ULED Displays Transforming Communication Interfaces
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED Display Evolution
The evolution of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays represents a significant leap in communication interface technology. This progression can be traced through several key developmental stages, each marked by notable advancements in display technology and its application in communication systems.
In the early stages, ULED technology emerged as a promising alternative to traditional LED and OLED displays. The initial focus was on improving brightness and energy efficiency, with researchers working to overcome the limitations of existing display technologies. This phase saw the development of ultra-thin, highly luminous diodes that could be integrated into flexible substrates.
As the technology matured, the emphasis shifted towards enhancing color reproduction and contrast ratios. ULED displays began to demonstrate superior performance in these areas, offering vibrant and lifelike images that surpassed the capabilities of conventional displays. This improvement in visual quality opened up new possibilities for more immersive and engaging communication interfaces.
The next significant milestone in ULED evolution was the integration of touch sensitivity and interactive features. This development transformed ULED displays from passive viewing screens into dynamic, responsive interfaces. The ability to combine high-quality visuals with touch interactivity revolutionized the way users interact with digital content and communication systems.
Recent advancements have focused on scalability and form factor flexibility. ULED technology has been adapted to various sizes and shapes, from small wearable devices to large-scale public displays. This versatility has enabled the integration of ULED displays into a wide range of communication devices and environments, fundamentally altering the landscape of human-computer interaction.
The latest phase in ULED display evolution is characterized by the incorporation of advanced features such as 3D capabilities, holographic projections, and augmented reality overlays. These innovations are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in visual communication, creating more immersive and intuitive interfaces that blur the line between digital and physical realities.
Throughout its evolution, ULED display technology has consistently aimed to address key challenges in communication interfaces, such as power consumption, visual clarity, and user engagement. The ongoing development of ULED displays continues to drive innovation in fields ranging from personal communication devices to large-scale public information systems, reshaping the way we interact with and perceive digital information.
In the early stages, ULED technology emerged as a promising alternative to traditional LED and OLED displays. The initial focus was on improving brightness and energy efficiency, with researchers working to overcome the limitations of existing display technologies. This phase saw the development of ultra-thin, highly luminous diodes that could be integrated into flexible substrates.
As the technology matured, the emphasis shifted towards enhancing color reproduction and contrast ratios. ULED displays began to demonstrate superior performance in these areas, offering vibrant and lifelike images that surpassed the capabilities of conventional displays. This improvement in visual quality opened up new possibilities for more immersive and engaging communication interfaces.
The next significant milestone in ULED evolution was the integration of touch sensitivity and interactive features. This development transformed ULED displays from passive viewing screens into dynamic, responsive interfaces. The ability to combine high-quality visuals with touch interactivity revolutionized the way users interact with digital content and communication systems.
Recent advancements have focused on scalability and form factor flexibility. ULED technology has been adapted to various sizes and shapes, from small wearable devices to large-scale public displays. This versatility has enabled the integration of ULED displays into a wide range of communication devices and environments, fundamentally altering the landscape of human-computer interaction.
The latest phase in ULED display evolution is characterized by the incorporation of advanced features such as 3D capabilities, holographic projections, and augmented reality overlays. These innovations are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in visual communication, creating more immersive and intuitive interfaces that blur the line between digital and physical realities.
Throughout its evolution, ULED display technology has consistently aimed to address key challenges in communication interfaces, such as power consumption, visual clarity, and user engagement. The ongoing development of ULED displays continues to drive innovation in fields ranging from personal communication devices to large-scale public information systems, reshaping the way we interact with and perceive digital information.
ULED Market Dynamics
The ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) display market is experiencing rapid growth and transformation, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality, energy-efficient display technologies across various sectors. As communication interfaces evolve, ULED displays are positioned to play a pivotal role in reshaping how we interact with digital content and information.
The global ULED market is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing traditional display technologies. This growth is fueled by the superior performance characteristics of ULED displays, including enhanced brightness, improved color accuracy, and longer lifespan compared to conventional LED and OLED displays.
Key market segments driving the adoption of ULED technology include consumer electronics, automotive displays, and digital signage. In the consumer electronics sector, ULED displays are gaining traction in high-end televisions, smartphones, and tablets, offering users an immersive viewing experience with vibrant colors and deep contrasts.
