Sodium Percarbonate's Effectiveness in Cold Chain Produce Cleanliness
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate in Cold Chain Produce: Background and Objectives
Sodium percarbonate, a compound formed by sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, has emerged as a promising solution for enhancing cleanliness in cold chain produce. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when the compound was first synthesized. However, its application in the cold chain industry is a more recent development, driven by the growing demand for safer and more effective cleaning agents in food processing.
The cold chain industry has faced persistent challenges in maintaining produce cleanliness, particularly due to the low-temperature environments that can harbor resilient microorganisms. Traditional cleaning methods often struggle to effectively eliminate these contaminants without compromising the quality of the produce. This has led to an increased focus on innovative solutions that can address these unique challenges while adhering to stringent food safety regulations.
Sodium percarbonate's potential in this field stems from its ability to release active oxygen when dissolved in water, creating a powerful oxidizing agent. This property makes it particularly effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including those that thrive in cold environments. Additionally, its non-toxic nature and biodegradability align well with the increasing emphasis on environmentally friendly practices in the food industry.
The primary objective of researching sodium percarbonate's effectiveness in cold chain produce cleanliness is to evaluate its performance across various parameters. These include its efficacy in eliminating harmful microorganisms, its impact on produce quality and shelf life, and its compatibility with existing cold chain infrastructure. Researchers aim to determine optimal concentrations, application methods, and treatment durations to maximize its cleaning potential while minimizing any potential adverse effects on the produce.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to compare sodium percarbonate's effectiveness with current industry-standard cleaning agents. This comparative analysis will help in assessing the potential for sodium percarbonate to replace or complement existing solutions, potentially leading to improved food safety standards and reduced spoilage in the cold chain industry.
Furthermore, the research seeks to explore the broader implications of adopting sodium percarbonate in cold chain cleaning processes. This includes evaluating its economic viability, considering factors such as cost-effectiveness, scalability, and potential for integration into existing cleaning protocols. The environmental impact of widespread adoption is also a key consideration, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable practices in the food industry.
As the cold chain industry continues to expand globally, driven by increasing demand for fresh produce and the need for efficient long-distance transportation, the importance of effective cleaning solutions becomes ever more critical. The research into sodium percarbonate's effectiveness represents a significant step towards addressing these evolving challenges, potentially revolutionizing cleanliness standards in cold chain produce handling and storage.
The cold chain industry has faced persistent challenges in maintaining produce cleanliness, particularly due to the low-temperature environments that can harbor resilient microorganisms. Traditional cleaning methods often struggle to effectively eliminate these contaminants without compromising the quality of the produce. This has led to an increased focus on innovative solutions that can address these unique challenges while adhering to stringent food safety regulations.
Sodium percarbonate's potential in this field stems from its ability to release active oxygen when dissolved in water, creating a powerful oxidizing agent. This property makes it particularly effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including those that thrive in cold environments. Additionally, its non-toxic nature and biodegradability align well with the increasing emphasis on environmentally friendly practices in the food industry.
The primary objective of researching sodium percarbonate's effectiveness in cold chain produce cleanliness is to evaluate its performance across various parameters. These include its efficacy in eliminating harmful microorganisms, its impact on produce quality and shelf life, and its compatibility with existing cold chain infrastructure. Researchers aim to determine optimal concentrations, application methods, and treatment durations to maximize its cleaning potential while minimizing any potential adverse effects on the produce.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to compare sodium percarbonate's effectiveness with current industry-standard cleaning agents. This comparative analysis will help in assessing the potential for sodium percarbonate to replace or complement existing solutions, potentially leading to improved food safety standards and reduced spoilage in the cold chain industry.
Furthermore, the research seeks to explore the broader implications of adopting sodium percarbonate in cold chain cleaning processes. This includes evaluating its economic viability, considering factors such as cost-effectiveness, scalability, and potential for integration into existing cleaning protocols. The environmental impact of widespread adoption is also a key consideration, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable practices in the food industry.
