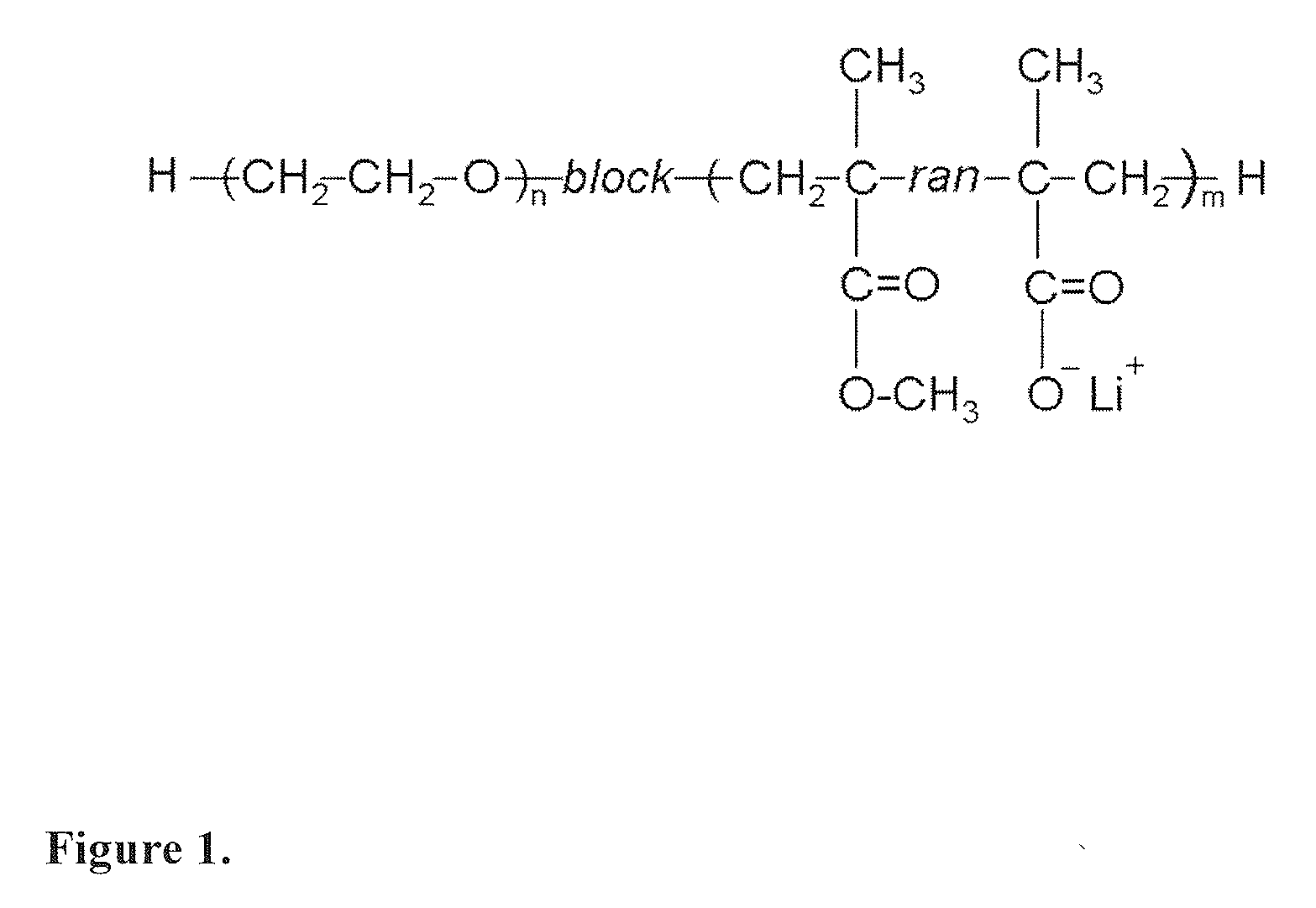How Have PU Solid Electrolytes Evolved in Batteries?
JUN 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PU Electrolyte Evolution
The evolution of polyurethane (PU) solid electrolytes in batteries represents a significant advancement in energy storage technology. This progression can be traced through several key stages, each marked by notable improvements in performance and functionality.
In the early stages of development, PU-based electrolytes were primarily explored as alternatives to liquid electrolytes due to their potential for enhanced safety and stability. Initial formulations focused on incorporating lithium salts into PU matrices, aiming to achieve sufficient ionic conductivity while maintaining the mechanical strength inherent to polymers.
