Sodium Percarbonate in Closed System Cleaning Protocols
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Background and Objectives
Sodium percarbonate, a compound of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, has gained significant attention in the cleaning industry due to its powerful oxidizing properties and eco-friendly nature. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when the first patents for its production were filed. Over the decades, sodium percarbonate has undergone continuous refinement in its manufacturing processes and application methods, leading to its widespread use in various cleaning products.
The primary objective of researching sodium percarbonate in closed system cleaning protocols is to optimize its effectiveness while minimizing environmental impact. This aligns with the growing global demand for sustainable cleaning solutions that maintain high efficacy. The closed system approach aims to enhance the controlled release of active oxygen, maximizing cleaning power while reducing waste and improving safety for both users and the environment.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving the stability of sodium percarbonate in aqueous solutions, a critical factor for its application in closed systems. This has led to the development of coated variants and stabilized formulations that prolong the compound's active life and ensure consistent performance throughout the cleaning cycle. These innovations address historical challenges related to premature decomposition and reduced effectiveness in certain conditions.
The research objectives extend beyond mere cleaning efficiency. They encompass the integration of sodium percarbonate into smart cleaning systems, where parameters such as concentration, temperature, and exposure time can be precisely controlled and optimized for specific cleaning tasks. This approach promises to revolutionize industrial and commercial cleaning processes by offering tailored solutions that maximize resource utilization and minimize environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the investigation into sodium percarbonate's role in closed system cleaning protocols aims to expand its application scope. While traditionally associated with laundry and household cleaning, researchers are exploring its potential in more specialized fields such as medical equipment sterilization, food processing plant sanitation, and water treatment systems. These new frontiers present exciting opportunities for innovation and market expansion.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent worldwide, the development of sodium percarbonate-based cleaning protocols in closed systems is also driven by compliance needs. The research seeks to establish best practices that not only meet but exceed regulatory standards, positioning sodium percarbonate as a future-proof solution in the evolving landscape of green chemistry and sustainable industrial practices.
The primary objective of researching sodium percarbonate in closed system cleaning protocols is to optimize its effectiveness while minimizing environmental impact. This aligns with the growing global demand for sustainable cleaning solutions that maintain high efficacy. The closed system approach aims to enhance the controlled release of active oxygen, maximizing cleaning power while reducing waste and improving safety for both users and the environment.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving the stability of sodium percarbonate in aqueous solutions, a critical factor for its application in closed systems. This has led to the development of coated variants and stabilized formulations that prolong the compound's active life and ensure consistent performance throughout the cleaning cycle. These innovations address historical challenges related to premature decomposition and reduced effectiveness in certain conditions.
The research objectives extend beyond mere cleaning efficiency. They encompass the integration of sodium percarbonate into smart cleaning systems, where parameters such as concentration, temperature, and exposure time can be precisely controlled and optimized for specific cleaning tasks. This approach promises to revolutionize industrial and commercial cleaning processes by offering tailored solutions that maximize resource utilization and minimize environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the investigation into sodium percarbonate's role in closed system cleaning protocols aims to expand its application scope. While traditionally associated with laundry and household cleaning, researchers are exploring its potential in more specialized fields such as medical equipment sterilization, food processing plant sanitation, and water treatment systems. These new frontiers present exciting opportunities for innovation and market expansion.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent worldwide, the development of sodium percarbonate-based cleaning protocols in closed systems is also driven by compliance needs. The research seeks to establish best practices that not only meet but exceed regulatory standards, positioning sodium percarbonate as a future-proof solution in the evolving landscape of green chemistry and sustainable industrial practices.
Market Analysis for Closed System Cleaning Solutions
The closed system cleaning solutions market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for efficient and environmentally friendly cleaning processes across various industries. This market segment encompasses a wide range of products and technologies designed to clean closed systems, such as pipelines, tanks, and industrial equipment, without the need for disassembly or manual intervention.
