Impact of government incentives on PHEV adoption
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PHEV Incentive Background
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) have emerged as a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels in the transportation sector. However, the adoption of PHEVs has been slower than anticipated, primarily due to higher upfront costs compared to conventional vehicles. Recognizing this challenge, governments worldwide have implemented various incentive programs to accelerate PHEV adoption.
These incentive programs typically aim to bridge the cost gap between PHEVs and traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, making PHEVs more financially attractive to consumers. The incentives come in various forms, including direct subsidies, tax credits, rebates, and non-monetary benefits such as access to high-occupancy vehicle lanes or free parking.
The United States introduced the Plug-in Electric Drive Vehicle Credit in 2010, offering tax credits of up to $7,500 for eligible PHEVs. This federal incentive has been complemented by state-level programs, creating a diverse landscape of PHEV incentives across the country. In Europe, countries like Norway have implemented aggressive incentive policies, including tax exemptions and reduced road tolls, resulting in one of the highest PHEV adoption rates globally.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has also been at the forefront of PHEV incentives. The country's New Energy Vehicle (NEV) subsidy program, launched in 2009, has undergone several iterations, adjusting subsidy amounts and eligibility criteria to promote technological advancements and market maturity.
The design and implementation of PHEV incentives have evolved over time, reflecting changing market conditions and policy objectives. Early incentive programs often focused on stimulating initial market demand and supporting nascent PHEV technologies. As the market has matured, many governments have begun to phase out or modify their incentive structures, shifting towards more targeted approaches that prioritize specific vehicle categories or consumer segments.
The effectiveness of government incentives in promoting PHEV adoption has been a subject of extensive research and debate. While incentives have generally been associated with increased PHEV sales, their impact varies significantly across different regions and time periods. Factors such as the incentive amount, program duration, and complementary policies (e.g., charging infrastructure development) all play crucial roles in determining the overall effectiveness of these initiatives.
As the automotive industry continues its transition towards electrification, understanding the impact of government incentives on PHEV adoption remains critical for policymakers, manufacturers, and consumers alike. This analysis aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the background and context surrounding PHEV incentives, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of their effects on market dynamics and consumer behavior.
These incentive programs typically aim to bridge the cost gap between PHEVs and traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, making PHEVs more financially attractive to consumers. The incentives come in various forms, including direct subsidies, tax credits, rebates, and non-monetary benefits such as access to high-occupancy vehicle lanes or free parking.
The United States introduced the Plug-in Electric Drive Vehicle Credit in 2010, offering tax credits of up to $7,500 for eligible PHEVs. This federal incentive has been complemented by state-level programs, creating a diverse landscape of PHEV incentives across the country. In Europe, countries like Norway have implemented aggressive incentive policies, including tax exemptions and reduced road tolls, resulting in one of the highest PHEV adoption rates globally.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has also been at the forefront of PHEV incentives. The country's New Energy Vehicle (NEV) subsidy program, launched in 2009, has undergone several iterations, adjusting subsidy amounts and eligibility criteria to promote technological advancements and market maturity.
The design and implementation of PHEV incentives have evolved over time, reflecting changing market conditions and policy objectives. Early incentive programs often focused on stimulating initial market demand and supporting nascent PHEV technologies. As the market has matured, many governments have begun to phase out or modify their incentive structures, shifting towards more targeted approaches that prioritize specific vehicle categories or consumer segments.
The effectiveness of government incentives in promoting PHEV adoption has been a subject of extensive research and debate. While incentives have generally been associated with increased PHEV sales, their impact varies significantly across different regions and time periods. Factors such as the incentive amount, program duration, and complementary policies (e.g., charging infrastructure development) all play crucial roles in determining the overall effectiveness of these initiatives.
As the automotive industry continues its transition towards electrification, understanding the impact of government incentives on PHEV adoption remains critical for policymakers, manufacturers, and consumers alike. This analysis aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the background and context surrounding PHEV incentives, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of their effects on market dynamics and consumer behavior.
Market Analysis for PHEVs
The market for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness, rising fuel costs, and government incentives. As consumers seek more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly transportation options, PHEVs have emerged as a viable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Global PHEV sales have experienced a steady increase, with major automotive markets such as China, Europe, and North America leading the adoption. The market size for PHEVs has expanded rapidly, with annual sales reaching millions of units worldwide. This growth trajectory is expected to continue as more automakers introduce PHEV models across various vehicle segments.