As research progressed, scientists began to optimize the chemical structure of PU electrolytes. This involved experimenting with different polyol and isocyanate combinations to create PU backbones that could facilitate ion transport more effectively. The introduction of soft and hard segments within the PU structure allowed for a balance between flexibility and mechanical integrity, crucial for maintaining contact with electrodes during battery cycling.
A significant breakthrough came with the development of cross-linked PU electrolytes. By introducing cross-linking agents, researchers were able to create three-dimensional networks that improved mechanical properties while maintaining high ionic conductivity. This approach addressed the challenge of balancing flexibility and strength, a persistent issue in polymer electrolyte design.
The incorporation of nanofillers marked another pivotal moment in PU electrolyte evolution. Ceramic particles, such as TiO2, Al2O3, and SiO2, were integrated into the PU matrix to create composite electrolytes. These nanofillers not only enhanced mechanical properties but also contributed to improved ionic conductivity through the creation of additional ion transport pathways.
Recent advancements have focused on the development of single-ion conducting PU electrolytes. By tethering anions to the polymer backbone, researchers have been able to achieve high lithium transference numbers, addressing the issue of concentration polarization that often plagues dual-ion conducting systems.
The latest frontier in PU electrolyte evolution involves the integration of functional groups capable of participating in redox reactions. These redox-active PU electrolytes not only serve as ion conductors but also contribute to the battery's capacity, potentially leading to higher energy densities.
Throughout this evolution, continuous improvements have been made in terms of ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and interfacial compatibility with electrodes. From initial conductivities in the range of 10^-6 S/cm, modern PU electrolytes can achieve conductivities approaching 10^-3 S/cm at room temperature, rivaling some liquid electrolytes while offering superior safety characteristics.
In the early stages of development, PU-based electrolytes were primarily explored as alternatives to liquid electrolytes due to their potential for enhanced safety and stability. Initial formulations focused on incorporating lithium salts into PU matrices, aiming to achieve sufficient ionic conductivity while maintaining the mechanical strength inherent to polymers.
As research progressed, scientists began to optimize the chemical structure of PU electrolytes. This involved experimenting with different polyol and isocyanate combinations to create PU backbones that could facilitate ion transport more effectively. The introduction of soft and hard segments within the PU structure allowed for a balance between flexibility and mechanical integrity, crucial for maintaining contact with electrodes during battery cycling.
A significant breakthrough came with the development of cross-linked PU electrolytes. By introducing cross-linking agents, researchers were able to create three-dimensional networks that improved mechanical properties while maintaining high ionic conductivity. This approach addressed the challenge of balancing flexibility and strength, a persistent issue in polymer electrolyte design.
The incorporation of nanofillers marked another pivotal moment in PU electrolyte evolution. Ceramic particles, such as TiO2, Al2O3, and SiO2, were integrated into the PU matrix to create composite electrolytes. These nanofillers not only enhanced mechanical properties but also contributed to improved ionic conductivity through the creation of additional ion transport pathways.
Recent advancements have focused on the development of single-ion conducting PU electrolytes. By tethering anions to the polymer backbone, researchers have been able to achieve high lithium transference numbers, addressing the issue of concentration polarization that often plagues dual-ion conducting systems.
The latest frontier in PU electrolyte evolution involves the integration of functional groups capable of participating in redox reactions. These redox-active PU electrolytes not only serve as ion conductors but also contribute to the battery's capacity, potentially leading to higher energy densities.
Throughout this evolution, continuous improvements have been made in terms of ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and interfacial compatibility with electrodes. From initial conductivities in the range of 10^-6 S/cm, modern PU electrolytes can achieve conductivities approaching 10^-3 S/cm at room temperature, rivaling some liquid electrolytes while offering superior safety characteristics.
Battery Market Trends
The battery market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage systems. This trend is expected to continue, with the global battery market projected to reach substantial value in the coming years. The shift towards cleaner energy sources and the push for electrification in various industries have been key factors in propelling this market expansion.
Lithium-ion batteries have dominated the market due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low cost. However, as the demand for higher performance and safer energy storage solutions grows, there is a rising interest in alternative battery technologies, including solid-state batteries. This has led to increased research and development efforts in solid electrolytes, with polyurethane (PU) solid electrolytes emerging as a promising candidate.
