus on fuel efficiency and electrification in aviation is expected to further boost the adoption of these advanced actuators.
The robotics and automation sector represents another significant market for smart actuators enhanced with PU magnetic nanoparticles. These actuators enable more precise and responsive movements in robotic arms, exoskeletons, and automated manufacturing equipment. As industries continue to embrace Industry 4.0 principles, the demand for high-performance actuators capable of supporting complex automation tasks is projected to rise steadily.
In the medical field, PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators are gaining traction for their potential in minimally invasive surgical tools, prosthetics, and drug delivery systems. The ability to achieve fine control and adaptability in medical devices is driving research and development efforts, with market analysts predicting substantial growth in this segment over the coming years.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also exploring the integration of PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators in devices such as smartphones, wearables, and haptic feedback systems. The compact size and energy efficiency of these actuators make them attractive for enhancing user experience and device functionality.
Market research indicates that the global smart actuator market, including those utilizing PU magnetic nanoparticles, is experiencing robust growth. Factors such as increasing automation across industries, the need for energy-efficient solutions, and the push for miniaturization in various applications are fueling this expansion. While specific market size figures vary among different research reports, there is a consensus on the strong upward trajectory of the smart actuator market, with compound annual growth rates projected to remain in the high single digits or low double digits for the foreseeable future.
Current State of PU-MNP Actuation Technology
The integration of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) into polyurethane (PU) matrices has significantly advanced the field of actuation technology. This combination has led to the development of smart materials capable of responding to external magnetic fields, offering enhanced control and precision in various applications.
Currently, PU-MNP actuators exhibit improved performance characteristics compared to traditional actuators. The incorporation of MNPs into the PU matrix allows for remote activation and control, eliminating the need for direct physical contact or wired connections. This feature has opened up new possibilities in fields such as biomedical engineering, robotics, and aerospace.
One of the key advancements in PU-MNP actuation technology is the ability to achieve complex and programmable deformations. By carefully designing the distribution and orientation of MNPs within the PU matrix, researchers have demonstrated the capacity to create actuators that can bend, twist, or elongate in response to applied magnetic fields. This level of control enables the development of more sophisticated and versatile actuator systems.
The current state of PU-MNP actuators also showcases improved response times and actuation speeds. The rapid alignment of MNPs within the polymer matrix upon exposure to a magnetic field results in faster actuation compared to some traditional methods. This quick response is particularly beneficial in applications requiring rapid and precise movements.
Another significant advancement is the enhancement of actuation force and strain. By optimizing the concentration and properties of MNPs, researchers have achieved higher force outputs and larger deformations in PU-MNP actuators. This improvement expands the range of potential applications, allowing these actuators to handle greater loads and perform more demanding tasks.
The durability and fatigue resistance of PU-MNP actuators have also seen notable improvements. The integration of MNPs often reinforces the polymer matrix, leading to enhanced mechanical properties. This increased robustness translates to longer operational lifetimes and improved reliability in various environmental conditions.
Recent developments have focused on creating multi-functional PU-MNP actuators. These advanced systems not only respond to magnetic fields but also exhibit additional properties such as self-healing capabilities, shape memory effects, or temperature sensitivity. This multi-functionality broadens the scope of applications and enhances the overall versatility of the actuators.
The current state of PU-MNP actuation technology also reflects progress in fabrication techniques. Researchers have developed methods for more uniform dispersion of MNPs within the PU matrix, leading to more consistent and predictable actuation behaviors. Advanced manufacturing processes, including 3D printing and microfluidic techniques, have enabled the creation of complex actuator geometries and structures.
Currently, PU-MNP actuators exhibit improved performance characteristics compared to traditional actuators. The incorporation of MNPs into the PU matrix allows for remote activation and control, eliminating the need for direct physical contact or wired connections. This feature has opened up new possibilities in fields such as biomedical engineering, robotics, and aerospace.
One of the key advancements in PU-MNP actuation technology is the ability to achieve complex and programmable deformations. By carefully designing the distribution and orientation of MNPs within the PU matrix, researchers have demonstrated the capacity to create actuators that can bend, twist, or elongate in response to applied magnetic fields. This level of control enables the development of more sophisticated and versatile actuator systems.
The current state of PU-MNP actuators also showcases improved response times and actuation speeds. The rapid alignment of MNPs within the polymer matrix upon exposure to a magnetic field results in faster actuation compared to some traditional methods. This quick response is particularly beneficial in applications requiring rapid and precise movements.
Another significant advancement is the enhancement of actuation force and strain. By optimizing the concentration and properties of MNPs, researchers have achieved higher force outputs and larger deformations in PU-MNP actuators. This improvement expands the range of potential applications, allowing these actuators to handle greater loads and perform more demanding tasks.
