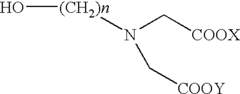
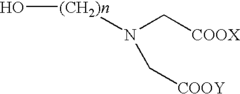
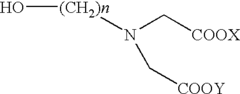
How Magnesium Nitrate Contributes to De-icing Formulations
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
De-icing Formulation Evolution and Objectives
De-icing formulations have undergone significant evolution since their inception, driven by the need for more effective, environmentally friendly, and cost-efficient solutions. The primary objective of these formulations has always been to prevent or remove ice formation on surfaces, particularly in transportation and infrastructure sectors. Initially, simple salt-based solutions were the norm, with sodium chloride being the most common ingredient.
As environmental concerns grew and the limitations of traditional methods became apparent, the industry began exploring more sophisticated formulations. The introduction of alternative chlorides, such as calcium chloride and magnesium chloride, marked a significant step forward. These compounds offered improved performance at lower temperatures and reduced corrosive effects compared to sodium chloride.
The evolution continued with the development of acetate-based de-icers, such as potassium acetate and sodium acetate. These formulations provided enhanced ice-melting capabilities while significantly reducing environmental impact. However, their higher cost limited widespread adoption, particularly in large-scale applications.
Recent years have seen a shift towards multi-component formulations, combining various salts, organic compounds, and corrosion inhibitors. This approach aims to leverage the strengths of different ingredients while mitigating their individual drawbacks. The inclusion of magnesium nitrate in these formulations represents a notable advancement in this direction.
The objectives of modern de-icing formulations have expanded beyond mere ice removal. Key goals now include minimizing environmental impact, reducing corrosion to infrastructure and vehicles, improving longevity of application, and enhancing performance across a wider temperature range. There is also a growing emphasis on developing formulations that are less harmful to vegetation and aquatic ecosystems.
Another critical objective is the reduction of overall salt usage while maintaining or improving de-icing effectiveness. This goal is driven by both environmental concerns and the need to optimize resource utilization. Innovations in application techniques and smart systems for de-icing complement these formulation advancements, aiming for more precise and efficient use of de-icing materials.
Looking forward, the evolution of de-icing formulations is likely to continue focusing on sustainability and performance optimization. Research into bio-based additives, nanotechnology applications, and synergistic combinations of existing materials promises to yield even more effective and environmentally responsible solutions. The contribution of magnesium nitrate to these formulations represents just one aspect of this ongoing evolution, offering new possibilities in the quest for ideal de-icing solutions.
As environmental concerns grew and the limitations of traditional methods became apparent, the industry began exploring more sophisticated formulations. The introduction of alternative chlorides, such as calcium chloride and magnesium chloride, marked a significant step forward. These compounds offered improved performance at lower temperatures and reduced corrosive effects compared to sodium chloride.
The evolution continued with the development of acetate-based de-icers, such as potassium acetate and sodium acetate. These formulations provided enhanced ice-melting capabilities while significantly reducing environmental impact. However, their higher cost limited widespread adoption, particularly in large-scale applications.
Recent years have seen a shift towards multi-component formulations, combining various salts, organic compounds, and corrosion inhibitors. This approach aims to leverage the strengths of different ingredients while mitigating their individual drawbacks. The inclusion of magnesium nitrate in these formulations represents a notable advancement in this direction.
The objectives of modern de-icing formulations have expanded beyond mere ice removal. Key goals now include minimizing environmental impact, reducing corrosion to infrastructure and vehicles, improving longevity of application, and enhancing performance across a wider temperature range. There is also a growing emphasis on developing formulations that are less harmful to vegetation and aquatic ecosystems.
Another critical objective is the reduction of overall salt usage while maintaining or improving de-icing effectiveness. This goal is driven by both environmental concerns and the need to optimize resource utilization. Innovations in application techniques and smart systems for de-icing complement these formulation advancements, aiming for more precise and efficient use of de-icing materials.
Looking forward, the evolution of de-icing formulations is likely to continue focusing on sustainability and performance optimization. Research into bio-based additives, nanotechnology applications, and synergistic combinations of existing materials promises to yield even more effective and environmentally responsible solutions. The contribution of magnesium nitrate to these formulations represents just one aspect of this ongoing evolution, offering new possibilities in the quest for ideal de-icing solutions.
