How Sodium Percarbonate Functions in Oxygen-Based Bleaching Processes
JUL 22, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Bleaching Background
Sodium percarbonate, a white crystalline compound with the chemical formula 2Na2CO3·3H2O2, has emerged as a key player in oxygen-based bleaching processes. This environmentally friendly bleaching agent has gained significant traction in recent years due to its effectiveness and eco-friendly nature. The compound's history dates back to the early 20th century, but its widespread use in commercial applications began in the 1960s.
The primary function of sodium percarbonate in bleaching processes is to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. This reaction produces oxygen, which acts as the active bleaching agent. The oxygen molecules attack and break down the chemical bonds of stains and colored substances, effectively removing them from fabrics or other materials. This process is particularly effective against organic stains such as food, beverages, and bodily fluids.
One of the key advantages of sodium percarbonate is its stability in dry form. Unlike liquid hydrogen peroxide, which can degrade over time, sodium percarbonate remains stable until it comes into contact with water. This property makes it an ideal ingredient for powdered laundry detergents and other cleaning products, as it allows for long-term storage without losing efficacy.
The bleaching mechanism of sodium percarbonate is pH-dependent. In alkaline conditions, which are typically maintained in most laundry detergents, the bleaching action is enhanced. This is because the alkaline environment promotes the formation of perhydroxyl ions, which are more effective at breaking down stains than hydrogen peroxide alone.
Sodium percarbonate's popularity in oxygen-based bleaching processes has grown due to several factors. Firstly, it is considered more environmentally friendly than chlorine-based bleaches, as it breaks down into harmless byproducts of water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. Secondly, it is gentler on fabrics compared to chlorine bleaches, making it suitable for a wider range of materials. Lastly, its ability to clean and brighten at lower temperatures aligns with the global trend towards energy-efficient washing practices.
In recent years, research has focused on improving the stability and efficacy of sodium percarbonate in various applications. This includes developing coatings to enhance its shelf life and exploring synergistic combinations with other cleaning agents to boost its performance. As consumer demand for eco-friendly cleaning solutions continues to rise, sodium percarbonate's role in oxygen-based bleaching processes is expected to expand further, driving innovation in both household and industrial cleaning sectors.
The primary function of sodium percarbonate in bleaching processes is to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. This reaction produces oxygen, which acts as the active bleaching agent. The oxygen molecules attack and break down the chemical bonds of stains and colored substances, effectively removing them from fabrics or other materials. This process is particularly effective against organic stains such as food, beverages, and bodily fluids.
One of the key advantages of sodium percarbonate is its stability in dry form. Unlike liquid hydrogen peroxide, which can degrade over time, sodium percarbonate remains stable until it comes into contact with water. This property makes it an ideal ingredient for powdered laundry detergents and other cleaning products, as it allows for long-term storage without losing efficacy.
The bleaching mechanism of sodium percarbonate is pH-dependent. In alkaline conditions, which are typically maintained in most laundry detergents, the bleaching action is enhanced. This is because the alkaline environment promotes the formation of perhydroxyl ions, which are more effective at breaking down stains than hydrogen peroxide alone.
Sodium percarbonate's popularity in oxygen-based bleaching processes has grown due to several factors. Firstly, it is considered more environmentally friendly than chlorine-based bleaches, as it breaks down into harmless byproducts of water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. Secondly, it is gentler on fabrics compared to chlorine bleaches, making it suitable for a wider range of materials. Lastly, its ability to clean and brighten at lower temperatures aligns with the global trend towards energy-efficient washing practices.
In recent years, research has focused on improving the stability and efficacy of sodium percarbonate in various applications. This includes developing coatings to enhance its shelf life and exploring synergistic combinations with other cleaning agents to boost its performance. As consumer demand for eco-friendly cleaning solutions continues to rise, sodium percarbonate's role in oxygen-based bleaching processes is expected to expand further, driving innovation in both household and industrial cleaning sectors.
