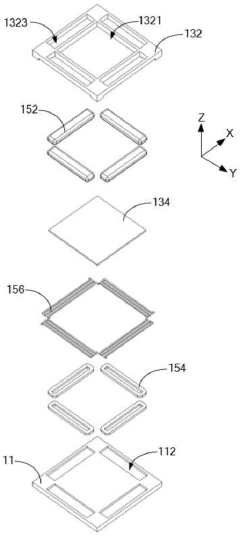
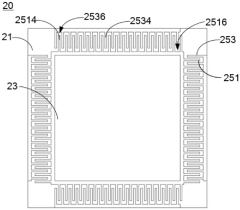
How to Implement Security Measures for ULED Displays?
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED Security Background and Objectives
Ultra-Light Emitting Diode (ULED) displays have emerged as a cutting-edge technology in the field of visual communication, offering unprecedented brightness, energy efficiency, and image quality. As these displays become increasingly prevalent in various sectors, including public spaces, transportation hubs, and critical infrastructure, the need for robust security measures has become paramount.
The evolution of ULED technology has been marked by rapid advancements in miniaturization, color reproduction, and power management. However, this progress has also introduced new vulnerabilities that malicious actors could potentially exploit. The primary objective of implementing security measures for ULED displays is to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the displayed information while ensuring the operational continuity of these systems.
One of the key drivers behind the push for enhanced security in ULED displays is the growing trend of interconnectivity and smart city initiatives. As these displays become integrated into broader networks and IoT ecosystems, they become potential entry points for cyber attacks. This interconnectedness amplifies the potential impact of security breaches, making it crucial to develop comprehensive protection strategies.
The security landscape for ULED displays encompasses both physical and digital threats. Physical security concerns include unauthorized access to display hardware, tampering with components, and environmental hazards. Digital security challenges range from data interception and manipulation to denial-of-service attacks and malware infections targeting the display's control systems.
To address these multifaceted security challenges, a holistic approach is required. This approach should combine hardware-based security features, such as tamper-resistant enclosures and secure boot processes, with software-based solutions like encryption, access control, and real-time monitoring systems. Additionally, the development of industry-wide security standards and best practices for ULED displays is essential to ensure a consistent and robust security posture across different implementations.
The objectives of implementing security measures for ULED displays are manifold. Firstly, they aim to protect the confidentiality of displayed information, preventing unauthorized access or interception. Secondly, they seek to maintain the integrity of the content, ensuring that displayed information cannot be altered or manipulated without detection. Thirdly, these measures strive to guarantee the availability of the display systems, safeguarding against disruptions that could impact critical communications or operations.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, so too must the security measures designed to protect it. This necessitates ongoing research and development efforts to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities. The ultimate goal is to create a resilient ecosystem where ULED displays can fulfill their potential as powerful communication tools while maintaining the highest standards of security and reliability.
The evolution of ULED technology has been marked by rapid advancements in miniaturization, color reproduction, and power management. However, this progress has also introduced new vulnerabilities that malicious actors could potentially exploit. The primary objective of implementing security measures for ULED displays is to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the displayed information while ensuring the operational continuity of these systems.
One of the key drivers behind the push for enhanced security in ULED displays is the growing trend of interconnectivity and smart city initiatives. As these displays become integrated into broader networks and IoT ecosystems, they become potential entry points for cyber attacks. This interconnectedness amplifies the potential impact of security breaches, making it crucial to develop comprehensive protection strategies.
The security landscape for ULED displays encompasses both physical and digital threats. Physical security concerns include unauthorized access to display hardware, tampering with components, and environmental hazards. Digital security challenges range from data interception and manipulation to denial-of-service attacks and malware infections targeting the display's control systems.
To address these multifaceted security challenges, a holistic approach is required. This approach should combine hardware-based security features, such as tamper-resistant enclosures and secure boot processes, with software-based solutions like encryption, access control, and real-time monitoring systems. Additionally, the development of industry-wide security standards and best practices for ULED displays is essential to ensure a consistent and robust security posture across different implementations.
