How to Elevate Construction Project Durability with Kevlar?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Kevlar in Construction: Background and Objectives
Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont in the 1960s, has revolutionized various industries with its exceptional properties. In the construction sector, Kevlar's potential to enhance project durability has gained significant attention in recent years. The evolution of construction materials has been driven by the need for stronger, lighter, and more durable alternatives to traditional options.
The construction industry faces ongoing challenges related to structural integrity, longevity, and resistance to environmental factors. As urbanization accelerates and infrastructure demands increase, there is a growing emphasis on developing innovative materials that can withstand extreme conditions and extend the lifespan of buildings and structures. Kevlar, with its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to various forms of degradation, presents a promising solution to these challenges.
The primary objective of incorporating Kevlar into construction projects is to elevate durability significantly. This encompasses improving resistance to wear and tear, enhancing structural integrity, and extending the overall lifespan of buildings and infrastructure. By integrating Kevlar into construction materials and techniques, the industry aims to create more resilient structures that can withstand environmental stressors, reduce maintenance requirements, and ultimately lower long-term costs.
Kevlar's unique properties make it particularly suitable for addressing specific durability concerns in construction. Its high tensile strength, which is five times stronger than steel on an equal-weight basis, offers potential for reinforcing concrete structures, enhancing the performance of composite materials, and improving the durability of protective coatings. Additionally, Kevlar's resistance to heat, chemicals, and fatigue makes it an attractive option for applications in harsh environments or areas prone to natural disasters.
The technological trajectory of Kevlar in construction is closely linked to advancements in material science and engineering. As research progresses, new formulations and applications of Kevlar are being explored to optimize its performance in various construction contexts. This includes developing Kevlar-reinforced concrete, creating hybrid materials that combine Kevlar with other high-performance fibers, and innovating new construction techniques that leverage Kevlar's unique properties.
Understanding the background and objectives of Kevlar in construction is crucial for identifying potential breakthroughs and areas for further research. The industry's focus on durability aligns with broader trends towards sustainability and resilience in the built environment. By harnessing the capabilities of Kevlar, construction professionals aim to create structures that not only meet current standards but also anticipate future challenges and demands.
The construction industry faces ongoing challenges related to structural integrity, longevity, and resistance to environmental factors. As urbanization accelerates and infrastructure demands increase, there is a growing emphasis on developing innovative materials that can withstand extreme conditions and extend the lifespan of buildings and structures. Kevlar, with its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to various forms of degradation, presents a promising solution to these challenges.
The primary objective of incorporating Kevlar into construction projects is to elevate durability significantly. This encompasses improving resistance to wear and tear, enhancing structural integrity, and extending the overall lifespan of buildings and infrastructure. By integrating Kevlar into construction materials and techniques, the industry aims to create more resilient structures that can withstand environmental stressors, reduce maintenance requirements, and ultimately lower long-term costs.
Kevlar's unique properties make it particularly suitable for addressing specific durability concerns in construction. Its high tensile strength, which is five times stronger than steel on an equal-weight basis, offers potential for reinforcing concrete structures, enhancing the performance of composite materials, and improving the durability of protective coatings. Additionally, Kevlar's resistance to heat, chemicals, and fatigue makes it an attractive option for applications in harsh environments or areas prone to natural disasters.
The technological trajectory of Kevlar in construction is closely linked to advancements in material science and engineering. As research progresses, new formulations and applications of Kevlar are being explored to optimize its performance in various construction contexts. This includes developing Kevlar-reinforced concrete, creating hybrid materials that combine Kevlar with other high-performance fibers, and innovating new construction techniques that leverage Kevlar's unique properties.
Understanding the background and objectives of Kevlar in construction is crucial for identifying potential breakthroughs and areas for further research. The industry's focus on durability aligns with broader trends towards sustainability and resilience in the built environment. By harnessing the capabilities of Kevlar, construction professionals aim to create structures that not only meet current standards but also anticipate future challenges and demands.
Market Analysis for Kevlar-Enhanced Construction Materials
The market for Kevlar-enhanced construction materials has shown significant growth potential in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-performance, durable building solutions. Kevlar, a synthetic fiber known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, has found applications beyond its traditional use in body armor and aerospace industries. In the construction sector, Kevlar-enhanced materials are gaining traction due to their ability to improve structural integrity, extend building lifespans, and enhance resistance to environmental factors.