Market Analysis for Oxygen Bleaches
The oxygen bleach market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly and safer cleaning alternatives. This segment of the cleaning products industry has shown robust expansion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall household cleaning market average. The rise in environmental consciousness and stricter regulations on traditional chlorine-based bleaches have been key factors propelling this growth.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards products that offer effective cleaning and stain removal while being gentler on fabrics and the environment. Oxygen bleaches, particularly those based on sodium percarbonate, have gained popularity due to their ability to break down into harmless byproducts of water and oxygen. This characteristic has resonated well with environmentally conscious consumers, leading to increased adoption in both household and commercial applications.
The market for oxygen bleaches spans various sectors, including laundry care, household cleaning, and industrial applications. In the laundry care segment, oxygen bleaches have become a staple ingredient in many detergent formulations, offering color-safe bleaching properties. The household cleaning sector has seen a surge in oxygen bleach-based products for surface cleaning, stain removal, and disinfection purposes. Industrial applications, such as in the textile and paper industries, have also contributed to market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe have been at the forefront of oxygen bleach adoption, with mature markets and high consumer awareness. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth potential as disposable incomes rise and environmental concerns gain traction. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, with increased focus on hygiene and sanitation driving demand for effective cleaning solutions.
Key market players have been investing in research and development to enhance the efficacy of oxygen bleaches, particularly in cold water conditions and for tough stains. Product innovations focusing on improved stability, longer shelf life, and enhanced performance have been crucial in maintaining competitive edges. Additionally, the trend towards concentrated formulations and sustainable packaging has been gaining momentum, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
Despite the positive outlook, the oxygen bleach market faces challenges such as price sensitivity in some regions and competition from other eco-friendly alternatives. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing consumer education about the benefits of oxygen-based bleaching processes are expected to sustain market growth in the foreseeable future.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards products that offer effective cleaning and stain removal while being gentler on fabrics and the environment. Oxygen bleaches, particularly those based on sodium percarbonate, have gained popularity due to their ability to break down into harmless byproducts of water and oxygen. This characteristic has resonated well with environmentally conscious consumers, leading to increased adoption in both household and commercial applications.
The market for oxygen bleaches spans various sectors, including laundry care, household cleaning, and industrial applications. In the laundry care segment, oxygen bleaches have become a staple ingredient in many detergent formulations, offering color-safe bleaching properties. The household cleaning sector has seen a surge in oxygen bleach-based products for surface cleaning, stain removal, and disinfection purposes. Industrial applications, such as in the textile and paper industries, have also contributed to market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe have been at the forefront of oxygen bleach adoption, with mature markets and high consumer awareness. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth potential as disposable incomes rise and environmental concerns gain traction. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, with increased focus on hygiene and sanitation driving demand for effective cleaning solutions.
Key market players have been investing in research and development to enhance the efficacy of oxygen bleaches, particularly in cold water conditions and for tough stains. Product innovations focusing on improved stability, longer shelf life, and enhanced performance have been crucial in maintaining competitive edges. Additionally, the trend towards concentrated formulations and sustainable packaging has been gaining momentum, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
Despite the positive outlook, the oxygen bleach market faces challenges such as price sensitivity in some regions and competition from other eco-friendly alternatives. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing consumer education about the benefits of oxygen-based bleaching processes are expected to sustain market growth in the foreseeable future.
Current Challenges in Percarbonate Bleaching
Despite the widespread use of sodium percarbonate in oxygen-based bleaching processes, several challenges persist in its application. One of the primary issues is the stability of sodium percarbonate in storage and during the bleaching process. The compound tends to decompose over time, especially in the presence of moisture and heat, leading to reduced efficacy and shelf life of bleaching products.
Another significant challenge is the optimization of bleaching performance across various fabric types and soil conditions. Different textiles and stains require specific bleaching conditions, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all solution. This necessitates careful formulation and process control to achieve optimal results without compromising fabric integrity.
