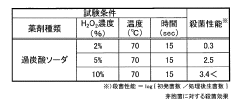
Use of Sodium Percarbonate in Cold Chain Supply Sanitation
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate in Cold Chain Sanitation: Overview and Objectives
Sodium percarbonate, a white crystalline compound, has emerged as a promising agent in cold chain supply sanitation. This eco-friendly oxidizing agent, composed of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, offers a potent solution to the persistent challenges of maintaining hygiene in temperature-controlled supply chains. The cold chain industry, crucial for preserving perishable goods during transportation and storage, faces unique sanitation hurdles due to low temperatures and moisture-rich environments.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium percarbonate in cold chain sanitation is to enhance the overall cleanliness and safety of storage facilities, transportation vehicles, and handling equipment. By leveraging its powerful oxidizing properties, sodium percarbonate aims to effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, which can proliferate in cold, damp conditions. This technology seeks to address the limitations of traditional cleaning methods that may be less effective at lower temperatures.
Another key goal is to provide a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional chemical sanitizers. Sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless byproducts of water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate, aligning with the growing demand for green solutions in industrial processes. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for use in food-related cold chains, where chemical residues are a significant concern.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate use in cold chain sanitation reflects broader trends in the industry towards more efficient, safe, and sustainable practices. Initially developed for household cleaning applications, its potential in industrial settings, particularly in cold environments, has gained recognition over the past decade. This shift has been driven by increasing regulatory pressures, consumer demand for safer food handling practices, and the cold chain industry's own pursuit of improved sanitation technologies.
As the cold chain sector continues to expand globally, driven by the growth of online grocery shopping and international food trade, the need for effective sanitation solutions becomes more critical. Sodium percarbonate technology aims to address this growing demand by offering a versatile, easy-to-use, and cost-effective sanitation option. Its development and implementation in cold chain applications represent a convergence of chemical innovation, environmental consciousness, and the specific needs of temperature-controlled logistics.
The exploration of sodium percarbonate in this context also opens avenues for further research and development. Future objectives include optimizing formulations for specific cold chain applications, investigating synergistic effects with other cleaning agents, and developing innovative delivery systems to maximize efficacy in challenging cold environments. These efforts are expected to contribute significantly to the advancement of cold chain sanitation practices, ultimately enhancing food safety and reducing waste in global supply chains.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium percarbonate in cold chain sanitation is to enhance the overall cleanliness and safety of storage facilities, transportation vehicles, and handling equipment. By leveraging its powerful oxidizing properties, sodium percarbonate aims to effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, which can proliferate in cold, damp conditions. This technology seeks to address the limitations of traditional cleaning methods that may be less effective at lower temperatures.
Another key goal is to provide a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional chemical sanitizers. Sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless byproducts of water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate, aligning with the growing demand for green solutions in industrial processes. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for use in food-related cold chains, where chemical residues are a significant concern.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate use in cold chain sanitation reflects broader trends in the industry towards more efficient, safe, and sustainable practices. Initially developed for household cleaning applications, its potential in industrial settings, particularly in cold environments, has gained recognition over the past decade. This shift has been driven by increasing regulatory pressures, consumer demand for safer food handling practices, and the cold chain industry's own pursuit of improved sanitation technologies.
As the cold chain sector continues to expand globally, driven by the growth of online grocery shopping and international food trade, the need for effective sanitation solutions becomes more critical. Sodium percarbonate technology aims to address this growing demand by offering a versatile, easy-to-use, and cost-effective sanitation option. Its development and implementation in cold chain applications represent a convergence of chemical innovation, environmental consciousness, and the specific needs of temperature-controlled logistics.
The exploration of sodium percarbonate in this context also opens avenues for further research and development. Future objectives include optimizing formulations for specific cold chain applications, investigating synergistic effects with other cleaning agents, and developing innovative delivery systems to maximize efficacy in challenging cold environments. These efforts are expected to contribute significantly to the advancement of cold chain sanitation practices, ultimately enhancing food safety and reducing waste in global supply chains.
