How to Develop Advanced Carbon Tetrachloride Utilization Techniques?
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
CCl4 Utilization Background and Objectives
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) has been a subject of significant concern in environmental and industrial circles due to its ozone-depleting properties and potential health hazards. Despite its phase-out under the Montreal Protocol, CCl4 remains present in the environment and continues to be produced as a byproduct in various industrial processes. This persistence has led to a growing interest in developing advanced utilization techniques for CCl4, aiming to transform this problematic compound into valuable resources or less harmful substances.
The evolution of CCl4 utilization techniques has been driven by the dual objectives of environmental protection and resource recovery. Initially, efforts focused primarily on destruction methods to eliminate CCl4 from the environment. However, as sustainability concerns have grown, the focus has shifted towards more efficient and economically viable approaches that can convert CCl4 into useful products or feedstocks for other industrial processes.
Recent technological advancements have opened up new possibilities for CCl4 utilization. These include catalytic conversion processes, electrochemical reduction methods, and photochemical decomposition techniques. Each of these approaches aims to break down the CCl4 molecule and rearrange its components into less harmful or more valuable compounds. The ultimate goal is to develop a suite of technologies that can effectively handle CCl4 from various sources, including legacy stockpiles, industrial byproducts, and environmental reservoirs.
The development of advanced CCl4 utilization techniques is expected to yield multiple benefits. From an environmental perspective, it offers a pathway to reduce the global burden of this persistent pollutant. Economically, it presents opportunities for industries to recover value from waste streams and potentially create new product lines. Additionally, the technologies developed for CCl4 utilization may have broader applications in handling other chlorinated compounds, contributing to overall advancements in green chemistry and sustainable industrial practices.
As research in this field progresses, several key objectives have emerged. These include improving the efficiency and selectivity of CCl4 conversion processes, developing more robust and scalable reactor designs, and exploring novel catalysts that can operate under milder conditions. There is also a growing emphasis on integrating CCl4 utilization techniques into existing industrial processes to minimize waste and maximize resource recovery.
The path forward in CCl4 utilization research is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from chemistry, chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental studies. This collaborative effort aims to address the complex challenges associated with CCl4 handling and transformation, paving the way for innovative solutions that align with global sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
The evolution of CCl4 utilization techniques has been driven by the dual objectives of environmental protection and resource recovery. Initially, efforts focused primarily on destruction methods to eliminate CCl4 from the environment. However, as sustainability concerns have grown, the focus has shifted towards more efficient and economically viable approaches that can convert CCl4 into useful products or feedstocks for other industrial processes.
Recent technological advancements have opened up new possibilities for CCl4 utilization. These include catalytic conversion processes, electrochemical reduction methods, and photochemical decomposition techniques. Each of these approaches aims to break down the CCl4 molecule and rearrange its components into less harmful or more valuable compounds. The ultimate goal is to develop a suite of technologies that can effectively handle CCl4 from various sources, including legacy stockpiles, industrial byproducts, and environmental reservoirs.
The development of advanced CCl4 utilization techniques is expected to yield multiple benefits. From an environmental perspective, it offers a pathway to reduce the global burden of this persistent pollutant. Economically, it presents opportunities for industries to recover value from waste streams and potentially create new product lines. Additionally, the technologies developed for CCl4 utilization may have broader applications in handling other chlorinated compounds, contributing to overall advancements in green chemistry and sustainable industrial practices.
As research in this field progresses, several key objectives have emerged. These include improving the efficiency and selectivity of CCl4 conversion processes, developing more robust and scalable reactor designs, and exploring novel catalysts that can operate under milder conditions. There is also a growing emphasis on integrating CCl4 utilization techniques into existing industrial processes to minimize waste and maximize resource recovery.
The path forward in CCl4 utilization research is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from chemistry, chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental studies. This collaborative effort aims to address the complex challenges associated with CCl4 handling and transformation, paving the way for innovative solutions that align with global sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
Market Analysis for CCl4 Recycling
The global market for carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) recycling has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental regulations and a growing emphasis on sustainable industrial practices. The demand for CCl4 recycling services is primarily fueled by industries such as chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, where CCl4 is used as a solvent or intermediate in various processes.