The environmental impact of percarbonate bleaching also presents ongoing concerns. While sodium percarbonate is generally considered more eco-friendly than chlorine-based bleaches, its production and use still contribute to water pollution and energy consumption. Improving the sustainability of the manufacturing process and reducing the environmental footprint of bleaching operations remain key challenges for the industry.
Temperature sensitivity is another hurdle in percarbonate bleaching. The compound's bleaching efficacy is highly dependent on temperature, with optimal performance typically achieved at higher temperatures. This can lead to increased energy consumption and potential fabric damage, particularly for delicate materials that cannot withstand high-temperature treatments.
The presence of metal ions in water used for bleaching can significantly impair the performance of sodium percarbonate. These ions catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, reducing bleaching efficiency and potentially causing fabric discoloration. Developing effective chelating agents or water treatment methods to mitigate this issue is an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of percarbonate bleaching compared to alternative methods remains a concern for many industries. While sodium percarbonate offers several advantages, its production costs and the need for specialized handling and storage can make it less economically viable for some applications. Balancing performance, environmental considerations, and cost-effectiveness continues to be a key challenge in the widespread adoption of percarbonate bleaching technologies.
Another significant challenge is the optimization of bleaching performance across various fabric types and soil conditions. Different textiles and stains require specific bleaching conditions, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all solution. This necessitates careful formulation and process control to achieve optimal results without compromising fabric integrity.
The environmental impact of percarbonate bleaching also presents ongoing concerns. While sodium percarbonate is generally considered more eco-friendly than chlorine-based bleaches, its production and use still contribute to water pollution and energy consumption. Improving the sustainability of the manufacturing process and reducing the environmental footprint of bleaching operations remain key challenges for the industry.
Temperature sensitivity is another hurdle in percarbonate bleaching. The compound's bleaching efficacy is highly dependent on temperature, with optimal performance typically achieved at higher temperatures. This can lead to increased energy consumption and potential fabric damage, particularly for delicate materials that cannot withstand high-temperature treatments.
The presence of metal ions in water used for bleaching can significantly impair the performance of sodium percarbonate. These ions catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, reducing bleaching efficiency and potentially causing fabric discoloration. Developing effective chelating agents or water treatment methods to mitigate this issue is an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of percarbonate bleaching compared to alternative methods remains a concern for many industries. While sodium percarbonate offers several advantages, its production costs and the need for specialized handling and storage can make it less economically viable for some applications. Balancing performance, environmental considerations, and cost-effectiveness continues to be a key challenge in the widespread adoption of percarbonate bleaching technologies.
Sodium Percarbonate Bleaching Mechanisms
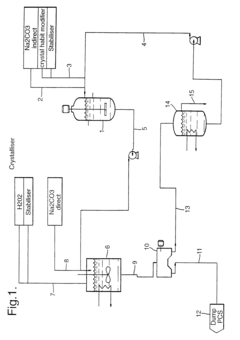
01 Composition and preparation of sodium percarbonate
Sodium percarbonate is a bleaching agent composed of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide. Its preparation involves combining these components in specific ratios and conditions to create a stable compound. The resulting product is an effective oxidizing agent used in various bleaching applications.- Composition and preparation of sodium percarbonate: Sodium percarbonate is a bleaching agent composed of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide. It is prepared through various methods, including crystallization or spray drying processes. The composition and preparation methods are optimized to improve stability, solubility, and bleaching efficiency.
- Application in laundry detergents and cleaning products: Sodium percarbonate is widely used in laundry detergents and cleaning products due to its effective bleaching and stain removal properties. It is often combined with other ingredients to enhance its performance and stability in various formulations for household and industrial cleaning applications.
