ULED Displays: A Boon for Remote Collaboration
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED Display Evolution and Objectives
Ultra-LED (ULED) display technology has emerged as a significant advancement in the field of visual communication, particularly in the context of remote collaboration. The evolution of ULED displays can be traced back to the early 2000s when LED technology began to gain traction in the display market. Initially, LED displays were primarily used for large outdoor screens and billboards due to their high brightness and durability.
As the technology progressed, manufacturers focused on miniaturizing LED components, leading to the development of Micro-LED and Mini-LED technologies. These advancements paved the way for ULED displays, which offer superior picture quality, higher contrast ratios, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD and OLED displays.
The primary objective of ULED display technology in remote collaboration is to create a more immersive and lifelike visual experience for participants. This is achieved through several key features, including high dynamic range (HDR) imaging, wide color gamut, and local dimming capabilities. These features allow for more accurate color reproduction, deeper blacks, and brighter highlights, resulting in a more realistic representation of remote participants and shared content.
Another crucial objective of ULED displays in remote collaboration is to reduce eye strain and fatigue during extended video conferencing sessions. The technology's ability to produce images with higher refresh rates and lower blue light emissions contributes to a more comfortable viewing experience, especially during long meetings or collaborative work sessions.
ULED displays also aim to address the challenges of varying lighting conditions in different remote work environments. With their high brightness capabilities and advanced local dimming algorithms, ULED screens can adapt to different ambient lighting situations, ensuring optimal visibility and clarity for all participants, regardless of their physical location.
The evolution of ULED technology has also focused on improving energy efficiency, an important consideration for both environmental sustainability and operational costs in remote collaboration setups. Modern ULED displays consume significantly less power than their predecessors while maintaining superior image quality, making them an attractive option for organizations looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy expenses.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ULED display technology in remote collaboration include further enhancements in resolution, with 8K and even 16K displays on the horizon. These advancements will enable more detailed and lifelike representations of remote participants and shared content, further blurring the line between in-person and virtual interactions.
As the technology progressed, manufacturers focused on miniaturizing LED components, leading to the development of Micro-LED and Mini-LED technologies. These advancements paved the way for ULED displays, which offer superior picture quality, higher contrast ratios, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD and OLED displays.
The primary objective of ULED display technology in remote collaboration is to create a more immersive and lifelike visual experience for participants. This is achieved through several key features, including high dynamic range (HDR) imaging, wide color gamut, and local dimming capabilities. These features allow for more accurate color reproduction, deeper blacks, and brighter highlights, resulting in a more realistic representation of remote participants and shared content.
Another crucial objective of ULED displays in remote collaboration is to reduce eye strain and fatigue during extended video conferencing sessions. The technology's ability to produce images with higher refresh rates and lower blue light emissions contributes to a more comfortable viewing experience, especially during long meetings or collaborative work sessions.
ULED displays also aim to address the challenges of varying lighting conditions in different remote work environments. With their high brightness capabilities and advanced local dimming algorithms, ULED screens can adapt to different ambient lighting situations, ensuring optimal visibility and clarity for all participants, regardless of their physical location.
The evolution of ULED technology has also focused on improving energy efficiency, an important consideration for both environmental sustainability and operational costs in remote collaboration setups. Modern ULED displays consume significantly less power than their predecessors while maintaining superior image quality, making them an attractive option for organizations looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy expenses.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ULED display technology in remote collaboration include further enhancements in resolution, with 8K and even 16K displays on the horizon. These advancements will enable more detailed and lifelike representations of remote participants and shared content, further blurring the line between in-person and virtual interactions.
Remote Collaboration Market Analysis
The remote collaboration market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by technological advancements, changing work dynamics, and global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. This market encompasses a wide range of tools and technologies designed to facilitate communication, project management, and teamwork among geographically dispersed teams.
The global remote collaboration market size was valued at $32.5 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $60.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of flexible work arrangements, the rise of digital nomadism, and the need for businesses to access talent pools beyond their local regions.