The objectives of implementing security measures for ULED displays are manifold. Firstly, they aim to protect the confidentiality of displayed information, preventing unauthorized access or interception. Secondly, they seek to maintain the integrity of the content, ensuring that displayed information cannot be altered or manipulated without detection. Thirdly, these measures strive to guarantee the availability of the display systems, safeguarding against disruptions that could impact critical communications or operations.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, so too must the security measures designed to protect it. This necessitates ongoing research and development efforts to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities. The ultimate goal is to create a resilient ecosystem where ULED displays can fulfill their potential as powerful communication tools while maintaining the highest standards of security and reliability.
Market Demand for Secure ULED Displays
The market demand for secure ULED displays has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing concerns over data privacy and the rising importance of information security across various industries. As ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology continues to advance and find applications in diverse sectors, the need for robust security measures has become paramount.
In the consumer electronics market, there is a significant demand for secure ULED displays in smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices. Users are increasingly aware of the potential vulnerabilities in their personal devices and are seeking products that offer enhanced protection against unauthorized access and data breaches. This trend has prompted manufacturers to prioritize security features in their ULED display implementations.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a key driver for secure ULED displays. With the rapid development of connected and autonomous vehicles, in-vehicle displays have become critical components for both information display and user interaction. Automakers are investing heavily in secure ULED technologies to protect sensitive vehicle data, prevent hacking attempts, and ensure the safety of passengers.
In the healthcare sector, the demand for secure ULED displays is particularly pronounced. Medical devices, patient monitoring systems, and hospital information displays require stringent security measures to safeguard patient data and comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA. The ability of ULED displays to offer high-quality visuals while maintaining data confidentiality has made them increasingly popular in healthcare settings.
The financial services industry has shown a strong interest in secure ULED displays for use in ATMs, trading floors, and banking kiosks. These displays must be capable of protecting sensitive financial information and preventing unauthorized access, making security a top priority for institutions adopting ULED technology.
Government and military applications represent another significant market for secure ULED displays. These sectors require displays that can handle classified information and withstand sophisticated cyber attacks. The demand for ruggedized, tamper-resistant ULED displays with advanced encryption capabilities continues to grow in this space.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem expands, the need for secure displays in smart city infrastructure, industrial control systems, and public information systems is also on the rise. These applications often involve the display of sensitive data in public or semi-public environments, necessitating robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or manipulation.
The market demand for secure ULED displays is not limited to hardware solutions alone. There is a growing emphasis on integrated security systems that combine hardware protection with advanced software solutions, including biometric authentication, real-time threat detection, and secure communication protocols. This holistic approach to display security is becoming increasingly popular among enterprise customers across various industries.
In the consumer electronics market, there is a significant demand for secure ULED displays in smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices. Users are increasingly aware of the potential vulnerabilities in their personal devices and are seeking products that offer enhanced protection against unauthorized access and data breaches. This trend has prompted manufacturers to prioritize security features in their ULED display implementations.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a key driver for secure ULED displays. With the rapid development of connected and autonomous vehicles, in-vehicle displays have become critical components for both information display and user interaction. Automakers are investing heavily in secure ULED technologies to protect sensitive vehicle data, prevent hacking attempts, and ensure the safety of passengers.
In the healthcare sector, the demand for secure ULED displays is particularly pronounced. Medical devices, patient monitoring systems, and hospital information displays require stringent security measures to safeguard patient data and comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA. The ability of ULED displays to offer high-quality visuals while maintaining data confidentiality has made them increasingly popular in healthcare settings.
The financial services industry has shown a strong interest in secure ULED displays for use in ATMs, trading floors, and banking kiosks. These displays must be capable of protecting sensitive financial information and preventing unauthorized access, making security a top priority for institutions adopting ULED technology.
Government and military applications represent another significant market for secure ULED displays. These sectors require displays that can handle classified information and withstand sophisticated cyber attacks. The demand for ruggedized, tamper-resistant ULED displays with advanced encryption capabilities continues to grow in this space.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem expands, the need for secure displays in smart city infrastructure, industrial control systems, and public information systems is also on the rise. These applications often involve the display of sensitive data in public or semi-public environments, necessitating robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or manipulation.
The market demand for secure ULED displays is not limited to hardware solutions alone. There is a growing emphasis on integrated security systems that combine hardware protection with advanced software solutions, including biometric authentication, real-time threat detection, and secure communication protocols. This holistic approach to display security is becoming increasingly popular among enterprise customers across various industries.