Consumer demand for PHEVs is influenced by several factors, including fuel economy, environmental impact, and total cost of ownership. The ability to operate in both electric and hybrid modes provides flexibility for consumers, addressing range anxiety concerns associated with fully electric vehicles. Additionally, PHEVs offer lower emissions compared to conventional vehicles, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Government incentives play a crucial role in shaping the PHEV market. Many countries have implemented policies to promote PHEV adoption, including tax credits, rebates, and preferential treatment in urban areas. These incentives have significantly impacted consumer purchasing decisions, making PHEVs more financially attractive and accelerating market growth.
The PHEV market is characterized by intense competition among established automakers and new entrants. Major players in the automotive industry have invested heavily in PHEV technology, expanding their product portfolios to meet diverse consumer needs. This has resulted in a wide range of PHEV options across different vehicle classes, from compact cars to SUVs and luxury vehicles.
Market trends indicate a shift towards larger battery capacities and improved electric-only ranges in PHEVs. This development aims to enhance the electric driving experience and further reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, advancements in charging infrastructure have positively impacted PHEV adoption, making it more convenient for users to charge their vehicles at home, work, or public charging stations.
The future outlook for the PHEV market remains positive, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. However, the market faces challenges such as the increasing popularity of fully electric vehicles and potential changes in government incentive programs. The long-term success of PHEVs will depend on technological advancements, cost reductions, and the ability to meet evolving consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
Global PHEV sales have experienced a steady increase, with major automotive markets such as China, Europe, and North America leading the adoption. The market size for PHEVs has expanded rapidly, with annual sales reaching millions of units worldwide. This growth trajectory is expected to continue as more automakers introduce PHEV models across various vehicle segments.
Consumer demand for PHEVs is influenced by several factors, including fuel economy, environmental impact, and total cost of ownership. The ability to operate in both electric and hybrid modes provides flexibility for consumers, addressing range anxiety concerns associated with fully electric vehicles. Additionally, PHEVs offer lower emissions compared to conventional vehicles, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Government incentives play a crucial role in shaping the PHEV market. Many countries have implemented policies to promote PHEV adoption, including tax credits, rebates, and preferential treatment in urban areas. These incentives have significantly impacted consumer purchasing decisions, making PHEVs more financially attractive and accelerating market growth.
The PHEV market is characterized by intense competition among established automakers and new entrants. Major players in the automotive industry have invested heavily in PHEV technology, expanding their product portfolios to meet diverse consumer needs. This has resulted in a wide range of PHEV options across different vehicle classes, from compact cars to SUVs and luxury vehicles.
Market trends indicate a shift towards larger battery capacities and improved electric-only ranges in PHEVs. This development aims to enhance the electric driving experience and further reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, advancements in charging infrastructure have positively impacted PHEV adoption, making it more convenient for users to charge their vehicles at home, work, or public charging stations.
The future outlook for the PHEV market remains positive, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. However, the market faces challenges such as the increasing popularity of fully electric vehicles and potential changes in government incentive programs. The long-term success of PHEVs will depend on technological advancements, cost reductions, and the ability to meet evolving consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
Current Incentive Challenges
Government incentives have played a crucial role in promoting the adoption of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs). However, several challenges currently hinder the effectiveness of these incentive programs. One of the primary issues is the inconsistency and unpredictability of incentive policies across different regions and countries. This lack of uniformity creates confusion among consumers and manufacturers, making it difficult to plan long-term strategies for PHEV production and adoption.
Another significant challenge is the limited duration and funding of many incentive programs. As governments face budgetary constraints, some incentive schemes are being phased out or reduced, leading to uncertainty in the market. This short-term approach to incentives can result in boom-and-bust cycles in PHEV sales, rather than sustained growth.
The complexity of incentive structures also poses a challenge. Many programs involve a combination of tax credits, rebates, and other benefits, which can be difficult for consumers to understand and navigate. This complexity may deter potential buyers who find the process of claiming incentives too cumbersome or confusing.
Furthermore, there is an ongoing debate about the fairness and effectiveness of PHEV incentives. Critics argue that these programs disproportionately benefit higher-income consumers who can afford more expensive vehicles, raising questions about social equity. Additionally, some studies suggest that a significant portion of PHEV purchases would have occurred even without incentives, leading to concerns about the cost-effectiveness of these programs.