Key segments within the remote collaboration market include video conferencing, project management tools, virtual whiteboards, and document sharing platforms. Among these, video conferencing has seen the most rapid growth, with market leaders like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet experiencing unprecedented user adoption rates during the pandemic.
The adoption of remote collaboration tools varies across industries, with the IT and telecom sector leading the way, followed closely by healthcare, education, and financial services. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly embracing these technologies to compete with larger organizations and access global markets.
Geographically, North America dominates the remote collaboration market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This is due to the presence of major technology companies, high internet penetration rates, and a culture of innovation. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid digitalization in countries like India and China.
Despite the overall positive outlook, the remote collaboration market faces challenges such as data security concerns, integration issues with existing systems, and the need for reliable high-speed internet infrastructure. Additionally, there is a growing demand for more immersive and engaging collaboration experiences, which is driving innovation in areas like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) for remote teamwork.
The emergence of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) display technology presents a significant opportunity in this evolving market. ULED displays offer superior image quality, energy efficiency, and potentially lower costs compared to traditional display technologies. These attributes make ULED displays particularly attractive for remote collaboration applications, where visual clarity and color accuracy are crucial for effective communication and teamwork.
The global remote collaboration market size was valued at $32.5 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $60.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of flexible work arrangements, the rise of digital nomadism, and the need for businesses to access talent pools beyond their local regions.
Key segments within the remote collaboration market include video conferencing, project management tools, virtual whiteboards, and document sharing platforms. Among these, video conferencing has seen the most rapid growth, with market leaders like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet experiencing unprecedented user adoption rates during the pandemic.
The adoption of remote collaboration tools varies across industries, with the IT and telecom sector leading the way, followed closely by healthcare, education, and financial services. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly embracing these technologies to compete with larger organizations and access global markets.
Geographically, North America dominates the remote collaboration market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This is due to the presence of major technology companies, high internet penetration rates, and a culture of innovation. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid digitalization in countries like India and China.
Despite the overall positive outlook, the remote collaboration market faces challenges such as data security concerns, integration issues with existing systems, and the need for reliable high-speed internet infrastructure. Additionally, there is a growing demand for more immersive and engaging collaboration experiences, which is driving innovation in areas like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) for remote teamwork.
The emergence of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) display technology presents a significant opportunity in this evolving market. ULED displays offer superior image quality, energy efficiency, and potentially lower costs compared to traditional display technologies. These attributes make ULED displays particularly attractive for remote collaboration applications, where visual clarity and color accuracy are crucial for effective communication and teamwork.
ULED Technology Status and Hurdles
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in recent years, positioning itself as a promising solution for high-quality displays in remote collaboration settings. However, the current state of ULED technology presents both advancements and challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
One of the primary advantages of ULED displays is their superior image quality. These displays offer enhanced brightness, contrast, and color accuracy compared to traditional LED and OLED technologies. This improvement in visual fidelity is particularly beneficial for remote collaboration, where clear and precise image reproduction is crucial for effective communication and shared visual experiences.
Despite these advancements, ULED technology faces several hurdles in its development and implementation. One significant challenge is the high production cost associated with manufacturing ULED displays. The intricate processes and materials required for ULED production currently limit its scalability and accessibility for mass-market applications.
Another obstacle is the power consumption of ULED displays. While they offer improved efficiency compared to some existing technologies, further optimization is needed to make them more suitable for portable devices and energy-conscious applications. This is particularly relevant in remote collaboration scenarios where battery life and energy efficiency are important considerations.
Durability and lifespan of ULED displays also present challenges. The technology must demonstrate long-term reliability and resistance to image retention or burn-in effects to be viable for extended use in professional settings. Addressing these concerns is crucial for ULED's adoption in remote collaboration tools that require consistent performance over time.
The integration of ULED technology with existing display ecosystems and standards poses another hurdle. Ensuring compatibility with various content formats, color spaces, and display interfaces is essential for seamless adoption in diverse remote collaboration environments.