Market Analysis for Cold Chain Sanitation Solutions
The cold chain sanitation solutions market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for food safety and stringent regulations in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors. The global cold chain market size was valued at $233.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $340.3 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 7.8%. Within this market, sanitation solutions play a crucial role in maintaining product integrity and preventing contamination.
The demand for effective cold chain sanitation solutions is particularly high in the food and beverage industry, which accounts for the largest share of the cold chain market. With consumers becoming more health-conscious and demanding fresher, safer products, companies are investing heavily in advanced sanitation technologies. The pharmaceutical sector is another major driver, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has highlighted the importance of maintaining sterile conditions throughout the supply chain.
Sodium percarbonate, as a key component in cold chain sanitation solutions, is gaining traction due to its effectiveness and eco-friendly nature. The global sodium percarbonate market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2021 to 2026, reaching a value of $627 million by the end of the forecast period. Its increasing adoption in cold chain applications is contributing significantly to this growth.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for cold chain sanitation solutions, owing to their well-established cold chain infrastructure and stringent regulatory frameworks. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid urbanization, changing consumer preferences, and increasing investments in cold chain logistics.
Key market trends include the adoption of IoT-enabled sanitation systems, which allow for real-time monitoring and automated cleaning processes. There is also a growing emphasis on sustainable sanitation solutions, with companies developing biodegradable and water-efficient products to meet environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
The competitive landscape of the cold chain sanitation solutions market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and specialized niche players. Major companies are focusing on product innovation and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. The increasing use of sodium percarbonate in these solutions presents opportunities for chemical manufacturers and sanitation equipment providers to collaborate and develop integrated offerings.
The demand for effective cold chain sanitation solutions is particularly high in the food and beverage industry, which accounts for the largest share of the cold chain market. With consumers becoming more health-conscious and demanding fresher, safer products, companies are investing heavily in advanced sanitation technologies. The pharmaceutical sector is another major driver, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has highlighted the importance of maintaining sterile conditions throughout the supply chain.
Sodium percarbonate, as a key component in cold chain sanitation solutions, is gaining traction due to its effectiveness and eco-friendly nature. The global sodium percarbonate market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2021 to 2026, reaching a value of $627 million by the end of the forecast period. Its increasing adoption in cold chain applications is contributing significantly to this growth.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for cold chain sanitation solutions, owing to their well-established cold chain infrastructure and stringent regulatory frameworks. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid urbanization, changing consumer preferences, and increasing investments in cold chain logistics.
Key market trends include the adoption of IoT-enabled sanitation systems, which allow for real-time monitoring and automated cleaning processes. There is also a growing emphasis on sustainable sanitation solutions, with companies developing biodegradable and water-efficient products to meet environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
The competitive landscape of the cold chain sanitation solutions market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and specialized niche players. Major companies are focusing on product innovation and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. The increasing use of sodium percarbonate in these solutions presents opportunities for chemical manufacturers and sanitation equipment providers to collaborate and develop integrated offerings.
Current Challenges in Cold Chain Sanitation Technologies
The cold chain supply industry faces several significant challenges in maintaining proper sanitation standards. One of the primary issues is the difficulty in achieving consistent and effective cleaning and disinfection across diverse environments and surfaces. Temperature-sensitive products require specialized handling, and traditional sanitation methods may not always be suitable or efficient in these conditions.
Microbial contamination remains a persistent threat, with pathogens like Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella posing serious risks to food safety. These microorganisms can thrive in cold environments and form biofilms, making them particularly challenging to eliminate. The industry struggles to find sanitation solutions that are both powerful enough to eradicate these pathogens and safe for use on food-contact surfaces.
Chemical residues from cleaning agents present another challenge. Many conventional sanitizers leave behind residues that can potentially contaminate products or affect their quality. This is especially problematic in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, where even trace amounts of chemicals can have significant implications.
Energy consumption and environmental impact are growing concerns in cold chain sanitation. Traditional cleaning methods often require high temperatures or large volumes of water, which can be energy-intensive and resource-demanding. The industry is under pressure to develop more sustainable sanitation practices that reduce water usage and energy consumption without compromising effectiveness.