The automotive sector has been a major driver of battery market growth, with electric vehicle adoption accelerating worldwide. Governments in many countries have implemented policies and incentives to promote electric vehicle usage, further stimulating battery demand. Additionally, the consumer electronics industry continues to be a significant contributor to battery market expansion, with smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices requiring increasingly efficient and compact energy storage solutions.
Energy storage systems for grid applications and renewable energy integration have also become a rapidly growing segment of the battery market. As countries aim to increase their renewable energy capacity and improve grid stability, large-scale battery storage systems are being deployed to address intermittency issues associated with solar and wind power generation.
The battery market has seen a geographical shift in recent years, with Asia-Pacific emerging as the dominant region for battery production and consumption. China, in particular, has become a major player in the battery industry, with significant investments in manufacturing capacity and technology development. However, other regions, including North America and Europe, are also ramping up their efforts to establish domestic battery supply chains and reduce dependence on imports.
As the battery market continues to evolve, there is a growing focus on sustainability and environmental concerns. This has led to increased efforts in battery recycling and the development of more environmentally friendly battery chemistries. The trend towards circular economy principles in battery production and end-of-life management is expected to shape the future of the industry.
Lithium-ion batteries have dominated the market due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low cost. However, as the demand for higher performance and safer energy storage solutions grows, there is a rising interest in alternative battery technologies, including solid-state batteries. This has led to increased research and development efforts in solid electrolytes, with polyurethane (PU) solid electrolytes emerging as a promising candidate.
The automotive sector has been a major driver of battery market growth, with electric vehicle adoption accelerating worldwide. Governments in many countries have implemented policies and incentives to promote electric vehicle usage, further stimulating battery demand. Additionally, the consumer electronics industry continues to be a significant contributor to battery market expansion, with smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices requiring increasingly efficient and compact energy storage solutions.
Energy storage systems for grid applications and renewable energy integration have also become a rapidly growing segment of the battery market. As countries aim to increase their renewable energy capacity and improve grid stability, large-scale battery storage systems are being deployed to address intermittency issues associated with solar and wind power generation.
The battery market has seen a geographical shift in recent years, with Asia-Pacific emerging as the dominant region for battery production and consumption. China, in particular, has become a major player in the battery industry, with significant investments in manufacturing capacity and technology development. However, other regions, including North America and Europe, are also ramping up their efforts to establish domestic battery supply chains and reduce dependence on imports.
As the battery market continues to evolve, there is a growing focus on sustainability and environmental concerns. This has led to increased efforts in battery recycling and the development of more environmentally friendly battery chemistries. The trend towards circular economy principles in battery production and end-of-life management is expected to shape the future of the industry.
PU Electrolyte Challenges
Polyurethane (PU) solid electrolytes have shown promise in battery applications, but they face several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is their relatively low ionic conductivity compared to liquid electrolytes. This limitation affects the overall performance of batteries, particularly in terms of power output and charging rates. Researchers are actively working on improving the ionic conductivity of PU electrolytes through various methods, such as incorporating ionic liquids or nanofillers, but achieving conductivity levels comparable to liquid electrolytes remains a formidable task.
Another critical challenge is the mechanical stability of PU solid electrolytes. While they offer better safety features than liquid electrolytes, PU electrolytes can suffer from poor interfacial contact with electrodes, leading to increased internal resistance and reduced battery efficiency. The expansion and contraction of electrodes during charge-discharge cycles can cause mechanical stress on the electrolyte, potentially leading to cracks or delamination. Enhancing the mechanical properties of PU electrolytes while maintaining their flexibility is crucial for long-term battery performance and durability.
The electrochemical stability of PU solid electrolytes is also a concern, particularly at high voltages. Some PU electrolytes may undergo degradation or decomposition when exposed to the highly reactive environment within a battery, especially at the electrode-electrolyte interface. This can lead to the formation of a resistive layer, known as the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI), which can impede ion transport and contribute to capacity fade over time. Developing PU electrolytes with improved electrochemical stability across a wide voltage range is essential for their application in high-energy-density batteries.
Manufacturing scalability presents another significant challenge for PU solid electrolytes. While laboratory-scale production has shown promising results, scaling up the manufacturing process to industrial levels while maintaining consistent quality and performance is complex. Issues such as uniform thickness control, elimination of defects, and cost-effective production methods need to be addressed to make PU solid electrolytes commercially viable for large-scale battery production.
