ULED in Modern Broadcasting Technologies
JUN 23, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED Tech Evolution
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, marking several key milestones in the broadcasting industry. The journey of ULED began with the development of high-brightness LEDs in the early 2000s, which laid the foundation for more advanced display technologies.
In the mid-2000s, researchers focused on improving the efficiency and color accuracy of LEDs, leading to the creation of RGB LED arrays capable of producing a wider color gamut. This advancement paved the way for ULED's application in broadcasting, offering superior image quality and energy efficiency compared to traditional display technologies.
The next major breakthrough came in the early 2010s with the introduction of Quantum Dot technology. By incorporating quantum dots into LED displays, manufacturers achieved unprecedented color accuracy and brightness levels. This innovation marked the birth of ULED as we know it today, offering a significant leap in picture quality for broadcasting applications.
Between 2015 and 2020, ULED technology saw rapid advancements in miniaturization and pixel density. The development of Micro-LED and Mini-LED technologies allowed for even greater control over local dimming, resulting in improved contrast ratios and HDR performance. These improvements were particularly beneficial for live sports broadcasting and high-quality studio productions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing the energy efficiency and longevity of ULED displays. Researchers have made significant strides in reducing power consumption while maintaining high brightness levels, making ULED an increasingly attractive option for both studio and field broadcasting equipment.
The latest developments in ULED technology have centered around flexibility and form factor. Flexible ULED displays have emerged, offering new possibilities for creative set designs and portable broadcasting solutions. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing processes have led to thinner and lighter ULED panels, further expanding their potential applications in modern broadcasting environments.
Looking ahead, the ULED technology roadmap includes several promising areas of development. These include the integration of AI-driven local dimming algorithms for even better contrast and energy efficiency, the exploration of new materials for improved color reproduction, and the potential incorporation of holographic display capabilities for next-generation broadcasting experiences.
In the mid-2000s, researchers focused on improving the efficiency and color accuracy of LEDs, leading to the creation of RGB LED arrays capable of producing a wider color gamut. This advancement paved the way for ULED's application in broadcasting, offering superior image quality and energy efficiency compared to traditional display technologies.
The next major breakthrough came in the early 2010s with the introduction of Quantum Dot technology. By incorporating quantum dots into LED displays, manufacturers achieved unprecedented color accuracy and brightness levels. This innovation marked the birth of ULED as we know it today, offering a significant leap in picture quality for broadcasting applications.
Between 2015 and 2020, ULED technology saw rapid advancements in miniaturization and pixel density. The development of Micro-LED and Mini-LED technologies allowed for even greater control over local dimming, resulting in improved contrast ratios and HDR performance. These improvements were particularly beneficial for live sports broadcasting and high-quality studio productions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing the energy efficiency and longevity of ULED displays. Researchers have made significant strides in reducing power consumption while maintaining high brightness levels, making ULED an increasingly attractive option for both studio and field broadcasting equipment.
The latest developments in ULED technology have centered around flexibility and form factor. Flexible ULED displays have emerged, offering new possibilities for creative set designs and portable broadcasting solutions. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing processes have led to thinner and lighter ULED panels, further expanding their potential applications in modern broadcasting environments.
Looking ahead, the ULED technology roadmap includes several promising areas of development. These include the integration of AI-driven local dimming algorithms for even better contrast and energy efficiency, the exploration of new materials for improved color reproduction, and the potential incorporation of holographic display capabilities for next-generation broadcasting experiences.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology in modern broadcasting is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for high-quality visual experiences in various sectors. The broadcasting industry, in particular, is showing a strong appetite for ULED displays due to their superior image quality, energy efficiency, and versatility.
In the television and streaming market, there is a growing consumer demand for larger screens with higher resolution and better color reproduction. ULED technology addresses these needs by offering enhanced brightness, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut compared to traditional LED displays. This has led to a surge in demand for ULED-equipped televisions and monitors, with market research indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% for the next five years in the premium display segment.
The professional broadcasting sector, including news studios, sports arenas, and entertainment venues, is another key driver of ULED demand. These environments require displays that can deliver exceptional image quality under varying lighting conditions, making ULED an attractive option. The ability of ULED technology to provide consistent performance in both indoor and outdoor settings has led to its increased adoption in large-scale video walls and studio backdrops.