The complexity of cold chain equipment and facilities adds another layer of difficulty to sanitation efforts. Intricate machinery, hard-to-reach areas, and the need to maintain low temperatures during cleaning processes all contribute to the challenges faced by sanitation teams. There is a growing demand for innovative solutions that can effectively clean and sanitize complex systems without disrupting operations or compromising temperature control.
Regulatory compliance and documentation pose ongoing challenges. With increasingly stringent food safety regulations, cold chain operators must not only implement effective sanitation practices but also maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance. This requires robust systems for monitoring, tracking, and reporting sanitation activities across the entire supply chain.
The use of sodium percarbonate in cold chain supply sanitation offers potential solutions to some of these challenges, but also presents its own set of difficulties. While it is an effective oxidizing agent capable of breaking down organic matter and killing microorganisms, its efficacy can be affected by temperature and pH levels. Ensuring optimal performance in cold environments and preventing potential corrosion of equipment are areas that require further research and development.
Microbial contamination remains a persistent threat, with pathogens like Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella posing serious risks to food safety. These microorganisms can thrive in cold environments and form biofilms, making them particularly challenging to eliminate. The industry struggles to find sanitation solutions that are both powerful enough to eradicate these pathogens and safe for use on food-contact surfaces.
Chemical residues from cleaning agents present another challenge. Many conventional sanitizers leave behind residues that can potentially contaminate products or affect their quality. This is especially problematic in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, where even trace amounts of chemicals can have significant implications.
Energy consumption and environmental impact are growing concerns in cold chain sanitation. Traditional cleaning methods often require high temperatures or large volumes of water, which can be energy-intensive and resource-demanding. The industry is under pressure to develop more sustainable sanitation practices that reduce water usage and energy consumption without compromising effectiveness.
The complexity of cold chain equipment and facilities adds another layer of difficulty to sanitation efforts. Intricate machinery, hard-to-reach areas, and the need to maintain low temperatures during cleaning processes all contribute to the challenges faced by sanitation teams. There is a growing demand for innovative solutions that can effectively clean and sanitize complex systems without disrupting operations or compromising temperature control.
Regulatory compliance and documentation pose ongoing challenges. With increasingly stringent food safety regulations, cold chain operators must not only implement effective sanitation practices but also maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance. This requires robust systems for monitoring, tracking, and reporting sanitation activities across the entire supply chain.
The use of sodium percarbonate in cold chain supply sanitation offers potential solutions to some of these challenges, but also presents its own set of difficulties. While it is an effective oxidizing agent capable of breaking down organic matter and killing microorganisms, its efficacy can be affected by temperature and pH levels. Ensuring optimal performance in cold environments and preventing potential corrosion of equipment are areas that require further research and development.
Existing Sodium Percarbonate-based Sanitation Methods
01 Composition and preparation of sodium percarbonate
Sodium percarbonate is a compound used for sanitation purposes. It is typically prepared by reacting sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide. The resulting product is a stable, solid form of hydrogen peroxide that releases oxygen when dissolved in water, making it an effective cleaning and disinfecting agent.- Sodium percarbonate as a bleaching and disinfecting agent: Sodium percarbonate is widely used as an effective bleaching and disinfecting agent in various applications. It releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, providing powerful oxidizing properties for cleaning and sanitizing purposes. This compound is particularly useful in laundry detergents, household cleaners, and water treatment systems.
- Stabilization of sodium percarbonate: Various methods and additives are employed to stabilize sodium percarbonate, enhancing its shelf life and effectiveness. Stabilization techniques include coating the particles, adding inorganic salts, or incorporating organic compounds. These methods help prevent premature decomposition and maintain the active oxygen content of the product during storage and use.
- Sodium percarbonate in personal care products: Sodium percarbonate is utilized in personal care products, particularly in dental and oral hygiene applications. It can be incorporated into toothpaste, mouthwash, and teeth whitening formulations. The controlled release of hydrogen peroxide provides gentle yet effective cleaning and whitening properties without causing significant irritation to oral tissues.
- Environmental applications of sodium percarbonate: Sodium percarbonate finds applications in environmental remediation and water treatment. It can be used to treat contaminated soil, groundwater, and industrial wastewater. The compound's ability to release oxygen and generate hydroxyl radicals makes it effective in breaking down organic pollutants and improving water quality.
