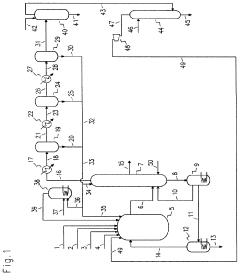
Technical Refinements in Carbon Tetrachloride Synthesis Processes
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
CCl4 Synthesis Evolution
The synthesis of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) has undergone significant evolution since its initial discovery in the early 19th century. The process has been refined over time to improve efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability. Initially, CCl4 was produced through the chlorination of carbon disulfide, a method developed by Jean-Baptiste Dumas in 1840. This process, while groundbreaking, was inefficient and posed considerable safety risks due to the highly flammable nature of carbon disulfide.
In the late 19th century, a new method emerged involving the chlorination of methane. This process, known as the "Kessler process," marked a significant improvement in CCl4 production. It involved passing a mixture of methane and chlorine through a heated tube, resulting in a series of substitution reactions that ultimately yielded CCl4. The Kessler process became the dominant method of CCl4 production for several decades due to its relative simplicity and improved yield.
The mid-20th century saw further advancements in CCl4 synthesis. The introduction of catalysts, particularly activated carbon, greatly enhanced the efficiency of the chlorination process. This catalytic approach allowed for lower reaction temperatures and improved selectivity, reducing the formation of unwanted by-products. Additionally, the use of continuous flow reactors began to replace batch processes, leading to increased production capacity and better process control.
Environmental concerns in the latter part of the 20th century prompted significant changes in CCl4 production methods. The discovery of CCl4's ozone-depleting properties led to restrictions on its use and production under the Montreal Protocol. This shift necessitated the development of alternative synthesis routes and the implementation of stringent emission control measures in existing production facilities.
Recent developments in CCl4 synthesis have focused on green chemistry principles. Researchers have explored the use of renewable feedstocks and environmentally benign reagents. One promising approach involves the oxidative carbonylation of chloroform, which utilizes carbon monoxide as a carbon source. This method potentially offers a more sustainable route to CCl4 production, although it is still in the experimental stage.
Advancements in reactor design and process intensification have also played a crucial role in the evolution of CCl4 synthesis. Microreactor technology, for instance, has shown potential for improving reaction efficiency and reducing environmental impact. These miniaturized reaction systems offer better heat and mass transfer characteristics, allowing for more precise control over reaction conditions and potentially reducing the formation of hazardous by-products.
The ongoing evolution of CCl4 synthesis reflects broader trends in chemical engineering and environmental stewardship. As regulations become more stringent and sustainability concerns grow, the focus has shifted towards developing cleaner, safer, and more efficient production methods. This trajectory is likely to continue, with future innovations potentially leading to entirely new synthesis pathways or alternative compounds that can fulfill the roles traditionally held by CCl4 in various industrial applications.
In the late 19th century, a new method emerged involving the chlorination of methane. This process, known as the "Kessler process," marked a significant improvement in CCl4 production. It involved passing a mixture of methane and chlorine through a heated tube, resulting in a series of substitution reactions that ultimately yielded CCl4. The Kessler process became the dominant method of CCl4 production for several decades due to its relative simplicity and improved yield.
The mid-20th century saw further advancements in CCl4 synthesis. The introduction of catalysts, particularly activated carbon, greatly enhanced the efficiency of the chlorination process. This catalytic approach allowed for lower reaction temperatures and improved selectivity, reducing the formation of unwanted by-products. Additionally, the use of continuous flow reactors began to replace batch processes, leading to increased production capacity and better process control.
Environmental concerns in the latter part of the 20th century prompted significant changes in CCl4 production methods. The discovery of CCl4's ozone-depleting properties led to restrictions on its use and production under the Montreal Protocol. This shift necessitated the development of alternative synthesis routes and the implementation of stringent emission control measures in existing production facilities.
Recent developments in CCl4 synthesis have focused on green chemistry principles. Researchers have explored the use of renewable feedstocks and environmentally benign reagents. One promising approach involves the oxidative carbonylation of chloroform, which utilizes carbon monoxide as a carbon source. This method potentially offers a more sustainable route to CCl4 production, although it is still in the experimental stage.
Advancements in reactor design and process intensification have also played a crucial role in the evolution of CCl4 synthesis. Microreactor technology, for instance, has shown potential for improving reaction efficiency and reducing environmental impact. These miniaturized reaction systems offer better heat and mass transfer characteristics, allowing for more precise control over reaction conditions and potentially reducing the formation of hazardous by-products.