ULED Security Challenges and Vulnerabilities
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays, while offering superior visual performance, face unique security challenges that require careful consideration. These vulnerabilities stem from both the inherent characteristics of the technology and its integration into various systems.
One of the primary security concerns for ULED displays is their susceptibility to electromagnetic interference (EMI). The high-frequency signals used to drive these displays can be intercepted and manipulated, potentially leading to unauthorized access or data theft. This vulnerability is particularly critical in environments where sensitive information is displayed, such as in military or financial institutions.
Another significant challenge lies in the potential for visual hacking. The high brightness and wide viewing angles of ULED displays make them more susceptible to shoulder surfing and other forms of visual data theft. This risk is amplified in public spaces or shared work environments where confidential information may be displayed.
The complex software systems that control ULED displays present another avenue for potential security breaches. These systems often require regular updates and patches, creating opportunities for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Furthermore, the increasing connectivity of ULED displays, particularly in smart environments, exposes them to network-based attacks.
Physical tampering is also a concern for ULED displays. The delicate nature of the ultra-thin LED components makes them potentially vulnerable to damage or manipulation. This could lead to display malfunctions or, in more severe cases, the insertion of malicious hardware components.
Data privacy is another critical vulnerability, especially for interactive ULED displays that may collect and process user information. Without proper safeguards, this data could be intercepted or misused, leading to privacy breaches and potential legal ramifications.
The power consumption patterns of ULED displays can also pose security risks. Advanced attackers might analyze power usage to infer displayed content or system activity, potentially compromising sensitive information through side-channel attacks.
Lastly, the supply chain for ULED components presents a unique set of security challenges. The global nature of the supply chain increases the risk of counterfeit components or the introduction of hardware-level vulnerabilities during the manufacturing process.
Addressing these security challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, combining hardware-level protections, robust software security measures, and comprehensive security protocols. As ULED technology continues to evolve and find new applications, ongoing research and development in security measures will be crucial to mitigate these vulnerabilities and ensure the safe and reliable use of ULED displays across various sectors.
One of the primary security concerns for ULED displays is their susceptibility to electromagnetic interference (EMI). The high-frequency signals used to drive these displays can be intercepted and manipulated, potentially leading to unauthorized access or data theft. This vulnerability is particularly critical in environments where sensitive information is displayed, such as in military or financial institutions.
Another significant challenge lies in the potential for visual hacking. The high brightness and wide viewing angles of ULED displays make them more susceptible to shoulder surfing and other forms of visual data theft. This risk is amplified in public spaces or shared work environments where confidential information may be displayed.
The complex software systems that control ULED displays present another avenue for potential security breaches. These systems often require regular updates and patches, creating opportunities for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Furthermore, the increasing connectivity of ULED displays, particularly in smart environments, exposes them to network-based attacks.
Physical tampering is also a concern for ULED displays. The delicate nature of the ultra-thin LED components makes them potentially vulnerable to damage or manipulation. This could lead to display malfunctions or, in more severe cases, the insertion of malicious hardware components.
Data privacy is another critical vulnerability, especially for interactive ULED displays that may collect and process user information. Without proper safeguards, this data could be intercepted or misused, leading to privacy breaches and potential legal ramifications.
The power consumption patterns of ULED displays can also pose security risks. Advanced attackers might analyze power usage to infer displayed content or system activity, potentially compromising sensitive information through side-channel attacks.
Lastly, the supply chain for ULED components presents a unique set of security challenges. The global nature of the supply chain increases the risk of counterfeit components or the introduction of hardware-level vulnerabilities during the manufacturing process.
Addressing these security challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, combining hardware-level protections, robust software security measures, and comprehensive security protocols. As ULED technology continues to evolve and find new applications, ongoing research and development in security measures will be crucial to mitigate these vulnerabilities and ensure the safe and reliable use of ULED displays across various sectors.
Current ULED Security Implementation Strategies
01 Security features for ULED displays
ULED displays incorporate various security features to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access. These may include encryption methods, secure boot processes, and tamper-resistant hardware designs. Such features enhance the overall security of devices using ULED technology, making them suitable for applications requiring high levels of data protection.- Enhanced security features for ULED displays: ULED displays incorporate advanced security measures to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access. These features may include encryption protocols, secure authentication methods, and tamper-resistant hardware components. Such security enhancements ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data displayed on ULED screens.