Digital signage and advertising represent another significant market for ULED technology. The superior brightness and contrast ratios of ULED displays make them ideal for high-traffic areas and outdoor installations where visibility is crucial. This sector is expected to see substantial growth, with analysts projecting a market expansion of over 20% annually for ULED-based digital signage solutions.
The events and rental market is also showing increased interest in ULED technology. Concert venues, trade shows, and corporate events are adopting ULED displays for their ability to create immersive visual experiences. The modular nature of many ULED systems allows for flexible and scalable installations, further driving demand in this sector.
As the broadcast industry continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. ULED technology's lower power consumption compared to traditional display technologies aligns well with these environmental concerns, potentially opening up new market opportunities in eco-conscious broadcasting environments.
The global pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote and virtual production techniques in broadcasting, leading to increased demand for high-quality displays in home studios and remote setups. ULED technology is well-positioned to meet this demand, offering professional-grade image quality in more compact and affordable formats suitable for home use.
In the television and streaming market, there is a growing consumer demand for larger screens with higher resolution and better color reproduction. ULED technology addresses these needs by offering enhanced brightness, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut compared to traditional LED displays. This has led to a surge in demand for ULED-equipped televisions and monitors, with market research indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% for the next five years in the premium display segment.
The professional broadcasting sector, including news studios, sports arenas, and entertainment venues, is another key driver of ULED demand. These environments require displays that can deliver exceptional image quality under varying lighting conditions, making ULED an attractive option. The ability of ULED technology to provide consistent performance in both indoor and outdoor settings has led to its increased adoption in large-scale video walls and studio backdrops.
Digital signage and advertising represent another significant market for ULED technology. The superior brightness and contrast ratios of ULED displays make them ideal for high-traffic areas and outdoor installations where visibility is crucial. This sector is expected to see substantial growth, with analysts projecting a market expansion of over 20% annually for ULED-based digital signage solutions.
The events and rental market is also showing increased interest in ULED technology. Concert venues, trade shows, and corporate events are adopting ULED displays for their ability to create immersive visual experiences. The modular nature of many ULED systems allows for flexible and scalable installations, further driving demand in this sector.
As the broadcast industry continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. ULED technology's lower power consumption compared to traditional display technologies aligns well with these environmental concerns, potentially opening up new market opportunities in eco-conscious broadcasting environments.
The global pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote and virtual production techniques in broadcasting, leading to increased demand for high-quality displays in home studios and remote setups. ULED technology is well-positioned to meet this demand, offering professional-grade image quality in more compact and affordable formats suitable for home use.
ULED Tech Challenges
Ultra-LED (ULED) technology in modern broadcasting faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost associated with ULED production and implementation. The complex manufacturing processes and expensive materials required for ULED displays contribute to elevated prices, making it difficult for broadcasters to justify the investment, especially for smaller operations or in developing markets.
Another major challenge lies in the power consumption of ULED displays. While they offer superior brightness and color accuracy compared to traditional LED technologies, ULEDs typically require more energy to operate. This increased power demand not only raises operational costs but also poses environmental concerns, particularly in an era where energy efficiency is paramount.
Heat management presents a substantial technical hurdle for ULED systems in broadcasting environments. The intense brightness and high pixel density of ULED displays generate significant heat, which can lead to performance degradation and reduced lifespan if not properly managed. Developing effective cooling solutions that do not compromise the slim profile and aesthetic appeal of ULED displays remains a critical challenge.
Color accuracy and consistency across large ULED displays pose another set of challenges. Achieving uniform color reproduction and maintaining it over time requires sophisticated calibration techniques and quality control measures. This is particularly crucial in broadcasting applications where color fidelity is essential for delivering high-quality visual content to viewers.
The integration of ULED technology with existing broadcasting infrastructure and workflows presents logistical and technical challenges. Many broadcasters have invested heavily in current systems, and the transition to ULED may require significant upgrades to supporting equipment, software, and transmission protocols. This integration process can be complex, time-consuming, and potentially disruptive to ongoing operations.
Durability and longevity of ULED displays in demanding broadcasting environments are ongoing concerns. The technology must withstand continuous operation, varying environmental conditions, and potential physical impacts without compromising performance or requiring frequent replacements. Developing robust ULED solutions that can maintain their quality over extended periods is crucial for their adoption in professional broadcasting settings.