The ongoing evolution of CCl4 synthesis reflects broader trends in chemical engineering and environmental stewardship. As regulations become more stringent and sustainability concerns grow, the focus has shifted towards developing cleaner, safer, and more efficient production methods. This trajectory is likely to continue, with future innovations potentially leading to entirely new synthesis pathways or alternative compounds that can fulfill the roles traditionally held by CCl4 in various industrial applications.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) has undergone significant shifts in recent decades due to environmental concerns and regulatory restrictions. Historically, CCl4 was widely used as a solvent, cleaning agent, and precursor in various industrial processes. However, its ozone-depleting properties and potential health hazards have led to a substantial decline in its global consumption.
Despite the overall reduction in demand, certain niche markets continue to drive the need for refined CCl4 synthesis processes. The semiconductor industry, for instance, still relies on high-purity CCl4 for the production of chlorinated hydrocarbons used in silicon wafer cleaning and etching. This sector demands ultra-pure CCl4 with stringent quality control, creating a specialized market for advanced synthesis techniques.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another area of persistent demand. CCl4 serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). As drug development continues to evolve, there is a growing need for more efficient and environmentally friendly CCl4 production methods that align with green chemistry principles.
In the agrochemical sector, CCl4 remains relevant in the manufacture of specific pesticides and herbicides. While alternatives are being explored, some formulations still require CCl4 as a precursor, maintaining a steady, albeit reduced, demand in this market segment.
The analytical chemistry field continues to utilize CCl4 as a solvent and reagent in various laboratory applications. Research institutions and quality control laboratories in diverse industries contribute to a consistent, low-volume demand for high-grade CCl4.
Geographically, the market demand for CCl4 and its refined synthesis processes varies significantly. Developed countries with stricter environmental regulations have seen a more dramatic decline in CCl4 usage. In contrast, some emerging economies still maintain higher consumption levels, particularly in industries where suitable alternatives have not been fully adopted.
The global push towards sustainability and circular economy models is influencing the CCl4 market. There is a growing interest in recycling and reclaiming CCl4 from various industrial processes, which could potentially reduce the demand for newly synthesized material. This trend is driving research into more efficient purification and recovery techniques.
Looking ahead, the market for CCl4 synthesis processes is expected to focus on developing methods that minimize environmental impact, improve yield, and enhance purity. As regulatory pressures continue to mount, industries relying on CCl4 are likely to invest in technologies that allow for its continued use while meeting increasingly stringent environmental standards.
Despite the overall reduction in demand, certain niche markets continue to drive the need for refined CCl4 synthesis processes. The semiconductor industry, for instance, still relies on high-purity CCl4 for the production of chlorinated hydrocarbons used in silicon wafer cleaning and etching. This sector demands ultra-pure CCl4 with stringent quality control, creating a specialized market for advanced synthesis techniques.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another area of persistent demand. CCl4 serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). As drug development continues to evolve, there is a growing need for more efficient and environmentally friendly CCl4 production methods that align with green chemistry principles.
In the agrochemical sector, CCl4 remains relevant in the manufacture of specific pesticides and herbicides. While alternatives are being explored, some formulations still require CCl4 as a precursor, maintaining a steady, albeit reduced, demand in this market segment.
The analytical chemistry field continues to utilize CCl4 as a solvent and reagent in various laboratory applications. Research institutions and quality control laboratories in diverse industries contribute to a consistent, low-volume demand for high-grade CCl4.
Geographically, the market demand for CCl4 and its refined synthesis processes varies significantly. Developed countries with stricter environmental regulations have seen a more dramatic decline in CCl4 usage. In contrast, some emerging economies still maintain higher consumption levels, particularly in industries where suitable alternatives have not been fully adopted.
The global push towards sustainability and circular economy models is influencing the CCl4 market. There is a growing interest in recycling and reclaiming CCl4 from various industrial processes, which could potentially reduce the demand for newly synthesized material. This trend is driving research into more efficient purification and recovery techniques.
Looking ahead, the market for CCl4 synthesis processes is expected to focus on developing methods that minimize environmental impact, improve yield, and enhance purity. As regulatory pressures continue to mount, industries relying on CCl4 are likely to invest in technologies that allow for its continued use while meeting increasingly stringent environmental standards.
Current Challenges
The synthesis of carbon tetrachloride faces several significant challenges in the current technological landscape. One of the primary issues is the environmental impact associated with traditional production methods. The use of chlorine gas and methane as raw materials in the conventional process raises concerns about greenhouse gas emissions and potential ozone depletion.