As the cold chain industry continues to expand globally, driven by increasing demand for fresh produce and the need for efficient long-distance transportation, the importance of effective cleaning solutions becomes ever more critical. The research into sodium percarbonate's effectiveness represents a significant step towards addressing these evolving challenges, potentially revolutionizing cleanliness standards in cold chain produce handling and storage.
Market Analysis for Cold Chain Produce Sanitization Solutions
The market for cold chain produce sanitization solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for fresh, safe, and high-quality produce. The global cold chain market, which includes sanitization solutions, is projected to reach $447.50 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.1% from 2020 to 2025. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising awareness of food safety, stringent regulations, and the expansion of organized retail in developing countries.
The demand for effective sanitization solutions in the cold chain industry is particularly high due to the perishable nature of fresh produce and the potential for contamination during transportation and storage. Traditional sanitization methods, such as chlorine-based solutions, have been widely used but are facing challenges due to environmental concerns and potential health risks. This has created a market opportunity for alternative sanitization solutions, including sodium percarbonate-based products.
Sodium percarbonate, as an eco-friendly and effective sanitizing agent, has gained attention in the cold chain produce industry. Its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water makes it an attractive option for produce sanitization. The market for sodium percarbonate-based sanitization solutions is expected to grow as food safety regulations become more stringent and consumers demand safer, chemical-free produce.
The cold chain produce sanitization market is segmented by product type, application, and geography. Product types include chemical-based solutions, physical methods (such as UV light and ozone treatment), and biological solutions. Among these, chemical-based solutions currently dominate the market, but there is a growing trend towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable options.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for cold chain produce sanitization solutions, owing to their well-established cold chain infrastructure and stringent food safety regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness of food safety among consumers.
Key market players in the cold chain produce sanitization industry include Ecolab Inc., Diversey Inc., Solvay S.A., and BASF SE. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative sanitization solutions that meet the evolving needs of the market. The entry of new players with novel technologies, such as sodium percarbonate-based solutions, is expected to further intensify market competition and drive innovation in the coming years.
The demand for effective sanitization solutions in the cold chain industry is particularly high due to the perishable nature of fresh produce and the potential for contamination during transportation and storage. Traditional sanitization methods, such as chlorine-based solutions, have been widely used but are facing challenges due to environmental concerns and potential health risks. This has created a market opportunity for alternative sanitization solutions, including sodium percarbonate-based products.
Sodium percarbonate, as an eco-friendly and effective sanitizing agent, has gained attention in the cold chain produce industry. Its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water makes it an attractive option for produce sanitization. The market for sodium percarbonate-based sanitization solutions is expected to grow as food safety regulations become more stringent and consumers demand safer, chemical-free produce.
The cold chain produce sanitization market is segmented by product type, application, and geography. Product types include chemical-based solutions, physical methods (such as UV light and ozone treatment), and biological solutions. Among these, chemical-based solutions currently dominate the market, but there is a growing trend towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable options.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for cold chain produce sanitization solutions, owing to their well-established cold chain infrastructure and stringent food safety regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness of food safety among consumers.
Key market players in the cold chain produce sanitization industry include Ecolab Inc., Diversey Inc., Solvay S.A., and BASF SE. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative sanitization solutions that meet the evolving needs of the market. The entry of new players with novel technologies, such as sodium percarbonate-based solutions, is expected to further intensify market competition and drive innovation in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Cold Chain Produce Cleanliness
The cold chain produce industry faces several significant challenges in maintaining cleanliness and food safety. One of the primary issues is the persistence of foodborne pathogens throughout the supply chain. Despite rigorous cleaning protocols, bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, and Escherichia coli continue to pose threats to produce safety. These microorganisms can form biofilms on surfaces, making them particularly resistant to traditional cleaning methods.
Temperature control during transportation and storage presents another critical challenge. Fluctuations in temperature can lead to condensation, creating an environment conducive to microbial growth. This issue is compounded by the fact that many cold chain facilities are not designed with optimal sanitation in mind, featuring hard-to-clean areas that can harbor pathogens.
The use of chemical sanitizers, while effective, brings its own set of challenges. Many conventional sanitizers leave residues that can affect the taste and quality of produce. There is also growing concern about the environmental impact of these chemicals and the potential for pathogens to develop resistance over time.