The global construction industry, valued at approximately $11 trillion, presents a vast opportunity for Kevlar-enhanced materials. Market research indicates that the advanced construction materials segment, which includes Kevlar-based products, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by urbanization trends, infrastructure development in emerging economies, and the increasing focus on sustainable and resilient construction practices.
Kevlar-enhanced construction materials find applications in various segments of the industry. In concrete reinforcement, Kevlar fibers are used to improve tensile strength and crack resistance, leading to longer-lasting structures. The market for Kevlar-reinforced concrete is particularly strong in regions prone to seismic activity or extreme weather conditions. In roofing applications, Kevlar-enhanced membranes offer superior durability and weather resistance, addressing the growing demand for long-lasting, low-maintenance building envelopes.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market for Kevlar-enhanced construction materials, driven by rapid urbanization and large-scale infrastructure projects in countries like China and India. North America and Europe also present significant opportunities, particularly in the renovation and retrofit markets, where building owners seek to enhance the durability and performance of existing structures.
Key market drivers include the increasing focus on sustainable construction practices and the growing awareness of life-cycle costs among building owners and developers. Kevlar-enhanced materials, with their potential to extend building lifespans and reduce maintenance requirements, align well with these trends. Additionally, stringent building codes and regulations in many countries are pushing the adoption of high-performance materials, further boosting the market for Kevlar-based solutions.
However, the market faces challenges, including the higher initial cost of Kevlar-enhanced materials compared to traditional alternatives. Education and awareness among architects, engineers, and contractors about the long-term benefits of these materials remain crucial for market expansion. Furthermore, competition from other advanced materials, such as carbon fiber and high-performance polymers, poses a challenge to market growth.
In conclusion, the market for Kevlar-enhanced construction materials shows promising growth potential, driven by the need for durable, high-performance building solutions. As the construction industry increasingly prioritizes longevity and sustainability, Kevlar-based products are well-positioned to capture a growing share of the advanced materials market.
The global construction industry, valued at approximately $11 trillion, presents a vast opportunity for Kevlar-enhanced materials. Market research indicates that the advanced construction materials segment, which includes Kevlar-based products, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by urbanization trends, infrastructure development in emerging economies, and the increasing focus on sustainable and resilient construction practices.
Kevlar-enhanced construction materials find applications in various segments of the industry. In concrete reinforcement, Kevlar fibers are used to improve tensile strength and crack resistance, leading to longer-lasting structures. The market for Kevlar-reinforced concrete is particularly strong in regions prone to seismic activity or extreme weather conditions. In roofing applications, Kevlar-enhanced membranes offer superior durability and weather resistance, addressing the growing demand for long-lasting, low-maintenance building envelopes.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market for Kevlar-enhanced construction materials, driven by rapid urbanization and large-scale infrastructure projects in countries like China and India. North America and Europe also present significant opportunities, particularly in the renovation and retrofit markets, where building owners seek to enhance the durability and performance of existing structures.
Key market drivers include the increasing focus on sustainable construction practices and the growing awareness of life-cycle costs among building owners and developers. Kevlar-enhanced materials, with their potential to extend building lifespans and reduce maintenance requirements, align well with these trends. Additionally, stringent building codes and regulations in many countries are pushing the adoption of high-performance materials, further boosting the market for Kevlar-based solutions.
However, the market faces challenges, including the higher initial cost of Kevlar-enhanced materials compared to traditional alternatives. Education and awareness among architects, engineers, and contractors about the long-term benefits of these materials remain crucial for market expansion. Furthermore, competition from other advanced materials, such as carbon fiber and high-performance polymers, poses a challenge to market growth.
In conclusion, the market for Kevlar-enhanced construction materials shows promising growth potential, driven by the need for durable, high-performance building solutions. As the construction industry increasingly prioritizes longevity and sustainability, Kevlar-based products are well-positioned to capture a growing share of the advanced materials market.
Current Challenges in Kevlar Integration for Construction
The integration of Kevlar into construction projects presents several significant challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost associated with Kevlar materials. As a high-performance synthetic fiber, Kevlar's production process is complex and resource-intensive, resulting in a premium price point that can significantly impact project budgets. This cost factor often leads to hesitation among construction firms and project managers when considering Kevlar as a reinforcement material.
Another challenge lies in the limited availability and supply chain complexities of Kevlar. Unlike more traditional construction materials, Kevlar is not as readily available in large quantities, which can lead to procurement delays and potential disruptions in construction timelines. The specialized nature of Kevlar production also means that there are fewer suppliers, potentially creating bottlenecks in the supply chain.