Market Analysis for Advanced De-icing Solutions
The global de-icing market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing safety concerns in transportation and infrastructure maintenance. Advanced de-icing solutions, particularly those incorporating magnesium nitrate, have gained traction due to their enhanced performance and environmental benefits. The market for these innovative formulations is projected to expand at a robust rate, outpacing traditional de-icing products.
Geographically, North America dominates the advanced de-icing solutions market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. This distribution is largely attributed to the harsh winter conditions in these regions and stringent safety regulations. The United States, Canada, and Northern European countries are key markets, with emerging economies in Eastern Europe and Asia showing rapid adoption rates.
The aviation sector represents a substantial portion of the advanced de-icing market, as airlines prioritize passenger safety and operational efficiency. Airports in cold climates are major consumers of these products, driving demand for more effective and less corrosive formulations. The automotive and road maintenance sectors also contribute significantly to market growth, with governments and transportation authorities increasingly favoring advanced solutions to ensure safer road conditions.
Magnesium nitrate-based de-icing formulations are carving out a growing niche within the broader market. These products offer several advantages over traditional salt-based de-icers, including lower freezing points, reduced corrosion on metal surfaces, and minimized environmental impact. As a result, they are gaining popularity in environmentally sensitive areas and for use on specialized infrastructure.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, with companies investing heavily in research and development to improve product efficacy and sustainability. Partnerships between chemical manufacturers and end-users, such as airport authorities and highway departments, are becoming more common, fostering innovation and tailored solutions.
Consumer awareness regarding the environmental impact of de-icing chemicals is influencing market dynamics. This shift in preference is driving demand for eco-friendly alternatives, including magnesium nitrate-based products. Regulatory bodies are also playing a crucial role in shaping the market, with increasingly stringent environmental standards favoring advanced formulations over traditional options.
Looking ahead, the market for advanced de-icing solutions is poised for continued growth. Factors such as climate change, which may lead to more frequent and severe winter weather events, and the expansion of transportation infrastructure in developing regions are expected to fuel demand. The integration of smart technologies and the development of multi-functional de-icing formulations represent promising avenues for future market expansion and product differentiation.
Geographically, North America dominates the advanced de-icing solutions market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. This distribution is largely attributed to the harsh winter conditions in these regions and stringent safety regulations. The United States, Canada, and Northern European countries are key markets, with emerging economies in Eastern Europe and Asia showing rapid adoption rates.
The aviation sector represents a substantial portion of the advanced de-icing market, as airlines prioritize passenger safety and operational efficiency. Airports in cold climates are major consumers of these products, driving demand for more effective and less corrosive formulations. The automotive and road maintenance sectors also contribute significantly to market growth, with governments and transportation authorities increasingly favoring advanced solutions to ensure safer road conditions.
Magnesium nitrate-based de-icing formulations are carving out a growing niche within the broader market. These products offer several advantages over traditional salt-based de-icers, including lower freezing points, reduced corrosion on metal surfaces, and minimized environmental impact. As a result, they are gaining popularity in environmentally sensitive areas and for use on specialized infrastructure.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, with companies investing heavily in research and development to improve product efficacy and sustainability. Partnerships between chemical manufacturers and end-users, such as airport authorities and highway departments, are becoming more common, fostering innovation and tailored solutions.
Consumer awareness regarding the environmental impact of de-icing chemicals is influencing market dynamics. This shift in preference is driving demand for eco-friendly alternatives, including magnesium nitrate-based products. Regulatory bodies are also playing a crucial role in shaping the market, with increasingly stringent environmental standards favoring advanced formulations over traditional options.
Looking ahead, the market for advanced de-icing solutions is poised for continued growth. Factors such as climate change, which may lead to more frequent and severe winter weather events, and the expansion of transportation infrastructure in developing regions are expected to fuel demand. The integration of smart technologies and the development of multi-functional de-icing formulations represent promising avenues for future market expansion and product differentiation.
Magnesium Nitrate in De-icing: Current Status and Challenges
The current status of magnesium nitrate in de-icing formulations presents both promising advancements and significant challenges. As a hygroscopic salt, magnesium nitrate has gained attention for its potential to enhance the performance of traditional de-icing agents. Its ability to absorb moisture from the atmosphere contributes to the formation of a brine solution, which can effectively lower the freezing point of water on road surfaces.