- Anti-counterfeiting technology in ULED displays: ULED displays can be equipped with anti-counterfeiting technologies to verify the authenticity of the device and its content. This may involve the use of unique identifiers, digital watermarks, or other verification methods integrated into the display hardware or software. Such measures help prevent the unauthorized replication or tampering of ULED displays.
- Secure data transmission for ULED displays: Implementing secure data transmission protocols for ULED displays ensures that information sent to and from the display remains protected. This may include the use of encrypted communication channels, secure APIs, and robust authentication mechanisms to prevent interception or manipulation of data during transmission.
- Privacy protection features in ULED displays: ULED displays can incorporate privacy protection features to prevent unauthorized viewing of sensitive information. This may include adjustable viewing angles, privacy filters, or dynamic content masking technologies that limit visibility to only intended viewers. Such features are particularly important for displays used in public or shared environments.
- Biometric authentication for ULED display access: Integrating biometric authentication methods into ULED displays enhances security by ensuring that only authorized individuals can access or control the display. This may involve the use of fingerprint sensors, facial recognition, or other biometric technologies embedded within the display or its associated hardware.
02 Authentication mechanisms for ULED display systems
Authentication mechanisms are implemented in ULED display systems to ensure that only authorized users can access certain functions or view specific content. These may include biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication, or secure token-based systems. Such measures help prevent unauthorized use and protect sensitive information displayed on ULED screens.Expand Specific Solutions03 Secure data transmission for ULED displays
ULED display systems employ secure data transmission protocols to protect information as it is sent to and from the display. This may involve end-to-end encryption, secure communication channels, or blockchain technology. These measures ensure that data displayed on ULED screens remains confidential and intact during transmission.Expand Specific Solutions04 Privacy protection features in ULED displays
ULED displays incorporate privacy protection features to prevent unauthorized viewing of sensitive information. These may include adjustable viewing angles, privacy filters, or dynamic content masking. Such features ensure that displayed information remains visible only to intended viewers, enhancing the security of ULED-equipped devices in public or shared spaces.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of ULED displays with security management systems
ULED displays can be integrated with broader security management systems to provide comprehensive protection. This integration may involve centralized control, real-time monitoring, and automated threat response mechanisms. By connecting ULED displays to larger security frameworks, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and respond more effectively to potential threats.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ULED Security Solutions
The security implementation for ULED displays is in a rapidly evolving phase, with the market size expanding as these displays gain popularity in various sectors. The technology's maturity is progressing, with key players like Shenzhen AOTO Electronics, Unilumin Group, and BOE Technology Group leading innovation. Companies such as Samsung Display and LG Electronics are also contributing to advancements. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics giants and specialized display manufacturers, each striving to enhance security features. As the technology matures, we're seeing increased focus on integrating advanced encryption, tamper-detection mechanisms, and secure data transmission protocols into ULED display systems.
Shenzhen AOTO Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: AOTO has developed a comprehensive security solution for ULED displays, incorporating both hardware and software measures. Their approach includes encrypted data transmission, secure boot processes, and real-time monitoring systems. They utilize advanced encryption algorithms to protect content and control signals, ensuring that only authorized devices can interact with the displays. Additionally, AOTO has implemented a multi-layer authentication system for both users and devices, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining hardware and software security measures. Weaknesses: May require more processing power, potentially affecting display performance.
Unilumin Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Unilumin has developed a proprietary security framework for their ULED displays, focusing on data protection and access control. Their solution includes a hardware-based security module that generates and manages encryption keys, ensuring secure communication between the display and control systems. They have also implemented a robust firewall system to prevent unauthorized network access. Unilumin's approach emphasizes regular security updates and patches to address emerging threats, maintaining the integrity of their ULED systems over time.
Strengths: Strong focus on data protection and regular security updates. Weaknesses: May require more frequent maintenance to keep security measures up-to-date.