The rapid evolution of PHEV technology also presents challenges for incentive programs. As battery technology improves and costs decrease, the justification for continued government support may weaken. Policymakers must continually reassess and adjust incentive structures to ensure they remain relevant and effective in the face of technological advancements.
Another challenge is the potential for unintended consequences. For instance, some incentive programs have led to the creation of "compliance cars" - PHEVs designed primarily to meet regulatory requirements rather than consumer needs. This can result in a mismatch between available PHEV models and market demand, potentially undermining the long-term success of PHEV adoption.
Lastly, the global nature of the automotive industry complicates the implementation of incentive programs. Differences in incentive structures across countries can lead to market distortions and challenges in global supply chain management for PHEV manufacturers. Harmonizing incentive policies internationally remains a significant challenge for policymakers and industry stakeholders alike.
Another significant challenge is the limited duration and funding of many incentive programs. As governments face budgetary constraints, some incentive schemes are being phased out or reduced, leading to uncertainty in the market. This short-term approach to incentives can result in boom-and-bust cycles in PHEV sales, rather than sustained growth.
The complexity of incentive structures also poses a challenge. Many programs involve a combination of tax credits, rebates, and other benefits, which can be difficult for consumers to understand and navigate. This complexity may deter potential buyers who find the process of claiming incentives too cumbersome or confusing.
Furthermore, there is an ongoing debate about the fairness and effectiveness of PHEV incentives. Critics argue that these programs disproportionately benefit higher-income consumers who can afford more expensive vehicles, raising questions about social equity. Additionally, some studies suggest that a significant portion of PHEV purchases would have occurred even without incentives, leading to concerns about the cost-effectiveness of these programs.
The rapid evolution of PHEV technology also presents challenges for incentive programs. As battery technology improves and costs decrease, the justification for continued government support may weaken. Policymakers must continually reassess and adjust incentive structures to ensure they remain relevant and effective in the face of technological advancements.
Another challenge is the potential for unintended consequences. For instance, some incentive programs have led to the creation of "compliance cars" - PHEVs designed primarily to meet regulatory requirements rather than consumer needs. This can result in a mismatch between available PHEV models and market demand, potentially undermining the long-term success of PHEV adoption.
Lastly, the global nature of the automotive industry complicates the implementation of incentive programs. Differences in incentive structures across countries can lead to market distortions and challenges in global supply chain management for PHEV manufacturers. Harmonizing incentive policies internationally remains a significant challenge for policymakers and industry stakeholders alike.
Existing Incentive Structures
01 Financial incentives for technology adoption
Governments offer various financial incentives to encourage the adoption of new technologies or practices. These may include tax credits, subsidies, grants, or low-interest loans. Such incentives can significantly reduce the cost barriers associated with adopting new technologies, thereby increasing the adoption rate among businesses and individuals.- Financial incentives to promote adoption: Governments offer various financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies to encourage the adoption of specific technologies or practices. These incentives aim to reduce the cost burden on individuals or businesses, making it more attractive to adopt new technologies or behaviors that align with policy goals.
- Policy frameworks for technology adoption: Governments implement policy frameworks to create a supportive environment for technology adoption. These may include regulations, standards, and guidelines that facilitate the integration of new technologies into existing systems. Such policies can help overcome barriers to adoption and provide clarity for businesses and consumers.
- Education and awareness programs: Governments invest in education and awareness programs to inform the public about the benefits of adopting certain technologies or practices. These initiatives can include public campaigns, workshops, and information dissemination to increase understanding and acceptance among potential adopters.
- Collaborative partnerships for adoption: Governments foster partnerships between public and private sectors to accelerate technology adoption. These collaborations can involve research institutions, industry players, and government agencies working together to develop, test, and implement new technologies, thereby increasing the rate of adoption.
- Monitoring and evaluation of adoption rates: Governments implement systems to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of their incentive programs and the resulting adoption rates. This involves collecting data, analyzing trends, and adjusting policies based on the outcomes to ensure that incentives are achieving their intended goals and maximizing adoption rates.