Lastly, the rapid pace of technological advancement in display technologies presents a challenge for ULED adoption. Broadcasters must weigh the benefits of investing in current ULED technology against the potential for newer, more advanced solutions emerging in the near future. This uncertainty can lead to hesitation in committing to large-scale ULED implementations, slowing the overall adoption rate in the broadcasting industry.
Another major challenge lies in the power consumption of ULED displays. While they offer superior brightness and color accuracy compared to traditional LED technologies, ULEDs typically require more energy to operate. This increased power demand not only raises operational costs but also poses environmental concerns, particularly in an era where energy efficiency is paramount.
Heat management presents a substantial technical hurdle for ULED systems in broadcasting environments. The intense brightness and high pixel density of ULED displays generate significant heat, which can lead to performance degradation and reduced lifespan if not properly managed. Developing effective cooling solutions that do not compromise the slim profile and aesthetic appeal of ULED displays remains a critical challenge.
Color accuracy and consistency across large ULED displays pose another set of challenges. Achieving uniform color reproduction and maintaining it over time requires sophisticated calibration techniques and quality control measures. This is particularly crucial in broadcasting applications where color fidelity is essential for delivering high-quality visual content to viewers.
The integration of ULED technology with existing broadcasting infrastructure and workflows presents logistical and technical challenges. Many broadcasters have invested heavily in current systems, and the transition to ULED may require significant upgrades to supporting equipment, software, and transmission protocols. This integration process can be complex, time-consuming, and potentially disruptive to ongoing operations.
Durability and longevity of ULED displays in demanding broadcasting environments are ongoing concerns. The technology must withstand continuous operation, varying environmental conditions, and potential physical impacts without compromising performance or requiring frequent replacements. Developing robust ULED solutions that can maintain their quality over extended periods is crucial for their adoption in professional broadcasting settings.
Lastly, the rapid pace of technological advancement in display technologies presents a challenge for ULED adoption. Broadcasters must weigh the benefits of investing in current ULED technology against the potential for newer, more advanced solutions emerging in the near future. This uncertainty can lead to hesitation in committing to large-scale ULED implementations, slowing the overall adoption rate in the broadcasting industry.
Current ULED Solutions
01 ULED structure and fabrication
Ultra Light Emitting Diodes (ULEDs) are advanced semiconductor devices with unique structural features and fabrication methods. They are designed to achieve higher efficiency and brightness compared to conventional LEDs. The structure may include specialized layers, quantum wells, or nanostructures to enhance light emission. Fabrication techniques focus on optimizing the active region and improving light extraction.- ULED structure and composition: Ultra Light Emitting Diodes (ULEDs) are advanced semiconductor devices with unique structural and compositional features. They are designed to emit light with high efficiency and brightness while maintaining a compact form factor. The structure typically includes specialized layers of semiconductor materials and may incorporate novel materials or quantum structures to enhance performance.
- ULED manufacturing processes: The manufacturing of ULEDs involves sophisticated processes to achieve their ultra-small size and high performance. These may include advanced epitaxial growth techniques, precise doping methods, and nanoscale fabrication processes. Special attention is given to maintaining high quality and uniformity in production to ensure consistent performance across devices.
- ULED applications in displays: ULEDs are increasingly being used in display technologies, offering advantages such as higher brightness, better color accuracy, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays. They are particularly suitable for high-resolution, small form factor displays used in various electronic devices.
- ULED power efficiency and thermal management: A key feature of ULEDs is their high power efficiency, which allows for brighter output with lower energy consumption. However, this also presents challenges in thermal management. Innovative cooling solutions and heat dissipation techniques are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of ULED devices.
- ULED integration with control circuits: The integration of ULEDs with sophisticated control circuits is essential for their operation in various applications. This includes the development of specialized drivers, power management systems, and control algorithms to optimize performance, enable dynamic control of brightness and color, and ensure compatibility with different electronic systems.