Lastly, the long-term stability and aging characteristics of PU solid electrolytes under various operating conditions remain areas of concern. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and prolonged cycling can affect the chemical and physical properties of the electrolyte over time. Understanding and mitigating these aging effects is crucial for ensuring the reliability and longevity of batteries employing PU solid electrolytes. Researchers are exploring various strategies, including the use of additives and novel polymer architectures, to enhance the long-term stability of these electrolytes.
Another critical challenge is the mechanical stability of PU solid electrolytes. While they offer better safety features than liquid electrolytes, PU electrolytes can suffer from poor interfacial contact with electrodes, leading to increased internal resistance and reduced battery efficiency. The expansion and contraction of electrodes during charge-discharge cycles can cause mechanical stress on the electrolyte, potentially leading to cracks or delamination. Enhancing the mechanical properties of PU electrolytes while maintaining their flexibility is crucial for long-term battery performance and durability.
The electrochemical stability of PU solid electrolytes is also a concern, particularly at high voltages. Some PU electrolytes may undergo degradation or decomposition when exposed to the highly reactive environment within a battery, especially at the electrode-electrolyte interface. This can lead to the formation of a resistive layer, known as the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI), which can impede ion transport and contribute to capacity fade over time. Developing PU electrolytes with improved electrochemical stability across a wide voltage range is essential for their application in high-energy-density batteries.
Manufacturing scalability presents another significant challenge for PU solid electrolytes. While laboratory-scale production has shown promising results, scaling up the manufacturing process to industrial levels while maintaining consistent quality and performance is complex. Issues such as uniform thickness control, elimination of defects, and cost-effective production methods need to be addressed to make PU solid electrolytes commercially viable for large-scale battery production.
Lastly, the long-term stability and aging characteristics of PU solid electrolytes under various operating conditions remain areas of concern. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and prolonged cycling can affect the chemical and physical properties of the electrolyte over time. Understanding and mitigating these aging effects is crucial for ensuring the reliability and longevity of batteries employing PU solid electrolytes. Researchers are exploring various strategies, including the use of additives and novel polymer architectures, to enhance the long-term stability of these electrolytes.
Current PU Electrolyte Tech
01 Polyurethane-based solid electrolytes
Polyurethane (PU) is used as a base material for solid electrolytes due to its flexibility, mechanical strength, and ability to incorporate ionic conductors. These PU-based solid electrolytes can be synthesized with various additives to enhance their ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability, making them suitable for use in batteries and other electrochemical devices.- Polyurethane-based solid electrolytes: Polyurethane (PU) is used as a base material for solid electrolytes due to its flexibility, mechanical strength, and ability to incorporate ionic conductors. These PU-based solid electrolytes can be synthesized with various additives to enhance their ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability, making them suitable for use in batteries and other electrochemical devices.
- Incorporation of lithium salts in PU electrolytes: Lithium salts are commonly incorporated into polyurethane matrices to create solid electrolytes with high ionic conductivity. These salts, such as lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) or lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), dissociate within the polymer matrix, allowing for efficient lithium ion transport. The concentration and type of lithium salt can be optimized to achieve desired conductivity and electrochemical properties.
- Cross-linking and network formation in PU electrolytes: Cross-linking techniques are employed to improve the mechanical and thermal stability of polyurethane-based solid electrolytes. By forming a three-dimensional network structure, the electrolyte can maintain its shape and prevent leakage while still allowing for ion transport. Various cross-linking agents and methods can be used to achieve the desired network properties and optimize the balance between mechanical strength and ionic conductivity.
- Nanocomposite PU solid electrolytes: Nanocomposite polyurethane solid electrolytes are developed by incorporating nanoparticles or nanofillers into the polymer matrix. These nanofillers, such as ceramic particles or carbon nanotubes, can enhance the mechanical properties, thermal stability, and ionic conductivity of the electrolyte. The interaction between the nanofillers and the polymer matrix creates additional pathways for ion transport and can also help suppress dendrite growth in lithium-based batteries.
- Plasticizers and additives for PU solid electrolytes: Various plasticizers and additives are used to modify the properties of polyurethane-based solid electrolytes. These additives can improve the flexibility, ionic conductivity, and electrochemical stability of the electrolyte. Common plasticizers include polyethylene glycol (PEG) and propylene carbonate, while additives such as ceramic particles or flame retardants can be incorporated to enhance specific properties like thermal stability or safety.