02 Policy frameworks to promote adoption
Governments implement policy frameworks and regulations to create a favorable environment for technology adoption. These may include mandates, standards, or guidelines that encourage or require the use of certain technologies. Such policies can drive adoption rates by creating market demand and ensuring a level playing field for businesses.Expand Specific Solutions03 Education and awareness programs
Governments invest in education and awareness programs to inform businesses and the public about the benefits of adopting new technologies or practices. These programs can include workshops, training sessions, and information campaigns. By increasing knowledge and understanding, these initiatives can help overcome resistance to change and boost adoption rates.Expand Specific Solutions04 Public-private partnerships for adoption
Governments collaborate with private sector entities to create partnerships that facilitate technology adoption. These partnerships can involve joint research and development efforts, pilot projects, or shared infrastructure investments. By leveraging private sector expertise and resources, these initiatives can accelerate adoption rates and ensure more effective implementation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and evaluation of adoption rates
Governments implement systems to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of their incentive programs and the resulting adoption rates. This involves collecting data, analyzing trends, and assessing the impact of various initiatives. By continuously monitoring adoption rates, governments can adjust their strategies and allocate resources more effectively to maximize the impact of their incentive programs.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Stakeholders Analysis
The adoption of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) is significantly influenced by government incentives, shaping a competitive landscape in various stages of development. The market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and supportive policies. While the technology is maturing, it's not yet fully mainstream. Key players like Ford, Toyota, and GM are leading the charge, with emerging competitors from China such as Guangzhou Automobile Group and Geely entering the market. These companies are investing heavily in PHEV technology, aiming to capitalize on government incentives and growing consumer demand for eco-friendly transportation options.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has been at the forefront of hybrid technology and has leveraged this expertise in its PHEV strategy. The company's approach focuses on offering PHEVs across various vehicle segments, with models like the Prius Prime and RAV4 Prime. Toyota has developed advanced powertrain systems that maximize electric range and fuel efficiency, ensuring eligibility for higher government incentives[2]. The company has also implemented a flexible manufacturing strategy, allowing it to adjust production volumes of PHEVs in response to changes in government incentives and market demand. Toyota actively engages with policymakers to shape incentive programs and has established partnerships with utility companies to promote PHEV adoption[4].
Strengths: Strong reputation in hybrid technology, extensive R&D capabilities, and global market presence. Weaknesses: Conservative approach to full electrification may limit long-term growth in markets shifting towards BEVs.
Zhejiang Geely Holding Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Geely has adopted an aggressive strategy to capitalize on government incentives for PHEV adoption, particularly in the Chinese market. The company has developed a range of PHEVs under its various brands, including Geely, Volvo, and Lynk & Co. Geely's approach includes leveraging its modular architecture to rapidly introduce PHEVs across different vehicle segments and price points. The company has invested in localized production to reduce costs and maximize eligibility for domestic incentives[9]. Geely has also focused on developing PHEVs with extended electric ranges to qualify for higher subsidy tiers in markets like China. The company has established partnerships with battery suppliers and charging infrastructure providers to create a comprehensive ecosystem supporting PHEV adoption. Geely actively engages with local governments to align its PHEV offerings with regional incentive programs and emissions regulations[10].
Strengths: Strong presence in the world's largest PHEV market (China), diverse brand portfolio, and cost-effective manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Limited brand recognition in some international markets, potential challenges in meeting varying global regulations.
Impactful Policy Innovations
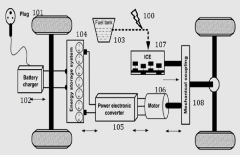
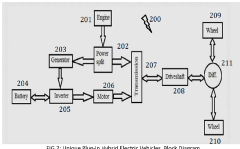
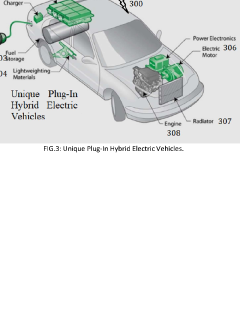
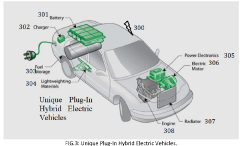
Unique plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
PatentPendingIN202241000869A
Innovation
- The development of advanced power hardware, energy-efficient powertrains, and innovative charging strategies, including smart grid integration and time-of-use pricing, to optimize battery charging and reduce peak demand, coupled with improved battery technology and vehicle design to enhance the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of PHEVs.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of government incentives on Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) adoption reveals a complex interplay between policy measures and ecological outcomes. These incentives, designed to promote PHEV uptake, have both direct and indirect environmental consequences that warrant careful consideration.