The market size for CCl4 recycling is expected to expand substantially over the next decade. This growth is attributed to the rising awareness of the environmental and health hazards associated with CCl4 emissions, coupled with stringent government regulations aimed at reducing ozone-depleting substances. Additionally, the circular economy concept has gained traction, encouraging industries to adopt closed-loop systems for chemical recycling.
Key market drivers include the implementation of the Montreal Protocol, which phases out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances, including CCl4. This has created a strong incentive for industries to invest in recycling technologies to maintain their supply of CCl4 for essential uses. Furthermore, the increasing cost of raw materials and waste disposal has made recycling a more economically viable option for many companies.
Regional analysis shows that North America and Europe currently dominate the CCl4 recycling market, owing to their advanced environmental policies and well-established recycling infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical companies offering in-house recycling services and specialized recycling firms. There is a trend towards the development of more efficient and cost-effective recycling technologies, including advanced distillation techniques and chemical transformation processes that convert CCl4 into less harmful substances.
Challenges in the CCl4 recycling market include the high initial investment required for recycling facilities and the technical complexities involved in purifying used CCl4 to meet industry standards. However, these challenges are offset by the long-term economic and environmental benefits of recycling, as well as potential regulatory incentives for companies that adopt sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, the CCl4 recycling market is poised for continued growth, with opportunities for innovation in recycling technologies and the potential for expansion into new geographic regions. The market is also likely to see increased collaboration between chemical manufacturers, recycling companies, and research institutions to develop more advanced and sustainable CCl4 utilization techniques.
The market size for CCl4 recycling is expected to expand substantially over the next decade. This growth is attributed to the rising awareness of the environmental and health hazards associated with CCl4 emissions, coupled with stringent government regulations aimed at reducing ozone-depleting substances. Additionally, the circular economy concept has gained traction, encouraging industries to adopt closed-loop systems for chemical recycling.
Key market drivers include the implementation of the Montreal Protocol, which phases out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances, including CCl4. This has created a strong incentive for industries to invest in recycling technologies to maintain their supply of CCl4 for essential uses. Furthermore, the increasing cost of raw materials and waste disposal has made recycling a more economically viable option for many companies.
Regional analysis shows that North America and Europe currently dominate the CCl4 recycling market, owing to their advanced environmental policies and well-established recycling infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical companies offering in-house recycling services and specialized recycling firms. There is a trend towards the development of more efficient and cost-effective recycling technologies, including advanced distillation techniques and chemical transformation processes that convert CCl4 into less harmful substances.
Challenges in the CCl4 recycling market include the high initial investment required for recycling facilities and the technical complexities involved in purifying used CCl4 to meet industry standards. However, these challenges are offset by the long-term economic and environmental benefits of recycling, as well as potential regulatory incentives for companies that adopt sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, the CCl4 recycling market is poised for continued growth, with opportunities for innovation in recycling technologies and the potential for expansion into new geographic regions. The market is also likely to see increased collaboration between chemical manufacturers, recycling companies, and research institutions to develop more advanced and sustainable CCl4 utilization techniques.
Current CCl4 Utilization Challenges
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) utilization faces significant challenges in the current technological landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the environmental impact associated with its use. CCl4 is a potent ozone-depleting substance and greenhouse gas, which has led to strict regulations and phase-out programs worldwide. This regulatory environment severely limits its applications and necessitates the development of alternative processes that minimize or eliminate CCl4 emissions.
Another major challenge is the toxicity of CCl4 to human health. Exposure can cause severe liver and kidney damage, as well as potential carcinogenic effects. This toxicity profile creates substantial safety concerns in industrial settings, requiring extensive protective measures and specialized handling procedures. The associated costs and risks often make CCl4-based processes less attractive compared to safer alternatives.