02 Composite PU solid electrolytes with inorganic fillers
Inorganic fillers, such as ceramic particles or metal oxides, are incorporated into PU matrices to create composite solid electrolytes. These fillers can improve the mechanical properties, thermal stability, and ionic conductivity of the electrolyte. The synergistic effect between the organic PU matrix and inorganic fillers results in enhanced overall performance of the solid electrolyte.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cross-linked PU solid electrolytes
Cross-linking techniques are applied to PU-based solid electrolytes to improve their mechanical strength and dimensional stability. This approach involves creating a network structure within the PU matrix, which can lead to better retention of electrolyte components and improved long-term performance. Various cross-linking agents and methods are employed to achieve the desired properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 PU solid electrolytes with ionic liquids
Ionic liquids are incorporated into PU-based solid electrolytes to enhance their ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability. These ionic liquid-containing PU electrolytes exhibit improved performance at elevated temperatures and can be tailored for specific applications in energy storage devices. The combination of PU and ionic liquids offers a balance between mechanical properties and ionic transport.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surface-modified PU solid electrolytes
Surface modification techniques are applied to PU-based solid electrolytes to improve their interfacial properties and compatibility with electrode materials. These modifications can enhance the electrochemical stability, reduce interfacial resistance, and improve the overall performance of devices utilizing PU solid electrolytes. Various surface treatment methods and coating materials are explored to achieve optimal results.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Battery Manufacturers
The evolution of PU solid electrolytes in batteries is at a critical juncture, with the industry transitioning from research to early commercialization. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by the demand for safer and higher-energy-density batteries. Technologically, PU solid electrolytes are progressing towards maturity, with companies like LG Energy Solution, Toyota Motor Corp., and Samsung SDI leading the charge. These firms are investing heavily in R&D to overcome challenges such as interfacial resistance and mechanical stability. Collaborations between industry leaders and research institutions, including the University of Maryland and Tokyo Institute of Technology, are accelerating innovation in this field, pushing the boundaries of PU solid electrolyte performance and manufacturability.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed advanced PU solid electrolytes for next-generation batteries. Their technology focuses on creating a cross-linked polymer network with high ionic conductivity and excellent mechanical properties. The company utilizes a unique blend of polyethylene oxide (PEO) and urethane-based monomers, which are then UV-cured to form a robust, flexible solid electrolyte. This approach allows for improved lithium-ion transport while maintaining structural integrity, addressing key challenges in solid-state battery development.
Strengths: High ionic conductivity, excellent mechanical properties, and improved safety. Weaknesses: Potential for high production costs and scalability challenges.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has made significant strides in PU solid electrolyte technology for electric vehicle applications. Their approach involves a novel composite system that combines polyurethane with ceramic fillers to create a hybrid solid electrolyte. This composite structure aims to leverage the flexibility of polymers and the high ionic conductivity of ceramics. Toyota's research focuses on optimizing the interface between the polymer and ceramic components to enhance overall performance. The company has also developed proprietary processing techniques to ensure uniform distribution of ceramic particles within the polymer matrix.
Strengths: Combines benefits of polymers and ceramics, potential for high energy density. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process, possible long-term stability issues.