The global market for closed system cleaning solutions is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of automated cleaning processes in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing, where maintaining strict hygiene standards is crucial.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations. Closed system cleaning solutions, particularly those utilizing sodium percarbonate, offer a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional cleaning methods. This aligns with the growing corporate sustainability initiatives and stringent environmental policies implemented by governments worldwide.
The food and beverage industry represents a significant portion of the market share for closed system cleaning solutions. The need for regular and thorough cleaning of production equipment to ensure food safety and comply with regulatory standards has led to increased adoption of these solutions. Similarly, the pharmaceutical industry has shown a growing interest in closed system cleaning technologies to maintain sterile manufacturing environments and meet Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for closed system cleaning solutions, owing to their well-established industrial sectors and stringent regulatory frameworks. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing awareness of hygiene standards, and the expansion of food and beverage manufacturing facilities.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Key market players are focusing on research and development to introduce advanced cleaning solutions that offer improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower environmental impact. The integration of IoT and automation technologies in closed system cleaning processes is emerging as a significant trend, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of cleaning cycles.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized training for operators. However, the long-term benefits of improved operational efficiency, reduced labor costs, and enhanced product quality are expected to outweigh these initial barriers, driving continued market growth and innovation in closed system cleaning solutions.
The global market for closed system cleaning solutions is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of automated cleaning processes in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing, where maintaining strict hygiene standards is crucial.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations. Closed system cleaning solutions, particularly those utilizing sodium percarbonate, offer a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional cleaning methods. This aligns with the growing corporate sustainability initiatives and stringent environmental policies implemented by governments worldwide.
The food and beverage industry represents a significant portion of the market share for closed system cleaning solutions. The need for regular and thorough cleaning of production equipment to ensure food safety and comply with regulatory standards has led to increased adoption of these solutions. Similarly, the pharmaceutical industry has shown a growing interest in closed system cleaning technologies to maintain sterile manufacturing environments and meet Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for closed system cleaning solutions, owing to their well-established industrial sectors and stringent regulatory frameworks. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing awareness of hygiene standards, and the expansion of food and beverage manufacturing facilities.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Key market players are focusing on research and development to introduce advanced cleaning solutions that offer improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower environmental impact. The integration of IoT and automation technologies in closed system cleaning processes is emerging as a significant trend, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of cleaning cycles.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized training for operators. However, the long-term benefits of improved operational efficiency, reduced labor costs, and enhanced product quality are expected to outweigh these initial barriers, driving continued market growth and innovation in closed system cleaning solutions.
Current Challenges in Closed System Cleaning
Closed system cleaning protocols face several significant challenges when incorporating sodium percarbonate as a cleaning agent. One of the primary issues is maintaining the stability and effectiveness of sodium percarbonate throughout the cleaning process. In closed systems, the controlled environment can lead to increased pressure and temperature, which may accelerate the decomposition of sodium percarbonate. This decomposition not only reduces the cleaning efficacy but also generates oxygen gas, potentially causing pressure build-up within the system.
Another challenge lies in achieving uniform distribution of sodium percarbonate within the closed system. The limited fluid dynamics in such environments can result in uneven dispersion of the cleaning agent, leading to inconsistent cleaning results. This is particularly problematic in systems with complex geometries or hard-to-reach areas, where stagnant zones may form, reducing the overall cleaning effectiveness.
The interaction between sodium percarbonate and the materials present in the closed system poses additional challenges. Some materials may catalyze the decomposition of sodium percarbonate, while others might be susceptible to oxidative damage from the released oxygen. This necessitates careful consideration of material compatibility when designing cleaning protocols, potentially limiting the applicability of sodium percarbonate in certain systems.
pH control presents another significant hurdle in closed system cleaning with sodium percarbonate. As the compound decomposes, it can cause fluctuations in pH levels, which may affect both the cleaning efficiency and the integrity of the system components. Maintaining an optimal pH range throughout the cleaning cycle is crucial but can be challenging in a closed environment with limited options for real-time adjustments.