Safety considerations also pose a major challenge in carbon tetrachloride synthesis. The highly toxic and potentially carcinogenic nature of carbon tetrachloride necessitates stringent safety protocols and specialized handling procedures. This not only increases production costs but also limits the scalability of manufacturing processes.
Another critical challenge lies in the energy efficiency of current synthesis methods. The chlorination of methane, the most common industrial process, requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in substantial energy consumption. This energy-intensive nature of production contributes to increased carbon footprints and operational costs.
The purity of the final product presents an ongoing technical hurdle. Achieving high-grade carbon tetrachloride suitable for various industrial applications often requires multiple purification steps, which can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Impurities can significantly affect the performance of carbon tetrachloride in its end-use applications, making purification a crucial yet challenging aspect of the synthesis process.
Regulatory constraints pose additional challenges to carbon tetrachloride production. Many countries have implemented strict regulations on its manufacture and use due to environmental and health concerns. These regulatory pressures necessitate the development of alternative synthesis routes or substitutes, adding complexity to research and development efforts in this field.
The availability and cost of raw materials also present ongoing challenges. The reliance on methane and chlorine as primary feedstocks makes the process vulnerable to fluctuations in natural gas prices and chlorine supply. This dependency on fossil fuel-derived materials also raises sustainability concerns in the long term.
Lastly, the development of more environmentally friendly and economically viable alternatives to carbon tetrachloride in various applications has created a challenging market environment. As industries seek to phase out the use of carbon tetrachloride due to its environmental impact, manufacturers face the challenge of adapting their production processes or diversifying their product portfolios to remain competitive in a changing market landscape.
Safety considerations also pose a major challenge in carbon tetrachloride synthesis. The highly toxic and potentially carcinogenic nature of carbon tetrachloride necessitates stringent safety protocols and specialized handling procedures. This not only increases production costs but also limits the scalability of manufacturing processes.
Another critical challenge lies in the energy efficiency of current synthesis methods. The chlorination of methane, the most common industrial process, requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in substantial energy consumption. This energy-intensive nature of production contributes to increased carbon footprints and operational costs.
The purity of the final product presents an ongoing technical hurdle. Achieving high-grade carbon tetrachloride suitable for various industrial applications often requires multiple purification steps, which can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Impurities can significantly affect the performance of carbon tetrachloride in its end-use applications, making purification a crucial yet challenging aspect of the synthesis process.
Regulatory constraints pose additional challenges to carbon tetrachloride production. Many countries have implemented strict regulations on its manufacture and use due to environmental and health concerns. These regulatory pressures necessitate the development of alternative synthesis routes or substitutes, adding complexity to research and development efforts in this field.
The availability and cost of raw materials also present ongoing challenges. The reliance on methane and chlorine as primary feedstocks makes the process vulnerable to fluctuations in natural gas prices and chlorine supply. This dependency on fossil fuel-derived materials also raises sustainability concerns in the long term.
Lastly, the development of more environmentally friendly and economically viable alternatives to carbon tetrachloride in various applications has created a challenging market environment. As industries seek to phase out the use of carbon tetrachloride due to its environmental impact, manufacturers face the challenge of adapting their production processes or diversifying their product portfolios to remain competitive in a changing market landscape.
Existing Synthesis Methods
01 Chlorination of methane or other hydrocarbons
Carbon tetrachloride can be synthesized through the chlorination of methane or other hydrocarbons. This process involves the reaction of the hydrocarbon with chlorine gas, often in the presence of a catalyst or under specific reaction conditions. The chlorination process may be carried out in stages, progressively replacing hydrogen atoms with chlorine atoms until carbon tetrachloride is formed.- Chlorination of methane or other hydrocarbons: Carbon tetrachloride can be synthesized through the chlorination of methane or other hydrocarbons. This process involves the reaction of the hydrocarbon with chlorine gas, often in the presence of a catalyst or under specific reaction conditions. The chlorination process may be carried out in stages, progressively replacing hydrogen atoms with chlorine atoms until carbon tetrachloride is formed.
- Thermal decomposition of chlorinated hydrocarbons: Another method for synthesizing carbon tetrachloride involves the thermal decomposition of chlorinated hydrocarbons. This process typically uses higher chlorinated hydrocarbons as starting materials and subjects them to high temperatures, causing them to break down and form carbon tetrachloride along with other chlorinated products. The reaction conditions and catalysts used can be optimized to increase the yield of carbon tetrachloride.