The chemical stability of CCl4 presents both advantages and challenges. While its stability makes it useful in certain applications, it also makes CCl4 resistant to degradation in the environment. This persistence contributes to its long-term environmental impact and complicates remediation efforts for contaminated sites. Developing effective degradation or transformation techniques for CCl4 remains a significant technical hurdle.
From a utilization perspective, the limited reactivity of CCl4 in certain desirable chemical transformations poses challenges for its use as a chemical feedstock. Many potential applications require the development of novel catalysts or reaction conditions to activate CCl4 efficiently. This limitation restricts its versatility in chemical synthesis and industrial processes.
The economic viability of CCl4 utilization is also a pressing concern. As regulations tighten and alternatives emerge, the cost-effectiveness of CCl4-based processes is increasingly questioned. Industries must weigh the benefits of CCl4 use against the expenses of compliance, safety measures, and potential environmental liabilities. This economic pressure drives the need for more efficient utilization techniques or complete replacement strategies.
Lastly, the technical challenges in CCl4 recycling and disposal contribute to the overall utilization problem. Effective recycling methods are crucial for minimizing environmental release, but they often involve complex and energy-intensive processes. Similarly, safe disposal of CCl4 waste requires specialized facilities and techniques, adding to the overall cost and complexity of its use.
Another major challenge is the toxicity of CCl4 to human health. Exposure can cause severe liver and kidney damage, as well as potential carcinogenic effects. This toxicity profile creates substantial safety concerns in industrial settings, requiring extensive protective measures and specialized handling procedures. The associated costs and risks often make CCl4-based processes less attractive compared to safer alternatives.
The chemical stability of CCl4 presents both advantages and challenges. While its stability makes it useful in certain applications, it also makes CCl4 resistant to degradation in the environment. This persistence contributes to its long-term environmental impact and complicates remediation efforts for contaminated sites. Developing effective degradation or transformation techniques for CCl4 remains a significant technical hurdle.
From a utilization perspective, the limited reactivity of CCl4 in certain desirable chemical transformations poses challenges for its use as a chemical feedstock. Many potential applications require the development of novel catalysts or reaction conditions to activate CCl4 efficiently. This limitation restricts its versatility in chemical synthesis and industrial processes.
The economic viability of CCl4 utilization is also a pressing concern. As regulations tighten and alternatives emerge, the cost-effectiveness of CCl4-based processes is increasingly questioned. Industries must weigh the benefits of CCl4 use against the expenses of compliance, safety measures, and potential environmental liabilities. This economic pressure drives the need for more efficient utilization techniques or complete replacement strategies.
Lastly, the technical challenges in CCl4 recycling and disposal contribute to the overall utilization problem. Effective recycling methods are crucial for minimizing environmental release, but they often involve complex and energy-intensive processes. Similarly, safe disposal of CCl4 waste requires specialized facilities and techniques, adding to the overall cost and complexity of its use.
Existing CCl4 Utilization Methods
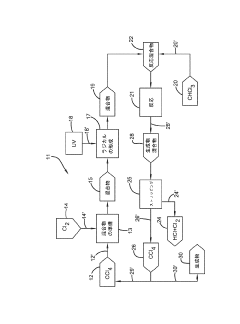
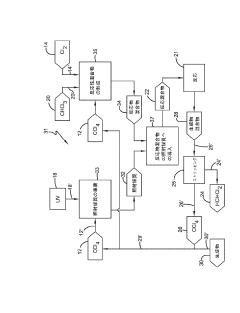
01 Production and purification of carbon tetrachloride
Various methods for producing and purifying carbon tetrachloride are described. These include chemical synthesis processes, distillation techniques, and purification methods to obtain high-quality carbon tetrachloride for industrial and laboratory use.- Production and purification of carbon tetrachloride: Various methods for producing and purifying carbon tetrachloride are described. These include chemical synthesis processes, distillation techniques, and purification methods to obtain high-quality carbon tetrachloride for industrial and laboratory use.