Innovative ULED Security Protocols and Algorithms
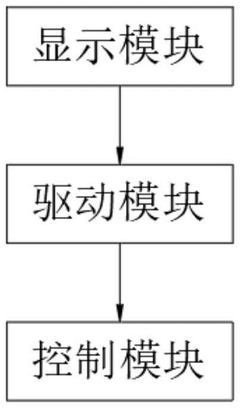
LED display screen with privacy protection function and method thereof
PatentPendingCN118824167A
Innovation
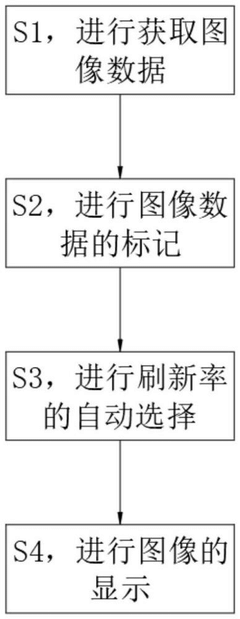
- By receiving image data on the LED display and adding special marks, the refresh rate is automatically selected based on the marks, and the refresh rate is increased to reduce the possibility of being out of sync with the shutter of the camera device, reducing stripes and flickering while ensuring the user viewing experience.
ULED packaging structure and imaging device
PatentPendingCN116741909A
Innovation
- By introducing a drive reset component into the uLED packaging structure, the drive frame moves in the second direction relative to the substrate to provide a reset force, using the persistence of vision of the human eye to reduce the impact of unlit uLEDs, stabilize imaging quality, and achieve a compact structure. change.
Regulatory Compliance for ULED Security
Regulatory compliance for ULED security is a critical aspect of implementing robust protection measures for Ultra Light Emitting Diode (ULED) displays. As these advanced display technologies continue to proliferate across various industries, adherence to established security standards and regulations becomes paramount.
The regulatory landscape for ULED security encompasses a wide range of standards and guidelines set forth by international organizations, national governments, and industry bodies. These regulations aim to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data displayed on ULED screens, as well as protect against potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
One of the primary regulatory frameworks applicable to ULED security is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. GDPR mandates strict data protection and privacy measures for all electronic devices, including ULED displays, that process personal information. Compliance with GDPR requires implementing robust encryption protocols, secure data storage mechanisms, and user consent management systems for ULED displays used in public spaces or interactive applications.
In the United States, the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) sets forth security standards for federal agencies and their contractors. ULED displays used in government facilities or for displaying sensitive information must adhere to FISMA guidelines, which include implementing access controls, conducting regular security assessments, and maintaining detailed audit logs of all display activities.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is another crucial regulatory framework that impacts ULED security, particularly in retail and financial sectors. ULED displays used for point-of-sale systems or displaying financial information must comply with PCI DSS requirements, such as encryption of cardholder data, network segmentation, and regular security testing.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in shaping ULED security measures. For instance, in the healthcare sector, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States mandates strict protection of patient information displayed on ULED screens in medical facilities. This includes implementing access controls, encryption, and audit trails for all patient data displayed or processed through ULED devices.
To ensure compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements, organizations deploying ULED displays must adopt a comprehensive security strategy. This typically involves conducting regular risk assessments, implementing multi-factor authentication for access control, encrypting data both at rest and in transit, and establishing incident response protocols.
Furthermore, as ULED technology continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to introduce new standards and guidelines specifically tailored to address emerging security challenges. Organizations must stay informed about these developments and be prepared to adapt their security measures accordingly to maintain compliance and protect their ULED infrastructure from potential threats.
The regulatory landscape for ULED security encompasses a wide range of standards and guidelines set forth by international organizations, national governments, and industry bodies. These regulations aim to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data displayed on ULED screens, as well as protect against potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
One of the primary regulatory frameworks applicable to ULED security is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. GDPR mandates strict data protection and privacy measures for all electronic devices, including ULED displays, that process personal information. Compliance with GDPR requires implementing robust encryption protocols, secure data storage mechanisms, and user consent management systems for ULED displays used in public spaces or interactive applications.
In the United States, the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) sets forth security standards for federal agencies and their contractors. ULED displays used in government facilities or for displaying sensitive information must adhere to FISMA guidelines, which include implementing access controls, conducting regular security assessments, and maintaining detailed audit logs of all display activities.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is another crucial regulatory framework that impacts ULED security, particularly in retail and financial sectors. ULED displays used for point-of-sale systems or displaying financial information must comply with PCI DSS requirements, such as encryption of cardholder data, network segmentation, and regular security testing.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in shaping ULED security measures. For instance, in the healthcare sector, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States mandates strict protection of patient information displayed on ULED screens in medical facilities. This includes implementing access controls, encryption, and audit trails for all patient data displayed or processed through ULED devices.