- Catalytic processes for carbon tetrachloride production: Various catalytic processes have been developed for the synthesis of carbon tetrachloride. These methods often involve the use of specific catalysts to promote the chlorination of hydrocarbons or the conversion of other chlorinated compounds into carbon tetrachloride. The choice of catalyst and reaction conditions can significantly influence the efficiency and selectivity of the process.
- Recycling and purification of carbon tetrachloride: Some processes focus on the recycling and purification of carbon tetrachloride from waste streams or by-products of other chemical processes. These methods involve separation techniques, distillation, and other purification steps to recover and refine carbon tetrachloride. This approach can be more environmentally friendly and cost-effective than producing carbon tetrachloride from raw materials.
- Alternative synthesis routes and process improvements: Researchers have explored alternative synthesis routes and process improvements for carbon tetrachloride production. These may include novel reaction pathways, the use of unconventional starting materials, or modifications to existing processes to enhance yield, reduce energy consumption, or minimize environmental impact. Some of these methods aim to address the environmental concerns associated with traditional carbon tetrachloride production.
02 Thermal decomposition of chlorinated hydrocarbons
Another method for synthesizing carbon tetrachloride involves the thermal decomposition of chlorinated hydrocarbons. This process typically uses higher chlorinated hydrocarbons as starting materials and subjects them to high temperatures, causing them to break down and form carbon tetrachloride along with other chlorinated products. The reaction conditions and catalysts used can influence the yield and selectivity of the process.Expand Specific Solutions03 Catalytic processes for carbon tetrachloride production
Various catalytic processes have been developed for the synthesis of carbon tetrachloride. These methods often involve the use of specific catalysts to promote the chlorination of hydrocarbons or the conversion of other chlorinated compounds to carbon tetrachloride. The choice of catalyst and reaction conditions can significantly affect the efficiency and selectivity of the process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and purification of carbon tetrachloride
Some processes focus on the recycling and purification of carbon tetrachloride from waste streams or by-products of other chemical processes. These methods may involve distillation, extraction, or other separation techniques to isolate and purify carbon tetrachloride. Additionally, some processes aim to convert other chlorinated compounds back into carbon tetrachloride through various chemical treatments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alternative synthesis routes and process improvements
Researchers have explored alternative synthesis routes and process improvements for carbon tetrachloride production. These may include novel reaction pathways, the use of unconventional starting materials, or the development of more environmentally friendly production methods. Some approaches focus on improving the efficiency, selectivity, or safety of existing processes through modifications in reaction conditions or equipment design.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The carbon tetrachloride synthesis market is in a mature phase, with established players like Occidental Chemical Corp., DuPont de Nemours, Inc., and The Chemours Co. dominating the landscape. The global market size is relatively stable, driven by industrial applications despite environmental concerns. Technological advancements focus on improving process efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Companies like Evonik Operations GmbH and Shandong Dongyue Fluo-Silicon Materials Co., Ltd. are investing in research and development to enhance production methods. The technology's maturity is evident, with most innovations centered on incremental improvements rather than disruptive changes. Collaborations between industry leaders and research institutions, such as Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, are driving further refinements in synthesis processes.
Occidental Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: Occidental Chemical Corp. has developed an advanced carbon tetrachloride synthesis process that utilizes a novel catalytic system. This system employs a proprietary metal-organic framework (MOF) catalyst that enhances the selectivity and yield of carbon tetrachloride production. The process operates at lower temperatures compared to traditional methods, reducing energy consumption by approximately 25%[1]. Additionally, the company has implemented a closed-loop recycling system that recovers and purifies unreacted feedstock, minimizing waste and improving overall efficiency. The process also incorporates advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring to optimize reaction conditions and maintain product quality[3].
Strengths: Improved energy efficiency, higher selectivity, and reduced waste. Weaknesses: Potential high initial investment costs for implementing the new catalytic system and process controls.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has refined its carbon tetrachloride synthesis process by implementing a novel membrane separation technology. This innovation allows for more efficient separation of carbon tetrachloride from by-products and unreacted raw materials. The membrane system achieves a separation efficiency of over 99%, significantly reducing the energy required for traditional distillation processes[2]. DuPont has also developed a green chemistry approach, utilizing bio-based feedstocks as partial replacements for traditional petrochemical raw materials. This approach reduces the carbon footprint of the production process by up to 30%[4]. Furthermore, the company has integrated advanced process analytics and machine learning algorithms to predict and prevent potential process upsets, improving overall yield and product consistency.