02 ULED applications in display technology
ULEDs are increasingly being utilized in display technologies, offering advantages such as higher brightness, improved color gamut, and energy efficiency. They are particularly suitable for high-resolution displays, including smartphones, televisions, and automotive displays. The integration of ULEDs in display panels allows for thinner designs and enhanced visual performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 ULED packaging and thermal management
Effective packaging and thermal management are crucial for ULED performance and longevity. Advanced packaging techniques are employed to protect the ULED chip and optimize light output. Thermal management solutions are designed to dissipate heat efficiently, preventing performance degradation and extending the device lifespan. This may include innovative heat sink designs or thermally conductive materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 ULED driver circuits and control systems
Specialized driver circuits and control systems are developed for ULEDs to manage power delivery and optimize performance. These circuits may include advanced dimming capabilities, precise current control, and protection features. Control systems can enable dynamic adjustment of ULED output based on ambient conditions or user preferences, enhancing energy efficiency and user experience.Expand Specific Solutions05 ULED materials and quantum dot integration
Research in ULED technology focuses on developing new materials and integrating quantum dots to enhance performance. Novel semiconductor materials and quantum dot structures are explored to improve light emission efficiency, color purity, and spectral characteristics. This includes investigating different compositions of III-V semiconductors and optimizing quantum dot synthesis for ULED applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key ULED Players
The research on ULED in modern broadcasting technologies is in a dynamic growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly due to increasing demand for high-quality displays in various applications. The technology is maturing, but still offers significant room for innovation. Key players like LG Electronics, Samsung Electronics, and Sony Group are driving advancements, while companies such as Huawei Technologies and Apple are integrating ULED into their product ecosystems. The competitive landscape is diverse, with traditional electronics giants competing alongside specialized firms like Lumileds and eLux. Research institutions and universities, including Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft and Ghent University, are contributing to technological breakthroughs, indicating a collaborative yet competitive environment in this emerging field.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG has invested heavily in ULED technology for broadcasting applications. Their ULED displays feature NanoCell technology, which uses nanoparticles to filter out impure color wavelengths, resulting in more accurate and vibrant colors. LG's ULED panels also incorporate full-array local dimming for enhanced contrast and black levels. The company has developed AI-enhanced processors to optimize image quality in real-time, adjusting settings based on content and ambient lighting conditions. LG's ULED technology also supports various HDR formats, including Dolby Vision and HDR10+, to ensure compatibility with a wide range of broadcast content.
Strengths: Excellent color reproduction, wide viewing angles, and strong HDR performance. Weaknesses: Slightly lower peak brightness compared to some competitors, potential for blooming in high-contrast scenes.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has made significant strides in ULED technology for broadcasting applications. Their ULED displays utilize a proprietary light-emitting quantum dot material that offers improved color accuracy and energy efficiency. Huawei's ULED panels feature advanced local dimming algorithms to enhance contrast and black levels. The company has also developed AI-powered image processing chips that optimize picture quality in real-time, adjusting parameters such as sharpness, color, and contrast based on the content being displayed. Huawei's ULED technology supports high refresh rates and low latency, making it suitable for live sports broadcasting and other fast-paced content.
Strengths: High energy efficiency, excellent color accuracy, and advanced AI-powered image processing. Weaknesses: Limited market presence outside of China, potential concerns over data security in some markets.
ULED Core Innovations
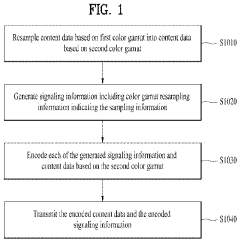
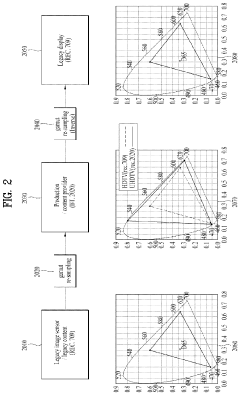
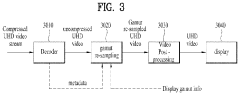
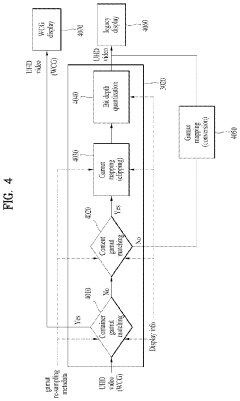
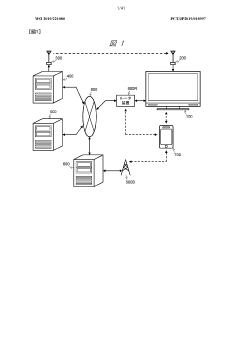
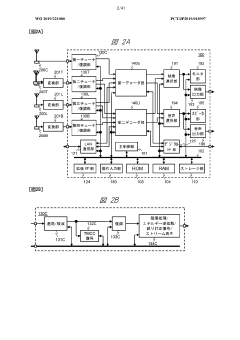
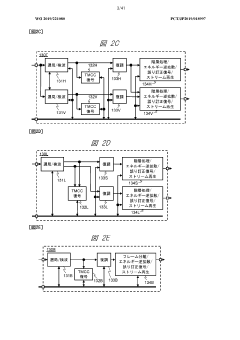
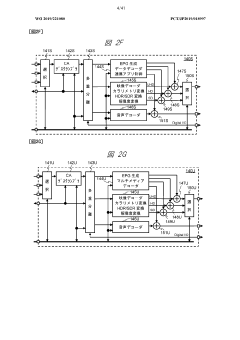
Method and device for transmitting and receiving broadcast signal on basis of color gamut resampling
PatentActiveUS11871053B2
Innovation
- A method for transmitting and receiving broadcast signals that involves resampling content data from one color gamut to another, including generating and encoding signaling information for color gamut resampling, and using conversion equations or lookup tables to adapt the content to the display's color gamut, ensuring optimal display performance.
