How to Navigate ULED Supply Chain Challenges?
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED Supply Chain Overview and Objectives
The ULED (Ultra-Light Emitting Diode) supply chain has become increasingly complex and challenging in recent years, driven by rapid technological advancements and growing market demand. This overview aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current ULED supply chain landscape and outline the objectives for navigating its challenges.
The ULED supply chain encompasses a wide range of components and processes, from raw material sourcing to final product assembly. Key elements include semiconductor materials, epitaxial wafers, chip fabrication, packaging, and integration into display panels or lighting systems. Each stage of the supply chain faces unique challenges, such as material scarcity, production bottlenecks, and quality control issues.
One of the primary objectives in addressing ULED supply chain challenges is to ensure a stable and reliable supply of critical components. This involves diversifying supplier networks, developing alternative sourcing strategies, and implementing robust inventory management systems. By reducing dependence on single suppliers or regions, companies can mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
Another crucial objective is to optimize production efficiency and reduce costs throughout the supply chain. This can be achieved through the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and artificial intelligence, to streamline processes and improve yield rates. Additionally, implementing lean manufacturing principles and just-in-time inventory management can help minimize waste and reduce carrying costs.
Enhancing supply chain visibility and transparency is also a key goal in navigating ULED supply chain challenges. This involves implementing advanced tracking and tracing systems, leveraging blockchain technology for secure and transparent record-keeping, and fostering closer collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. Improved visibility enables better decision-making, faster response times to disruptions, and more accurate demand forecasting.
Sustainability and environmental considerations have become increasingly important objectives in the ULED supply chain. Companies are focusing on reducing carbon footprints, minimizing waste, and ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials. This includes developing more energy-efficient production processes, implementing circular economy principles, and working with suppliers to improve their environmental practices.
Lastly, addressing the skills gap and workforce development is a critical objective for the ULED industry. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, there is a growing need for skilled professionals in areas such as advanced manufacturing, materials science, and supply chain management. Investing in training programs, partnerships with educational institutions, and fostering a culture of continuous learning are essential strategies to meet this objective.
The ULED supply chain encompasses a wide range of components and processes, from raw material sourcing to final product assembly. Key elements include semiconductor materials, epitaxial wafers, chip fabrication, packaging, and integration into display panels or lighting systems. Each stage of the supply chain faces unique challenges, such as material scarcity, production bottlenecks, and quality control issues.
One of the primary objectives in addressing ULED supply chain challenges is to ensure a stable and reliable supply of critical components. This involves diversifying supplier networks, developing alternative sourcing strategies, and implementing robust inventory management systems. By reducing dependence on single suppliers or regions, companies can mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
Another crucial objective is to optimize production efficiency and reduce costs throughout the supply chain. This can be achieved through the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and artificial intelligence, to streamline processes and improve yield rates. Additionally, implementing lean manufacturing principles and just-in-time inventory management can help minimize waste and reduce carrying costs.
Enhancing supply chain visibility and transparency is also a key goal in navigating ULED supply chain challenges. This involves implementing advanced tracking and tracing systems, leveraging blockchain technology for secure and transparent record-keeping, and fostering closer collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. Improved visibility enables better decision-making, faster response times to disruptions, and more accurate demand forecasting.
Sustainability and environmental considerations have become increasingly important objectives in the ULED supply chain. Companies are focusing on reducing carbon footprints, minimizing waste, and ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials. This includes developing more energy-efficient production processes, implementing circular economy principles, and working with suppliers to improve their environmental practices.
Lastly, addressing the skills gap and workforce development is a critical objective for the ULED industry. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, there is a growing need for skilled professionals in areas such as advanced manufacturing, materials science, and supply chain management. Investing in training programs, partnerships with educational institutions, and fostering a culture of continuous learning are essential strategies to meet this objective.
ULED Market Demand Analysis
The ULED (Ultra-Light Emitting Diode) market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-performance display technologies across various industries. The global ULED market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next five years.
One of the primary factors fueling market demand is the rising adoption of ULED technology in consumer electronics, particularly in televisions and smartphones. Consumers are increasingly seeking devices with superior display quality, energy efficiency, and longer lifespan, all of which are hallmarks of ULED technology. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for advanced display technologies.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a significant driver of ULED demand. As vehicle manufacturers focus on enhancing in-car entertainment systems and dashboard displays, ULED technology is becoming increasingly prevalent in high-end and mid-range vehicles. The technology's ability to provide bright, clear displays even in challenging lighting conditions makes it particularly suitable for automotive applications.