- Formulation of cleaning products with sodium percarbonate: Sodium percarbonate is a key ingredient in many cleaning product formulations. It is often combined with other cleaning agents, surfactants, and enzymes to create effective all-purpose cleaners, laundry detergents, and stain removers. The formulation process involves optimizing the balance between cleaning efficacy, stability, and safety for various applications.
02 Application in cleaning and disinfecting products
Sodium percarbonate is widely used in various cleaning and disinfecting products due to its ability to release active oxygen. It is commonly incorporated into laundry detergents, household cleaners, and water treatment systems. The compound's effectiveness in removing stains, whitening, and sanitizing makes it a versatile ingredient in many consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization and storage of sodium percarbonate
To maintain the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate, stabilization techniques are employed. These may include coating the particles, adding stabilizing agents, or controlling moisture content. Proper storage conditions, such as keeping the product in a cool, dry place, are essential to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations
Sodium percarbonate is considered an environmentally friendly alternative to chlorine-based bleaches and sanitizers. It breaks down into harmless byproducts of water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. However, proper handling and storage are necessary to prevent accidental exposure or ingestion, as the compound can be an irritant in its concentrated form.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synergistic effects with other cleaning agents
Sodium percarbonate can be combined with other cleaning agents to enhance its effectiveness. For example, it may be used in conjunction with enzymes, surfactants, or other oxidizing agents to create more powerful cleaning formulations. These combinations can improve the overall sanitation performance and broaden the range of applications for sodium percarbonate-based products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cold Chain Sanitation Industry
The use of sodium percarbonate in cold chain supply sanitation is an emerging market with significant growth potential. The industry is in its early growth stage, driven by increasing demand for effective and environmentally friendly sanitation solutions in the food and beverage sector. The global market size is expected to expand rapidly, fueled by stringent hygiene regulations and growing awareness of food safety. Technologically, the field is evolving, with companies like Solvay SA, Ecolab Inc., and Evonik Operations GmbH leading innovation. These firms are developing advanced formulations and application methods to enhance the efficacy of sodium percarbonate in cold chain environments, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity with room for further advancements.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed advanced sodium percarbonate formulations specifically tailored for cold chain supply sanitation. Their technology focuses on enhancing the stability and efficacy of sodium percarbonate in low-temperature environments. The company has engineered a proprietary coating process that protects the sodium percarbonate particles, allowing for controlled release of active oxygen even in cold conditions[1]. This innovation ensures consistent sanitizing performance throughout the cold chain. Solvay's formulations also incorporate synergistic ingredients that boost the antimicrobial activity of sodium percarbonate, providing broad-spectrum disinfection against common cold chain contaminants[2]. The company has conducted extensive testing to validate the effectiveness of their solutions in various cold chain scenarios, including refrigerated transport and storage facilities[3].
Strengths: Specialized formulations for cold environments, controlled release technology, enhanced stability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to standard sodium percarbonate products, may require specific handling procedures.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab USA, Inc. has developed a comprehensive cold chain sanitation program incorporating sodium percarbonate-based solutions. Their approach combines specially formulated sodium percarbonate products with advanced application systems designed for cold environments. Ecolab's technology includes temperature-compensated dosing equipment that adjusts the concentration of sodium percarbonate solutions based on ambient conditions, ensuring optimal sanitizing efficacy[4]. The company has also developed cold-resistant foam and gel formulations that enhance contact time and coverage on surfaces in refrigerated areas. Ecolab's sodium percarbonate solutions are integrated with their data-driven monitoring systems, allowing for real-time tracking of sanitation efficacy and compliance throughout the cold chain[5]. This holistic approach addresses the unique challenges of maintaining hygiene in low-temperature supply chains.
Strengths: Integrated sanitation systems, temperature-compensated dosing, data-driven monitoring. Weaknesses: May require significant investment in equipment and training, potential dependency on Ecolab's ecosystem.