The durability and fatigue resistance of PU-MNP actuators have also seen notable improvements. The integration of MNPs often reinforces the polymer matrix, leading to enhanced mechanical properties. This increased robustness translates to longer operational lifetimes and improved reliability in various environmental conditions.
Recent developments have focused on creating multi-functional PU-MNP actuators. These advanced systems not only respond to magnetic fields but also exhibit additional properties such as self-healing capabilities, shape memory effects, or temperature sensitivity. This multi-functionality broadens the scope of applications and enhances the overall versatility of the actuators.
The current state of PU-MNP actuation technology also reflects progress in fabrication techniques. Researchers have developed methods for more uniform dispersion of MNPs within the PU matrix, leading to more consistent and predictable actuation behaviors. Advanced manufacturing processes, including 3D printing and microfluidic techniques, have enabled the creation of complex actuator geometries and structures.
Existing PU-MNP Actuation Solutions
01 Synthesis and characterization of PU magnetic nanoparticles
Methods for synthesizing polyurethane (PU) magnetic nanoparticles and techniques for characterizing their properties. This includes controlling particle size, shape, and magnetic properties through various synthesis methods and analyzing the resulting nanoparticles using advanced characterization techniques.- Synthesis and characterization of PU magnetic nanoparticles: Methods for synthesizing polyurethane (PU) magnetic nanoparticles and techniques for characterizing their properties. This includes processes for incorporating magnetic materials into PU matrices and analyzing the resulting nanocomposites for their magnetic, structural, and physical properties.
- Actuation mechanisms for PU magnetic nanoparticles: Various techniques for actuating PU magnetic nanoparticles using external magnetic fields. This includes methods for controlling the movement, deformation, or alignment of the nanoparticles for applications in sensors, actuators, and smart materials.
- Applications of PU magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical field: Utilization of PU magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications such as drug delivery, magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents, and tissue engineering. This includes methods for functionalizing the nanoparticles for specific biological interactions and controlling their behavior in physiological environments.
- Magnetic data storage using PU nanoparticles: Development of high-density magnetic data storage systems using PU magnetic nanoparticles. This includes techniques for creating stable magnetic domains, improving read/write processes, and enhancing the overall storage capacity and performance of magnetic recording media.
- Environmental and energy applications of PU magnetic nanoparticles: Use of PU magnetic nanoparticles in environmental remediation and energy-related applications. This includes methods for removing contaminants from water and soil, enhancing energy conversion processes, and developing novel energy storage systems using the unique properties of these nanocomposites.
02 Actuation mechanisms for PU magnetic nanoparticles
Various actuation mechanisms for PU magnetic nanoparticles, including external magnetic field manipulation, electromagnetic stimulation, and thermal activation. These mechanisms enable precise control over the movement and behavior of the nanoparticles for applications in various fields.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of PU magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical field
Utilization of PU magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications such as drug delivery, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast enhancement, hyperthermia treatment, and biosensing. The unique properties of these nanoparticles make them suitable for targeted therapies and diagnostic imaging.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of PU magnetic nanoparticles in smart materials
Incorporation of PU magnetic nanoparticles into smart materials and composites for applications in actuators, sensors, and responsive systems. These materials exhibit tunable properties that can be controlled through external magnetic fields, enabling the development of adaptive and multifunctional structures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial applications of PU magnetic nanoparticles
Use of PU magnetic nanoparticles in environmental remediation, waste treatment, and industrial processes. These applications leverage the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles for efficient separation, filtration, and catalysis in various chemical and industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PU-MNP Actuation Research
The integration of PU magnetic nanoparticles in actuation technology is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The market is expanding due to the enhanced performance and efficiency offered by these nanoparticles in various applications. Companies like BASF Corp., Bridgestone Corp., and Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft eV are at the forefront of this technology, developing innovative solutions. Universities such as Zhejiang University of Technology, Chongqing University, and Xi'an Jiaotong University are contributing significantly to research and development. The technology's maturity is progressing rapidly, with collaborations between industry leaders and academic institutions driving improvements in actuation systems across multiple sectors.
BYK-Chemie GmbH
Technical Solution: BYK-Chemie GmbH has developed a novel approach to integrating PU magnetic nanoparticles for improved actuation. Their technology involves synthesizing core-shell magnetic nanoparticles with a polyurethane outer layer. These nanoparticles are then dispersed uniformly within a polyurethane matrix, creating a responsive magnetic-PU composite. The company has optimized the particle size and distribution to enhance magnetic responsiveness while maintaining the elasticity of the PU material. This integration allows for precise control of the material's shape and movement when exposed to external magnetic fields, significantly improving actuation capabilities.