PU Electrolyte Innovations
Polymer Solid Electrolyte for Flexible Batteries
PatentActiveUS20100255383A1
Innovation
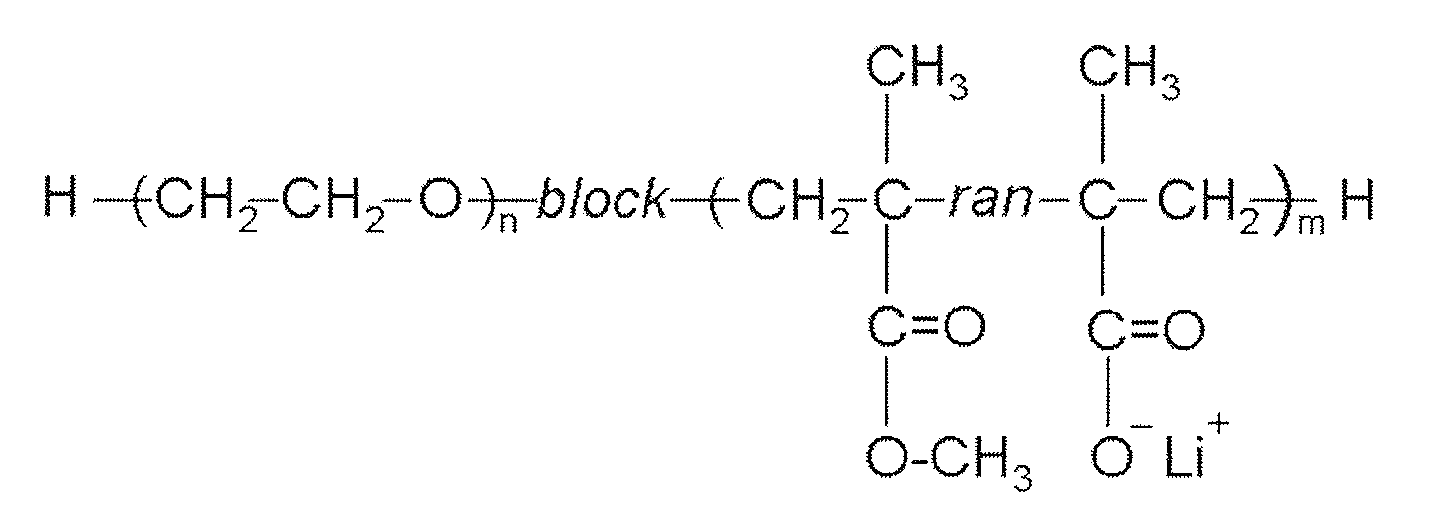
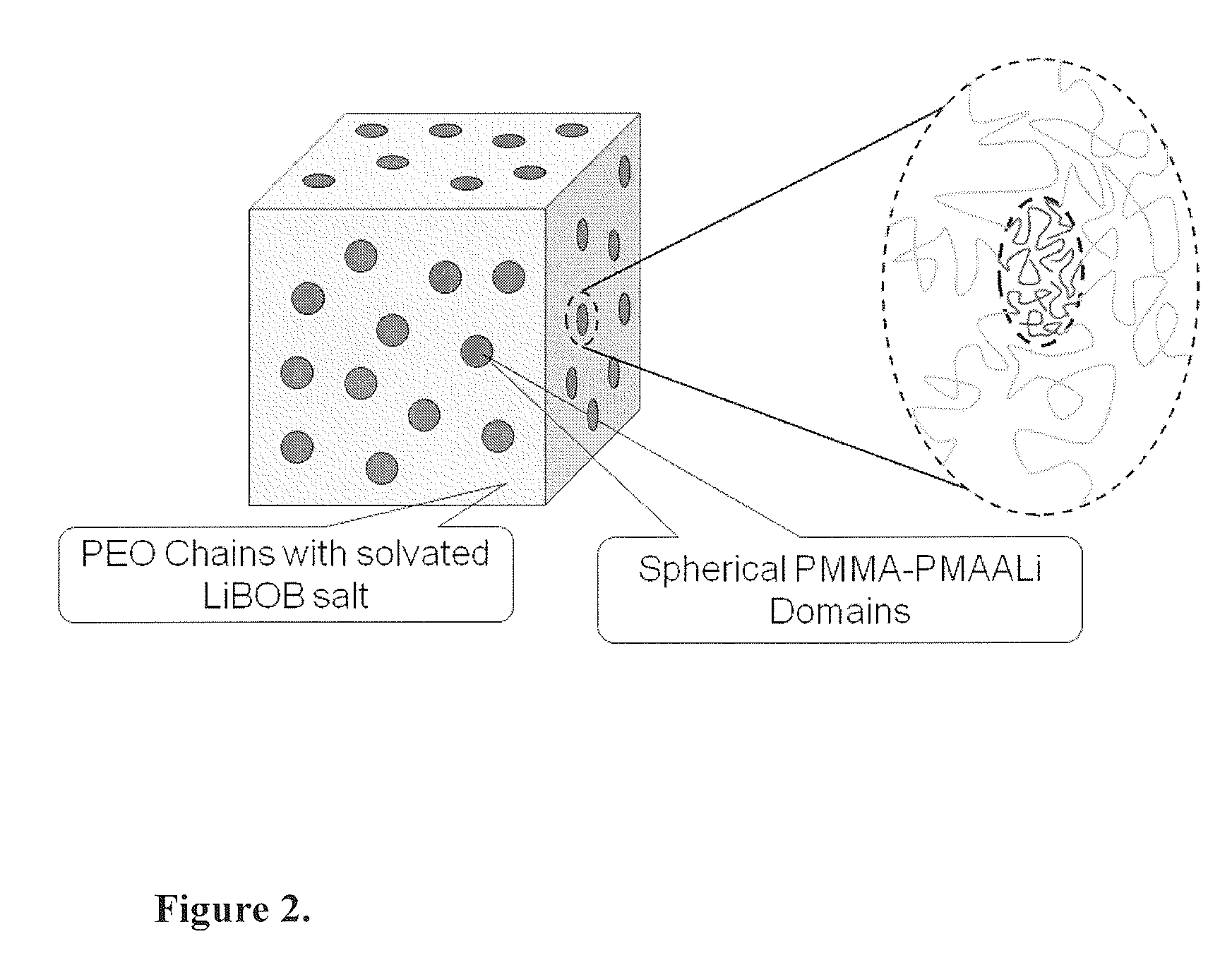
- A flexible solid polymer electrolyte is developed, comprising a diblock copolymer with a polyether block and an acrylate block, incorporating lithium ions within microphase-separated spherical domains, and a second lithium salt, such as lithium bis(oxalato)borate, to enhance conductivity and reduce crystallinity.
