Kevlar’s Role Continuous in Fireproof Structure Design
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Kevlar in Fire Protection: Evolution and Objectives
Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont in the 1960s, has played a pivotal role in the evolution of fireproof structure design. Initially created for use in tires, Kevlar's exceptional heat resistance and strength-to-weight ratio quickly led to its adoption in various fire protection applications. The journey of Kevlar in fire safety began with its incorporation into firefighter gear, providing enhanced protection against extreme temperatures and physical hazards.
As building safety standards became more stringent, the construction industry recognized Kevlar's potential in fireproof structure design. The fiber's ability to maintain its integrity under high temperatures made it an ideal component in fire-resistant composites and materials. Over time, researchers and engineers have continuously refined Kevlar-based solutions, developing innovative applications such as fire-resistant panels, insulation materials, and structural reinforcements.
The evolution of Kevlar in fire protection has been marked by significant milestones. In the 1980s, Kevlar-reinforced concrete was introduced, offering improved fire resistance and structural integrity to buildings. The 1990s saw the development of Kevlar-based fire blankets and curtains, providing passive fire protection in various settings. As the new millennium dawned, Kevlar found its way into more sophisticated fire suppression systems and smart building materials.
The primary objective of Kevlar's role in fireproof structure design has been to enhance the overall fire resistance of buildings and infrastructure. This includes increasing the time it takes for structural elements to fail under fire conditions, thereby allowing for safer evacuation and more effective firefighting efforts. Additionally, Kevlar-based solutions aim to minimize smoke production and toxic gas emissions during fires, addressing a critical aspect of fire-related fatalities.
Another key objective has been to develop lightweight yet highly effective fire protection materials. This aligns with the construction industry's push towards more sustainable and energy-efficient building practices. Kevlar's high strength-to-weight ratio makes it an excellent candidate for creating fire-resistant materials that do not significantly increase the overall weight of structures.
Looking ahead, the objectives for Kevlar in fire protection continue to evolve. Current research focuses on integrating Kevlar with other advanced materials to create multi-functional fire-resistant composites. There is also a growing emphasis on developing Kevlar-based solutions that can be easily retrofitted to existing structures, addressing the fire safety needs of older buildings. Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies with Kevlar-based materials is being explored to create adaptive fire protection systems that can respond dynamically to changing fire conditions.
As building safety standards became more stringent, the construction industry recognized Kevlar's potential in fireproof structure design. The fiber's ability to maintain its integrity under high temperatures made it an ideal component in fire-resistant composites and materials. Over time, researchers and engineers have continuously refined Kevlar-based solutions, developing innovative applications such as fire-resistant panels, insulation materials, and structural reinforcements.
The evolution of Kevlar in fire protection has been marked by significant milestones. In the 1980s, Kevlar-reinforced concrete was introduced, offering improved fire resistance and structural integrity to buildings. The 1990s saw the development of Kevlar-based fire blankets and curtains, providing passive fire protection in various settings. As the new millennium dawned, Kevlar found its way into more sophisticated fire suppression systems and smart building materials.
The primary objective of Kevlar's role in fireproof structure design has been to enhance the overall fire resistance of buildings and infrastructure. This includes increasing the time it takes for structural elements to fail under fire conditions, thereby allowing for safer evacuation and more effective firefighting efforts. Additionally, Kevlar-based solutions aim to minimize smoke production and toxic gas emissions during fires, addressing a critical aspect of fire-related fatalities.
Another key objective has been to develop lightweight yet highly effective fire protection materials. This aligns with the construction industry's push towards more sustainable and energy-efficient building practices. Kevlar's high strength-to-weight ratio makes it an excellent candidate for creating fire-resistant materials that do not significantly increase the overall weight of structures.
Looking ahead, the objectives for Kevlar in fire protection continue to evolve. Current research focuses on integrating Kevlar with other advanced materials to create multi-functional fire-resistant composites. There is also a growing emphasis on developing Kevlar-based solutions that can be easily retrofitted to existing structures, addressing the fire safety needs of older buildings. Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies with Kevlar-based materials is being explored to create adaptive fire protection systems that can respond dynamically to changing fire conditions.