The removal of cleaning residues after the process is complete also presents difficulties in closed systems. The breakdown products of sodium percarbonate, including sodium carbonate and oxygen, need to be thoroughly flushed from the system to prevent any interference with subsequent processes or product quality. This can be particularly challenging in systems with intricate designs or those that cannot be easily rinsed.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of using sodium percarbonate in closed system cleaning protocols must be addressed. While sodium percarbonate is generally considered environmentally friendly, the concentrated oxygen release in a confined space can create potential safety hazards. Developing protocols that maximize cleaning efficiency while minimizing risks associated with oxygen generation and handling is a complex challenge that requires careful engineering and safety measures.
Another challenge lies in achieving uniform distribution of sodium percarbonate within the closed system. The limited fluid dynamics in such environments can result in uneven dispersion of the cleaning agent, leading to inconsistent cleaning results. This is particularly problematic in systems with complex geometries or hard-to-reach areas, where stagnant zones may form, reducing the overall cleaning effectiveness.
The interaction between sodium percarbonate and the materials present in the closed system poses additional challenges. Some materials may catalyze the decomposition of sodium percarbonate, while others might be susceptible to oxidative damage from the released oxygen. This necessitates careful consideration of material compatibility when designing cleaning protocols, potentially limiting the applicability of sodium percarbonate in certain systems.
pH control presents another significant hurdle in closed system cleaning with sodium percarbonate. As the compound decomposes, it can cause fluctuations in pH levels, which may affect both the cleaning efficiency and the integrity of the system components. Maintaining an optimal pH range throughout the cleaning cycle is crucial but can be challenging in a closed environment with limited options for real-time adjustments.
The removal of cleaning residues after the process is complete also presents difficulties in closed systems. The breakdown products of sodium percarbonate, including sodium carbonate and oxygen, need to be thoroughly flushed from the system to prevent any interference with subsequent processes or product quality. This can be particularly challenging in systems with intricate designs or those that cannot be easily rinsed.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of using sodium percarbonate in closed system cleaning protocols must be addressed. While sodium percarbonate is generally considered environmentally friendly, the concentrated oxygen release in a confined space can create potential safety hazards. Developing protocols that maximize cleaning efficiency while minimizing risks associated with oxygen generation and handling is a complex challenge that requires careful engineering and safety measures.
Existing Sodium Percarbonate Cleaning Protocols
01 Synthesis and production of sodium percarbonate
Various methods for synthesizing and producing sodium percarbonate are described. These processes typically involve the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide under specific conditions to form stable sodium percarbonate crystals. The production methods may include steps such as crystallization, drying, and stabilization to enhance the quality and shelf life of the final product.- Synthesis and production of sodium percarbonate: Various methods for synthesizing and producing sodium percarbonate are described. These methods involve the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide under specific conditions to form stable sodium percarbonate crystals. The processes may include steps such as crystallization, drying, and stabilization to improve the quality and stability of the final product.
- Stabilization of sodium percarbonate: Techniques for stabilizing sodium percarbonate to improve its shelf life and performance are discussed. These may include coating the particles with stabilizing agents, incorporating additives to reduce decomposition, or modifying the crystal structure. Stabilization is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in various applications.
- Applications in cleaning and bleaching: Sodium percarbonate is widely used in cleaning and bleaching applications. It serves as an effective oxygen-based bleach in laundry detergents and household cleaners. The compound releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, providing powerful stain removal and disinfecting properties while being environmentally friendly.
- Formulation in personal care products: Sodium percarbonate is incorporated into various personal care products, such as toothpaste, mouthwash, and hair care formulations. Its oxidizing properties make it useful for teeth whitening and hair bleaching applications. The formulations often include stabilizers and other ingredients to enhance efficacy and safety.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental profile and safety of sodium percarbonate. This includes developing more eco-friendly production processes, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing the biodegradability of the compound. Safety measures for handling and storage are also addressed to prevent accidental decomposition or reactions.