The integration of Kevlar into existing construction practices and methodologies poses a significant technical challenge. Construction professionals and engineers need to develop new techniques and processes to effectively incorporate Kevlar into building structures. This includes understanding how Kevlar interacts with other materials, such as concrete and steel, and how it affects the overall structural integrity of buildings. The learning curve associated with these new techniques can lead to initial inefficiencies and potential resistance from traditional construction practitioners.
Furthermore, there is a lack of comprehensive long-term performance data for Kevlar in construction applications. While Kevlar has proven its durability in other industries, its behavior over extended periods in various construction environments is not yet fully understood. This knowledge gap creates uncertainty regarding the material's long-term effectiveness and potential maintenance requirements, which can deter some stakeholders from adopting Kevlar-based solutions.
Regulatory and code compliance issues also present challenges. Many existing building codes and standards do not explicitly address the use of advanced materials like Kevlar in construction. This regulatory ambiguity can lead to difficulties in obtaining necessary approvals and certifications for Kevlar-reinforced structures, potentially slowing down adoption rates and limiting its use in certain types of projects or regions.
Lastly, there are environmental considerations to address. While Kevlar itself is durable and potentially contributes to more sustainable construction through increased building longevity, its production process has environmental impacts that need to be carefully evaluated. Balancing the long-term durability benefits against the immediate environmental costs of production is a complex challenge that requires thorough life-cycle assessments and sustainability analyses.
Another challenge lies in the limited availability and supply chain complexities of Kevlar. Unlike more traditional construction materials, Kevlar is not as readily available in large quantities, which can lead to procurement delays and potential disruptions in construction timelines. The specialized nature of Kevlar production also means that there are fewer suppliers, potentially creating bottlenecks in the supply chain.
The integration of Kevlar into existing construction practices and methodologies poses a significant technical challenge. Construction professionals and engineers need to develop new techniques and processes to effectively incorporate Kevlar into building structures. This includes understanding how Kevlar interacts with other materials, such as concrete and steel, and how it affects the overall structural integrity of buildings. The learning curve associated with these new techniques can lead to initial inefficiencies and potential resistance from traditional construction practitioners.
Furthermore, there is a lack of comprehensive long-term performance data for Kevlar in construction applications. While Kevlar has proven its durability in other industries, its behavior over extended periods in various construction environments is not yet fully understood. This knowledge gap creates uncertainty regarding the material's long-term effectiveness and potential maintenance requirements, which can deter some stakeholders from adopting Kevlar-based solutions.
Regulatory and code compliance issues also present challenges. Many existing building codes and standards do not explicitly address the use of advanced materials like Kevlar in construction. This regulatory ambiguity can lead to difficulties in obtaining necessary approvals and certifications for Kevlar-reinforced structures, potentially slowing down adoption rates and limiting its use in certain types of projects or regions.
Lastly, there are environmental considerations to address. While Kevlar itself is durable and potentially contributes to more sustainable construction through increased building longevity, its production process has environmental impacts that need to be carefully evaluated. Balancing the long-term durability benefits against the immediate environmental costs of production is a complex challenge that requires thorough life-cycle assessments and sustainability analyses.
Existing Kevlar Implementation Strategies in Construction
01 Kevlar reinforcement in protective gear
Kevlar is used to enhance the durability of protective equipment such as helmets, body armor, and gloves. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance make it ideal for improving the longevity and effectiveness of safety gear in various industries and applications.- Kevlar fiber reinforcement in composites: Kevlar fibers are used to reinforce various composite materials, enhancing their durability and strength. These composites find applications in protective gear, automotive parts, and aerospace components. The incorporation of Kevlar fibers significantly improves the impact resistance and overall longevity of the composite structures.
- Surface treatment of Kevlar for improved durability: Various surface treatment methods are employed to enhance the durability of Kevlar fibers. These treatments can improve the fiber's resistance to environmental factors, increase its adhesion to matrix materials, and enhance its overall performance in composite structures. Such treatments may include chemical modifications or physical processes to alter the fiber surface properties.
- Kevlar-based protective clothing and equipment: Kevlar is extensively used in the production of durable protective clothing and equipment. This includes bulletproof vests, helmets, and other personal protective gear. The high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent cut resistance of Kevlar make it ideal for these applications, providing enhanced durability and protection against various threats.