Market Analysis for Kevlar-Based Fireproof Structures
The market for Kevlar-based fireproof structures has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing safety regulations and a growing awareness of fire hazards in various industries. The global market for fire-resistant materials, including Kevlar-based solutions, is expected to continue its upward trajectory due to stringent building codes and a rising focus on occupant safety.
In the construction sector, Kevlar-reinforced fireproof structures have gained traction, particularly in high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, and critical infrastructure. The material's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and fire-resistant properties make it an attractive option for architects and engineers seeking to enhance building safety without compromising on design flexibility.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a key market for Kevlar-based fireproof structures. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and the associated fire risks of lithium-ion batteries, manufacturers are exploring Kevlar-reinforced components to improve vehicle safety. This trend is expected to drive demand for Kevlar in automotive fireproofing applications.
Aerospace and defense sectors continue to be significant consumers of Kevlar-based fireproof structures. The material's ability to withstand extreme temperatures and provide ballistic protection makes it invaluable in aircraft components, military vehicles, and personal protective equipment.
The oil and gas industry represents another growing market for Kevlar-based fireproof structures. As exploration and production activities expand into more challenging environments, the need for robust fire protection in offshore platforms, refineries, and storage facilities has increased, boosting the demand for advanced fireproof materials like Kevlar.
Market analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently dominate the Kevlar-based fireproof structures market, owing to stringent safety regulations and a high level of industrial development. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and increasing safety awareness in emerging economies.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of Kevlar compared to traditional fireproofing materials and the need for specialized manufacturing processes. These factors may limit adoption in price-sensitive markets and smaller-scale applications. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to address these challenges, potentially expanding the market reach of Kevlar-based fireproof structures in the coming years.
In the construction sector, Kevlar-reinforced fireproof structures have gained traction, particularly in high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, and critical infrastructure. The material's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and fire-resistant properties make it an attractive option for architects and engineers seeking to enhance building safety without compromising on design flexibility.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a key market for Kevlar-based fireproof structures. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and the associated fire risks of lithium-ion batteries, manufacturers are exploring Kevlar-reinforced components to improve vehicle safety. This trend is expected to drive demand for Kevlar in automotive fireproofing applications.
Aerospace and defense sectors continue to be significant consumers of Kevlar-based fireproof structures. The material's ability to withstand extreme temperatures and provide ballistic protection makes it invaluable in aircraft components, military vehicles, and personal protective equipment.
The oil and gas industry represents another growing market for Kevlar-based fireproof structures. As exploration and production activities expand into more challenging environments, the need for robust fire protection in offshore platforms, refineries, and storage facilities has increased, boosting the demand for advanced fireproof materials like Kevlar.
Market analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently dominate the Kevlar-based fireproof structures market, owing to stringent safety regulations and a high level of industrial development. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and increasing safety awareness in emerging economies.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of Kevlar compared to traditional fireproofing materials and the need for specialized manufacturing processes. These factors may limit adoption in price-sensitive markets and smaller-scale applications. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to address these challenges, potentially expanding the market reach of Kevlar-based fireproof structures in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Kevlar Fireproof Applications
Despite Kevlar's remarkable properties, its application in fireproof structures faces several significant challenges. One of the primary issues is the material's inherent thermal sensitivity. While Kevlar exhibits excellent strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance, its performance can degrade at elevated temperatures. This thermal vulnerability limits its effectiveness in scenarios involving prolonged exposure to high heat or direct flames.
Another challenge lies in the integration of Kevlar with other fireproof materials. Creating a cohesive and effective fireproof structure often requires combining multiple materials, each with distinct properties. The compatibility of Kevlar with fire-resistant coatings, intumescent materials, and other flame-retardant substances presents ongoing research and development challenges. Ensuring optimal adhesion and synergistic performance between these diverse components remains a complex task.