Innovative Applications of Sodium Percarbonate in Cold Chain
Sterilization method
PatentInactiveJP2012101825A
Innovation
- Sodium percarbonate, a stable alkaline granular powder, is used as a sterilizing agent, which is dissolved in sterile water to generate hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate, allowing for stable storage and reduced transportation costs, while maintaining effective sterilization performance.
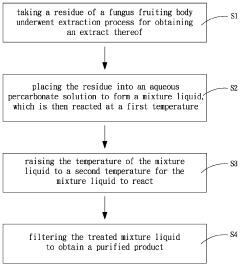
Purification method of fungal cell wall composition
PatentActiveUS20230310529A1
Innovation
- An aqueous percarbonate solution is used for decolorization and digestion, replacing the two-stage treatment with sodium hydroxide and hypochlorite or hydrogen peroxide, allowing for simultaneous decolorization and decomposition at controlled temperatures, reducing waste burden and increasing recovery rates.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Percarbonate Use
The use of sodium percarbonate in cold chain supply sanitation has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As a powerful oxidizing agent, sodium percarbonate breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate when dissolved in water, providing effective cleaning and disinfection properties. However, its environmental impact extends beyond its primary function.
One of the key environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. Unlike some traditional cleaning agents, it decomposes into harmless byproducts: water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental burden associated with its use in cold chain sanitation processes. The oxygen released during decomposition can potentially contribute to increased dissolved oxygen levels in water bodies, which is generally beneficial for aquatic ecosystems.
However, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate is not entirely benign. The release of sodium carbonate can lead to localized increases in water alkalinity, potentially affecting pH-sensitive aquatic organisms. While this effect is typically temporary and localized, repeated or large-scale use in areas with limited water exchange could lead to more persistent changes in water chemistry.
The production process of sodium percarbonate also bears environmental considerations. It requires energy-intensive manufacturing, contributing to carbon emissions and resource consumption. However, when compared to the production of some alternative sanitation chemicals, sodium percarbonate often has a lower overall environmental footprint due to its simpler composition and production methods.
In terms of ecotoxicity, sodium percarbonate is generally considered to have low toxicity to aquatic life when used as directed. However, at high concentrations or in cases of accidental spills, it can cause temporary stress to aquatic organisms due to rapid oxygen release and pH changes. This underscores the importance of proper handling and dosage in cold chain applications to minimize environmental risks.
The use of sodium percarbonate in cold chain supply sanitation can indirectly contribute to environmental protection by reducing the need for more harmful chemical alternatives. Its effectiveness in controlling microbial growth at lower temperatures means less energy is required for sanitation processes, potentially leading to reduced energy consumption and associated carbon emissions in cold chain operations.
Lastly, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate extends to waste management considerations. While the compound itself is environmentally friendly, its packaging and transportation contribute to the overall environmental footprint. Efforts to optimize packaging, reduce transportation distances, and implement recycling programs can further mitigate these secondary environmental impacts associated with its use in cold chain sanitation.
One of the key environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. Unlike some traditional cleaning agents, it decomposes into harmless byproducts: water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental burden associated with its use in cold chain sanitation processes. The oxygen released during decomposition can potentially contribute to increased dissolved oxygen levels in water bodies, which is generally beneficial for aquatic ecosystems.
However, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate is not entirely benign. The release of sodium carbonate can lead to localized increases in water alkalinity, potentially affecting pH-sensitive aquatic organisms. While this effect is typically temporary and localized, repeated or large-scale use in areas with limited water exchange could lead to more persistent changes in water chemistry.
The production process of sodium percarbonate also bears environmental considerations. It requires energy-intensive manufacturing, contributing to carbon emissions and resource consumption. However, when compared to the production of some alternative sanitation chemicals, sodium percarbonate often has a lower overall environmental footprint due to its simpler composition and production methods.
In terms of ecotoxicity, sodium percarbonate is generally considered to have low toxicity to aquatic life when used as directed. However, at high concentrations or in cases of accidental spills, it can cause temporary stress to aquatic organisms due to rapid oxygen release and pH changes. This underscores the importance of proper handling and dosage in cold chain applications to minimize environmental risks.