02 Stabilization and coating of sodium percarbonate
Techniques for stabilizing and coating sodium percarbonate particles are discussed. These methods aim to improve the stability, storage properties, and handling characteristics of sodium percarbonate. Coating materials may include inorganic compounds, polymers, or other additives that protect the particles from moisture and prevent decomposition during storage and use.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in cleaning and bleaching products
Sodium percarbonate is widely used in cleaning and bleaching formulations. It serves as an effective oxygen-based bleaching agent in laundry detergents, dishwashing products, and other household cleaners. The compound releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, providing powerful stain removal and disinfecting properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations
The environmental impact and safety aspects of sodium percarbonate are addressed. As an oxygen-based compound, it is considered more environmentally friendly compared to chlorine-based bleaches. Safety considerations include proper handling, storage, and disposal methods to prevent accidental decomposition or reactions with other materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods and quality control
Various analytical techniques and quality control methods for sodium percarbonate are described. These include methods for determining purity, active oxygen content, and stability of the compound. Quality control measures ensure consistent product performance and compliance with industry standards.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Cleaning Solutions
The research on Sodium Percarbonate in Closed System Cleaning Protocols is in a mature stage, with established market players and growing applications. The global market size for sodium percarbonate is substantial, driven by increasing demand in cleaning and laundry sectors. Technologically, the field is well-developed, with companies like Solvay SA, Evonik Operations GmbH, and Kemira Oyj leading innovation. These firms, along with others such as Zhejiang Jinke Daily Chemical Co. Ltd. and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, have advanced the technology's efficiency and application range. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical conglomerates and specialized manufacturers, indicating a consolidated yet diverse market structure.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed advanced sodium percarbonate formulations for closed system cleaning protocols. Their technology focuses on enhancing the stability and efficacy of sodium percarbonate in various cleaning applications. Solvay's approach involves encapsulation techniques to protect the active oxygen content, ensuring prolonged shelf life and improved performance in closed systems[1]. They have also optimized the particle size distribution to enhance dissolution rates and cleaning efficiency. Solvay's research has led to the development of sodium percarbonate products with controlled release properties, allowing for sustained cleaning action in closed system applications[3]. Additionally, they have incorporated stabilizers and activators to boost the cleaning power at lower temperatures, making their solutions more energy-efficient[5].
Strengths: Advanced encapsulation technology, optimized particle size distribution, and controlled release properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to specialized formulations.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik Operations GmbH has pioneered innovative sodium percarbonate solutions for closed system cleaning protocols. Their research focuses on developing high-purity sodium percarbonate with enhanced stability and performance characteristics. Evonik's technology incorporates proprietary coating processes that significantly improve the moisture resistance of sodium percarbonate particles, crucial for maintaining efficacy in closed systems[2]. They have also developed synergistic blends of sodium percarbonate with other cleaning agents, optimizing the overall cleaning performance. Evonik's research has led to the creation of sodium percarbonate formulations with improved oxygen release kinetics, ensuring consistent and prolonged cleaning action in closed system applications[4]. Furthermore, they have implemented advanced production techniques to minimize impurities, resulting in a more stable and effective product for industrial cleaning processes[6].
Strengths: High-purity formulations, moisture-resistant coatings, and optimized oxygen release kinetics. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to advanced production techniques and specialized formulations.
Innovations in Sodium Percarbonate Formulations
A method for preparing sodium percarbonate particles with improved stability
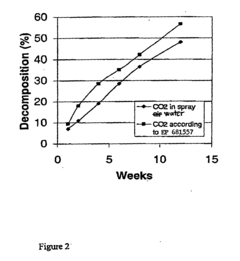
PatentInactiveEP0681557B2
Innovation
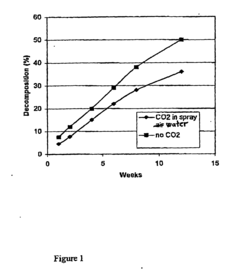
- Coating sodium percarbonate particles with a thin, impermeable layer of sodium bicarbonate formed by reacting with CO2 in the presence of moisture, which can be enhanced with additional conventional coating methods using sodium bicarbonate or sodium sulphate solutions.