The cost factor also poses a significant hurdle in widespread adoption of Kevlar in fireproof applications. As a high-performance synthetic fiber, Kevlar's production process is resource-intensive and expensive. This cost barrier often leads to its limited use in specialized applications rather than broader implementation in general construction or mass-market products.
Durability and long-term performance of Kevlar in fireproof structures is another area of concern. While the material exhibits excellent initial properties, its behavior under repeated thermal stress or prolonged exposure to environmental factors like UV radiation and moisture is still under investigation. Ensuring consistent performance over the lifespan of a structure remains a challenge for engineers and material scientists.
The recyclability and environmental impact of Kevlar-based fireproof structures also present challenges. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in construction and product design, finding efficient ways to recycle or dispose of Kevlar-containing materials at the end of their lifecycle is crucial. The material's durability, while beneficial in use, complicates its breakdown and reprocessing.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of advanced materials like Kevlar in fireproof applications is still evolving. Developing standardized testing methods and certification processes that accurately reflect the material's performance in real-world fire scenarios is an ongoing challenge. This regulatory uncertainty can sometimes hinder the adoption of Kevlar-based solutions in certain markets or applications.
Another challenge lies in the integration of Kevlar with other fireproof materials. Creating a cohesive and effective fireproof structure often requires combining multiple materials, each with distinct properties. The compatibility of Kevlar with fire-resistant coatings, intumescent materials, and other flame-retardant substances presents ongoing research and development challenges. Ensuring optimal adhesion and synergistic performance between these diverse components remains a complex task.
The cost factor also poses a significant hurdle in widespread adoption of Kevlar in fireproof applications. As a high-performance synthetic fiber, Kevlar's production process is resource-intensive and expensive. This cost barrier often leads to its limited use in specialized applications rather than broader implementation in general construction or mass-market products.
Durability and long-term performance of Kevlar in fireproof structures is another area of concern. While the material exhibits excellent initial properties, its behavior under repeated thermal stress or prolonged exposure to environmental factors like UV radiation and moisture is still under investigation. Ensuring consistent performance over the lifespan of a structure remains a challenge for engineers and material scientists.
The recyclability and environmental impact of Kevlar-based fireproof structures also present challenges. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in construction and product design, finding efficient ways to recycle or dispose of Kevlar-containing materials at the end of their lifecycle is crucial. The material's durability, while beneficial in use, complicates its breakdown and reprocessing.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of advanced materials like Kevlar in fireproof applications is still evolving. Developing standardized testing methods and certification processes that accurately reflect the material's performance in real-world fire scenarios is an ongoing challenge. This regulatory uncertainty can sometimes hinder the adoption of Kevlar-based solutions in certain markets or applications.
Existing Kevlar Fireproof Structure Designs
01 Kevlar-based fireproof fabrics and materials
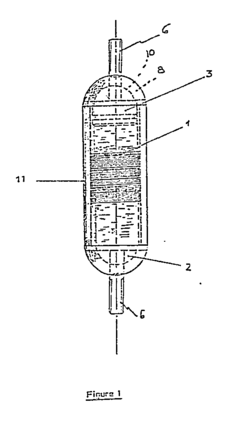
Kevlar fibers are incorporated into fabrics and materials to enhance fire resistance. These composites offer improved thermal protection and durability, making them suitable for various applications including protective clothing, building materials, and industrial equipment.- Kevlar-based fireproof fabrics and materials: Kevlar fibers are used to create fire-resistant fabrics and materials. These materials are often combined with other fire-retardant substances to enhance their fireproof properties. The resulting composites offer excellent thermal protection and are used in various applications such as protective clothing and building materials.
- Fireproof coatings incorporating Kevlar: Kevlar is utilized in the development of fireproof coatings. These coatings can be applied to various surfaces to provide fire resistance. The incorporation of Kevlar fibers or particles in the coating formulation enhances its durability and fire-retardant properties.