One of the primary advantages of incorporating magnesium nitrate into de-icing formulations is its synergistic effect with other commonly used salts, such as sodium chloride. This combination has shown improved ice-melting capacity at lower temperatures compared to single-salt solutions. Additionally, magnesium nitrate exhibits a lower corrosivity profile than some alternative de-icing agents, potentially reducing damage to infrastructure and vehicles.
However, the widespread adoption of magnesium nitrate in de-icing applications faces several obstacles. The cost of production and transportation remains a significant barrier, particularly when compared to more economical options like rock salt. This economic factor has limited its use to specific high-priority areas or as a component in premium de-icing blends.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the extensive use of magnesium nitrate. While it is less harmful than some alternatives, there are still potential impacts on soil and water ecosystems that require careful consideration. Regulatory bodies in various regions have implemented restrictions on the use of certain de-icing chemicals, necessitating ongoing research to fully understand and mitigate the environmental effects of magnesium nitrate.
Technical challenges in formulation and application persist. Achieving the optimal balance of magnesium nitrate with other components to maximize effectiveness while minimizing negative impacts requires sophisticated blending techniques. Moreover, the hygroscopic nature of magnesium nitrate can lead to storage and handling difficulties, as it tends to clump and absorb moisture during storage.
Research efforts are currently focused on addressing these challenges. Scientists and engineers are exploring novel formulation methods to enhance the stability and ease of application of magnesium nitrate-based de-icing products. Additionally, studies are underway to develop more environmentally friendly versions that maintain efficacy while reducing potential ecological impacts.
The integration of magnesium nitrate into smart de-icing systems represents an emerging trend. These systems aim to optimize the application of de-icing agents based on real-time weather and road condition data, potentially improving the efficiency and reducing the overall environmental footprint of winter road maintenance operations.
One of the primary advantages of incorporating magnesium nitrate into de-icing formulations is its synergistic effect with other commonly used salts, such as sodium chloride. This combination has shown improved ice-melting capacity at lower temperatures compared to single-salt solutions. Additionally, magnesium nitrate exhibits a lower corrosivity profile than some alternative de-icing agents, potentially reducing damage to infrastructure and vehicles.
However, the widespread adoption of magnesium nitrate in de-icing applications faces several obstacles. The cost of production and transportation remains a significant barrier, particularly when compared to more economical options like rock salt. This economic factor has limited its use to specific high-priority areas or as a component in premium de-icing blends.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the extensive use of magnesium nitrate. While it is less harmful than some alternatives, there are still potential impacts on soil and water ecosystems that require careful consideration. Regulatory bodies in various regions have implemented restrictions on the use of certain de-icing chemicals, necessitating ongoing research to fully understand and mitigate the environmental effects of magnesium nitrate.
Technical challenges in formulation and application persist. Achieving the optimal balance of magnesium nitrate with other components to maximize effectiveness while minimizing negative impacts requires sophisticated blending techniques. Moreover, the hygroscopic nature of magnesium nitrate can lead to storage and handling difficulties, as it tends to clump and absorb moisture during storage.
Research efforts are currently focused on addressing these challenges. Scientists and engineers are exploring novel formulation methods to enhance the stability and ease of application of magnesium nitrate-based de-icing products. Additionally, studies are underway to develop more environmentally friendly versions that maintain efficacy while reducing potential ecological impacts.
The integration of magnesium nitrate into smart de-icing systems represents an emerging trend. These systems aim to optimize the application of de-icing agents based on real-time weather and road condition data, potentially improving the efficiency and reducing the overall environmental footprint of winter road maintenance operations.
Existing Magnesium Nitrate-based De-icing Formulations
01 Magnesium nitrate as a primary de-icing agent
Magnesium nitrate is used as a primary component in de-icing formulations due to its effective ice-melting properties and relatively low environmental impact. It can be applied in various forms, such as solutions or granules, to roads, runways, and other surfaces to prevent ice formation or melt existing ice.- Magnesium nitrate as a primary de-icing agent: Magnesium nitrate is used as a primary component in de-icing formulations due to its effective ice-melting properties and relatively low environmental impact. It can be applied in various forms, including solutions and granules, to roads, runways, and other surfaces prone to ice formation.