In the commercial sector, ULED displays are gaining traction in digital signage and large-format displays. Retail stores, airports, and other public spaces are adopting ULED technology for its superior brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays. This trend is expected to accelerate as businesses seek to create more engaging and immersive visual experiences for their customers.
The healthcare industry represents another growing market for ULED technology. Medical imaging devices, surgical displays, and patient monitoring systems are increasingly incorporating ULED displays due to their high resolution and color accuracy, which are crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Despite the positive market outlook, several factors could potentially impact ULED demand. The ongoing global semiconductor shortage has created supply chain challenges, potentially affecting production capacity and leading to increased costs. Additionally, the emergence of competing display technologies, such as OLED and MicroLED, may impact ULED market share in certain segments.
To navigate these supply chain challenges and maintain market growth, ULED manufacturers and suppliers need to focus on diversifying their supply sources, investing in research and development to improve production efficiency, and exploring vertical integration strategies. Collaboration with key stakeholders across the supply chain, including raw material suppliers and equipment manufacturers, will be crucial in mitigating risks and ensuring a stable supply of ULED components.
One of the primary factors fueling market demand is the rising adoption of ULED technology in consumer electronics, particularly in televisions and smartphones. Consumers are increasingly seeking devices with superior display quality, energy efficiency, and longer lifespan, all of which are hallmarks of ULED technology. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for advanced display technologies.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a significant driver of ULED demand. As vehicle manufacturers focus on enhancing in-car entertainment systems and dashboard displays, ULED technology is becoming increasingly prevalent in high-end and mid-range vehicles. The technology's ability to provide bright, clear displays even in challenging lighting conditions makes it particularly suitable for automotive applications.
In the commercial sector, ULED displays are gaining traction in digital signage and large-format displays. Retail stores, airports, and other public spaces are adopting ULED technology for its superior brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays. This trend is expected to accelerate as businesses seek to create more engaging and immersive visual experiences for their customers.
The healthcare industry represents another growing market for ULED technology. Medical imaging devices, surgical displays, and patient monitoring systems are increasingly incorporating ULED displays due to their high resolution and color accuracy, which are crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Despite the positive market outlook, several factors could potentially impact ULED demand. The ongoing global semiconductor shortage has created supply chain challenges, potentially affecting production capacity and leading to increased costs. Additionally, the emergence of competing display technologies, such as OLED and MicroLED, may impact ULED market share in certain segments.
To navigate these supply chain challenges and maintain market growth, ULED manufacturers and suppliers need to focus on diversifying their supply sources, investing in research and development to improve production efficiency, and exploring vertical integration strategies. Collaboration with key stakeholders across the supply chain, including raw material suppliers and equipment manufacturers, will be crucial in mitigating risks and ensuring a stable supply of ULED components.
ULED Supply Chain Challenges and Bottlenecks
The ULED (Ultra-Light Emitting Diode) supply chain faces several significant challenges and bottlenecks that impact the industry's growth and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the limited availability of key raw materials, particularly rare earth elements essential for ULED production. The scarcity of these materials leads to price volatility and potential supply disruptions, affecting the entire manufacturing process.
Another major challenge is the concentration of production capabilities in specific geographic regions, primarily in East Asia. This concentration creates vulnerabilities in the supply chain, as evidenced by recent global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions. Diversifying production locations has become a critical concern for many companies in the industry.
The complexity of ULED manufacturing processes also presents a significant bottleneck. The production of high-quality ULEDs requires advanced technology and expertise, which are not widely available. This limitation restricts the number of capable suppliers, potentially leading to production bottlenecks and increased costs.
Intellectual property issues further complicate the ULED supply chain. Many key technologies are protected by patents, creating barriers for new entrants and potentially limiting innovation. Navigating this complex landscape of intellectual property rights can be challenging for companies looking to expand their presence in the ULED market.
Quality control is another critical challenge in the ULED supply chain. The performance and longevity of ULEDs are highly dependent on manufacturing precision. Ensuring consistent quality across different suppliers and production batches remains a significant hurdle, particularly as demand for higher-performance ULEDs grows.