- Kevlar in high-performance ropes and cables: Kevlar fibers are utilized in the manufacture of high-performance ropes and cables. These products exhibit exceptional strength, low weight, and resistance to environmental factors. The durability of Kevlar-based ropes and cables makes them suitable for demanding applications in marine, industrial, and recreational sectors.
- Hybrid materials incorporating Kevlar for enhanced durability: Innovative hybrid materials that combine Kevlar with other high-performance fibers or materials are being developed to further enhance durability. These hybrid structures can offer improved resistance to specific environmental factors, better overall performance, and extended lifespan compared to traditional Kevlar-only materials.
02 Kevlar composites for improved durability
Combining Kevlar with other materials to create composites can significantly enhance its durability. These composites often exhibit improved resistance to wear, tear, and environmental factors, making them suitable for use in demanding applications such as aerospace, automotive, and marine industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface treatments to enhance Kevlar durability
Various surface treatments and coatings can be applied to Kevlar fibers to improve their durability. These treatments can enhance resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and chemicals, thereby extending the lifespan of Kevlar-based products in harsh environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Kevlar fiber modifications for increased durability
Modifications to the Kevlar fiber structure or composition can lead to improved durability. These modifications may include changes in the polymer chain, introduction of additives, or alterations in the fiber production process to enhance properties such as tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Kevlar in durable textile applications
Kevlar is incorporated into textiles to create highly durable fabrics for various applications. These include cut-resistant clothing, fire-resistant garments, and high-performance sportswear. The integration of Kevlar fibers enhances the overall durability, strength, and longevity of these textile products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Kevlar-Based Construction Materials
The construction industry is experiencing a transformative phase with the integration of advanced materials like Kevlar to enhance project durability. This market is rapidly expanding, driven by increasing demand for high-performance, long-lasting structures. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with companies like Northrop Grumman Systems Corp. and Indian Institutes of Technology leading in research and development. Universities such as Donghua University and Harbin Institute of Technology are contributing significantly to the advancement of Kevlar applications in construction. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established players and innovative startups vying for market share in this growing sector.
Northrop Grumman Systems Corp.
Technical Solution: Northrop Grumman has developed a Kevlar-reinforced concrete technology for enhancing construction project durability. This innovative approach involves incorporating Kevlar fibers into concrete mixtures, significantly improving tensile strength and crack resistance. The company's method includes a proprietary fiber dispersion technique that ensures uniform distribution of Kevlar throughout the concrete matrix[1]. This results in a composite material that exhibits superior durability, impact resistance, and longevity compared to traditional concrete. The Kevlar-reinforced concrete has been successfully applied in various high-stress environments, including military installations and infrastructure projects exposed to extreme weather conditions[2].
Strengths: Exceptional tensile strength, improved crack resistance, and enhanced durability in harsh environments. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to traditional concrete, potential complexity in mixing and application processes.
Huazhong Agricultural University
Technical Solution: Researchers at Huazhong Agricultural University have developed a novel approach to incorporating Kevlar into agricultural construction projects to enhance durability. Their method involves creating a Kevlar-reinforced biocomposite material that combines the strength of Kevlar fibers with biodegradable polymers derived from agricultural waste. This eco-friendly construction material offers improved durability for agricultural structures such as greenhouses, storage facilities, and livestock housing. The university's research has shown that the Kevlar-biocomposite can withstand harsh weather conditions, resist pest infestations, and maintain structural integrity for extended periods[9]. Additionally, the material's partial biodegradability allows for reduced environmental impact at the end of its lifecycle, addressing sustainability concerns in agricultural construction[10].
Strengths: Eco-friendly solution, improved durability for agricultural structures, pest resistance. Weaknesses: Limited application outside of agricultural construction, potential higher costs compared to traditional materials.