- Combination with other de-icing compounds: Magnesium nitrate is often combined with other de-icing agents such as calcium chloride, sodium chloride, or potassium acetate to enhance its effectiveness and reduce overall salt usage. These combinations can provide improved performance across a wider range of temperatures and conditions.
- Corrosion inhibition in magnesium nitrate de-icers: To mitigate the corrosive effects of magnesium nitrate on metal surfaces, corrosion inhibitors are often incorporated into the de-icing formulations. These additives help protect infrastructure and vehicles from damage caused by repeated exposure to the de-icing agent.
- Environmental considerations in magnesium nitrate de-icing: Magnesium nitrate-based de-icers are developed with a focus on minimizing environmental impact. Formulations often include biodegradable components and are designed to reduce chloride content, which can be harmful to vegetation and aquatic ecosystems.
- Application methods and equipment for magnesium nitrate de-icers: Specialized equipment and application techniques are developed for the efficient distribution of magnesium nitrate de-icers. This includes automated spraying systems, precision applicators, and methods for pre-wetting road surfaces to improve the effectiveness of the de-icing process.
02 Combination with other de-icing compounds
Magnesium nitrate is often combined with other de-icing compounds to enhance its effectiveness and reduce overall environmental impact. Common combinations include mixtures with calcium chloride, sodium chloride, or organic compounds. These blends can provide improved performance across a wider range of temperatures and conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application methods and equipment
Various application methods and specialized equipment have been developed for the efficient distribution of magnesium nitrate-based de-icing solutions. These include automated spraying systems, precision applicators, and vehicles equipped with customized spreading mechanisms to ensure optimal coverage and minimize waste.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and corrosion considerations
Research has focused on minimizing the environmental impact and corrosive effects of magnesium nitrate de-icing solutions. This includes developing eco-friendly additives, optimizing application rates, and creating corrosion-resistant formulations to protect infrastructure and vehicles exposed to the de-icing agents.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with smart de-icing systems
Advanced de-icing systems incorporating magnesium nitrate solutions have been developed, integrating sensors, weather prediction algorithms, and automated application controls. These smart systems optimize the use of de-icing agents based on real-time conditions, improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in De-icing Chemical Industry
The de-icing formulations market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for safer and more environmentally friendly solutions. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a focus on developing advanced formulations. The technology is relatively mature, with ongoing research to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Key players like Compass Minerals America, Inc. and Envirotech Services LLC are leading innovation in this field, while companies such as BASF Corp. and Air Products & Chemicals, Inc. contribute their expertise in chemical manufacturing. Academic institutions like Sichuan University and AGH University of Krakow are also actively involved in research, potentially driving future advancements in magnesium nitrate-based de-icing formulations.
Compass Minerals America, Inc.
Technical Solution: Compass Minerals has developed advanced de-icing formulations incorporating magnesium nitrate as a key component. Their proprietary blend combines magnesium nitrate with other chloride-based salts to create a more effective and environmentally friendly de-icing solution. The company's research has shown that magnesium nitrate contributes to lowering the freezing point of water more effectively than traditional rock salt alone, allowing for improved performance at lower temperatures[1]. Additionally, their formulation utilizes the hygroscopic properties of magnesium nitrate to attract moisture from the air, which helps to initiate the melting process more quickly[3]. Compass Minerals has also focused on optimizing the particle size distribution of their de-icing products to ensure better coverage and longer-lasting effects on treated surfaces[5].
Strengths: Enhanced low-temperature performance, faster melting initiation, and improved environmental profile. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs compared to traditional rock salt formulations, and may require specialized application equipment.
Envirotech Services LLC
Technical Solution: Envirotech Services has pioneered a liquid de-icing formulation that incorporates magnesium nitrate as a central component. Their approach focuses on creating a synergistic blend of magnesium nitrate with organic compounds derived from agricultural by-products. This combination results in a de-icing solution that not only melts ice effectively but also provides residual de-icing properties for extended periods[2]. The company's research has demonstrated that the inclusion of magnesium nitrate in their liquid formulation significantly reduces the corrosive effects typically associated with chloride-based de-icers[4]. Envirotech's technology also leverages the exothermic reaction of magnesium nitrate when it comes into contact with water, generating heat that further aids in the ice-melting process[6].