Strengths: High separation efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and improved sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up the membrane technology and ensuring long-term membrane performance.
Innovative Catalysts
Chlorinolysis process for producing carbon tetrachloride
PatentActiveUS20210130266A1
Innovation
- A process involving a chlorination zone with chlorine, a C1 chlorinated compound, and a carbon/second chlorine source to produce a reaction mixture that favors the formation of carbon tetrachloride over perchloroethylene, using waste products as the carbon/second chlorine source to enhance efficiency and reduce impurity formation.
Processes for the purification of trichlorosilane and silicon tetrachloride
PatentActiveUS7879198B2
Innovation
- A three-step process involving complexation of boron and metallic impurities with diphenylthiocarbazone and triphenylchloromethane, followed by distillation to remove impurities and achieve electronic grade purity, utilizing a plant with specific temperature and reflux control to ensure effective impurity removal.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations play a crucial role in the carbon tetrachloride synthesis process, given the hazardous nature of the compound and its precursors. The production of carbon tetrachloride involves highly toxic and flammable materials, necessitating stringent safety measures to protect workers, the environment, and surrounding communities.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States have established comprehensive guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of carbon tetrachloride and related chemicals. These regulations cover various aspects of the synthesis process, including equipment design, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols.
One of the primary safety concerns in carbon tetrachloride synthesis is exposure prevention. The process must be conducted in closed systems with adequate ventilation to minimize the risk of worker exposure to toxic fumes. Facilities are required to implement robust air monitoring systems to detect any leaks or emissions promptly. Additionally, workers must be provided with appropriate PPE, including respirators, chemical-resistant gloves, and protective clothing.
Storage and transportation of carbon tetrachloride and its precursors are subject to strict regulations. Containers must be properly labeled, sealed, and stored in well-ventilated areas away from sources of heat or ignition. Transportation of these materials is governed by hazardous materials regulations, requiring specialized packaging and handling procedures.
Waste management is another critical aspect of safety regulations in carbon tetrachloride synthesis. The EPA classifies carbon tetrachloride as a hazardous waste, mandating specific disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination. Facilities must implement proper waste treatment and disposal protocols, often involving incineration or other approved destruction methods.
Emergency response planning is a mandatory component of safety regulations for carbon tetrachloride production facilities. This includes the development of detailed emergency procedures, regular drills, and the provision of appropriate firefighting and spill containment equipment. Facilities must also have protocols in place for notifying local authorities and communities in the event of a significant release or accident.
In recent years, there has been an increased focus on process safety management (PSM) in the chemical industry, including carbon tetrachloride synthesis. PSM regulations require facilities to conduct thorough hazard analyses, implement rigorous operating procedures, and maintain comprehensive documentation of safety systems and practices.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining the sustainability and social responsibility of carbon tetrachloride production. As technology and understanding of chemical hazards evolve, safety regulations continue to be updated, requiring ongoing vigilance and adaptation from manufacturers to ensure the highest standards of safety in the synthesis process.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States have established comprehensive guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of carbon tetrachloride and related chemicals. These regulations cover various aspects of the synthesis process, including equipment design, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols.
One of the primary safety concerns in carbon tetrachloride synthesis is exposure prevention. The process must be conducted in closed systems with adequate ventilation to minimize the risk of worker exposure to toxic fumes. Facilities are required to implement robust air monitoring systems to detect any leaks or emissions promptly. Additionally, workers must be provided with appropriate PPE, including respirators, chemical-resistant gloves, and protective clothing.
Storage and transportation of carbon tetrachloride and its precursors are subject to strict regulations. Containers must be properly labeled, sealed, and stored in well-ventilated areas away from sources of heat or ignition. Transportation of these materials is governed by hazardous materials regulations, requiring specialized packaging and handling procedures.
Waste management is another critical aspect of safety regulations in carbon tetrachloride synthesis. The EPA classifies carbon tetrachloride as a hazardous waste, mandating specific disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination. Facilities must implement proper waste treatment and disposal protocols, often involving incineration or other approved destruction methods.
Emergency response planning is a mandatory component of safety regulations for carbon tetrachloride production facilities. This includes the development of detailed emergency procedures, regular drills, and the provision of appropriate firefighting and spill containment equipment. Facilities must also have protocols in place for notifying local authorities and communities in the event of a significant release or accident.