Cross-contamination remains a persistent problem in cold chain facilities. The movement of personnel, equipment, and produce between different areas can spread contaminants if proper hygiene protocols are not strictly followed. This is particularly challenging in high-volume operations where speed and efficiency are prioritized.
Water management in cleaning processes is another area of concern. Many facilities struggle to balance the need for thorough cleaning with water conservation efforts. Inefficient water use not only increases operational costs but can also create moisture-rich environments that promote microbial growth.
The increasing demand for organic and minimally processed produce adds another layer of complexity to cleanliness challenges. These products often cannot be treated with the same chemical sanitizers used on conventional produce, necessitating alternative cleaning methods that may be less effective or more time-consuming.
Lastly, the cold chain industry faces challenges in implementing and maintaining consistent cleaning standards across diverse global supply chains. Variations in regulatory requirements, cultural practices, and available resources can lead to inconsistencies in cleanliness protocols, potentially compromising food safety.
Temperature control during transportation and storage presents another critical challenge. Fluctuations in temperature can lead to condensation, creating an environment conducive to microbial growth. This issue is compounded by the fact that many cold chain facilities are not designed with optimal sanitation in mind, featuring hard-to-clean areas that can harbor pathogens.
The use of chemical sanitizers, while effective, brings its own set of challenges. Many conventional sanitizers leave residues that can affect the taste and quality of produce. There is also growing concern about the environmental impact of these chemicals and the potential for pathogens to develop resistance over time.
Cross-contamination remains a persistent problem in cold chain facilities. The movement of personnel, equipment, and produce between different areas can spread contaminants if proper hygiene protocols are not strictly followed. This is particularly challenging in high-volume operations where speed and efficiency are prioritized.
Water management in cleaning processes is another area of concern. Many facilities struggle to balance the need for thorough cleaning with water conservation efforts. Inefficient water use not only increases operational costs but can also create moisture-rich environments that promote microbial growth.
The increasing demand for organic and minimally processed produce adds another layer of complexity to cleanliness challenges. These products often cannot be treated with the same chemical sanitizers used on conventional produce, necessitating alternative cleaning methods that may be less effective or more time-consuming.
Lastly, the cold chain industry faces challenges in implementing and maintaining consistent cleaning standards across diverse global supply chains. Variations in regulatory requirements, cultural practices, and available resources can lead to inconsistencies in cleanliness protocols, potentially compromising food safety.
Existing Sodium Percarbonate Applications in Produce Cleaning
01 Bleaching and cleaning effectiveness
Sodium percarbonate is highly effective as a bleaching and cleaning agent. It releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, which provides powerful oxidizing properties. This makes it suitable for various applications in laundry detergents, household cleaners, and industrial cleaning processes. The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in removing stains and disinfecting surfaces has been demonstrated in numerous studies and formulations.- Bleaching effectiveness: Sodium percarbonate is an effective bleaching agent due to its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. This property makes it useful in various cleaning and whitening applications, including laundry detergents and stain removers. The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate as a bleaching agent is attributed to its oxidizing properties, which can break down and remove organic stains and discoloration.
- Stability and storage: The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate can be influenced by its stability during storage. Various methods and compositions have been developed to improve the stability of sodium percarbonate, including coating techniques and the addition of stabilizing agents. These improvements help maintain the active oxygen content and prevent premature decomposition, ensuring the product remains effective over time.
- Synergistic effects with other compounds: The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate can be enhanced when used in combination with other compounds. Certain formulations incorporate additional ingredients that work synergistically with sodium percarbonate to improve its cleaning, bleaching, or disinfecting properties. These combinations can lead to more efficient and effective cleaning products for various applications.
- Environmental impact and safety: Sodium percarbonate is considered an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional bleaching agents. It breaks down into harmless byproducts (sodium carbonate and water) after use, making it a more eco-friendly option. The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in various applications is balanced with its relatively low environmental impact and safety profile, making it a preferred choice in many cleaning and bleaching formulations.