Strengths: Reduced corrosivity, extended residual effects, and utilization of sustainable agricultural by-products. Weaknesses: May require specialized storage and application equipment for liquid formulations, potentially limiting widespread adoption.
Core Innovations in Magnesium Nitrate De-icing Technology
Defrosting agent based on acetates and/or formates, and process for melting, using said agent, snow and ice on areas for traffic
PatentInactiveEP0902817A1
Innovation
- A de-icing agent composed of 87-99.45% alkali metal acetate or formate, 0.5-10% alkali metal silicate, and 0.05-3% alkali metal phosphate, which is free of chloride and nitrite, effectively inhibits magnesium corrosion and provides rapid thawing.
Anticorrosion agents for halide brines
PatentActiveUS20100009073A1
Innovation
- Incorporating alcohol diglycinate as an anticorrosion agent in halide brine solutions to significantly reduce corrosion rates while maintaining effectiveness in anti-icing and dust control applications.
Environmental Impact of Magnesium Nitrate De-icers
The environmental impact of magnesium nitrate de-icers is a critical consideration in their application and widespread use. These de-icing formulations, while effective in melting ice and snow, can have significant effects on surrounding ecosystems and infrastructure.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for soil and water contamination. When magnesium nitrate de-icers are applied to roads and other surfaces, they can be washed off by rain or melting snow, leading to increased concentrations of magnesium and nitrate ions in nearby soil and water bodies. This can alter the chemical composition of these environments, potentially affecting plant growth and aquatic life.
The introduction of excess nitrates into water systems can contribute to eutrophication, a process where increased nutrient levels lead to algal blooms and oxygen depletion in water bodies. This can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, disrupting the balance of flora and fauna in affected areas.
Magnesium nitrate de-icers may also impact vegetation along roadsides and in adjacent areas. The accumulation of magnesium and nitrate in soil can alter soil pH and nutrient balance, potentially affecting plant growth and species composition in these areas. Some plants may benefit from the additional nutrients, while others may struggle to adapt to the changed soil conditions.
The corrosive nature of magnesium nitrate can also have indirect environmental impacts through its effects on infrastructure. Accelerated corrosion of metal structures, such as bridges and vehicles, can lead to increased maintenance requirements and potentially shorter lifespans for these assets. This, in turn, may result in increased resource consumption and waste generation associated with repairs and replacements.
However, it is important to note that magnesium nitrate de-icers generally have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional chloride-based de-icers. They typically require lower application rates and have less severe effects on vegetation and aquatic life than their chloride counterparts.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of magnesium nitrate de-icers include optimizing application rates, improving drainage systems to reduce runoff, and developing more environmentally friendly formulations. Ongoing research is focused on finding a balance between de-icing effectiveness and environmental sustainability.
In conclusion, while magnesium nitrate de-icers offer certain advantages over traditional de-icing agents, their environmental impact remains a significant consideration. Continued research and development in this area are crucial to minimize negative effects on ecosystems and infrastructure while maintaining road safety during winter conditions.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for soil and water contamination. When magnesium nitrate de-icers are applied to roads and other surfaces, they can be washed off by rain or melting snow, leading to increased concentrations of magnesium and nitrate ions in nearby soil and water bodies. This can alter the chemical composition of these environments, potentially affecting plant growth and aquatic life.
The introduction of excess nitrates into water systems can contribute to eutrophication, a process where increased nutrient levels lead to algal blooms and oxygen depletion in water bodies. This can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, disrupting the balance of flora and fauna in affected areas.
Magnesium nitrate de-icers may also impact vegetation along roadsides and in adjacent areas. The accumulation of magnesium and nitrate in soil can alter soil pH and nutrient balance, potentially affecting plant growth and species composition in these areas. Some plants may benefit from the additional nutrients, while others may struggle to adapt to the changed soil conditions.
The corrosive nature of magnesium nitrate can also have indirect environmental impacts through its effects on infrastructure. Accelerated corrosion of metal structures, such as bridges and vehicles, can lead to increased maintenance requirements and potentially shorter lifespans for these assets. This, in turn, may result in increased resource consumption and waste generation associated with repairs and replacements.