- Applications of carbon tetrachloride in chemical processes: Carbon tetrachloride is utilized in various chemical processes, including as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals. Its unique properties make it valuable in specific industrial applications and chemical reactions.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Due to its environmental impact and health hazards, research focuses on alternatives to carbon tetrachloride and methods for its safe handling, storage, and disposal. This includes developing eco-friendly substitutes and improving containment strategies.
- Detection and analysis methods: Various techniques and apparatus are developed for detecting and analyzing carbon tetrachloride in different environments. These methods are crucial for monitoring air and water quality, as well as ensuring workplace safety in industries where carbon tetrachloride is used.
- Historical uses and patents: Early patents and historical documents reveal the diverse applications of carbon tetrachloride in the past, including its use in fire extinguishers, dry cleaning, and as a refrigerant. Many of these applications have been phased out due to safety and environmental concerns.
02 Applications of carbon tetrachloride in chemical processes
Carbon tetrachloride is utilized in various chemical processes as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate. It finds applications in organic synthesis, extraction processes, and as a raw material for the production of other chlorinated compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental and safety considerations
Due to its environmental impact and health hazards, research focuses on developing alternatives to carbon tetrachloride and methods for its safe handling, storage, and disposal. This includes techniques for detecting and monitoring carbon tetrachloride in various environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Carbon tetrachloride in analytical chemistry
Carbon tetrachloride is used in various analytical chemistry applications, including as a solvent for spectroscopic studies, in chromatography, and for the preparation of samples in chemical analysis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Historical uses and regulations
The historical uses of carbon tetrachloride, such as in fire extinguishers and dry cleaning, are discussed along with the subsequent regulations and phase-out of its use due to environmental concerns and health risks.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in CCl4 Utilization
The development of advanced carbon tetrachloride utilization techniques is in a nascent stage, with the market still emerging and significant potential for growth. The global market size for this technology is relatively small but expected to expand as environmental regulations tighten and demand for sustainable chemical processes increases. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Companies like DuPont de Nemours, Occidental Chemical Corp., and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are at the forefront, investing in R&D to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Academic institutions such as Central South University and Ulsan National Institute of Science & Technology are also contributing to advancements, indicating a collaborative ecosystem between industry and academia in this domain.
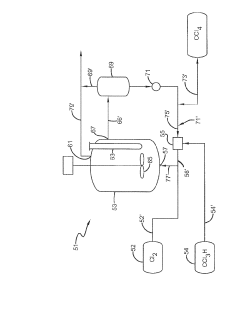
Occidental Chemical Corp.
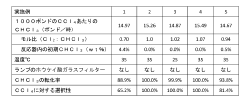
Technical Solution: Occidental Chemical Corp. has developed advanced carbon tetrachloride utilization techniques focusing on conversion to valuable chlorinated products. Their process involves catalytic hydrogenolysis of carbon tetrachloride to produce methylene chloride and chloroform[1]. The company employs a proprietary catalyst system that achieves high selectivity and conversion rates, operating at moderate temperatures and pressures. This method not only reduces carbon tetrachloride waste but also generates commercially valuable chlorinated solvents. Additionally, Occidental has implemented a closed-loop recycling system to capture and reuse unreacted carbon tetrachloride, minimizing emissions and improving overall process efficiency[2].
Strengths: High conversion rates, production of valuable chemicals, closed-loop recycling. Weaknesses: Energy-intensive process, potential for catalyst deactivation over time.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has pioneered a novel approach to carbon tetrachloride utilization through its innovative photocatalytic decomposition process. This technique employs specially designed titanium dioxide nanoparticles as photocatalysts, activated by UV light to break down carbon tetrachloride into less harmful compounds[3]. The process operates at ambient temperature and pressure, significantly reducing energy requirements. DuPont's method achieves a decomposition efficiency of over 95% within a short reaction time[4]. Furthermore, the company has developed a regeneration process for the photocatalyst, extending its lifespan and reducing operational costs. This technology also produces valuable by-products such as hydrochloric acid, which can be used in other industrial processes.