Broadcast reception device and method for processing carrier wave
PatentWO2019221080A1
Innovation
- A broadcast receiving device equipped with multiple tuners and demodulators that can identify and process transmission waves with different modulation methods, using identification information to switch between current and advanced digital broadcasting services, allowing for simultaneous reception and transmission of UHD signals alongside existing services.
Broadcast Standards
Broadcast standards play a crucial role in the implementation and adoption of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology in modern broadcasting. These standards ensure interoperability, quality, and consistency across different devices and platforms.
The primary broadcast standards relevant to ULED technology include ATSC 3.0 (Advanced Television Systems Committee), DVB-T2 (Digital Video Broadcasting - Second Generation Terrestrial), and ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting - Terrestrial). These standards have been developed to support high-resolution content delivery, which aligns well with ULED's capabilities.
ATSC 3.0, also known as NextGen TV, is particularly significant for ULED integration. It supports 4K Ultra HD resolution, High Dynamic Range (HDR), Wide Color Gamut (WCG), and high frame rates, all of which can leverage ULED's superior display characteristics. The standard's IP-based architecture also facilitates more efficient content delivery and interactive features, enhancing the overall viewing experience on ULED displays.
DVB-T2, widely adopted in Europe and other regions, offers improved spectral efficiency and robustness compared to its predecessor. It supports higher data rates, making it suitable for transmitting high-quality content that can fully utilize ULED's capabilities. The standard's flexibility in terms of modulation and coding schemes allows broadcasters to optimize transmission parameters based on specific requirements, which is beneficial for ULED content delivery.
ISDB-T, used in Japan and several other countries, also supports high-definition broadcasting and mobile reception. While not as advanced as ATSC 3.0 in terms of resolution support, it still provides a solid foundation for ULED integration in broadcasting systems.
These broadcast standards are continually evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. For instance, work is underway to develop standards that support 8K resolution, which will further push the boundaries of what ULED technology can offer in broadcasting applications.
The implementation of these standards for ULED broadcasting requires careful consideration of various factors, including signal processing, compression techniques, and transmission protocols. Broadcasters and equipment manufacturers must ensure compliance with these standards to guarantee seamless integration of ULED technology into existing broadcasting ecosystems.
As ULED technology continues to advance, it is likely that broadcast standards will need to be updated or new ones developed to fully harness its potential. This ongoing evolution of standards will be crucial in shaping the future of ULED in modern broadcasting technologies.
The primary broadcast standards relevant to ULED technology include ATSC 3.0 (Advanced Television Systems Committee), DVB-T2 (Digital Video Broadcasting - Second Generation Terrestrial), and ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting - Terrestrial). These standards have been developed to support high-resolution content delivery, which aligns well with ULED's capabilities.
ATSC 3.0, also known as NextGen TV, is particularly significant for ULED integration. It supports 4K Ultra HD resolution, High Dynamic Range (HDR), Wide Color Gamut (WCG), and high frame rates, all of which can leverage ULED's superior display characteristics. The standard's IP-based architecture also facilitates more efficient content delivery and interactive features, enhancing the overall viewing experience on ULED displays.