The rapid pace of technological advancement in the ULED industry also creates challenges for the supply chain. As new ULED technologies emerge, suppliers must quickly adapt their production processes and capabilities. This constant evolution can lead to obsolescence of existing equipment and processes, requiring significant ongoing investment.
Lastly, environmental and regulatory concerns pose increasing challenges to the ULED supply chain. The production of ULEDs involves materials and processes that can have environmental impacts. Stricter regulations on manufacturing practices and material sourcing are likely to impact the supply chain, potentially increasing costs and complexity.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including diversifying supply sources, investing in research and development, improving manufacturing processes, and fostering closer collaboration between suppliers and manufacturers. As the ULED industry continues to grow, overcoming these supply chain bottlenecks will be crucial for ensuring sustainable growth and meeting increasing market demand.
Another major challenge is the concentration of production capabilities in specific geographic regions, primarily in East Asia. This concentration creates vulnerabilities in the supply chain, as evidenced by recent global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions. Diversifying production locations has become a critical concern for many companies in the industry.
The complexity of ULED manufacturing processes also presents a significant bottleneck. The production of high-quality ULEDs requires advanced technology and expertise, which are not widely available. This limitation restricts the number of capable suppliers, potentially leading to production bottlenecks and increased costs.
Intellectual property issues further complicate the ULED supply chain. Many key technologies are protected by patents, creating barriers for new entrants and potentially limiting innovation. Navigating this complex landscape of intellectual property rights can be challenging for companies looking to expand their presence in the ULED market.
Quality control is another critical challenge in the ULED supply chain. The performance and longevity of ULEDs are highly dependent on manufacturing precision. Ensuring consistent quality across different suppliers and production batches remains a significant hurdle, particularly as demand for higher-performance ULEDs grows.
The rapid pace of technological advancement in the ULED industry also creates challenges for the supply chain. As new ULED technologies emerge, suppliers must quickly adapt their production processes and capabilities. This constant evolution can lead to obsolescence of existing equipment and processes, requiring significant ongoing investment.
Lastly, environmental and regulatory concerns pose increasing challenges to the ULED supply chain. The production of ULEDs involves materials and processes that can have environmental impacts. Stricter regulations on manufacturing practices and material sourcing are likely to impact the supply chain, potentially increasing costs and complexity.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including diversifying supply sources, investing in research and development, improving manufacturing processes, and fostering closer collaboration between suppliers and manufacturers. As the ULED industry continues to grow, overcoming these supply chain bottlenecks will be crucial for ensuring sustainable growth and meeting increasing market demand.
Current ULED Supply Chain Strategies
01 Supply chain management for ULED production
Efficient supply chain management systems for ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) production, including inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and supplier coordination. These systems optimize the flow of materials and components, reducing costs and improving production efficiency in the ULED industry.- Supply chain management for ULED production: Efficient supply chain management is crucial for ULED production. This involves coordinating various stages of the manufacturing process, from raw material procurement to final product delivery. Advanced software systems are used to optimize inventory levels, track components, and manage logistics, ensuring smooth production flow and minimizing disruptions.
- Demand forecasting and inventory optimization for ULED components: Accurate demand forecasting is essential for maintaining optimal inventory levels of ULED components. This involves analyzing market trends, historical data, and customer preferences to predict future demand. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are employed to improve forecast accuracy and optimize inventory management, reducing costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
- Supplier relationship management in ULED industry: Effective supplier relationship management is critical in the ULED supply chain. This includes evaluating and selecting reliable suppliers, negotiating contracts, and maintaining collaborative relationships. Regular performance assessments and quality control measures are implemented to ensure consistent supply of high-quality components for ULED production.
- Risk management and resilience in ULED supply chain: Managing risks and building resilience in the ULED supply chain is crucial for maintaining continuous production. This involves identifying potential disruptions, developing contingency plans, and implementing strategies to mitigate risks. Diversifying suppliers, maintaining safety stocks, and employing real-time monitoring systems are some of the approaches used to enhance supply chain resilience.
- Technology integration in ULED supply chain: Integration of advanced technologies is transforming ULED supply chain management. This includes the use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time tracking, blockchain for enhanced transparency and traceability, and artificial intelligence for predictive analytics and decision-making. These technologies improve visibility, efficiency, and responsiveness throughout the supply chain.