The automotive industry is another major contributor to ULED market growth, with manufacturers integrating these displays into infotainment systems, instrument clusters, and heads-up displays. The enhanced visibility and durability of ULED technology make it particularly suitable for automotive applications, where readability in various lighting conditions is crucial.
Digital signage represents a significant opportunity for ULED displays, especially in outdoor advertising and large-format displays. The technology's ability to deliver high brightness and energy efficiency makes it ideal for public spaces, stadiums, and retail environments.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the ULED market, driven by the presence of major display manufacturers and the region's robust consumer electronics industry. North America and Europe are also anticipated to witness substantial growth, particularly in automotive and commercial applications.
Despite the positive outlook, the ULED market faces challenges such as high initial costs and competition from other emerging display technologies. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving manufacturing processes and reducing production costs, which is likely to enhance the technology's competitiveness in the long term.
As communication interfaces continue to evolve, ULED displays are poised to enable new forms of interaction and information display. The technology's potential for flexible and transparent displays opens up possibilities for innovative applications in augmented reality, wearable devices, and smart surfaces, further expanding its market potential.
The global ULED market is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing traditional display technologies. This growth is fueled by the superior performance characteristics of ULED displays, including enhanced brightness, improved color accuracy, and longer lifespan compared to conventional LED and OLED displays.
Key market segments driving the adoption of ULED technology include consumer electronics, automotive displays, and digital signage. In the consumer electronics sector, ULED displays are gaining traction in high-end televisions, smartphones, and tablets, offering users an immersive viewing experience with vibrant colors and deep contrasts.
The automotive industry is another major contributor to ULED market growth, with manufacturers integrating these displays into infotainment systems, instrument clusters, and heads-up displays. The enhanced visibility and durability of ULED technology make it particularly suitable for automotive applications, where readability in various lighting conditions is crucial.
Digital signage represents a significant opportunity for ULED displays, especially in outdoor advertising and large-format displays. The technology's ability to deliver high brightness and energy efficiency makes it ideal for public spaces, stadiums, and retail environments.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the ULED market, driven by the presence of major display manufacturers and the region's robust consumer electronics industry. North America and Europe are also anticipated to witness substantial growth, particularly in automotive and commercial applications.
Despite the positive outlook, the ULED market faces challenges such as high initial costs and competition from other emerging display technologies. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving manufacturing processes and reducing production costs, which is likely to enhance the technology's competitiveness in the long term.
As communication interfaces continue to evolve, ULED displays are poised to enable new forms of interaction and information display. The technology's potential for flexible and transparent displays opens up possibilities for innovative applications in augmented reality, wearable devices, and smart surfaces, further expanding its market potential.
ULED Tech Challenges
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays face several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize their potential in transforming communication interfaces. One of the primary hurdles is the development of efficient and stable blue ULED materials. While red and green ULEDs have shown promising performance, blue ULEDs still lag behind in terms of efficiency and longevity, which is crucial for achieving a full-color display with balanced color reproduction.
Another major challenge lies in the miniaturization of ULED chips while maintaining high brightness and efficiency. As communication interfaces demand higher resolution and pixel density, reducing the size of individual ULED elements without compromising their performance becomes increasingly difficult. This challenge is compounded by the need to develop advanced manufacturing processes capable of precisely placing and connecting these miniaturized components at scale.
Heat management presents a significant obstacle in ULED display development. As ULEDs are driven at high current densities to achieve the desired brightness, they generate substantial heat. This can lead to decreased efficiency, shortened lifespan, and potential color shifts. Developing effective thermal management solutions that can be integrated into thin, flexible display designs is a complex engineering challenge.
The integration of ULEDs with flexible substrates and driving circuits poses another set of technical hurdles. Creating bendable and even stretchable displays requires the development of new materials and manufacturing techniques that can withstand repeated deformation while maintaining electrical and optical performance. This includes challenges in developing flexible encapsulation methods to protect ULEDs from moisture and oxygen degradation.
Color management and uniformity across large ULED displays represent additional technical challenges. Ensuring consistent color reproduction and brightness across millions of individual ULED elements requires sophisticated control systems and compensation algorithms. This becomes even more complex when considering the potential for flexible or curved display surfaces.