From a global perspective, the development of ULED technology is concentrated in a few key regions, primarily in East Asia. This geographical concentration may lead to supply chain vulnerabilities and potential geopolitical implications for widespread adoption.
Research and development efforts are ongoing to address these challenges. Focus areas include improving manufacturing processes to reduce costs, enhancing energy efficiency, and developing more robust ULED materials. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize ULED technology for specific applications in remote collaboration, such as large-format displays for virtual meeting rooms and high-resolution portable devices for mobile professionals.
As the technology matures, overcoming these hurdles will be crucial for ULED displays to realize their full potential as a transformative tool in remote collaboration. The industry's ability to address these challenges will significantly influence the timeline and extent of ULED adoption in collaborative technologies.
One of the primary advantages of ULED displays is their superior image quality. These displays offer enhanced brightness, contrast, and color accuracy compared to traditional LED and OLED technologies. This improvement in visual fidelity is particularly beneficial for remote collaboration, where clear and precise image reproduction is crucial for effective communication and shared visual experiences.
Despite these advancements, ULED technology faces several hurdles in its development and implementation. One significant challenge is the high production cost associated with manufacturing ULED displays. The intricate processes and materials required for ULED production currently limit its scalability and accessibility for mass-market applications.
Another obstacle is the power consumption of ULED displays. While they offer improved efficiency compared to some existing technologies, further optimization is needed to make them more suitable for portable devices and energy-conscious applications. This is particularly relevant in remote collaboration scenarios where battery life and energy efficiency are important considerations.
Durability and lifespan of ULED displays also present challenges. The technology must demonstrate long-term reliability and resistance to image retention or burn-in effects to be viable for extended use in professional settings. Addressing these concerns is crucial for ULED's adoption in remote collaboration tools that require consistent performance over time.
The integration of ULED technology with existing display ecosystems and standards poses another hurdle. Ensuring compatibility with various content formats, color spaces, and display interfaces is essential for seamless adoption in diverse remote collaboration environments.
From a global perspective, the development of ULED technology is concentrated in a few key regions, primarily in East Asia. This geographical concentration may lead to supply chain vulnerabilities and potential geopolitical implications for widespread adoption.
Research and development efforts are ongoing to address these challenges. Focus areas include improving manufacturing processes to reduce costs, enhancing energy efficiency, and developing more robust ULED materials. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize ULED technology for specific applications in remote collaboration, such as large-format displays for virtual meeting rooms and high-resolution portable devices for mobile professionals.
As the technology matures, overcoming these hurdles will be crucial for ULED displays to realize their full potential as a transformative tool in remote collaboration. The industry's ability to address these challenges will significantly influence the timeline and extent of ULED adoption in collaborative technologies.
Current ULED Solutions for Remote Work
01 ULED display structure and manufacturing
ULED displays utilize ultra-small LED chips for high-resolution and energy-efficient screens. The manufacturing process involves precise placement and bonding of micro-LEDs on a substrate, with advanced techniques for improved yield and performance. These displays offer superior brightness, contrast, and color gamut compared to traditional LED displays.- ULED display structure and manufacturing: ULED displays incorporate advanced structural designs and manufacturing techniques to enhance performance. This includes innovations in pixel arrangements, substrate materials, and fabrication processes to improve efficiency, brightness, and color accuracy. The technology often involves miniaturized LED components and specialized driving circuits to achieve high-resolution displays with superior image quality.
- Backlight and light emission control: ULED displays utilize sophisticated backlight systems and light emission control mechanisms. These may include advanced local dimming techniques, quantum dot technology for color enhancement, and precise control over individual LED elements. Such innovations contribute to improved contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and more vibrant colors, resulting in a superior viewing experience.
- Heat dissipation and power efficiency: Effective heat management and power efficiency are crucial aspects of ULED display technology. Innovations in this area include advanced thermal management systems, energy-efficient driving methods, and optimized power distribution across the display panel. These improvements help maintain display performance while reducing power consumption and extending the lifespan of the display.