02 Risk assessment in ULED supply chains
Methods for identifying and mitigating risks in ULED supply chains, including supplier reliability assessment, geopolitical risk analysis, and contingency planning. These approaches help maintain a stable supply of components and materials for ULED manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sustainable practices in ULED supply chains
Integration of sustainable practices in ULED supply chains, focusing on reducing environmental impact, improving energy efficiency, and implementing circular economy principles. This includes sourcing eco-friendly materials and optimizing logistics to minimize carbon footprint.Expand Specific Solutions04 Collaborative platforms for ULED supply chain partners
Development of collaborative digital platforms that connect various stakeholders in the ULED supply chain, facilitating real-time information sharing, joint problem-solving, and coordinated decision-making. These platforms enhance transparency and responsiveness across the supply network.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality control in ULED component sourcing
Advanced quality control methods for sourcing and validating ULED components, ensuring consistency and reliability in the supply chain. This includes automated inspection systems, traceability solutions, and supplier quality management programs tailored for the ULED industry.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ULED Supply Chain
The ULED supply chain landscape is characterized by a complex and competitive environment, currently in a growth phase with increasing market size and technological advancements. Key players like Lumileds LLC, Xiamen San'an Optoelectronics, and Samsung Electronics are driving innovation in this space. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with companies such as BOE Technology Group and LG Electronics pushing boundaries in display technologies. Emerging players like eLux, Inc. and Micledi Microdisplays BV are introducing novel approaches, while established firms like Osram and Crystal IS continue to refine existing technologies. The involvement of research institutions like King Abdullah University of Science & Technology and University College Cork suggests ongoing development and potential for future breakthroughs in ULED technology.
Lumileds LLC
Technical Solution: Lumileds has developed a robust supply chain management strategy for ULED production. They utilize a multi-sourcing approach for critical components and materials, maintaining relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate risks. The company has also invested in advanced inventory management systems and predictive analytics to anticipate supply chain disruptions. Lumileds has implemented a just-in-time manufacturing process, optimizing production schedules based on real-time demand forecasts. Additionally, they have established strategic partnerships with key suppliers, ensuring priority access to essential materials and components.
Strengths: Diversified supplier base, advanced analytics for demand forecasting, and strategic partnerships. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs due to multi-sourcing and maintaining larger inventory buffers.
Xiamen San'an Optoelectronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: San'an Optoelectronics has developed a vertically integrated supply chain for ULED production. The company controls multiple stages of the manufacturing process, from epitaxial wafer production to chip packaging. They have invested in large-scale production facilities to achieve economies of scale and reduce dependency on external suppliers. San'an has also implemented an advanced quality control system throughout their supply chain, ensuring consistent product quality. To address potential raw material shortages, the company has secured long-term contracts with key suppliers and is actively exploring alternative materials for ULED production.
Strengths: Vertical integration reduces supply chain risks, economies of scale, and strong quality control. Weaknesses: High capital investment required for vertical integration, potential inflexibility in adapting to rapid market changes.
Innovative ULED Supply Chain Solutions
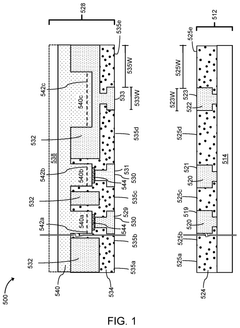
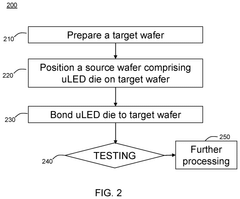
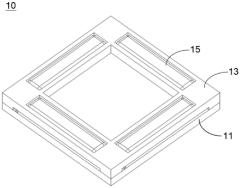
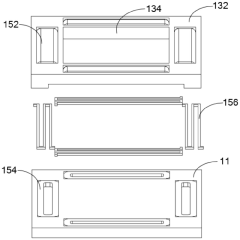
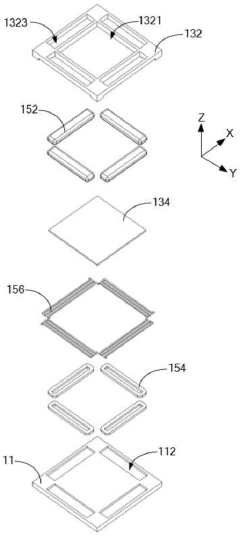
Hybrid Bonding With Micro-Light Emitting Diode (LED) Devices
PatentPendingUS20250056921A1
Innovation
- The development of micro-light emitting diode (uLED) devices utilizing hybrid bonding techniques, which combine metal-to-metal and dielectric-to-dielectric bonds between a source wafer and a target wafer, to ensure reliable electrical communication and assembly.