Solid electrolyte, solid electrolyte manufacturing method, battery, and article
PatentWO2022145180A1
Innovation
- A solid electrolyte is developed by curing a composition containing monofunctional urethane (meth)acrylate and an electrolyte salt, which has a polyether chain and a urethane bond, providing excellent ionic conductivity and flexibility at low temperatures and repeated bending durability.
Safety Regulations
The evolution of polyurethane (PU) solid electrolytes in batteries has necessitated the development and implementation of comprehensive safety regulations. These regulations are crucial to ensure the safe production, use, and disposal of batteries incorporating PU solid electrolytes. As the technology has advanced, safety standards have become increasingly stringent to address potential risks associated with these novel materials.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations for PU solid electrolytes is thermal stability. Given the potential for thermal runaway in batteries, regulatory bodies have established strict temperature thresholds and testing protocols to evaluate the thermal performance of PU-based electrolytes. These tests typically involve subjecting the electrolytes to extreme temperature conditions to assess their stability and potential for degradation or combustion.
Chemical compatibility is another critical aspect addressed by safety regulations. PU solid electrolytes must demonstrate long-term stability when in contact with electrode materials and other battery components. Regulatory standards now require extensive compatibility testing to ensure that no adverse reactions occur over the battery's lifetime, which could compromise safety or performance.
Mechanical integrity has also become a key consideration in safety regulations for PU solid electrolytes. As these materials serve as both ion conductors and separators, they must maintain their structural integrity under various mechanical stresses. Regulations now mandate rigorous mechanical testing, including compression, tension, and impact resistance evaluations, to ensure the electrolytes can withstand real-world conditions without failure.
Electrical safety is paramount in battery regulations, and PU solid electrolytes are no exception. Safety standards have evolved to include specific requirements for electrical conductivity, dielectric strength, and short-circuit prevention. These regulations aim to minimize the risk of electrical failures that could lead to safety hazards or battery malfunction.
Environmental and health considerations have also shaped the regulatory landscape for PU solid electrolytes. As awareness of environmental impacts has grown, regulations now encompass the entire lifecycle of these materials, from production to disposal. This includes guidelines for safe handling during manufacturing, requirements for non-toxic formulations, and protocols for environmentally responsible recycling or disposal at the end of the battery's life.
Standardization efforts have played a crucial role in the evolution of safety regulations for PU solid electrolytes. International organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) have developed specific standards for solid-state batteries, including those using PU electrolytes. These standards provide a unified framework for safety assessment and certification across different regions and applications.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations for PU solid electrolytes is thermal stability. Given the potential for thermal runaway in batteries, regulatory bodies have established strict temperature thresholds and testing protocols to evaluate the thermal performance of PU-based electrolytes. These tests typically involve subjecting the electrolytes to extreme temperature conditions to assess their stability and potential for degradation or combustion.
Chemical compatibility is another critical aspect addressed by safety regulations. PU solid electrolytes must demonstrate long-term stability when in contact with electrode materials and other battery components. Regulatory standards now require extensive compatibility testing to ensure that no adverse reactions occur over the battery's lifetime, which could compromise safety or performance.