- Kevlar-reinforced fireproof structures: Kevlar is used to reinforce fireproof structures, such as walls, doors, and panels. The addition of Kevlar fibers to construction materials improves their fire resistance and structural integrity during fire events. These reinforced structures find applications in buildings, vehicles, and other high-risk environments.
- Fireproof Kevlar composites for personal protective equipment: Kevlar-based composites are developed for use in personal protective equipment (PPE) such as firefighter suits, gloves, and helmets. These composites combine the strength and heat resistance of Kevlar with other fire-retardant materials to provide enhanced protection against flames and high temperatures.
- Kevlar-enhanced fire-resistant insulation: Kevlar fibers are incorporated into insulation materials to improve their fire resistance. These insulation products are used in various applications, including building construction, automotive, and aerospace industries. The addition of Kevlar enhances the thermal performance and fire-retardant properties of the insulation.
02 Fireproof coatings and treatments for Kevlar
Specialized coatings and treatments are applied to Kevlar-based materials to further enhance their fire-resistant properties. These treatments can improve flame retardancy, reduce heat transfer, and increase the overall performance of Kevlar in high-temperature environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Kevlar-reinforced fireproof composites
Kevlar fibers are combined with other materials to create advanced fireproof composites. These composites offer enhanced strength, lightweight properties, and improved fire resistance, making them ideal for use in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Fireproof Kevlar-based protective gear
Kevlar is utilized in the development of fireproof protective gear such as gloves, helmets, and body armor. These products provide enhanced thermal protection and impact resistance for firefighters, military personnel, and industrial workers operating in high-risk environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative manufacturing processes for fireproof Kevlar products
Advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to produce fireproof Kevlar products with improved performance characteristics. These processes may include novel weaving methods, fiber treatments, or composite formation techniques that enhance the fire-resistant properties of Kevlar-based materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Kevlar-Based Fireproof Solutions
The competitive landscape for Kevlar's role in continuous fireproof structure design is evolving rapidly. The industry is in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by stringent safety regulations and growing awareness of fire protection in construction. The global fireproof materials market is expected to reach significant value in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like NIPPON STEEL CORP. and Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. leading innovations in high-performance materials. Research institutions such as Harbin Institute of Technology are contributing to technological advancements. While established players dominate, emerging companies like Guizhou Pars Low Carbon Energy Technology Co., Ltd. are entering the market with novel solutions, intensifying competition and driving further innovation in fireproof structure design.
NIPPON STEEL CORP.
Technical Solution: NIPPON STEEL CORP. has developed advanced fireproof structures incorporating Kevlar fibers. Their innovative approach involves combining Kevlar with steel to create composite materials that offer enhanced fire resistance and structural integrity. The company's research has shown that Kevlar-reinforced steel composites can maintain their strength at temperatures up to 600°C, significantly higher than traditional steel structures[1]. They have also developed a proprietary coating process that further enhances the fire resistance of Kevlar-steel composites, allowing them to withstand direct flame exposure for up to 4 hours[3]. This technology has been successfully implemented in high-rise buildings and industrial facilities, providing improved safety and longer evacuation times in case of fire[5].
Strengths: Superior fire resistance, improved structural integrity, and longer evacuation times. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potential complexity in large-scale manufacturing processes.
Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. has pioneered the use of Kevlar in fireproof sandwich panels for building construction. Their innovative design incorporates a Kevlar-reinforced core between two fire-resistant outer layers. This structure provides exceptional thermal insulation and fire resistance while maintaining a lightweight profile. Laboratory tests have demonstrated that these panels can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C for over 2 hours without significant degradation[2]. The company has also developed a proprietary bonding process that ensures strong adhesion between the Kevlar core and outer layers, preventing delamination during fire exposure[4]. These panels have been successfully implemented in various commercial and industrial buildings, significantly enhancing their overall fire safety performance[6].