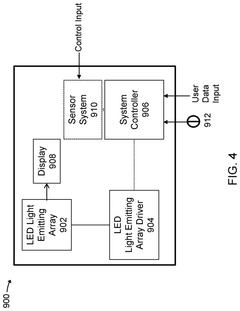
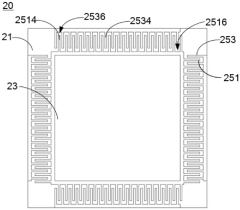
ULED packaging structure and imaging device
PatentPendingCN116741909A
Innovation
- By introducing a drive reset component into the uLED packaging structure, the drive frame moves in the second direction relative to the substrate to provide a reset force, using the persistence of vision of the human eye to reduce the impact of unlit uLEDs, stabilize imaging quality, and achieve a compact structure. change.
ULED Supply Chain Risk Management
In the rapidly evolving landscape of ULED (Ultra-Light Emitting Diode) technology, supply chain risk management has become a critical factor for manufacturers and suppliers. The complex nature of ULED production, coupled with global economic uncertainties, necessitates a robust risk management strategy to ensure continuity and efficiency in the supply chain.
One of the primary challenges in ULED supply chains is the sourcing of rare earth materials, which are essential components in ULED production. The limited geographical distribution of these materials and geopolitical tensions can lead to supply disruptions and price volatility. To mitigate this risk, companies are exploring alternative materials and investing in recycling technologies to reduce dependence on primary sources.
Another significant risk factor is the concentration of manufacturing capabilities in specific regions, particularly in East Asia. This geographical concentration exposes the supply chain to regional disruptions, such as natural disasters or political instability. Diversification of manufacturing locations and the development of redundant supply sources are becoming increasingly important strategies to enhance supply chain resilience.
The intricate nature of ULED technology also poses quality control challenges throughout the supply chain. Maintaining consistent quality across multiple suppliers and manufacturing stages requires sophisticated monitoring systems and stringent quality assurance protocols. Implementation of advanced tracking technologies, such as blockchain and IoT sensors, can improve traceability and help identify potential quality issues early in the supply chain.
Intellectual property (IP) protection is another critical aspect of ULED supply chain risk management. As the technology advances, safeguarding proprietary innovations becomes paramount. Companies are implementing stricter IP protection measures, including enhanced cybersecurity protocols and careful vetting of suppliers and partners to prevent unauthorized technology transfer or infringement.
The ongoing global chip shortage has highlighted the vulnerability of electronic component supply chains, including those for ULED technology. To address this, companies are adopting strategies such as long-term supplier partnerships, increased inventory buffers for critical components, and investment in domestic semiconductor production capabilities.
Lastly, the environmental impact of ULED production and disposal is an emerging risk factor that cannot be ignored. As sustainability becomes a key focus for consumers and regulators, companies must develop eco-friendly production processes and implement effective recycling programs to mitigate environmental risks and ensure long-term viability in the market.
One of the primary challenges in ULED supply chains is the sourcing of rare earth materials, which are essential components in ULED production. The limited geographical distribution of these materials and geopolitical tensions can lead to supply disruptions and price volatility. To mitigate this risk, companies are exploring alternative materials and investing in recycling technologies to reduce dependence on primary sources.
Another significant risk factor is the concentration of manufacturing capabilities in specific regions, particularly in East Asia. This geographical concentration exposes the supply chain to regional disruptions, such as natural disasters or political instability. Diversification of manufacturing locations and the development of redundant supply sources are becoming increasingly important strategies to enhance supply chain resilience.
The intricate nature of ULED technology also poses quality control challenges throughout the supply chain. Maintaining consistent quality across multiple suppliers and manufacturing stages requires sophisticated monitoring systems and stringent quality assurance protocols. Implementation of advanced tracking technologies, such as blockchain and IoT sensors, can improve traceability and help identify potential quality issues early in the supply chain.
Intellectual property (IP) protection is another critical aspect of ULED supply chain risk management. As the technology advances, safeguarding proprietary innovations becomes paramount. Companies are implementing stricter IP protection measures, including enhanced cybersecurity protocols and careful vetting of suppliers and partners to prevent unauthorized technology transfer or infringement.