Strengths: Low energy consumption, high decomposition efficiency, valuable by-product generation. Weaknesses: Requires UV light source, potential for incomplete decomposition of intermediates.
Innovative CCl4 Conversion Processes
Producing carbon tetrachloride by photochlorination of chloroform
PatentActiveJP2024069268A
Innovation
- A method involving the photochlorination of chloroform with chlorine in the presence of electromagnetic radiation, maintaining a low concentration of chloroform and a stoichiometric concentration of chlorine, to produce carbon tetrachloride with high selectivity and minimize the formation of hexachloroethane.
Improved methods and apparatus for producing trichloro-hydrosilicon and polysilicon
PatentInactiveEP2179965A1
Innovation
- A hydrochlorination process involving a gas-solid catalytic reaction of silicon tetrachloride, hydrogen, and hydrogen chloride with metallurgical silicon in a fluidized bed reactor, optimizing molar ratios and temperatures to enhance trichlorosilane production, followed by multistage distillation and recycling of by-products to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of advanced carbon tetrachloride utilization techniques is crucial for ensuring sustainable development and minimizing potential harm to ecosystems and human health. Carbon tetrachloride, a potent ozone-depleting substance and greenhouse gas, poses significant environmental risks if not properly managed.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for atmospheric emissions during the utilization process. Advanced techniques must incorporate robust containment and emission control systems to prevent the release of carbon tetrachloride into the air. This is particularly important given its high global warming potential and ozone depletion potential. Monitoring and quantification of emissions are essential for assessing the overall environmental impact and ensuring compliance with international regulations.
Water contamination is another critical aspect to consider. Carbon tetrachloride can persist in aquatic environments and potentially contaminate groundwater sources. Advanced utilization techniques should include measures to prevent spills and leaks, as well as implement effective wastewater treatment processes to remove any traces of the compound before discharge.
Soil contamination is a long-term concern associated with carbon tetrachloride usage. Advanced techniques must incorporate proper handling, storage, and disposal methods to prevent soil contamination. This includes the use of impermeable surfaces, containment systems, and regular soil monitoring programs to detect any potential leaks or spills.
The impact on biodiversity and ecosystems must also be carefully evaluated. Carbon tetrachloride can have toxic effects on various organisms, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystem balance. Comprehensive ecological risk assessments should be conducted to understand the potential impacts on local flora and fauna, with particular attention to sensitive species and habitats.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a valuable tool for evaluating the overall environmental impact of advanced carbon tetrachloride utilization techniques. This approach considers all stages of the process, from raw material extraction to final disposal, providing a holistic view of the environmental footprint. LCA can help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable utilization methods.
The assessment should also consider the potential for indirect environmental impacts. For instance, the energy requirements of advanced utilization techniques may lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions from power generation. Evaluating these indirect effects is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the environmental implications.
Finally, the environmental impact assessment should address the potential for accidental releases and emergency scenarios. Advanced utilization techniques must incorporate robust safety measures and emergency response plans to mitigate the environmental consequences of potential accidents or equipment failures.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for atmospheric emissions during the utilization process. Advanced techniques must incorporate robust containment and emission control systems to prevent the release of carbon tetrachloride into the air. This is particularly important given its high global warming potential and ozone depletion potential. Monitoring and quantification of emissions are essential for assessing the overall environmental impact and ensuring compliance with international regulations.
Water contamination is another critical aspect to consider. Carbon tetrachloride can persist in aquatic environments and potentially contaminate groundwater sources. Advanced utilization techniques should include measures to prevent spills and leaks, as well as implement effective wastewater treatment processes to remove any traces of the compound before discharge.
Soil contamination is a long-term concern associated with carbon tetrachloride usage. Advanced techniques must incorporate proper handling, storage, and disposal methods to prevent soil contamination. This includes the use of impermeable surfaces, containment systems, and regular soil monitoring programs to detect any potential leaks or spills.