- Display panel integration and modular design: ULED displays often feature modular designs and innovative integration techniques. This approach allows for easier manufacturing, maintenance, and scalability of display panels. Modular designs can facilitate the creation of large-scale displays with seamless connections between modules, as well as enable flexible configurations for various applications and environments.
- Image processing and display control: Advanced image processing algorithms and display control systems are integral to ULED technology. These may include real-time image enhancement techniques, adaptive brightness control, and color management systems. Such features ensure optimal picture quality across various content types and viewing conditions, while also addressing potential issues like image retention or motion blur.
02 Driving and control systems for ULED displays
Specialized driving circuits and control systems are crucial for ULED displays. These systems manage the individual addressing and current control of micro-LED pixels, ensuring uniform brightness and color accuracy across the display. Advanced algorithms and hardware solutions are implemented to optimize power consumption and image quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 ULED display panel design and integration
ULED display panels are designed for seamless integration into various devices and applications. This includes considerations for thin form factors, flexible substrates, and modular designs. The integration process involves addressing challenges such as heat dissipation, electrical interconnects, and optical performance optimization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color management and image processing for ULED displays
Advanced color management techniques and image processing algorithms are employed in ULED displays to achieve superior visual quality. This includes methods for color calibration, gamut mapping, and high dynamic range (HDR) content rendering. Specialized hardware and software solutions are developed to handle the unique characteristics of micro-LED pixels.Expand Specific Solutions05 ULED display applications and innovations
ULED technology is being applied to a wide range of display applications, including smartphones, televisions, automotive displays, and augmented reality devices. Ongoing innovations focus on improving energy efficiency, expanding color gamut, enhancing durability, and exploring new form factors such as transparent and flexible ULED displays.Expand Specific Solutions
Key ULED Industry Players
The ULED display market for remote collaboration is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-quality visual communication tools. The market size is expanding rapidly, with major players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and Sony Group investing heavily in research and development. Technologically, ULED displays are advancing quickly, with companies such as Universal Display Corp. and Lumileds LLC pushing the boundaries of efficiency and color accuracy. While established tech giants like Microsoft and Qualcomm are integrating ULED technology into their collaboration platforms, emerging players like Appotronics Corp. and VIZIO are also making significant strides, indicating a competitive and innovative landscape.
Universal Display Corp.
Technical Solution: Universal Display Corporation has developed advanced OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology, which can be applied to ULED displays for remote collaboration. Their phosphorescent OLED (PHOLED) materials and technology offer superior energy efficiency, color accuracy, and display quality. For remote collaboration, ULED displays using this technology can provide high-resolution, vibrant images with excellent contrast ratios, making it easier for remote participants to see fine details and facial expressions. The company's flexible OLED technology also allows for the creation of curved or foldable displays, which can enhance the immersive experience in virtual meeting spaces.
Strengths: Superior energy efficiency, excellent color accuracy, and flexibility for innovative display designs. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional LED displays, and potential for image retention in static content scenarios.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed Quantum Dot LED (QLED) technology, which can be applied to ULED displays for remote collaboration. Their QLED displays use quantum dots to produce highly saturated colors and improved brightness levels. For remote collaboration, these displays offer excellent color volume and peak brightness, ensuring that participants can see clear, vivid images even in varying lighting conditions. Samsung has also integrated AI-powered upscaling technology in their displays, which can enhance lower resolution content to near-ULED quality, beneficial for handling various input sources in remote collaboration scenarios.
Strengths: Excellent color reproduction, high brightness levels, and AI-enhanced image processing. Weaknesses: Slightly lower contrast ratios compared to OLED technology, and potential for higher power consumption at peak brightness levels.