The ongoing global chip shortage has highlighted the vulnerability of electronic component supply chains, including those for ULED technology. To address this, companies are adopting strategies such as long-term supplier partnerships, increased inventory buffers for critical components, and investment in domestic semiconductor production capabilities.
Lastly, the environmental impact of ULED production and disposal is an emerging risk factor that cannot be ignored. As sustainability becomes a key focus for consumers and regulators, companies must develop eco-friendly production processes and implement effective recycling programs to mitigate environmental risks and ensure long-term viability in the market.
Sustainability in ULED Supply Chain
Sustainability in the ULED (Ultra-Light Emitting Diode) supply chain is becoming increasingly crucial as the industry faces growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. To navigate these challenges, companies must adopt a holistic approach that addresses environmental, social, and economic aspects of their operations.
One key area of focus is the reduction of energy consumption and carbon emissions throughout the supply chain. This involves optimizing manufacturing processes, implementing energy-efficient technologies, and transitioning to renewable energy sources where possible. Companies are also exploring ways to minimize waste generation and improve recycling practices, particularly for rare earth elements used in ULED production.
Water management is another critical aspect of sustainability in the ULED supply chain. Manufacturers are implementing water conservation measures and developing closed-loop systems to reduce water usage and minimize the discharge of pollutants. This not only helps protect local ecosystems but also ensures long-term resource availability.
Responsible sourcing of raw materials is gaining prominence in the industry. Companies are working to establish transparent supply chains, ensuring that materials are ethically sourced and free from conflict minerals. This involves conducting due diligence on suppliers and implementing traceability systems to track materials from source to final product.
Social sustainability is also a key consideration in the ULED supply chain. This includes ensuring fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and community engagement throughout the supply chain. Companies are increasingly adopting codes of conduct and social responsibility programs to address these issues.
Innovation plays a crucial role in enhancing sustainability in the ULED supply chain. Research and development efforts are focused on developing more efficient manufacturing processes, exploring alternative materials with lower environmental impact, and improving product design for easier recycling and longer lifespan.
Collaboration across the industry is essential for addressing sustainability challenges in the ULED supply chain. Companies are forming partnerships with suppliers, customers, and even competitors to share best practices, develop industry-wide standards, and drive collective action towards sustainability goals.
Lastly, companies are recognizing the importance of measuring and reporting on their sustainability performance. This includes adopting standardized metrics and frameworks for sustainability reporting, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) guidelines. By providing transparent and comprehensive sustainability data, companies can build trust with stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices.
One key area of focus is the reduction of energy consumption and carbon emissions throughout the supply chain. This involves optimizing manufacturing processes, implementing energy-efficient technologies, and transitioning to renewable energy sources where possible. Companies are also exploring ways to minimize waste generation and improve recycling practices, particularly for rare earth elements used in ULED production.
Water management is another critical aspect of sustainability in the ULED supply chain. Manufacturers are implementing water conservation measures and developing closed-loop systems to reduce water usage and minimize the discharge of pollutants. This not only helps protect local ecosystems but also ensures long-term resource availability.
Responsible sourcing of raw materials is gaining prominence in the industry. Companies are working to establish transparent supply chains, ensuring that materials are ethically sourced and free from conflict minerals. This involves conducting due diligence on suppliers and implementing traceability systems to track materials from source to final product.
Social sustainability is also a key consideration in the ULED supply chain. This includes ensuring fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and community engagement throughout the supply chain. Companies are increasingly adopting codes of conduct and social responsibility programs to address these issues.
Innovation plays a crucial role in enhancing sustainability in the ULED supply chain. Research and development efforts are focused on developing more efficient manufacturing processes, exploring alternative materials with lower environmental impact, and improving product design for easier recycling and longer lifespan.
Collaboration across the industry is essential for addressing sustainability challenges in the ULED supply chain. Companies are forming partnerships with suppliers, customers, and even competitors to share best practices, develop industry-wide standards, and drive collective action towards sustainability goals.
Lastly, companies are recognizing the importance of measuring and reporting on their sustainability performance. This includes adopting standardized metrics and frameworks for sustainability reporting, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) guidelines. By providing transparent and comprehensive sustainability data, companies can build trust with stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!