To ensure compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements, organizations deploying ULED displays must adopt a comprehensive security strategy. This typically involves conducting regular risk assessments, implementing multi-factor authentication for access control, encrypting data both at rest and in transit, and establishing incident response protocols.
Furthermore, as ULED technology continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to introduce new standards and guidelines specifically tailored to address emerging security challenges. Organizations must stay informed about these developments and be prepared to adapt their security measures accordingly to maintain compliance and protect their ULED infrastructure from potential threats.
ULED Security Testing and Certification
ULED security testing and certification play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and reliability of Ultra Light Emitting Diode (ULED) displays. As these advanced display technologies become more prevalent in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics, the need for robust security measures has become paramount.
The testing process for ULED security typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of both hardware and software components. Hardware security testing focuses on the physical aspects of the display, including tamper-resistant enclosures, secure boot mechanisms, and hardware-based encryption modules. These tests aim to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive components and protect against physical attacks.
Software security testing for ULED displays encompasses a wide range of assessments, including vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and code reviews. These evaluations help identify potential weaknesses in the display's firmware, operating system, and applications. Additionally, security testing often includes an analysis of data transmission protocols and encryption methods used to protect information displayed on the ULED screen.
Certification processes for ULED security vary depending on the industry and intended application. Common standards include ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management, Common Criteria for IT security evaluation, and industry-specific certifications such as FIPS 140-2 for cryptographic modules. These certifications provide assurance that the ULED display meets specific security requirements and has undergone rigorous testing.
One of the key challenges in ULED security testing is addressing the unique characteristics of these displays, such as their high brightness, wide color gamut, and ultra-thin form factor. These features can introduce new attack vectors that may not be present in traditional display technologies. As a result, security testing methodologies must be adapted to account for these specific attributes.
To ensure comprehensive security coverage, ULED display manufacturers often employ a combination of in-house testing and third-party security assessments. This multi-layered approach helps identify potential vulnerabilities from different perspectives and ensures that security measures are thoroughly evaluated before the product is released to market.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, security testing and certification processes must adapt to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This includes developing new testing methodologies for advanced features such as integrated touch sensors, biometric authentication systems, and AI-powered display optimization algorithms. By staying ahead of potential security risks, manufacturers can maintain the trust of their customers and ensure the long-term viability of ULED display technology in security-sensitive applications.
The testing process for ULED security typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of both hardware and software components. Hardware security testing focuses on the physical aspects of the display, including tamper-resistant enclosures, secure boot mechanisms, and hardware-based encryption modules. These tests aim to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive components and protect against physical attacks.
Software security testing for ULED displays encompasses a wide range of assessments, including vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and code reviews. These evaluations help identify potential weaknesses in the display's firmware, operating system, and applications. Additionally, security testing often includes an analysis of data transmission protocols and encryption methods used to protect information displayed on the ULED screen.
Certification processes for ULED security vary depending on the industry and intended application. Common standards include ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management, Common Criteria for IT security evaluation, and industry-specific certifications such as FIPS 140-2 for cryptographic modules. These certifications provide assurance that the ULED display meets specific security requirements and has undergone rigorous testing.
One of the key challenges in ULED security testing is addressing the unique characteristics of these displays, such as their high brightness, wide color gamut, and ultra-thin form factor. These features can introduce new attack vectors that may not be present in traditional display technologies. As a result, security testing methodologies must be adapted to account for these specific attributes.
To ensure comprehensive security coverage, ULED display manufacturers often employ a combination of in-house testing and third-party security assessments. This multi-layered approach helps identify potential vulnerabilities from different perspectives and ensures that security measures are thoroughly evaluated before the product is released to market.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, security testing and certification processes must adapt to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This includes developing new testing methodologies for advanced features such as integrated touch sensors, biometric authentication systems, and AI-powered display optimization algorithms. By staying ahead of potential security risks, manufacturers can maintain the trust of their customers and ensure the long-term viability of ULED display technology in security-sensitive applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!