- Coating and stabilization techniques: Various coating and stabilization techniques are employed to improve the stability and shelf life of sodium percarbonate. These methods include applying protective layers, using stabilizing agents, or modifying the crystal structure to prevent decomposition and maintain bleaching efficacy during storage and use.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Sodium percarbonate is considered an environmentally friendly bleaching agent as it decomposes into harmless byproducts. Research focuses on improving its safety profile, reducing potential irritation, and optimizing its use in eco-friendly cleaning products and industrial applications.
- Synergistic effects with other compounds: Studies explore the synergistic effects of combining sodium percarbonate with other compounds to enhance its bleaching performance. This includes investigating interactions with enzymes, surfactants, or other oxidizing agents to improve overall cleaning and stain removal efficiency in various applications.
02 Application in laundry detergents
Sodium percarbonate is widely used in laundry detergents as a bleaching agent. It releases active oxygen when dissolved in water, effectively removing stains and brightening fabrics. The compound is often combined with other detergent ingredients to enhance its cleaning and whitening performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization techniques
Various methods are employed to stabilize sodium percarbonate, improving its shelf life and performance. These techniques include coating the particles, adding stabilizing agents, or modifying the crystal structure. Stabilization helps prevent premature decomposition and ensures consistent bleaching action.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations
Sodium percarbonate is considered an environmentally friendly bleaching agent as it decomposes into harmless byproducts. Its use in household and industrial applications is generally regarded as safe when proper handling procedures are followed. Research focuses on further improving its eco-friendly profile and reducing potential risks associated with its use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial bleaching applications
Beyond laundry use, sodium percarbonate finds applications in various industrial bleaching processes. It is used in paper and pulp industries, textile manufacturing, and water treatment. The compound's effectiveness in these applications is due to its strong oxidizing properties and ability to work at different temperatures and pH levels.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Suppliers
The competitive landscape for sodium percarbonate in oxygen-based bleaching processes is characterized by a mature market with established players and growing demand. The global market size for sodium percarbonate is expected to reach $1.5 billion by 2027, driven by increasing applications in laundry detergents and water treatment. Technologically, the process is well-established, with companies like Solvay SA, Evonik Operations GmbH, and Kemira Oyj leading in production capacity and innovation. Chinese manufacturers such as Zhejiang Jinke Daily Chemical Co. Ltd. and Shandong Tianli Energy Co., Ltd. are emerging as significant players, leveraging cost advantages and expanding production capabilities. The technology's maturity is evident in the diverse applications across consumer and industrial sectors, with ongoing research focused on enhancing efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed advanced sodium percarbonate (SPC) technology for oxygen-based bleaching processes. Their SPC particles are coated with a protective layer that enhances stability and prevents premature decomposition[1]. This coating technology allows for controlled release of active oxygen during the washing process, improving bleaching efficiency. Solvay's SPC formulation achieves optimal bleaching performance at lower temperatures (30-40°C), reducing energy consumption[2]. The company has also implemented a continuous production process that ensures consistent particle size and quality, leading to better dissolution rates and bleaching uniformity[3].
Strengths: Enhanced stability, controlled oxygen release, energy-efficient bleaching. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to coating process, may require specialized handling and storage.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has innovated in sodium percarbonate technology by developing a unique stabilization system called PERSYNT®. This system involves incorporating specific inorganic salts into the SPC crystal structure during the production process[4]. The result is a more stable SPC that resists decomposition in humid conditions and during storage. Evonik's SPC products demonstrate improved shelf life and maintain high active oxygen content even after prolonged storage[5]. Additionally, they have optimized the particle size distribution of their SPC, which enhances its dissolution profile in various detergent formulations, leading to more efficient bleaching action[6].
Strengths: Excellent stability in humid conditions, prolonged shelf life, optimized dissolution. Weaknesses: May have higher production costs, potential limitations in extreme temperature conditions.
Innovative Percarbonate Formulations
Sodium percarbonate and process for producing sodium percarbonate
PatentInactiveUS6482385B2
Innovation
- A continuous process that controls the concentration of sodium carbonate and temperature in the dissolution tank, and maintains a specific mole ratio of hydrogen peroxide to sodium carbonate, allowing for the production of sodium percarbonate without a salting-out agent, thereby minimizing hydrogen peroxide decomposition and improving product quality.