Strengths: Enhanced magnetic responsiveness, improved dispersion stability, and maintained PU elasticity. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up production and higher cost compared to traditional PU materials.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has pioneered a method for integrating PU magnetic nanoparticles to enhance actuation performance. Their approach involves in-situ polymerization of polyurethane around pre-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. This process ensures a strong interface between the nanoparticles and the PU matrix, leading to improved mechanical properties and magnetic responsiveness. BASF has also developed a proprietary surface modification technique for the nanoparticles, which prevents agglomeration and ensures uniform distribution within the PU matrix. The resulting composite material exhibits rapid and reversible shape changes when exposed to magnetic fields, making it ideal for various actuation applications.
Strengths: Strong particle-matrix interface, uniform particle distribution, and rapid actuation response. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process and potential limitations in achieving high magnetic particle loading.
Core Innovations in PU-MNP Integration
Block copolymer and nanofiller composites
PatentActiveUS20050239939A1
Innovation
- The use of nanoscale fillers such as metal, ceramic, and organic nanoparticles, and nanoclays, with modified surface chemistries, to chemically tether or interact with block copolymers, controlling their self-assembly and microdomain structure, thereby modifying their properties.
process for obtaining magnetic nanoparticles using ionic liquids as solvents and their application in the preparation of stable dispersions in non-polar solvents
PatentActiveBRPI1000298A2
Innovation
- A process using ionic liquids as solvents for the thermal decomposition of metal complexes at low temperatures, allowing surface modification and stabilization of magnetic nanoparticles in non-polar solvents without the need for stabilizing additives, enabling recyclable and less toxic synthesis.
Environmental Impact of PU-MNP Actuators
The integration of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) into polyurethane (PU) matrices for actuation purposes has raised important environmental considerations. As these actuators gain prominence in various applications, it is crucial to assess their potential impact on ecosystems and human health.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential release of nanoparticles into the environment during the production, use, and disposal of PU-MNP actuators. Magnetic nanoparticles, particularly those containing heavy metals, may pose risks to aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems if not properly contained. Studies have shown that nanoparticles can accumulate in organisms and potentially disrupt food chains.
However, the encapsulation of MNPs within the PU matrix provides a significant barrier against nanoparticle release. This encapsulation effect has been demonstrated to greatly reduce the potential for environmental contamination compared to free nanoparticles. The stability of the PU-MNP composite over time and under various environmental conditions is a critical factor in assessing long-term environmental impact.
The production process of PU-MNP actuators also warrants consideration. The synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles and their integration into polyurethane may involve the use of solvents and other chemicals. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting green chemistry principles to minimize the environmental footprint of production, including the use of less toxic solvents and more efficient synthesis methods.
End-of-life management of PU-MNP actuators is another important aspect of their environmental impact. The composite nature of these materials presents challenges for recycling and disposal. Research is ongoing to develop effective methods for separating and recovering the magnetic nanoparticles from the polymer matrix, which could enable the recycling of both components and reduce waste.
On the positive side, PU-MNP actuators have the potential to contribute to environmental sustainability in certain applications. For instance, their use in energy harvesting devices or smart materials for building efficiency could lead to reduced energy consumption and associated environmental benefits. Additionally, the improved performance and longevity of PU-MNP actuators compared to traditional alternatives may result in less frequent replacement and lower overall resource consumption.
Lifecycle assessments of PU-MNP actuators are being conducted to provide a comprehensive understanding of their environmental impact from production to disposal. These studies aim to quantify factors such as energy consumption, carbon footprint, and potential for environmental release of nanoparticles throughout the actuator's lifecycle.
As research progresses, there is a growing focus on developing more environmentally friendly formulations of PU-MNP actuators. This includes exploring biodegradable polyurethane matrices and utilizing magnetic nanoparticles derived from more abundant and less toxic elements. Such advancements could significantly mitigate the environmental concerns associated with these innovative actuators.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential release of nanoparticles into the environment during the production, use, and disposal of PU-MNP actuators. Magnetic nanoparticles, particularly those containing heavy metals, may pose risks to aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems if not properly contained. Studies have shown that nanoparticles can accumulate in organisms and potentially disrupt food chains.
However, the encapsulation of MNPs within the PU matrix provides a significant barrier against nanoparticle release. This encapsulation effect has been demonstrated to greatly reduce the potential for environmental contamination compared to free nanoparticles. The stability of the PU-MNP composite over time and under various environmental conditions is a critical factor in assessing long-term environmental impact.