Method for the preparation of sodium percarbonate granules having enhanced stability
PatentInactiveEP1227063B1
Innovation
- A method involving the formation of a dense thin film of sodium bicarbonate on the surface of sodium percarbonate granules using carbon dioxide dissolved in water, which is sprayed onto the granules in a fluidized bed reactor, followed by drying, to enhance stability, with optional additional coating layers.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Percarbonate Use
The use of sodium percarbonate in closed system cleaning protocols has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As a powerful oxidizing agent, sodium percarbonate breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate when dissolved in water, providing an effective cleaning and bleaching solution. However, its environmental impact extends beyond its immediate cleaning efficacy.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. Unlike many traditional cleaning agents, sodium percarbonate decomposes into harmless byproducts: water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. This characteristic significantly reduces the long-term environmental burden associated with its use, particularly in aquatic ecosystems where many cleaning agents ultimately end up.
The oxygen released during the decomposition process can have both positive and negative effects on the environment. In water bodies, it can temporarily increase dissolved oxygen levels, potentially benefiting aquatic life. However, excessive oxygen release in confined spaces or poorly ventilated areas could pose risks to human health and safety, necessitating proper handling and application protocols.
Sodium percarbonate's ability to effectively clean without the need for high temperatures or aggressive mechanical action contributes to energy savings and reduced wear on cleaning equipment. This indirect environmental benefit translates to lower carbon emissions associated with the cleaning process, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
The alkaline nature of sodium carbonate, a byproduct of sodium percarbonate decomposition, can affect the pH of water systems. While this can be beneficial in neutralizing acidic pollutants, it may also disrupt the natural pH balance of aquatic environments if released in large quantities. Proper dosing and containment strategies are crucial to mitigate potential negative impacts on sensitive ecosystems.
In closed system cleaning protocols, the controlled environment offers opportunities to optimize sodium percarbonate use, minimizing waste and environmental exposure. Recycling and reuse of cleaning solutions within the closed system can further reduce the overall environmental footprint of the cleaning process. However, the disposal of spent cleaning solutions still requires careful management to prevent localized environmental impacts.
The production of sodium percarbonate itself has environmental considerations. While it can be manufactured using relatively simple processes, the energy requirements and potential emissions associated with large-scale production must be factored into comprehensive environmental assessments. Advancements in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are continually improving the overall lifecycle environmental profile of sodium percarbonate.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. Unlike many traditional cleaning agents, sodium percarbonate decomposes into harmless byproducts: water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. This characteristic significantly reduces the long-term environmental burden associated with its use, particularly in aquatic ecosystems where many cleaning agents ultimately end up.
The oxygen released during the decomposition process can have both positive and negative effects on the environment. In water bodies, it can temporarily increase dissolved oxygen levels, potentially benefiting aquatic life. However, excessive oxygen release in confined spaces or poorly ventilated areas could pose risks to human health and safety, necessitating proper handling and application protocols.
Sodium percarbonate's ability to effectively clean without the need for high temperatures or aggressive mechanical action contributes to energy savings and reduced wear on cleaning equipment. This indirect environmental benefit translates to lower carbon emissions associated with the cleaning process, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
The alkaline nature of sodium carbonate, a byproduct of sodium percarbonate decomposition, can affect the pH of water systems. While this can be beneficial in neutralizing acidic pollutants, it may also disrupt the natural pH balance of aquatic environments if released in large quantities. Proper dosing and containment strategies are crucial to mitigate potential negative impacts on sensitive ecosystems.
In closed system cleaning protocols, the controlled environment offers opportunities to optimize sodium percarbonate use, minimizing waste and environmental exposure. Recycling and reuse of cleaning solutions within the closed system can further reduce the overall environmental footprint of the cleaning process. However, the disposal of spent cleaning solutions still requires careful management to prevent localized environmental impacts.