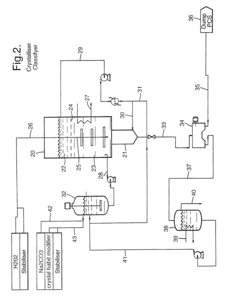
Process for preparing a sodium percarbonate product
PatentInactiveEP0799154A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of sodium bicarbonate with an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution, followed by heating and drying, to produce a sodium percarbonate/sodium bicarbonate mixed compound with controlled active oxygen content and pH stability, using stabilizers like organic phosphonates and chelating agents to enhance stability and bleaching performance.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of sodium percarbonate in oxygen-based bleaching processes has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. This compound, when dissolved in water, releases hydrogen peroxide, which acts as the primary bleaching agent. While effective for cleaning and stain removal, its environmental impact extends across various domains.
In aquatic ecosystems, the release of sodium percarbonate can lead to temporary increases in oxygen levels due to the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. This may initially benefit some aquatic organisms but can disrupt the natural balance of dissolved oxygen in water bodies. The sudden oxygen spike followed by depletion can stress aquatic life and potentially alter local ecosystems.
Soil environments may also be affected by the use of sodium percarbonate-based bleaches. When these products enter the soil, they can temporarily alter pH levels, potentially impacting soil microorganisms and plant root systems. However, the effects are generally short-lived due to the rapid breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
From an atmospheric perspective, the use of sodium percarbonate in bleaching processes has minimal direct impact. The decomposition products are primarily water and oxygen, which are naturally abundant in the atmosphere. This makes sodium percarbonate a more environmentally friendly alternative to chlorine-based bleaches, which can produce harmful chlorine gas.
Water treatment facilities may face challenges in managing effluents containing sodium percarbonate. While the compound itself is not toxic, high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide can interfere with biological treatment processes. Proper dilution and treatment protocols are necessary to mitigate potential disruptions to wastewater treatment systems.
The production of sodium percarbonate also has environmental considerations. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, contributing to industrial carbon footprints. However, advancements in production technologies have led to more efficient and less environmentally impactful manufacturing methods.
In terms of biodegradability, sodium percarbonate scores favorably. It breaks down into sodium carbonate, water, and oxygen, all of which are naturally occurring and non-toxic substances. This characteristic makes it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious consumers and industries seeking to reduce their ecological footprint.
In aquatic ecosystems, the release of sodium percarbonate can lead to temporary increases in oxygen levels due to the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. This may initially benefit some aquatic organisms but can disrupt the natural balance of dissolved oxygen in water bodies. The sudden oxygen spike followed by depletion can stress aquatic life and potentially alter local ecosystems.
Soil environments may also be affected by the use of sodium percarbonate-based bleaches. When these products enter the soil, they can temporarily alter pH levels, potentially impacting soil microorganisms and plant root systems. However, the effects are generally short-lived due to the rapid breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
From an atmospheric perspective, the use of sodium percarbonate in bleaching processes has minimal direct impact. The decomposition products are primarily water and oxygen, which are naturally abundant in the atmosphere. This makes sodium percarbonate a more environmentally friendly alternative to chlorine-based bleaches, which can produce harmful chlorine gas.
Water treatment facilities may face challenges in managing effluents containing sodium percarbonate. While the compound itself is not toxic, high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide can interfere with biological treatment processes. Proper dilution and treatment protocols are necessary to mitigate potential disruptions to wastewater treatment systems.
The production of sodium percarbonate also has environmental considerations. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, contributing to industrial carbon footprints. However, advancements in production technologies have led to more efficient and less environmentally impactful manufacturing methods.