Lastly, the development of efficient, compact, and cost-effective driving circuits for ULED displays remains a significant challenge. These circuits must be capable of precisely controlling the current through each ULED element while minimizing power consumption and heat generation. As display resolutions increase, the complexity of these driving circuits grows exponentially, necessitating innovative approaches to circuit design and integration.
Overcoming these technical challenges will be crucial for ULED displays to revolutionize communication interfaces, offering unprecedented visual quality, form factor flexibility, and energy efficiency. Continued research and development efforts in materials science, manufacturing processes, and electronic design will be key to addressing these hurdles and unlocking the full potential of ULED technology.
Another major challenge lies in the miniaturization of ULED chips while maintaining high brightness and efficiency. As communication interfaces demand higher resolution and pixel density, reducing the size of individual ULED elements without compromising their performance becomes increasingly difficult. This challenge is compounded by the need to develop advanced manufacturing processes capable of precisely placing and connecting these miniaturized components at scale.
Heat management presents a significant obstacle in ULED display development. As ULEDs are driven at high current densities to achieve the desired brightness, they generate substantial heat. This can lead to decreased efficiency, shortened lifespan, and potential color shifts. Developing effective thermal management solutions that can be integrated into thin, flexible display designs is a complex engineering challenge.
The integration of ULEDs with flexible substrates and driving circuits poses another set of technical hurdles. Creating bendable and even stretchable displays requires the development of new materials and manufacturing techniques that can withstand repeated deformation while maintaining electrical and optical performance. This includes challenges in developing flexible encapsulation methods to protect ULEDs from moisture and oxygen degradation.
Color management and uniformity across large ULED displays represent additional technical challenges. Ensuring consistent color reproduction and brightness across millions of individual ULED elements requires sophisticated control systems and compensation algorithms. This becomes even more complex when considering the potential for flexible or curved display surfaces.
Lastly, the development of efficient, compact, and cost-effective driving circuits for ULED displays remains a significant challenge. These circuits must be capable of precisely controlling the current through each ULED element while minimizing power consumption and heat generation. As display resolutions increase, the complexity of these driving circuits grows exponentially, necessitating innovative approaches to circuit design and integration.
Overcoming these technical challenges will be crucial for ULED displays to revolutionize communication interfaces, offering unprecedented visual quality, form factor flexibility, and energy efficiency. Continued research and development efforts in materials science, manufacturing processes, and electronic design will be key to addressing these hurdles and unlocking the full potential of ULED technology.
ULED Solutions Overview
01 Display interface protocols
ULED displays utilize various communication protocols for interfacing with host systems. These protocols enable high-speed data transfer, supporting features like high refresh rates and color depth. Common interfaces include MIPI, eDP, and custom protocols optimized for ULED technology.- Display interface protocols: ULED displays utilize various communication protocols for interfacing with host systems. These protocols enable high-speed data transfer, synchronization, and control of display elements. Common interfaces include MIPI, eDP, and custom protocols optimized for ULED technology, allowing for efficient transmission of image data and control signals between the display and the driving electronics.
- Timing controllers for ULED displays: Timing controllers play a crucial role in managing communication between the host system and ULED display panels. These controllers handle signal processing, data formatting, and synchronization, ensuring proper timing of display updates and maintaining image quality. Advanced timing controllers may incorporate features such as frame rate control, dynamic refresh rate adjustment, and power management for optimal display performance.
- Multi-display communication systems: ULED display systems often involve multiple display panels or modules working together. Communication interfaces for these systems must support synchronized data transfer and control across multiple units. This may involve daisy-chaining displays, implementing master-slave configurations, or utilizing distributed control architectures to ensure seamless integration and operation of large-scale ULED display installations.
- Wireless communication for ULED displays: Wireless communication technologies are increasingly being integrated into ULED display systems. These interfaces allow for greater flexibility in installation and control, enabling remote management, content updates, and system diagnostics. Wireless protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and proprietary RF solutions are being adapted to meet the specific requirements of ULED display communication, including low latency and high bandwidth for video streaming.
- Power management and communication: Communication interfaces for ULED displays often incorporate power management features. These interfaces may include protocols for controlling power states, managing energy consumption, and optimizing display brightness based on ambient conditions or content. Advanced power management communication allows for dynamic adjustment of display parameters to balance performance and energy efficiency, extending the lifespan of ULED display systems.