In recent years, there has been an increased focus on process safety management (PSM) in the chemical industry, including carbon tetrachloride synthesis. PSM regulations require facilities to conduct thorough hazard analyses, implement rigorous operating procedures, and maintain comprehensive documentation of safety systems and practices.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining the sustainability and social responsibility of carbon tetrachloride production. As technology and understanding of chemical hazards evolve, safety regulations continue to be updated, requiring ongoing vigilance and adaptation from manufacturers to ensure the highest standards of safety in the synthesis process.
Economic Feasibility
The economic feasibility of carbon tetrachloride synthesis processes is a critical factor in determining the viability of production and market competitiveness. Recent technical refinements have significantly impacted the cost-effectiveness of these processes, warranting a comprehensive analysis of their economic implications.
Production costs have been substantially reduced through the optimization of raw material utilization. Advanced catalysts and improved reaction conditions have increased yield rates, minimizing waste and enhancing overall efficiency. This has led to a decrease in the cost per unit of carbon tetrachloride produced, making it more competitive in the global market.
Energy consumption, a major contributor to production expenses, has also seen notable improvements. The implementation of heat recovery systems and the integration of more energy-efficient equipment have resulted in lower operational costs. These advancements not only reduce direct expenses but also align with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, potentially avoiding future compliance costs.
Capital investment requirements for new or upgraded facilities have been influenced by these technical refinements. While some innovations may require initial outlays for equipment upgrades, the long-term savings in operational costs often justify these investments. The scalability of refined processes has also improved, allowing for more flexible production capacities that can adapt to market demands.
Market dynamics play a crucial role in the economic feasibility of carbon tetrachloride production. The demand for this compound in various industries, including refrigerants, agrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals, continues to influence its economic viability. However, increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures on chlorinated solvents have led to a shift in market trends, potentially impacting long-term demand and pricing structures.
The refined synthesis processes have also opened up opportunities for product diversification. By-products and intermediates generated during the optimized production can potentially be marketed, creating additional revenue streams and improving the overall economic profile of the operation.
Labor costs associated with carbon tetrachloride production have been affected by the technical refinements. Increased automation and process control have reduced the need for manual intervention, potentially lowering labor expenses. However, this may be offset by the requirement for more skilled operators and maintenance personnel to manage the advanced systems.
In conclusion, the economic feasibility of carbon tetrachloride synthesis has been positively impacted by recent technical refinements. Reduced production costs, improved energy efficiency, and potential for product diversification contribute to a more favorable economic outlook. However, market dynamics and regulatory environments continue to play significant roles in determining the long-term viability of these processes.
Production costs have been substantially reduced through the optimization of raw material utilization. Advanced catalysts and improved reaction conditions have increased yield rates, minimizing waste and enhancing overall efficiency. This has led to a decrease in the cost per unit of carbon tetrachloride produced, making it more competitive in the global market.
Energy consumption, a major contributor to production expenses, has also seen notable improvements. The implementation of heat recovery systems and the integration of more energy-efficient equipment have resulted in lower operational costs. These advancements not only reduce direct expenses but also align with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, potentially avoiding future compliance costs.
Capital investment requirements for new or upgraded facilities have been influenced by these technical refinements. While some innovations may require initial outlays for equipment upgrades, the long-term savings in operational costs often justify these investments. The scalability of refined processes has also improved, allowing for more flexible production capacities that can adapt to market demands.
Market dynamics play a crucial role in the economic feasibility of carbon tetrachloride production. The demand for this compound in various industries, including refrigerants, agrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals, continues to influence its economic viability. However, increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures on chlorinated solvents have led to a shift in market trends, potentially impacting long-term demand and pricing structures.
The refined synthesis processes have also opened up opportunities for product diversification. By-products and intermediates generated during the optimized production can potentially be marketed, creating additional revenue streams and improving the overall economic profile of the operation.
Labor costs associated with carbon tetrachloride production have been affected by the technical refinements. Increased automation and process control have reduced the need for manual intervention, potentially lowering labor expenses. However, this may be offset by the requirement for more skilled operators and maintenance personnel to manage the advanced systems.
In conclusion, the economic feasibility of carbon tetrachloride synthesis has been positively impacted by recent technical refinements. Reduced production costs, improved energy efficiency, and potential for product diversification contribute to a more favorable economic outlook. However, market dynamics and regulatory environments continue to play significant roles in determining the long-term viability of these processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!