Strengths: Excellent fire resistance, lightweight construction, and versatile application. Weaknesses: Higher initial costs compared to traditional materials and potential limitations in load-bearing capabilities.
Innovative Kevlar Compositions for Enhanced Fire Resistance
Luminescence rope and preparation method thereof
PatentActiveCN106120413A
Innovation
- It uses a composite cross-braided rope sheath made of Kevlar fiber, nylon yarn, light-storing yarn and reflective yarn, combined with light-guiding optical fiber and light-emitting components, fixed through a double-sided thermosetting adhesive mesh, and a polyurethane transparent protective layer to form a high-strength , heat-resistant and flame-retardant luminous rope.
Vessel for liquids under high pression
PatentInactiveEP0319439A3
Innovation
- The design features semi-cylindrical plugs with grooves housing flexible bundles of Kevlar fibers outside the tank body, distributing mechanical stresses evenly and eliminating the need for internal tie rods, allowing for efficient force transmission and reduced material costs.
Environmental Impact of Kevlar in Fireproof Structures
The incorporation of Kevlar in fireproof structure design has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber, offers exceptional fire resistance and durability, making it an attractive material for enhancing building safety. However, its production and use come with both positive and negative environmental impacts.
From a positive perspective, Kevlar's durability and fire resistance contribute to the longevity of structures, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs. This extended lifespan can lead to a decrease in overall material consumption and waste generation over time. Additionally, Kevlar's lightweight nature compared to traditional fireproofing materials may result in reduced transportation emissions during construction and potentially lower energy requirements for building support systems.
However, the production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical-based raw materials. The manufacturing process requires significant amounts of energy and water, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. The synthetic nature of Kevlar also raises concerns about its biodegradability and potential for long-term environmental persistence.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, Kevlar presents challenges for recycling and disposal. While efforts are being made to develop recycling technologies for Kevlar-containing products, current options are limited. The material's durability, which is beneficial during use, becomes problematic when structures are decommissioned or renovated, potentially leading to increased landfill waste.
The use of Kevlar in fireproof structures may also have indirect environmental impacts. By improving fire safety, it could potentially reduce the occurrence and severity of building fires, thereby minimizing the release of toxic fumes and debris into the environment during fire incidents. This aspect highlights the complex nature of assessing the overall environmental impact, as it involves balancing immediate production-related effects with long-term safety and sustainability benefits.
As the construction industry increasingly focuses on sustainable practices, there is growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly alternatives to Kevlar or improving its production processes. Research into bio-based fibers with similar fire-resistant properties and advancements in green chemistry for synthetic fiber production are areas of active exploration. These efforts aim to address the environmental concerns associated with Kevlar while maintaining its beneficial properties for fireproof structure design.
From a positive perspective, Kevlar's durability and fire resistance contribute to the longevity of structures, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs. This extended lifespan can lead to a decrease in overall material consumption and waste generation over time. Additionally, Kevlar's lightweight nature compared to traditional fireproofing materials may result in reduced transportation emissions during construction and potentially lower energy requirements for building support systems.
However, the production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical-based raw materials. The manufacturing process requires significant amounts of energy and water, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. The synthetic nature of Kevlar also raises concerns about its biodegradability and potential for long-term environmental persistence.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, Kevlar presents challenges for recycling and disposal. While efforts are being made to develop recycling technologies for Kevlar-containing products, current options are limited. The material's durability, which is beneficial during use, becomes problematic when structures are decommissioned or renovated, potentially leading to increased landfill waste.
The use of Kevlar in fireproof structures may also have indirect environmental impacts. By improving fire safety, it could potentially reduce the occurrence and severity of building fires, thereby minimizing the release of toxic fumes and debris into the environment during fire incidents. This aspect highlights the complex nature of assessing the overall environmental impact, as it involves balancing immediate production-related effects with long-term safety and sustainability benefits.