The production process of PU-MNP actuators also warrants consideration. The synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles and their integration into polyurethane may involve the use of solvents and other chemicals. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting green chemistry principles to minimize the environmental footprint of production, including the use of less toxic solvents and more efficient synthesis methods.
End-of-life management of PU-MNP actuators is another important aspect of their environmental impact. The composite nature of these materials presents challenges for recycling and disposal. Research is ongoing to develop effective methods for separating and recovering the magnetic nanoparticles from the polymer matrix, which could enable the recycling of both components and reduce waste.
On the positive side, PU-MNP actuators have the potential to contribute to environmental sustainability in certain applications. For instance, their use in energy harvesting devices or smart materials for building efficiency could lead to reduced energy consumption and associated environmental benefits. Additionally, the improved performance and longevity of PU-MNP actuators compared to traditional alternatives may result in less frequent replacement and lower overall resource consumption.
Lifecycle assessments of PU-MNP actuators are being conducted to provide a comprehensive understanding of their environmental impact from production to disposal. These studies aim to quantify factors such as energy consumption, carbon footprint, and potential for environmental release of nanoparticles throughout the actuator's lifecycle.
As research progresses, there is a growing focus on developing more environmentally friendly formulations of PU-MNP actuators. This includes exploring biodegradable polyurethane matrices and utilizing magnetic nanoparticles derived from more abundant and less toxic elements. Such advancements could significantly mitigate the environmental concerns associated with these innovative actuators.
Scalability and Manufacturing Challenges
The integration of PU magnetic nanoparticles into actuators has shown significant promise, but scaling up production and manufacturing processes presents several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is achieving consistent dispersion of nanoparticles within the polyurethane matrix at larger scales. While laboratory-scale production can maintain uniform distribution, industrial-scale manufacturing often struggles with agglomeration issues, leading to inconsistent material properties and reduced actuation performance.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control of nanoparticle concentration and orientation during the manufacturing process. As production volumes increase, maintaining the optimal particle alignment that contributes to enhanced actuation becomes increasingly difficult. This can result in variations in the magnetic response and overall actuator performance across batches, potentially limiting the technology's widespread adoption in commercial applications.
The complexity of the manufacturing process also poses scalability issues. The integration of magnetic nanoparticles often requires specialized equipment and carefully controlled environmental conditions. Scaling up these processes while maintaining the necessary precision and quality control measures can be both technically challenging and cost-prohibitive for many manufacturers.
Furthermore, the long-term stability of PU magnetic nanoparticle composites in various environmental conditions remains a concern. Ensuring consistent performance over time and under different operating conditions is crucial for commercial viability. This necessitates extensive testing and validation procedures, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive when scaled to industrial production levels.
Safety considerations in large-scale manufacturing of nanoparticle-infused materials also present challenges. Proper handling and containment of nanoparticles during production require sophisticated safety protocols and equipment, which can be difficult to implement across larger manufacturing facilities.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of scaling up production remains a significant hurdle. While the benefits of PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators are evident in small-scale applications, the economic viability of mass production is still uncertain. The increased material costs, specialized equipment requirements, and potential yield issues associated with larger-scale manufacturing may offset the performance gains, making it challenging to compete with existing actuation technologies in terms of cost-effectiveness.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control of nanoparticle concentration and orientation during the manufacturing process. As production volumes increase, maintaining the optimal particle alignment that contributes to enhanced actuation becomes increasingly difficult. This can result in variations in the magnetic response and overall actuator performance across batches, potentially limiting the technology's widespread adoption in commercial applications.
The complexity of the manufacturing process also poses scalability issues. The integration of magnetic nanoparticles often requires specialized equipment and carefully controlled environmental conditions. Scaling up these processes while maintaining the necessary precision and quality control measures can be both technically challenging and cost-prohibitive for many manufacturers.
Furthermore, the long-term stability of PU magnetic nanoparticle composites in various environmental conditions remains a concern. Ensuring consistent performance over time and under different operating conditions is crucial for commercial viability. This necessitates extensive testing and validation procedures, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive when scaled to industrial production levels.
Safety considerations in large-scale manufacturing of nanoparticle-infused materials also present challenges. Proper handling and containment of nanoparticles during production require sophisticated safety protocols and equipment, which can be difficult to implement across larger manufacturing facilities.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of scaling up production remains a significant hurdle. While the benefits of PU magnetic nanoparticle actuators are evident in small-scale applications, the economic viability of mass production is still uncertain. The increased material costs, specialized equipment requirements, and potential yield issues associated with larger-scale manufacturing may offset the performance gains, making it challenging to compete with existing actuation technologies in terms of cost-effectiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!