02 Timing controllers for ULED displays
Timing controllers play a crucial role in managing communication between the display panel and the host system. They handle signal processing, frame rate control, and coordinate data transmission. Advanced timing controllers for ULED displays often incorporate features like local dimming control and power management.Expand Specific Solutions03 Multi-display communication systems
ULED technology can be applied to multi-display setups, requiring sophisticated communication interfaces to synchronize content across multiple panels. These systems often employ daisy-chaining or hub-based architectures to distribute signals efficiently while maintaining image quality and timing accuracy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Wireless connectivity for ULED displays
Wireless communication interfaces are being developed for ULED displays, enabling more flexible installation options and reducing cable clutter. These interfaces must overcome challenges such as bandwidth limitations and latency to deliver high-quality video signals wirelessly to ULED panels.Expand Specific Solutions05 Power management in ULED communication interfaces
Efficient power management is crucial for ULED displays, particularly in portable devices. Communication interfaces incorporate power-saving features such as selective refresh, adaptive brightness control, and low-power standby modes. These features are often integrated into the display driver IC or timing controller to optimize energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions
ULED Industry Leaders
The ULED display technology market is in a dynamic growth phase, with significant potential to revolutionize communication interfaces. The industry is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-quality, energy-efficient displays across various sectors. Major players like Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, and BOE Technology Group are investing heavily in R&D to advance ULED technology. The market is characterized by intense competition and continuous innovation, with companies like Meta Platforms Technologies and Microsoft Technology Licensing also entering the space. While ULED technology is still evolving, it has reached a level of maturity that allows for practical applications, particularly in consumer electronics and professional display systems. The involvement of diverse players, from established electronics giants to specialized display manufacturers, indicates a robust ecosystem poised for further growth and technological breakthroughs.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed advanced ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) display technology for communication interfaces. Their approach combines micro-LED technology with quantum dot color conversion layers to achieve ultra-high brightness, wide color gamut, and high contrast ratios. The displays utilize a unique pixel structure that allows for higher pixel density and improved energy efficiency. Samsung's ULED displays also incorporate advanced local dimming techniques to enhance contrast and reduce power consumption in dark scenes.
Strengths: Superior image quality, high brightness, wide color gamut, and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: High production costs and complexity in manufacturing process.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG's ULED display technology for communication interfaces focuses on integrating transparent and flexible display elements. Their approach uses a combination of organic and inorganic materials to create ultra-thin, bendable displays that can be seamlessly integrated into various surfaces. LG's ULED displays feature self-emitting pixels that eliminate the need for backlighting, resulting in deeper blacks and improved contrast. The company has also developed advanced touch and gesture recognition capabilities for these displays, enhancing user interaction in communication interfaces.
Strengths: Flexibility, transparency, and innovative form factors. Weaknesses: Durability concerns and limited mass production capabilities.
ULED Core Innovations
Light emitting diode communication device, method of forming and operating the same
PatentActiveUS20200259564A1
Innovation
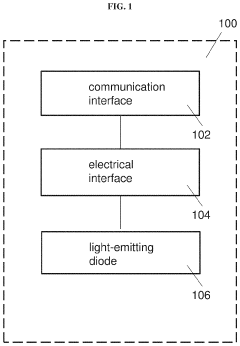
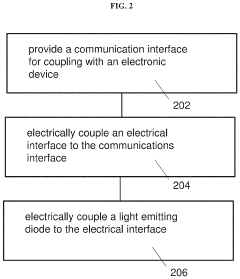
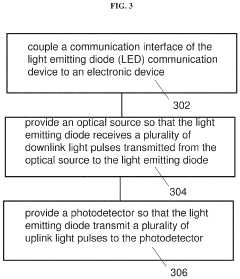
- A compact Li-Fi communication device with a light emitting diode (LED) that includes a communication interface, an electrical interface, and a light emitting diode configured to convert data signals into light pulses for uplink and sensing signals into data signals for downlink, using a Fresnel lens for collimation and a swivel for optimal alignment, enhancing signal collection and transmission speed.