Mechanical integrity has also become a key consideration in safety regulations for PU solid electrolytes. As these materials serve as both ion conductors and separators, they must maintain their structural integrity under various mechanical stresses. Regulations now mandate rigorous mechanical testing, including compression, tension, and impact resistance evaluations, to ensure the electrolytes can withstand real-world conditions without failure.
Electrical safety is paramount in battery regulations, and PU solid electrolytes are no exception. Safety standards have evolved to include specific requirements for electrical conductivity, dielectric strength, and short-circuit prevention. These regulations aim to minimize the risk of electrical failures that could lead to safety hazards or battery malfunction.
Environmental and health considerations have also shaped the regulatory landscape for PU solid electrolytes. As awareness of environmental impacts has grown, regulations now encompass the entire lifecycle of these materials, from production to disposal. This includes guidelines for safe handling during manufacturing, requirements for non-toxic formulations, and protocols for environmentally responsible recycling or disposal at the end of the battery's life.
Standardization efforts have played a crucial role in the evolution of safety regulations for PU solid electrolytes. International organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) have developed specific standards for solid-state batteries, including those using PU electrolytes. These standards provide a unified framework for safety assessment and certification across different regions and applications.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of PU solid electrolytes in batteries has become an increasingly important consideration as the technology evolves. These electrolytes offer potential advantages in terms of sustainability and reduced environmental footprint compared to traditional liquid electrolytes.
One of the key environmental benefits of PU solid electrolytes is their improved safety profile. Unlike liquid electrolytes, which can be flammable and pose risks of leakage, PU solid electrolytes are inherently safer. This reduces the potential for environmental contamination in case of battery damage or improper disposal.
The production process of PU solid electrolytes generally requires less energy and fewer toxic solvents compared to liquid electrolyte manufacturing. This translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced environmental pollution during the manufacturing phase. Additionally, the solid nature of these electrolytes allows for simpler and more environmentally friendly recycling processes at the end of the battery's life cycle.
PU solid electrolytes have also shown promise in extending battery lifespan, which can significantly reduce electronic waste. Longer-lasting batteries mean fewer replacements and less frequent disposal of battery components, ultimately decreasing the overall environmental impact of battery production and waste management.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of PU solid electrolytes is not entirely positive. The production of some PU materials may involve petrochemical-based processes, which can have their own environmental implications. Researchers are actively working on developing more sustainable and bio-based PU materials to further improve the environmental profile of these electrolytes.
The use of PU solid electrolytes can also contribute to the development of more energy-dense batteries. This has indirect environmental benefits, as it enables the creation of more efficient electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems, potentially reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering overall carbon emissions.
As the technology continues to evolve, ongoing research is focused on optimizing the environmental performance of PU solid electrolytes. This includes exploring greener synthesis methods, improving recyclability, and enhancing the overall lifecycle sustainability of batteries incorporating these materials. The environmental impact of PU solid electrolytes remains a critical factor in their development and adoption in next-generation battery technologies.
One of the key environmental benefits of PU solid electrolytes is their improved safety profile. Unlike liquid electrolytes, which can be flammable and pose risks of leakage, PU solid electrolytes are inherently safer. This reduces the potential for environmental contamination in case of battery damage or improper disposal.
The production process of PU solid electrolytes generally requires less energy and fewer toxic solvents compared to liquid electrolyte manufacturing. This translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced environmental pollution during the manufacturing phase. Additionally, the solid nature of these electrolytes allows for simpler and more environmentally friendly recycling processes at the end of the battery's life cycle.
PU solid electrolytes have also shown promise in extending battery lifespan, which can significantly reduce electronic waste. Longer-lasting batteries mean fewer replacements and less frequent disposal of battery components, ultimately decreasing the overall environmental impact of battery production and waste management.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of PU solid electrolytes is not entirely positive. The production of some PU materials may involve petrochemical-based processes, which can have their own environmental implications. Researchers are actively working on developing more sustainable and bio-based PU materials to further improve the environmental profile of these electrolytes.
The use of PU solid electrolytes can also contribute to the development of more energy-dense batteries. This has indirect environmental benefits, as it enables the creation of more efficient electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems, potentially reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering overall carbon emissions.
As the technology continues to evolve, ongoing research is focused on optimizing the environmental performance of PU solid electrolytes. This includes exploring greener synthesis methods, improving recyclability, and enhancing the overall lifecycle sustainability of batteries incorporating these materials. The environmental impact of PU solid electrolytes remains a critical factor in their development and adoption in next-generation battery technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!