The use of sodium percarbonate in cold chain supply sanitation can indirectly contribute to environmental protection by reducing the need for more harmful chemical alternatives. Its effectiveness in controlling microbial growth at lower temperatures means less energy is required for sanitation processes, potentially leading to reduced energy consumption and associated carbon emissions in cold chain operations.
Lastly, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate extends to waste management considerations. While the compound itself is environmentally friendly, its packaging and transportation contribute to the overall environmental footprint. Efforts to optimize packaging, reduce transportation distances, and implement recycling programs can further mitigate these secondary environmental impacts associated with its use in cold chain sanitation.
Regulatory Framework for Cold Chain Sanitation Chemicals
The regulatory framework for cold chain sanitation chemicals, including sodium percarbonate, is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international standards. In the United States, the primary regulatory body overseeing these chemicals is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which regulates antimicrobial pesticides used in food processing facilities under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA).
The EPA requires that all antimicrobial products used in food processing environments be registered and approved before use. This process involves rigorous testing to ensure the safety and efficacy of the product. For sodium percarbonate, manufacturers must demonstrate its effectiveness in sanitizing cold chain environments without posing undue risks to human health or the environment.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a crucial role in regulating chemicals used in food processing facilities. Under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), the FDA has established preventive controls for food safety, which include requirements for sanitation practices in cold chain supply. While the FDA does not directly approve sanitizers, it does require that food facilities use EPA-registered antimicrobial products in a manner consistent with their labeling.
Internationally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides guidelines for food hygiene that are widely adopted globally. These guidelines influence national regulations and industry standards for cold chain sanitation chemicals.
In the European Union, the use of sodium percarbonate and other sanitizers in food processing is regulated under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). This regulation requires that all biocidal products, including those used in cold chain sanitation, undergo a thorough assessment before being authorized for use in the EU market.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has also developed standards relevant to cold chain sanitation, such as ISO 22000 for food safety management systems. These standards, while not legally binding, are often adopted by companies to demonstrate compliance with best practices in food safety and sanitation.
Industry-specific guidelines, such as those provided by the Global Cold Chain Alliance (GCCA), offer additional recommendations for the use of sanitation chemicals in cold chain facilities. These guidelines often incorporate regulatory requirements and industry best practices to ensure food safety and quality throughout the cold chain.
As environmental concerns grow, regulations are evolving to address the sustainability of sanitation chemicals. Many jurisdictions are implementing stricter controls on chemical runoff and disposal, which may impact the use of sodium percarbonate and similar compounds in cold chain sanitation processes.
The EPA requires that all antimicrobial products used in food processing environments be registered and approved before use. This process involves rigorous testing to ensure the safety and efficacy of the product. For sodium percarbonate, manufacturers must demonstrate its effectiveness in sanitizing cold chain environments without posing undue risks to human health or the environment.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a crucial role in regulating chemicals used in food processing facilities. Under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), the FDA has established preventive controls for food safety, which include requirements for sanitation practices in cold chain supply. While the FDA does not directly approve sanitizers, it does require that food facilities use EPA-registered antimicrobial products in a manner consistent with their labeling.
Internationally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides guidelines for food hygiene that are widely adopted globally. These guidelines influence national regulations and industry standards for cold chain sanitation chemicals.
In the European Union, the use of sodium percarbonate and other sanitizers in food processing is regulated under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). This regulation requires that all biocidal products, including those used in cold chain sanitation, undergo a thorough assessment before being authorized for use in the EU market.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has also developed standards relevant to cold chain sanitation, such as ISO 22000 for food safety management systems. These standards, while not legally binding, are often adopted by companies to demonstrate compliance with best practices in food safety and sanitation.
Industry-specific guidelines, such as those provided by the Global Cold Chain Alliance (GCCA), offer additional recommendations for the use of sanitation chemicals in cold chain facilities. These guidelines often incorporate regulatory requirements and industry best practices to ensure food safety and quality throughout the cold chain.
As environmental concerns grow, regulations are evolving to address the sustainability of sanitation chemicals. Many jurisdictions are implementing stricter controls on chemical runoff and disposal, which may impact the use of sodium percarbonate and similar compounds in cold chain sanitation processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!