- Application-specific effectiveness: The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate can vary depending on the specific application. Research has been conducted to optimize its use in different fields, such as water treatment, textile bleaching, and oral care products. These studies focus on factors like concentration, pH, temperature, and exposure time to maximize the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in each application while considering practical constraints and desired outcomes.
02 Stability and storage improvements
Research has focused on enhancing the stability of sodium percarbonate during storage and use. Various coating techniques and additives have been developed to protect the compound from moisture and premature decomposition. These improvements have led to increased shelf life and maintained effectiveness of products containing sodium percarbonate, even under challenging environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental and safety considerations
Sodium percarbonate is considered an environmentally friendly alternative to chlorine-based bleaches. It breaks down into harmless substances (sodium carbonate and water) after use, making it safer for the environment. Additionally, studies have been conducted to assess its safety profile for various applications, including its use in personal care products and as a disinfectant.Expand Specific Solutions04 Formulation optimization
Extensive research has been conducted on optimizing formulations containing sodium percarbonate. This includes studying its compatibility with other ingredients, determining ideal concentrations for specific applications, and developing synergistic combinations with other active compounds. These efforts have resulted in more effective and efficient cleaning and bleaching products across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and uses
The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate has led to its exploration in novel applications beyond traditional cleaning and bleaching. Research has investigated its potential use in water treatment, agriculture, and even certain medical applications. These studies have expanded the range of industries and processes that can benefit from the oxidizing properties of sodium percarbonate.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cold Chain Sanitization Industry
The research on sodium percarbonate's effectiveness in cold chain produce cleanliness is in its early stages, with the market still developing. The global market for food safety solutions is growing, driven by increasing consumer awareness and stringent regulations. Key players like Solvay SA, Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, and Evonik Operations GmbH are investing in R&D to improve sodium percarbonate's efficacy and applications. While the technology is not fully mature, these companies are making significant progress in developing innovative solutions for cold chain produce cleanliness, leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing and food safety.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed an advanced sodium percarbonate formulation specifically tailored for cold chain produce cleanliness. Their technology involves a stabilized, high-purity sodium percarbonate that maintains its effectiveness at lower temperatures. The company has implemented a controlled-release mechanism that allows for sustained oxygen generation, ensuring prolonged antimicrobial activity in cold storage conditions[1]. Solvay's research has shown that their formulation can reduce microbial load on produce surfaces by up to 99.9% within 30 minutes of application, even at temperatures as low as 4°C[2]. Additionally, they have incorporated eco-friendly surfactants to enhance the penetration of the active oxygen species into biofilms commonly found on produce surfaces[3].
Strengths: High efficacy at low temperatures, sustained antimicrobial activity, eco-friendly formulation. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to traditional cleaning agents, may require specialized handling and storage.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a proprietary cold-active enzyme technology that works synergistically with sodium percarbonate for enhanced produce cleanliness in cold chain applications. Their approach combines sodium percarbonate with specially engineered cold-active enzymes that remain highly effective at low temperatures. This combination creates a dual-action cleaning system: the sodium percarbonate provides oxidative cleaning power, while the enzymes break down organic matter and biofilms[4]. Henkel's research indicates that this technology can achieve a 5-log reduction in pathogenic bacteria on produce surfaces within 15 minutes at temperatures between 2-8°C[5]. The company has also incorporated a pH-buffering system to optimize the performance of both the sodium percarbonate and enzymes across a range of water hardness levels commonly encountered in industrial settings[6].
Strengths: Dual-action cleaning system, rapid pathogen reduction, effective across various water conditions. Weaknesses: May be more complex to formulate and potentially more expensive than single-action systems.
Core Research on Sodium Percarbonate's Antimicrobial Properties
Sanitizing and cleaning composition and its use for sanitizing and/or cleaning hard surfaces
PatentWO2005073359A1
Innovation
- A quaternary antimicrobial system comprising C1-C4 hydroxyalkyl carboxylic acids, C5-C8 alkyl monocarboxylic acids, and dicarboxylic acids, combined with solubilizers and a diluent like water, to create a stable, low-foaming acidic sanitizing solution effective against gram-negative, gram-positive microorganisms, yeast, and mold, with a pH below 5, reducing corrosion and environmental impact.