However, it is important to note that magnesium nitrate de-icers generally have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional chloride-based de-icers. They typically require lower application rates and have less severe effects on vegetation and aquatic life than their chloride counterparts.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of magnesium nitrate de-icers include optimizing application rates, improving drainage systems to reduce runoff, and developing more environmentally friendly formulations. Ongoing research is focused on finding a balance between de-icing effectiveness and environmental sustainability.
In conclusion, while magnesium nitrate de-icers offer certain advantages over traditional de-icing agents, their environmental impact remains a significant consideration. Continued research and development in this area are crucial to minimize negative effects on ecosystems and infrastructure while maintaining road safety during winter conditions.
Safety Regulations for De-icing Chemical Applications
The application of de-icing chemicals is subject to stringent safety regulations to protect human health, infrastructure, and the environment. These regulations vary across jurisdictions but generally focus on several key areas. Firstly, there are strict guidelines on the types and quantities of chemicals that can be used in de-icing formulations. Magnesium nitrate, as a component in some de-icing mixtures, must adhere to specific concentration limits to minimize potential adverse effects.
Environmental protection agencies often mandate regular testing and monitoring of water bodies near areas where de-icing chemicals are frequently applied. This is to ensure that runoff does not lead to excessive nutrient loading or other forms of water pollution. Manufacturers and users of de-icing formulations containing magnesium nitrate must provide detailed environmental impact assessments and mitigation plans.
Occupational health and safety regulations play a crucial role in protecting workers who handle and apply de-icing chemicals. Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are typically specified, including respiratory protection, eye protection, and chemical-resistant gloves. Training programs for proper handling and application techniques are often mandated to reduce the risk of accidents and exposure.
Storage and transportation of de-icing chemicals are also heavily regulated. Facilities must meet specific design criteria to prevent leaks and spills, and transportation vehicles must be properly equipped and labeled according to hazardous materials regulations. Emergency response plans are required to address potential accidents or spills during storage or transport.
Many jurisdictions have implemented regulations to promote the use of more environmentally friendly de-icing alternatives. This has led to increased scrutiny of traditional chemical formulations and a push towards products with lower environmental impacts. As a result, manufacturers must continually assess and improve their formulations to meet evolving regulatory standards.
Reporting and documentation requirements are another critical aspect of safety regulations. Users of de-icing chemicals must maintain detailed records of application rates, locations, and environmental monitoring data. These records are subject to regular audits by regulatory agencies to ensure compliance with established guidelines.
Public safety considerations also factor into regulations, with requirements for clear signage and public notifications when de-icing chemicals are applied in areas accessible to the general population. This is particularly important in urban areas where pedestrians and vehicles may come into contact with treated surfaces.
Environmental protection agencies often mandate regular testing and monitoring of water bodies near areas where de-icing chemicals are frequently applied. This is to ensure that runoff does not lead to excessive nutrient loading or other forms of water pollution. Manufacturers and users of de-icing formulations containing magnesium nitrate must provide detailed environmental impact assessments and mitigation plans.
Occupational health and safety regulations play a crucial role in protecting workers who handle and apply de-icing chemicals. Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are typically specified, including respiratory protection, eye protection, and chemical-resistant gloves. Training programs for proper handling and application techniques are often mandated to reduce the risk of accidents and exposure.
Storage and transportation of de-icing chemicals are also heavily regulated. Facilities must meet specific design criteria to prevent leaks and spills, and transportation vehicles must be properly equipped and labeled according to hazardous materials regulations. Emergency response plans are required to address potential accidents or spills during storage or transport.
Many jurisdictions have implemented regulations to promote the use of more environmentally friendly de-icing alternatives. This has led to increased scrutiny of traditional chemical formulations and a push towards products with lower environmental impacts. As a result, manufacturers must continually assess and improve their formulations to meet evolving regulatory standards.
Reporting and documentation requirements are another critical aspect of safety regulations. Users of de-icing chemicals must maintain detailed records of application rates, locations, and environmental monitoring data. These records are subject to regular audits by regulatory agencies to ensure compliance with established guidelines.
Public safety considerations also factor into regulations, with requirements for clear signage and public notifications when de-icing chemicals are applied in areas accessible to the general population. This is particularly important in urban areas where pedestrians and vehicles may come into contact with treated surfaces.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!