Innovative Kevlar Composites for Structural Reinforcement
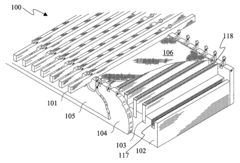
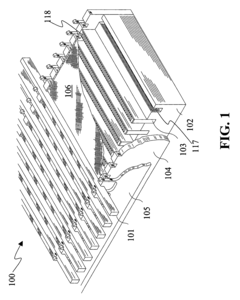
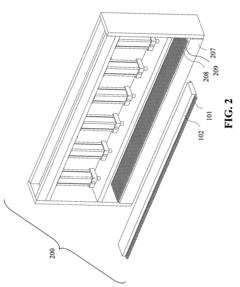
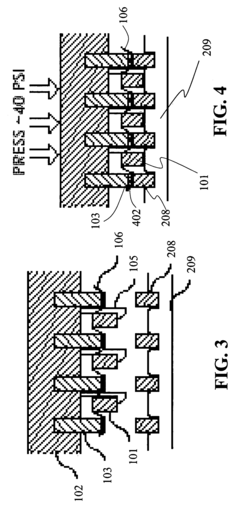
Honeycomb core composite article and method and apparatus for making same
PatentInactiveUS7083753B2
Innovation
- A process involving the use of thermo-set polymer impregnated fabrics, such as KEVLAR®, where the fabric is aligned and held by bolster plates with heating elements and pins to concentrate pressure and heat, allowing for node-by-node curing and co-curing of plies to form a honeycomb core with controlled orientation for optimal mechanical properties.
Method and device for joining and/or sealing and/or statically reinforcing two rigid surfaces or surfaces which can move towards each other
PatentWO2003074802A1
Innovation
- The method involves enlarging the surface of high-strength tapes or films, such as carbon lamellae, by mechanical or chemical means to enhance adhesive pull-off torque, allowing for better force transmission and crack bridging, thereby preventing water ingress and structural damage.
Environmental Impact of Kevlar in Construction Projects
The incorporation of Kevlar in construction projects has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. While Kevlar offers exceptional durability and strength, its production and use in construction have both positive and negative environmental impacts.
From a positive perspective, the use of Kevlar in construction can lead to more durable structures with longer lifespans. This increased longevity reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements, ultimately conserving resources and minimizing waste generation over time. Additionally, Kevlar's lightweight nature can contribute to reduced transportation emissions during the construction phase.
However, the production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical-based materials. The manufacturing of Kevlar fibers requires substantial energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and potentially exacerbating climate change concerns. Moreover, the chemicals used in Kevlar production, such as sulfuric acid and terephthaloyl chloride, pose potential risks to ecosystems if not properly managed.
The disposal of Kevlar-reinforced construction materials at the end of their lifecycle presents another environmental challenge. Kevlar is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. While recycling technologies for Kevlar exist, they are not yet widely implemented in the construction industry, leading to potential accumulation in landfills.
On the other hand, the integration of Kevlar in construction can enhance the resilience of structures against extreme weather events and natural disasters. This increased resilience can reduce the environmental impact associated with post-disaster reconstruction and waste generation.
The use of Kevlar in construction also has implications for indoor environmental quality. As a synthetic material, Kevlar does not emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or contribute to off-gassing, potentially improving indoor air quality compared to some traditional construction materials.
When considering the overall environmental footprint, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments of Kevlar-reinforced construction projects. These assessments should account for raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation, installation, use phase, and end-of-life management to provide a holistic view of the environmental impact.
To mitigate negative environmental effects, research into more sustainable production methods for Kevlar and improved recycling technologies is essential. Additionally, optimizing the use of Kevlar in construction to maximize its benefits while minimizing material consumption can help strike a balance between durability and environmental responsibility.
From a positive perspective, the use of Kevlar in construction can lead to more durable structures with longer lifespans. This increased longevity reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements, ultimately conserving resources and minimizing waste generation over time. Additionally, Kevlar's lightweight nature can contribute to reduced transportation emissions during the construction phase.
However, the production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical-based materials. The manufacturing of Kevlar fibers requires substantial energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and potentially exacerbating climate change concerns. Moreover, the chemicals used in Kevlar production, such as sulfuric acid and terephthaloyl chloride, pose potential risks to ecosystems if not properly managed.
The disposal of Kevlar-reinforced construction materials at the end of their lifecycle presents another environmental challenge. Kevlar is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. While recycling technologies for Kevlar exist, they are not yet widely implemented in the construction industry, leading to potential accumulation in landfills.
On the other hand, the integration of Kevlar in construction can enhance the resilience of structures against extreme weather events and natural disasters. This increased resilience can reduce the environmental impact associated with post-disaster reconstruction and waste generation.
The use of Kevlar in construction also has implications for indoor environmental quality. As a synthetic material, Kevlar does not emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or contribute to off-gassing, potentially improving indoor air quality compared to some traditional construction materials.