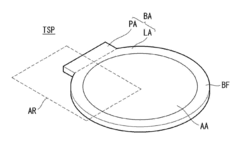
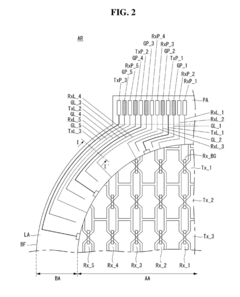
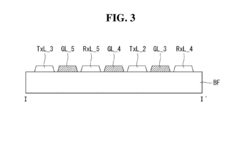
Touchscreen panel
PatentActiveUS20180239489A1
Innovation
- A touchscreen panel design featuring a base film with a bezel area and active area, where first and second touch electrodes intersect, connected by routing lines and guard pads and lines that extend between adjacent touch pads and lines, with a bridge pattern over an insulating film to reduce signal interference and static electricity, and a guard line connected to ground voltage to discharge static electricity.
ULED Supply Chain
The ULED (Ultra-Light Emitting Diode) supply chain plays a crucial role in the development and production of advanced display technologies. This intricate network encompasses various stages, from raw material sourcing to final product assembly, involving multiple stakeholders and specialized processes.
At the foundation of the ULED supply chain are the suppliers of essential raw materials, including rare earth elements and semiconductor compounds. These materials are critical for producing the ultra-small, high-performance LEDs that form the basis of ULED displays. The extraction and refinement of these materials require specialized expertise and often involve geopolitical considerations due to the limited geographical distribution of certain resources.
Moving up the chain, we find the manufacturers of ULED chips and components. These companies employ cutting-edge fabrication techniques to produce miniaturized LEDs with exceptional brightness and energy efficiency. The manufacturing process involves precision engineering and stringent quality control measures to ensure consistent performance across millions of individual diodes.
Assembly and integration form the next crucial link in the ULED supply chain. Here, specialized equipment manufacturers provide the tools and machinery necessary for accurately placing and connecting the tiny ULED components. This stage requires advanced robotics and automation systems to achieve the high level of precision needed for ULED display production.
Display panel manufacturers represent another key segment of the supply chain. These companies integrate the ULED components into larger display panels, incorporating additional technologies such as color filters, backplanes, and driver circuits. The complexity of this integration process necessitates close collaboration between ULED component suppliers and panel manufacturers to optimize performance and yield.
Logistics and distribution networks form an essential part of the ULED supply chain, ensuring the timely delivery of components and finished products across global markets. The fragility and sensitivity of ULED components require specialized handling and transportation methods to maintain product integrity throughout the distribution process.
Finally, the supply chain culminates with device manufacturers and brands that incorporate ULED displays into consumer electronics, professional equipment, and communication interfaces. These end-product manufacturers rely on the entire upstream supply chain to deliver innovative and high-quality ULED-based devices to end-users.
The ULED supply chain is characterized by its global nature, with different stages often distributed across multiple countries and regions. This geographical dispersion can introduce challenges related to supply chain resilience, trade regulations, and intellectual property protection. As ULED technology continues to evolve, the supply chain must adapt to new materials, manufacturing processes, and market demands, driving ongoing innovation and collaboration among industry players.
At the foundation of the ULED supply chain are the suppliers of essential raw materials, including rare earth elements and semiconductor compounds. These materials are critical for producing the ultra-small, high-performance LEDs that form the basis of ULED displays. The extraction and refinement of these materials require specialized expertise and often involve geopolitical considerations due to the limited geographical distribution of certain resources.
Moving up the chain, we find the manufacturers of ULED chips and components. These companies employ cutting-edge fabrication techniques to produce miniaturized LEDs with exceptional brightness and energy efficiency. The manufacturing process involves precision engineering and stringent quality control measures to ensure consistent performance across millions of individual diodes.
Assembly and integration form the next crucial link in the ULED supply chain. Here, specialized equipment manufacturers provide the tools and machinery necessary for accurately placing and connecting the tiny ULED components. This stage requires advanced robotics and automation systems to achieve the high level of precision needed for ULED display production.
Display panel manufacturers represent another key segment of the supply chain. These companies integrate the ULED components into larger display panels, incorporating additional technologies such as color filters, backplanes, and driver circuits. The complexity of this integration process necessitates close collaboration between ULED component suppliers and panel manufacturers to optimize performance and yield.
Logistics and distribution networks form an essential part of the ULED supply chain, ensuring the timely delivery of components and finished products across global markets. The fragility and sensitivity of ULED components require specialized handling and transportation methods to maintain product integrity throughout the distribution process.