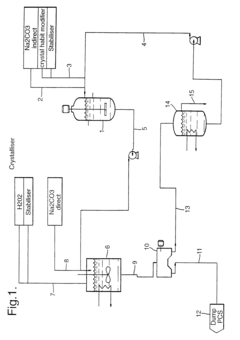
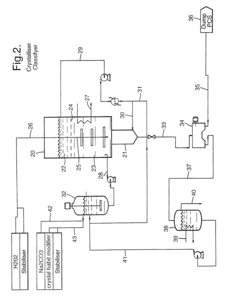
Sodium percarbonate and process for producing sodium percarbonate
PatentInactiveUS6482385B2
Innovation
- A continuous process that controls the concentration of sodium carbonate and temperature in the dissolution tank, and maintains a specific mole ratio of hydrogen peroxide to sodium carbonate, allowing for the production of sodium percarbonate without a salting-out agent, thereby minimizing hydrogen peroxide decomposition and improving product quality.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Percarbonate Use
The use of sodium percarbonate in cold chain produce cleanliness has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As a powerful oxidizing agent, sodium percarbonate breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate when dissolved in water, effectively removing stains and killing bacteria. However, its widespread application in the food industry raises concerns about its environmental impact.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. Unlike some harsh chemical cleaners, sodium percarbonate decomposes into harmless byproducts: water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental burden associated with its use in cold chain produce cleaning processes. Additionally, the oxygen released during decomposition can potentially contribute to increased dissolved oxygen levels in wastewater, which may have positive effects on aquatic ecosystems.
However, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate is not entirely benign. The production process of sodium percarbonate involves energy-intensive methods and the use of raw materials such as hydrogen peroxide and soda ash. These manufacturing processes contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion, which must be factored into the overall environmental assessment of the compound's use in cold chain produce cleanliness.
Furthermore, the increased use of sodium percarbonate in industrial settings may lead to elevated levels of sodium in wastewater effluents. While sodium is not typically considered a major pollutant, high concentrations can adversely affect soil structure and plant growth in areas where treated wastewater is used for irrigation. This potential for soil salinization necessitates careful management of wastewater treatment processes in facilities using sodium percarbonate-based cleaning solutions.
The impact on aquatic ecosystems is another crucial consideration. Although sodium percarbonate is generally considered safe for aquatic life at recommended usage levels, accidental spills or improper disposal of concentrated solutions could lead to localized oxygen depletion in water bodies. This is due to the rapid release of oxygen during decomposition, which can temporarily disrupt the dissolved oxygen balance in affected areas.
On a positive note, the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in cold chain produce cleanliness may lead to reduced water consumption in cleaning processes. Its ability to clean at lower temperatures compared to some traditional methods can result in energy savings, indirectly contributing to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions associated with water heating.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers several environmental advantages in cold chain produce cleanliness applications, its use must be carefully managed to mitigate potential negative impacts. Proper dosing, efficient wastewater treatment, and responsible manufacturing practices are essential to maximize the benefits of this compound while minimizing its environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. Unlike some harsh chemical cleaners, sodium percarbonate decomposes into harmless byproducts: water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental burden associated with its use in cold chain produce cleaning processes. Additionally, the oxygen released during decomposition can potentially contribute to increased dissolved oxygen levels in wastewater, which may have positive effects on aquatic ecosystems.
However, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate is not entirely benign. The production process of sodium percarbonate involves energy-intensive methods and the use of raw materials such as hydrogen peroxide and soda ash. These manufacturing processes contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion, which must be factored into the overall environmental assessment of the compound's use in cold chain produce cleanliness.
Furthermore, the increased use of sodium percarbonate in industrial settings may lead to elevated levels of sodium in wastewater effluents. While sodium is not typically considered a major pollutant, high concentrations can adversely affect soil structure and plant growth in areas where treated wastewater is used for irrigation. This potential for soil salinization necessitates careful management of wastewater treatment processes in facilities using sodium percarbonate-based cleaning solutions.