When considering the overall environmental footprint, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments of Kevlar-reinforced construction projects. These assessments should account for raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation, installation, use phase, and end-of-life management to provide a holistic view of the environmental impact.
To mitigate negative environmental effects, research into more sustainable production methods for Kevlar and improved recycling technologies is essential. Additionally, optimizing the use of Kevlar in construction to maximize its benefits while minimizing material consumption can help strike a balance between durability and environmental responsibility.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Kevlar Integration in Buildings
The integration of Kevlar into construction projects presents a complex cost-benefit scenario that requires careful analysis. Initially, the incorporation of Kevlar fibers into building materials such as concrete, steel reinforcements, or composite panels significantly increases upfront costs. Kevlar, being a high-performance synthetic fiber, commands a premium price compared to traditional construction materials. This elevated material cost can lead to a substantial increase in the overall project budget, potentially deterring some developers or property owners from adopting this technology.
However, the long-term benefits of Kevlar integration can potentially outweigh these initial expenses. The exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability of Kevlar contribute to enhanced structural integrity and longevity of buildings. This increased durability translates into reduced maintenance costs over the lifespan of the structure. Buildings reinforced with Kevlar are likely to require fewer repairs, less frequent renovations, and exhibit greater resistance to environmental degradation, potentially resulting in significant cost savings in the long run.
Furthermore, the improved resilience of Kevlar-enhanced structures against extreme weather events, seismic activities, and other natural disasters can lead to reduced insurance premiums. Insurance companies may offer more favorable rates for buildings that demonstrate superior structural integrity and disaster resistance. This ongoing cost reduction can contribute to the overall financial viability of Kevlar integration.
The energy efficiency implications of Kevlar-reinforced buildings also factor into the cost-benefit analysis. The material's lightweight nature allows for more efficient designs, potentially reducing the overall mass of the structure. This can lead to savings in foundation costs and may contribute to improved thermal insulation properties, resulting in lower heating and cooling expenses over time.
When considering the lifecycle costs of a building, the extended lifespan offered by Kevlar integration becomes a crucial factor. While traditional structures may require major renovations or even replacement after several decades, Kevlar-reinforced buildings have the potential to remain structurally sound for much longer periods. This extended service life can significantly alter the long-term economic calculations, potentially justifying the higher initial investment.
It's important to note that the cost-benefit ratio of Kevlar integration can vary depending on the specific application, building type, and local environmental conditions. High-rise structures in seismically active regions, for instance, may derive greater benefits from Kevlar reinforcement compared to low-rise buildings in stable areas. Therefore, a tailored analysis considering these factors is essential for each project to determine the economic viability of Kevlar integration.
However, the long-term benefits of Kevlar integration can potentially outweigh these initial expenses. The exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability of Kevlar contribute to enhanced structural integrity and longevity of buildings. This increased durability translates into reduced maintenance costs over the lifespan of the structure. Buildings reinforced with Kevlar are likely to require fewer repairs, less frequent renovations, and exhibit greater resistance to environmental degradation, potentially resulting in significant cost savings in the long run.
Furthermore, the improved resilience of Kevlar-enhanced structures against extreme weather events, seismic activities, and other natural disasters can lead to reduced insurance premiums. Insurance companies may offer more favorable rates for buildings that demonstrate superior structural integrity and disaster resistance. This ongoing cost reduction can contribute to the overall financial viability of Kevlar integration.
The energy efficiency implications of Kevlar-reinforced buildings also factor into the cost-benefit analysis. The material's lightweight nature allows for more efficient designs, potentially reducing the overall mass of the structure. This can lead to savings in foundation costs and may contribute to improved thermal insulation properties, resulting in lower heating and cooling expenses over time.
When considering the lifecycle costs of a building, the extended lifespan offered by Kevlar integration becomes a crucial factor. While traditional structures may require major renovations or even replacement after several decades, Kevlar-reinforced buildings have the potential to remain structurally sound for much longer periods. This extended service life can significantly alter the long-term economic calculations, potentially justifying the higher initial investment.
It's important to note that the cost-benefit ratio of Kevlar integration can vary depending on the specific application, building type, and local environmental conditions. High-rise structures in seismically active regions, for instance, may derive greater benefits from Kevlar reinforcement compared to low-rise buildings in stable areas. Therefore, a tailored analysis considering these factors is essential for each project to determine the economic viability of Kevlar integration.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!