The impact on biodiversity and ecosystems must also be carefully evaluated. Carbon tetrachloride can have toxic effects on various organisms, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystem balance. Comprehensive ecological risk assessments should be conducted to understand the potential impacts on local flora and fauna, with particular attention to sensitive species and habitats.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a valuable tool for evaluating the overall environmental impact of advanced carbon tetrachloride utilization techniques. This approach considers all stages of the process, from raw material extraction to final disposal, providing a holistic view of the environmental footprint. LCA can help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable utilization methods.
The assessment should also consider the potential for indirect environmental impacts. For instance, the energy requirements of advanced utilization techniques may lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions from power generation. Evaluating these indirect effects is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the environmental implications.
Finally, the environmental impact assessment should address the potential for accidental releases and emergency scenarios. Advanced utilization techniques must incorporate robust safety measures and emergency response plans to mitigate the environmental consequences of potential accidents or equipment failures.
Regulatory Framework for CCl4 Handling
The regulatory framework for handling carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a critical aspect of developing advanced utilization techniques for this compound. Due to its ozone-depleting properties and potential health hazards, CCl4 is subject to strict regulations globally.
At the international level, the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer plays a pivotal role in controlling CCl4 production and consumption. Signatory countries are required to phase out the use of CCl4 in various applications, with exceptions for essential uses and as feedstock for other chemical processes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates CCl4 under multiple statutes. The Clean Air Act classifies CCl4 as a hazardous air pollutant, mandating stringent emission controls. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) imposes reporting requirements for manufacturers and importers of CCl4. Additionally, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) governs the disposal of CCl4 waste.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes strict controls on CCl4 use and handling. Companies must register CCl4 with the European Chemicals Agency and comply with specific safety and environmental standards.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S., set permissible exposure limits for workers handling CCl4. These regulations require employers to implement engineering controls, provide personal protective equipment, and conduct regular monitoring of workplace air quality.
Transportation of CCl4 is regulated under various dangerous goods codes, including the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These regulations specify packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements for the safe transport of CCl4.
Developing advanced CCl4 utilization techniques must account for these regulatory constraints. Researchers and industry professionals must design processes that minimize CCl4 emissions, ensure worker safety, and comply with waste management regulations. This may involve exploring closed-loop systems, developing more efficient catalysts for CCl4 conversion, or investigating alternative compounds that can replace CCl4 in certain applications.
Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in pollution control technologies, safety equipment, and personnel training. However, adherence to these standards is essential for the sustainable development of CCl4 utilization techniques and for maintaining environmental and public health safeguards.
At the international level, the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer plays a pivotal role in controlling CCl4 production and consumption. Signatory countries are required to phase out the use of CCl4 in various applications, with exceptions for essential uses and as feedstock for other chemical processes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates CCl4 under multiple statutes. The Clean Air Act classifies CCl4 as a hazardous air pollutant, mandating stringent emission controls. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) imposes reporting requirements for manufacturers and importers of CCl4. Additionally, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) governs the disposal of CCl4 waste.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes strict controls on CCl4 use and handling. Companies must register CCl4 with the European Chemicals Agency and comply with specific safety and environmental standards.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S., set permissible exposure limits for workers handling CCl4. These regulations require employers to implement engineering controls, provide personal protective equipment, and conduct regular monitoring of workplace air quality.
Transportation of CCl4 is regulated under various dangerous goods codes, including the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These regulations specify packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements for the safe transport of CCl4.
Developing advanced CCl4 utilization techniques must account for these regulatory constraints. Researchers and industry professionals must design processes that minimize CCl4 emissions, ensure worker safety, and comply with waste management regulations. This may involve exploring closed-loop systems, developing more efficient catalysts for CCl4 conversion, or investigating alternative compounds that can replace CCl4 in certain applications.
Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in pollution control technologies, safety equipment, and personnel training. However, adherence to these standards is essential for the sustainable development of CCl4 utilization techniques and for maintaining environmental and public health safeguards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!