The impact on aquatic ecosystems is another crucial consideration. Although sodium percarbonate is generally considered safe for aquatic life at recommended usage levels, accidental spills or improper disposal of concentrated solutions could lead to localized oxygen depletion in water bodies. This is due to the rapid release of oxygen during decomposition, which can temporarily disrupt the dissolved oxygen balance in affected areas.
On a positive note, the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in cold chain produce cleanliness may lead to reduced water consumption in cleaning processes. Its ability to clean at lower temperatures compared to some traditional methods can result in energy savings, indirectly contributing to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions associated with water heating.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers several environmental advantages in cold chain produce cleanliness applications, its use must be carefully managed to mitigate potential negative impacts. Proper dosing, efficient wastewater treatment, and responsible manufacturing practices are essential to maximize the benefits of this compound while minimizing its environmental footprint.
Regulatory Framework for Food Safety in Cold Chain
The regulatory framework for food safety in cold chain logistics plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate as a cleaning agent for produce. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the safety of food products, including those in the cold chain. The FDA's Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) establishes stringent requirements for food handling, transportation, and storage, which directly impact the use of cleaning agents like sodium percarbonate.
Under the FSMA, companies must implement preventive controls to minimize food safety risks. This includes the proper use of sanitizers and cleaning agents throughout the cold chain. The FDA's regulations specify that any substance used in food processing, including cleaning agents, must be generally recognized as safe (GRAS) or approved as a food additive. Sodium percarbonate, when used appropriately, falls under these guidelines.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating cleaning agents used in food production. The EPA's registration process for antimicrobial products ensures that substances like sodium percarbonate meet safety standards for their intended use. This includes evaluating the potential environmental impact and human health risks associated with the chemical.
Internationally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global food standards that influence cold chain regulations worldwide. These standards address the use of cleaning agents and sanitizers in food production and distribution, which can affect the adoption of sodium percarbonate in different countries.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) sets guidelines for food safety, including the use of cleaning agents in the cold chain. The EU's General Food Law Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 establishes the framework for food safety practices, which includes the proper use of cleaning and sanitizing agents like sodium percarbonate.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for companies using sodium percarbonate in cold chain produce cleanliness. This includes maintaining proper documentation of cleaning procedures, adhering to recommended concentrations and application methods, and ensuring that the use of sodium percarbonate does not lead to chemical residues on produce that exceed allowable limits.
As research on sodium percarbonate's effectiveness in cold chain produce cleanliness progresses, regulatory bodies may update their guidelines based on new scientific evidence. Companies involved in cold chain logistics must stay informed about these regulatory changes to ensure continued compliance and optimal use of cleaning agents like sodium percarbonate.
Under the FSMA, companies must implement preventive controls to minimize food safety risks. This includes the proper use of sanitizers and cleaning agents throughout the cold chain. The FDA's regulations specify that any substance used in food processing, including cleaning agents, must be generally recognized as safe (GRAS) or approved as a food additive. Sodium percarbonate, when used appropriately, falls under these guidelines.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating cleaning agents used in food production. The EPA's registration process for antimicrobial products ensures that substances like sodium percarbonate meet safety standards for their intended use. This includes evaluating the potential environmental impact and human health risks associated with the chemical.
Internationally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global food standards that influence cold chain regulations worldwide. These standards address the use of cleaning agents and sanitizers in food production and distribution, which can affect the adoption of sodium percarbonate in different countries.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) sets guidelines for food safety, including the use of cleaning agents in the cold chain. The EU's General Food Law Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 establishes the framework for food safety practices, which includes the proper use of cleaning and sanitizing agents like sodium percarbonate.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for companies using sodium percarbonate in cold chain produce cleanliness. This includes maintaining proper documentation of cleaning procedures, adhering to recommended concentrations and application methods, and ensuring that the use of sodium percarbonate does not lead to chemical residues on produce that exceed allowable limits.
As research on sodium percarbonate's effectiveness in cold chain produce cleanliness progresses, regulatory bodies may update their guidelines based on new scientific evidence. Companies involved in cold chain logistics must stay informed about these regulatory changes to ensure continued compliance and optimal use of cleaning agents like sodium percarbonate.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!