ULED Display Core Patents and Research
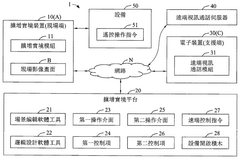
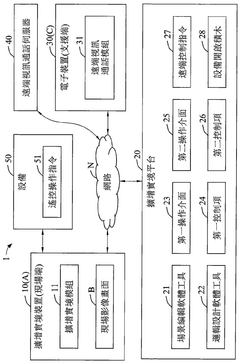
Remote device control system, method and computer readable medium for augmented reality collaboration
PatentActiveTW202343228A
Innovation
- Integration of augmented reality with remote device control for enhanced collaboration between field and support terminals.
- Real-time overlay of operation interfaces on live image screens for both field and support terminals.
- Seamless video collaboration allowing support terminal to view and control field devices remotely.
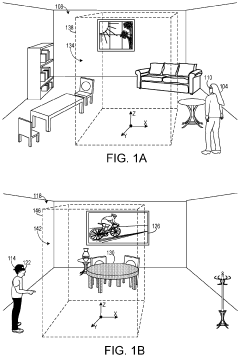
Remote collaborations with volumetric space indications
PatentActiveUS11968475B2
Innovation
- A head-mounted display (HMD) device generates and displays volumetric spaces in both environments that satisfy collaboration criteria, such as absence of objects, allowing users to visualize these spaces and share virtual content without obstructions, using spatial mapping and recognition techniques to identify suitable areas for interaction.
ULED Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays have emerged as a promising technology for remote collaboration, offering significant advantages in energy efficiency and sustainability. These displays utilize advanced semiconductor materials and innovative manufacturing processes to achieve superior energy performance compared to traditional LED and OLED technologies.
The energy efficiency of ULED displays is primarily attributed to their unique structure and operating principles. ULEDs employ quantum dot technology, which allows for precise control of light emission at the nanoscale level. This results in highly efficient conversion of electrical energy into light, with minimal energy loss through heat dissipation. Studies have shown that ULED displays can achieve up to 30% higher energy efficiency compared to conventional LED displays and up to 50% higher efficiency than OLED displays.
In terms of sustainability, ULED technology offers several key benefits. The manufacturing process for ULEDs requires fewer rare earth materials compared to traditional LED and OLED production, reducing the environmental impact associated with mining and processing these resources. Additionally, the longer lifespan of ULED displays, typically ranging from 50,000 to 100,000 hours, contributes to reduced electronic waste and lower replacement frequencies.
The power consumption of ULED displays is significantly lower than that of their counterparts, particularly in remote collaboration scenarios where displays may be in use for extended periods. This reduced energy demand translates to lower carbon emissions and decreased strain on power grids, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainable technology adoption.
Furthermore, ULED displays exhibit excellent color accuracy and brightness levels while consuming less power. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for remote collaboration, as it allows for high-quality visual communication without compromising on energy efficiency. The ability to maintain vibrant and accurate colors at lower brightness settings further contributes to energy savings in various lighting conditions.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring ways to further enhance the energy efficiency and sustainability of ULED displays. Current areas of focus include improving the quantum yield of the quantum dot materials, optimizing the display's light extraction efficiency, and developing more eco-friendly manufacturing processes. These advancements are expected to solidify ULED's position as a sustainable choice for remote collaboration technologies in the coming years.
The energy efficiency of ULED displays is primarily attributed to their unique structure and operating principles. ULEDs employ quantum dot technology, which allows for precise control of light emission at the nanoscale level. This results in highly efficient conversion of electrical energy into light, with minimal energy loss through heat dissipation. Studies have shown that ULED displays can achieve up to 30% higher energy efficiency compared to conventional LED displays and up to 50% higher efficiency than OLED displays.
In terms of sustainability, ULED technology offers several key benefits. The manufacturing process for ULEDs requires fewer rare earth materials compared to traditional LED and OLED production, reducing the environmental impact associated with mining and processing these resources. Additionally, the longer lifespan of ULED displays, typically ranging from 50,000 to 100,000 hours, contributes to reduced electronic waste and lower replacement frequencies.