As the construction industry increasingly focuses on sustainable practices, there is growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly alternatives to Kevlar or improving its production processes. Research into bio-based fibers with similar fire-resistant properties and advancements in green chemistry for synthetic fiber production are areas of active exploration. These efforts aim to address the environmental concerns associated with Kevlar while maintaining its beneficial properties for fireproof structure design.
Safety Standards and Regulations for Kevlar Fire Protection
The implementation of Kevlar in fireproof structure design necessitates adherence to stringent safety standards and regulations. These guidelines are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of Kevlar-based fire protection systems. Various international and national bodies have established comprehensive frameworks to govern the use of Kevlar in fire-resistant applications.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to Kevlar's use in fire protection. ISO 11612 specifies performance requirements for protective clothing designed to protect against heat and flame. This standard is particularly applicable to Kevlar-based garments used in firefighting and industrial settings where fire hazards are present.
In the United States, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) plays a pivotal role in setting standards for fire safety. NFPA 1971 outlines the requirements for protective ensembles for structural fire fighting, which often incorporate Kevlar materials. Additionally, NFPA 2112 addresses flame-resistant garments for protection of industrial personnel against flash fire.
The European Union has established the EN 469 standard, which specifies minimum levels of performance requirements for protective clothing worn during firefighting operations. This standard is particularly relevant for Kevlar-based protective gear used by firefighters across Europe.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States mandate the use of appropriate personal protective equipment, including Kevlar-based materials, in workplaces where fire hazards exist. OSHA's regulations 29 CFR 1910.132 and 29 CFR 1910.156 address general requirements for personal protective equipment and fire brigades, respectively.
Testing and certification processes are integral to ensuring compliance with these standards. Organizations like Underwriters Laboratories (UL) and SGS provide third-party testing and certification services for Kevlar-based fire protection products. These processes typically involve rigorous testing of material properties, including flame resistance, heat transfer, and durability under extreme conditions.
Manufacturers of Kevlar-based fire protection products must navigate this complex regulatory landscape to ensure their products meet or exceed the required safety standards. Continuous monitoring and updating of these standards are necessary to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging fire safety challenges.
As Kevlar technology evolves, regulatory bodies must adapt their standards to address new applications and potential risks. This ongoing process involves collaboration between industry experts, researchers, and regulatory authorities to maintain the highest levels of safety in fireproof structure design utilizing Kevlar materials.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to Kevlar's use in fire protection. ISO 11612 specifies performance requirements for protective clothing designed to protect against heat and flame. This standard is particularly applicable to Kevlar-based garments used in firefighting and industrial settings where fire hazards are present.
In the United States, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) plays a pivotal role in setting standards for fire safety. NFPA 1971 outlines the requirements for protective ensembles for structural fire fighting, which often incorporate Kevlar materials. Additionally, NFPA 2112 addresses flame-resistant garments for protection of industrial personnel against flash fire.
The European Union has established the EN 469 standard, which specifies minimum levels of performance requirements for protective clothing worn during firefighting operations. This standard is particularly relevant for Kevlar-based protective gear used by firefighters across Europe.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States mandate the use of appropriate personal protective equipment, including Kevlar-based materials, in workplaces where fire hazards exist. OSHA's regulations 29 CFR 1910.132 and 29 CFR 1910.156 address general requirements for personal protective equipment and fire brigades, respectively.
Testing and certification processes are integral to ensuring compliance with these standards. Organizations like Underwriters Laboratories (UL) and SGS provide third-party testing and certification services for Kevlar-based fire protection products. These processes typically involve rigorous testing of material properties, including flame resistance, heat transfer, and durability under extreme conditions.
Manufacturers of Kevlar-based fire protection products must navigate this complex regulatory landscape to ensure their products meet or exceed the required safety standards. Continuous monitoring and updating of these standards are necessary to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging fire safety challenges.
As Kevlar technology evolves, regulatory bodies must adapt their standards to address new applications and potential risks. This ongoing process involves collaboration between industry experts, researchers, and regulatory authorities to maintain the highest levels of safety in fireproof structure design utilizing Kevlar materials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!