In terms of biodegradability, sodium percarbonate scores favorably. It breaks down into sodium carbonate, water, and oxygen, all of which are naturally occurring and non-toxic substances. This characteristic makes it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious consumers and industries seeking to reduce their ecological footprint.
Safety Regulations for Bleaching Agents
Safety regulations for bleaching agents, particularly those involving sodium percarbonate in oxygen-based bleaching processes, are crucial for ensuring the protection of workers, consumers, and the environment. These regulations typically cover various aspects of handling, storage, transportation, and usage of such chemicals.
In many countries, regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States or the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the European Union, set strict guidelines for the use of bleaching agents. These guidelines often require manufacturers and users to implement comprehensive safety measures and provide detailed safety data sheets (SDS) for their products.
For sodium percarbonate specifically, safety regulations often focus on its oxidizing properties and potential hazards. As a strong oxidizer, it can react vigorously with reducing agents and combustible materials. Therefore, regulations typically mandate proper storage conditions, including keeping the chemical in a cool, dry place away from heat sources and incompatible materials.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are another critical aspect of safety regulations. Workers handling sodium percarbonate are usually required to wear appropriate eye protection, such as safety goggles or face shields, as well as protective gloves and clothing to prevent skin contact. Respiratory protection may also be necessary in situations where dust or mist inhalation is possible.
Regulations often address the need for proper ventilation in areas where sodium percarbonate is used or stored. This is particularly important in industrial settings where large quantities of the chemical may be present. Adequate ventilation helps to minimize the risk of dust accumulation and potential inhalation hazards.
Emergency response procedures are typically outlined in safety regulations as well. This includes guidelines for handling spills, fires, and accidental exposures. Facilities using sodium percarbonate are often required to have appropriate fire-fighting equipment readily available, as well as eyewash stations and safety showers for immediate decontamination in case of accidental exposure.
Transportation regulations for sodium percarbonate are also stringent, given its classification as an oxidizing solid. These regulations often require specific packaging, labeling, and documentation to ensure safe transport and handling throughout the supply chain.
Environmental considerations are increasingly becoming a focus of safety regulations for bleaching agents. This includes guidelines for proper disposal of sodium percarbonate and its solutions, as well as measures to prevent environmental contamination in case of accidental release.
In many countries, regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States or the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the European Union, set strict guidelines for the use of bleaching agents. These guidelines often require manufacturers and users to implement comprehensive safety measures and provide detailed safety data sheets (SDS) for their products.
For sodium percarbonate specifically, safety regulations often focus on its oxidizing properties and potential hazards. As a strong oxidizer, it can react vigorously with reducing agents and combustible materials. Therefore, regulations typically mandate proper storage conditions, including keeping the chemical in a cool, dry place away from heat sources and incompatible materials.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are another critical aspect of safety regulations. Workers handling sodium percarbonate are usually required to wear appropriate eye protection, such as safety goggles or face shields, as well as protective gloves and clothing to prevent skin contact. Respiratory protection may also be necessary in situations where dust or mist inhalation is possible.
Regulations often address the need for proper ventilation in areas where sodium percarbonate is used or stored. This is particularly important in industrial settings where large quantities of the chemical may be present. Adequate ventilation helps to minimize the risk of dust accumulation and potential inhalation hazards.
Emergency response procedures are typically outlined in safety regulations as well. This includes guidelines for handling spills, fires, and accidental exposures. Facilities using sodium percarbonate are often required to have appropriate fire-fighting equipment readily available, as well as eyewash stations and safety showers for immediate decontamination in case of accidental exposure.
Transportation regulations for sodium percarbonate are also stringent, given its classification as an oxidizing solid. These regulations often require specific packaging, labeling, and documentation to ensure safe transport and handling throughout the supply chain.
Environmental considerations are increasingly becoming a focus of safety regulations for bleaching agents. This includes guidelines for proper disposal of sodium percarbonate and its solutions, as well as measures to prevent environmental contamination in case of accidental release.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!