The power consumption of ULED displays is significantly lower than that of their counterparts, particularly in remote collaboration scenarios where displays may be in use for extended periods. This reduced energy demand translates to lower carbon emissions and decreased strain on power grids, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainable technology adoption.
Furthermore, ULED displays exhibit excellent color accuracy and brightness levels while consuming less power. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for remote collaboration, as it allows for high-quality visual communication without compromising on energy efficiency. The ability to maintain vibrant and accurate colors at lower brightness settings further contributes to energy savings in various lighting conditions.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring ways to further enhance the energy efficiency and sustainability of ULED displays. Current areas of focus include improving the quantum yield of the quantum dot materials, optimizing the display's light extraction efficiency, and developing more eco-friendly manufacturing processes. These advancements are expected to solidify ULED's position as a sustainable choice for remote collaboration technologies in the coming years.
ULED Display Integration Challenges
The integration of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays into remote collaboration systems presents several significant challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost associated with ULED technology, which may limit its widespread adoption in various collaboration environments. The manufacturing process for ULED displays is complex and requires specialized equipment, contributing to the overall expense.
Another challenge lies in the power consumption of ULED displays. While they offer superior brightness and color accuracy compared to traditional LED displays, they also tend to consume more energy. This increased power requirement may pose difficulties in portable or battery-operated devices used for remote collaboration, potentially limiting their mobility and usage duration.
Heat management is a critical concern in ULED display integration. The high brightness levels achieved by ULED technology generate substantial heat, which can affect the longevity and performance of the display if not properly managed. Implementing effective cooling systems without compromising the sleek design of collaboration devices is a significant engineering challenge.
Compatibility with existing software and hardware systems is another hurdle in ULED display integration. Many current remote collaboration platforms and devices may not be optimized for the advanced capabilities of ULED displays, requiring substantial updates or redesigns to fully leverage the technology's potential.
The durability and lifespan of ULED displays in high-use collaboration environments is an area that requires further research and development. The intense brightness and constant operation in professional settings may lead to faster degradation of display quality over time, necessitating more frequent replacements or maintenance.
Color calibration and consistency across different ULED displays used in remote collaboration setups present another challenge. Ensuring that all participants in a remote meeting perceive colors and details identically is crucial for effective collaboration, especially in fields where color accuracy is paramount, such as design or medical imaging.
Lastly, the integration of touch functionality with ULED displays for interactive collaboration tools poses technical difficulties. Combining the high brightness and resolution of ULED technology with responsive and accurate touch sensors requires innovative solutions to maintain display quality while enabling intuitive user interaction.
Another challenge lies in the power consumption of ULED displays. While they offer superior brightness and color accuracy compared to traditional LED displays, they also tend to consume more energy. This increased power requirement may pose difficulties in portable or battery-operated devices used for remote collaboration, potentially limiting their mobility and usage duration.
Heat management is a critical concern in ULED display integration. The high brightness levels achieved by ULED technology generate substantial heat, which can affect the longevity and performance of the display if not properly managed. Implementing effective cooling systems without compromising the sleek design of collaboration devices is a significant engineering challenge.
Compatibility with existing software and hardware systems is another hurdle in ULED display integration. Many current remote collaboration platforms and devices may not be optimized for the advanced capabilities of ULED displays, requiring substantial updates or redesigns to fully leverage the technology's potential.
The durability and lifespan of ULED displays in high-use collaboration environments is an area that requires further research and development. The intense brightness and constant operation in professional settings may lead to faster degradation of display quality over time, necessitating more frequent replacements or maintenance.
Color calibration and consistency across different ULED displays used in remote collaboration setups present another challenge. Ensuring that all participants in a remote meeting perceive colors and details identically is crucial for effective collaboration, especially in fields where color accuracy is paramount, such as design or medical imaging.
Lastly, the integration of touch functionality with ULED displays for interactive collaboration tools poses technical difficulties. Combining the high brightness and resolution of ULED technology with responsive and accurate touch sensors requires innovative solutions to maintain display quality while enabling intuitive user interaction.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!