Finally, the supply chain culminates with device manufacturers and brands that incorporate ULED displays into consumer electronics, professional equipment, and communication interfaces. These end-product manufacturers rely on the entire upstream supply chain to deliver innovative and high-quality ULED-based devices to end-users.
The ULED supply chain is characterized by its global nature, with different stages often distributed across multiple countries and regions. This geographical dispersion can introduce challenges related to supply chain resilience, trade regulations, and intellectual property protection. As ULED technology continues to evolve, the supply chain must adapt to new materials, manufacturing processes, and market demands, driving ongoing innovation and collaboration among industry players.
ULED Energy Efficiency
ULED (Ultra-Light Emitting Diode) displays have emerged as a promising technology in the field of energy-efficient communication interfaces. These displays offer significant advantages in terms of power consumption, making them an attractive option for a wide range of applications, from mobile devices to large-scale digital signage.
One of the key factors contributing to the energy efficiency of ULED displays is their unique pixel structure. Unlike traditional LED displays, ULEDs utilize a more refined semiconductor material composition, allowing for improved electron mobility and reduced power leakage. This results in a substantial decrease in the energy required to produce light, with some estimates suggesting up to 30% reduction in power consumption compared to conventional LED displays.
The power-saving capabilities of ULED displays are further enhanced by their advanced light management techniques. These displays incorporate sophisticated optical structures that optimize light extraction and distribution, minimizing energy loss due to internal reflection and absorption. As a result, ULEDs can achieve higher luminous efficacy, producing more light output per unit of electrical input.
Another significant aspect of ULED energy efficiency lies in their superior color rendering capabilities. By utilizing quantum dot technology, ULEDs can produce a wider color gamut with greater precision, reducing the need for excessive power consumption to achieve vibrant and accurate colors. This not only contributes to energy savings but also enhances the overall visual experience for users.
The thermal management of ULED displays also plays a crucial role in their energy efficiency. Advanced heat dissipation techniques, such as improved substrate materials and innovative packaging designs, help to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This not only extends the lifespan of the display but also reduces the energy required for cooling systems, further contributing to overall power savings.
In the context of communication interfaces, the energy efficiency of ULED displays translates into extended battery life for portable devices and reduced operational costs for large-scale installations. This makes them particularly suitable for applications such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, where power consumption is a critical factor.
As research in ULED technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in energy efficiency. Current developments focus on enhancing the quantum efficiency of the light-emitting materials, optimizing driver circuits, and exploring new pixel architectures. These advancements promise to push the boundaries of energy-efficient display technology, potentially revolutionizing the way we interact with digital information in our daily lives.
One of the key factors contributing to the energy efficiency of ULED displays is their unique pixel structure. Unlike traditional LED displays, ULEDs utilize a more refined semiconductor material composition, allowing for improved electron mobility and reduced power leakage. This results in a substantial decrease in the energy required to produce light, with some estimates suggesting up to 30% reduction in power consumption compared to conventional LED displays.
The power-saving capabilities of ULED displays are further enhanced by their advanced light management techniques. These displays incorporate sophisticated optical structures that optimize light extraction and distribution, minimizing energy loss due to internal reflection and absorption. As a result, ULEDs can achieve higher luminous efficacy, producing more light output per unit of electrical input.
Another significant aspect of ULED energy efficiency lies in their superior color rendering capabilities. By utilizing quantum dot technology, ULEDs can produce a wider color gamut with greater precision, reducing the need for excessive power consumption to achieve vibrant and accurate colors. This not only contributes to energy savings but also enhances the overall visual experience for users.
The thermal management of ULED displays also plays a crucial role in their energy efficiency. Advanced heat dissipation techniques, such as improved substrate materials and innovative packaging designs, help to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This not only extends the lifespan of the display but also reduces the energy required for cooling systems, further contributing to overall power savings.
In the context of communication interfaces, the energy efficiency of ULED displays translates into extended battery life for portable devices and reduced operational costs for large-scale installations. This makes them particularly suitable for applications such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, where power consumption is a critical factor.
As research in ULED technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in energy efficiency. Current developments focus on enhancing the quantum efficiency of the light-emitting materials, optimizing driver circuits, and exploring new pixel architectures. These advancements promise to push the boundaries of energy-efficient display technology, potentially revolutionizing the way we interact with digital information in our daily lives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!