DVB-T2, widely adopted in Europe and other regions, offers improved spectral efficiency and robustness compared to its predecessor. It supports higher data rates, making it suitable for transmitting high-quality content that can fully utilize ULED's capabilities. The standard's flexibility in terms of modulation and coding schemes allows broadcasters to optimize transmission parameters based on specific requirements, which is beneficial for ULED content delivery.
ISDB-T, used in Japan and several other countries, also supports high-definition broadcasting and mobile reception. While not as advanced as ATSC 3.0 in terms of resolution support, it still provides a solid foundation for ULED integration in broadcasting systems.
These broadcast standards are continually evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. For instance, work is underway to develop standards that support 8K resolution, which will further push the boundaries of what ULED technology can offer in broadcasting applications.
The implementation of these standards for ULED broadcasting requires careful consideration of various factors, including signal processing, compression techniques, and transmission protocols. Broadcasters and equipment manufacturers must ensure compliance with these standards to guarantee seamless integration of ULED technology into existing broadcasting ecosystems.
As ULED technology continues to advance, it is likely that broadcast standards will need to be updated or new ones developed to fully harness its potential. This ongoing evolution of standards will be crucial in shaping the future of ULED in modern broadcasting technologies.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology in modern broadcasting. ULED displays have made significant strides in reducing power consumption compared to traditional LED and LCD screens, offering substantial benefits for both broadcasters and viewers.
The primary mechanism for improved energy efficiency in ULED technology lies in its advanced light management system. ULED displays utilize a combination of local dimming and quantum dot technology to achieve higher brightness levels while consuming less power. This allows for more precise control over individual LED zones, enabling the display to selectively illuminate only the necessary areas of the screen.
Furthermore, ULED technology incorporates advanced power management algorithms that dynamically adjust the display's brightness based on ambient lighting conditions and content being displayed. This adaptive approach ensures optimal viewing experience while minimizing unnecessary power consumption, particularly beneficial in broadcasting environments where lighting conditions can vary significantly.
Another key factor contributing to ULED's energy efficiency is its improved thermal management. The technology employs advanced heat dissipation techniques, reducing the need for energy-intensive cooling systems often required in traditional broadcasting equipment. This not only lowers direct power consumption but also decreases the overall environmental impact of broadcasting facilities.
In the context of modern broadcasting, the energy efficiency of ULED technology translates to significant cost savings for broadcasters. The reduced power consumption leads to lower operational expenses, particularly in large-scale broadcasting setups where multiple displays are in use simultaneously. This efficiency also aligns with growing industry trends towards sustainable and environmentally responsible broadcasting practices.
Moreover, the energy efficiency of ULED technology extends beyond the broadcasting studio. As ULED displays become more prevalent in consumer electronics, including televisions and mobile devices, the cumulative energy savings across the entire broadcasting ecosystem become substantial. This widespread adoption of energy-efficient display technology contributes to a reduction in overall energy demand and associated carbon emissions in the broadcasting sector.
The primary mechanism for improved energy efficiency in ULED technology lies in its advanced light management system. ULED displays utilize a combination of local dimming and quantum dot technology to achieve higher brightness levels while consuming less power. This allows for more precise control over individual LED zones, enabling the display to selectively illuminate only the necessary areas of the screen.
Furthermore, ULED technology incorporates advanced power management algorithms that dynamically adjust the display's brightness based on ambient lighting conditions and content being displayed. This adaptive approach ensures optimal viewing experience while minimizing unnecessary power consumption, particularly beneficial in broadcasting environments where lighting conditions can vary significantly.
Another key factor contributing to ULED's energy efficiency is its improved thermal management. The technology employs advanced heat dissipation techniques, reducing the need for energy-intensive cooling systems often required in traditional broadcasting equipment. This not only lowers direct power consumption but also decreases the overall environmental impact of broadcasting facilities.
In the context of modern broadcasting, the energy efficiency of ULED technology translates to significant cost savings for broadcasters. The reduced power consumption leads to lower operational expenses, particularly in large-scale broadcasting setups where multiple displays are in use simultaneously. This efficiency also aligns with growing industry trends towards sustainable and environmentally responsible broadcasting practices.
Moreover, the energy efficiency of ULED technology extends beyond the broadcasting studio. As ULED displays become more prevalent in consumer electronics, including televisions and mobile devices, the cumulative energy savings across the entire broadcasting ecosystem become substantial. This widespread adoption of energy-efficient display technology contributes to a reduction in overall energy demand and associated carbon emissions in the broadcasting sector.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!