The production of sodium percarbonate itself has environmental considerations. While it can be manufactured using relatively simple processes, the energy requirements and potential emissions associated with large-scale production must be factored into comprehensive environmental assessments. Advancements in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are continually improving the overall lifecycle environmental profile of sodium percarbonate.
Safety Regulations for Industrial Cleaning Agents
Safety regulations for industrial cleaning agents are crucial in ensuring the proper handling, storage, and use of sodium percarbonate in closed system cleaning protocols. These regulations are designed to protect workers, the environment, and the integrity of the cleaning process itself.
In many countries, regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States or the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the European Union, set forth stringent guidelines for the use of industrial cleaning agents. These guidelines typically cover aspects such as proper labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency procedures.
For sodium percarbonate specifically, safety regulations often focus on its oxidizing properties and potential hazards. As a strong oxidizer, it can react vigorously with reducing agents and combustible materials. Therefore, storage regulations usually mandate keeping sodium percarbonate away from heat sources, flammable substances, and incompatible materials.
Personal protective equipment requirements for handling sodium percarbonate generally include chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection when dust or mist may be present. Proper ventilation in the work area is also typically mandated to prevent the accumulation of dust or vapors.
Disposal regulations for sodium percarbonate and its solutions are another critical aspect of safety protocols. Many jurisdictions require that waste containing this compound be treated as hazardous and disposed of according to specific procedures to prevent environmental contamination.
In closed system cleaning protocols, additional safety measures are often required. These may include regular inspections of the cleaning system for leaks or damage, proper sealing of all access points, and the use of pressure relief valves to prevent over-pressurization. Automated monitoring systems are frequently mandated to detect any unexpected changes in temperature or pressure that could indicate a safety issue.
Training requirements form a significant part of safety regulations. Workers involved in handling sodium percarbonate or operating closed cleaning systems must typically undergo comprehensive safety training. This training often covers proper handling techniques, emergency response procedures, and the correct use of safety equipment.
Regulatory compliance also extends to record-keeping and reporting. Companies using sodium percarbonate in industrial cleaning processes are usually required to maintain detailed logs of usage, storage conditions, and any incidents or near-misses. Regular safety audits and inspections by regulatory authorities are common to ensure ongoing compliance with these safety regulations.
In many countries, regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States or the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the European Union, set forth stringent guidelines for the use of industrial cleaning agents. These guidelines typically cover aspects such as proper labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency procedures.
For sodium percarbonate specifically, safety regulations often focus on its oxidizing properties and potential hazards. As a strong oxidizer, it can react vigorously with reducing agents and combustible materials. Therefore, storage regulations usually mandate keeping sodium percarbonate away from heat sources, flammable substances, and incompatible materials.
Personal protective equipment requirements for handling sodium percarbonate generally include chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection when dust or mist may be present. Proper ventilation in the work area is also typically mandated to prevent the accumulation of dust or vapors.
Disposal regulations for sodium percarbonate and its solutions are another critical aspect of safety protocols. Many jurisdictions require that waste containing this compound be treated as hazardous and disposed of according to specific procedures to prevent environmental contamination.
In closed system cleaning protocols, additional safety measures are often required. These may include regular inspections of the cleaning system for leaks or damage, proper sealing of all access points, and the use of pressure relief valves to prevent over-pressurization. Automated monitoring systems are frequently mandated to detect any unexpected changes in temperature or pressure that could indicate a safety issue.
Training requirements form a significant part of safety regulations. Workers involved in handling sodium percarbonate or operating closed cleaning systems must typically undergo comprehensive safety training. This training often covers proper handling techniques, emergency response procedures, and the correct use of safety equipment.
Regulatory compliance also extends to record-keeping and reporting. Companies using sodium percarbonate in industrial cleaning processes are usually required to maintain detailed logs of usage, storage conditions, and any incidents or near-misses. Regular safety audits and inspections by regulatory authorities are common to ensure ongoing compliance with these safety regulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!