Primarily, increased PHEV adoption leads to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector. PHEVs, when operating in electric mode, produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly lowering the carbon footprint of daily commutes and short trips. This shift contributes to improved air quality in urban areas, reducing the concentration of harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
However, the environmental benefits of PHEVs are not without caveats. The production of batteries for these vehicles involves energy-intensive processes and the extraction of rare earth metals, which can have negative environmental impacts. The sourcing of these materials often occurs in regions with less stringent environmental regulations, potentially leading to localized ecological damage and biodiversity loss.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of PHEVs is heavily dependent on the electricity grid's composition. In regions where electricity is predominantly generated from fossil fuels, the overall emissions reduction from PHEV adoption may be less significant. Conversely, in areas with a high proportion of renewable energy sources, the environmental benefits are substantially amplified.
Government incentives also indirectly affect the broader automotive industry. As manufacturers shift focus towards PHEV production to capitalize on these incentives, there is a potential for accelerated innovation in battery technology and electric drivetrain efficiency. This could lead to improvements in energy density and longevity of batteries, reducing the environmental impact of their production and disposal over time.
The lifecycle assessment of PHEVs, influenced by government incentives, must also consider end-of-life management. As more PHEVs enter the market, there is an increasing need for efficient recycling and disposal processes for batteries and electronic components. Effective policies can encourage the development of circular economy practices in the automotive sector, minimizing waste and resource depletion.
In conclusion, while government incentives for PHEV adoption generally yield positive environmental outcomes, a holistic approach is necessary to maximize benefits and mitigate potential negative impacts. Policymakers must consider the entire lifecycle of PHEVs and the broader energy ecosystem to ensure that incentives truly contribute to sustainable transportation solutions.
Primarily, increased PHEV adoption leads to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector. PHEVs, when operating in electric mode, produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly lowering the carbon footprint of daily commutes and short trips. This shift contributes to improved air quality in urban areas, reducing the concentration of harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
However, the environmental benefits of PHEVs are not without caveats. The production of batteries for these vehicles involves energy-intensive processes and the extraction of rare earth metals, which can have negative environmental impacts. The sourcing of these materials often occurs in regions with less stringent environmental regulations, potentially leading to localized ecological damage and biodiversity loss.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of PHEVs is heavily dependent on the electricity grid's composition. In regions where electricity is predominantly generated from fossil fuels, the overall emissions reduction from PHEV adoption may be less significant. Conversely, in areas with a high proportion of renewable energy sources, the environmental benefits are substantially amplified.
Government incentives also indirectly affect the broader automotive industry. As manufacturers shift focus towards PHEV production to capitalize on these incentives, there is a potential for accelerated innovation in battery technology and electric drivetrain efficiency. This could lead to improvements in energy density and longevity of batteries, reducing the environmental impact of their production and disposal over time.
The lifecycle assessment of PHEVs, influenced by government incentives, must also consider end-of-life management. As more PHEVs enter the market, there is an increasing need for efficient recycling and disposal processes for batteries and electronic components. Effective policies can encourage the development of circular economy practices in the automotive sector, minimizing waste and resource depletion.
In conclusion, while government incentives for PHEV adoption generally yield positive environmental outcomes, a holistic approach is necessary to maximize benefits and mitigate potential negative impacts. Policymakers must consider the entire lifecycle of PHEVs and the broader energy ecosystem to ensure that incentives truly contribute to sustainable transportation solutions.
Consumer Behavior Analysis
Consumer behavior plays a crucial role in the adoption of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) and is significantly influenced by government incentives. Understanding the complex interplay between these factors is essential for predicting and promoting PHEV adoption rates.
Financial incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies, have been shown to have a substantial impact on consumer decision-making processes. These incentives effectively reduce the upfront costs of PHEVs, making them more competitive with conventional vehicles. Studies have consistently demonstrated a positive correlation between the availability of financial incentives and PHEV sales, with regions offering more generous incentives typically experiencing higher adoption rates.
However, the effectiveness of financial incentives is not uniform across all consumer segments. High-income consumers, who are often early adopters of new technologies, may be less sensitive to financial incentives compared to middle-income consumers. This suggests that targeted incentive programs may be more effective in promoting widespread PHEV adoption.
Non-financial incentives also play a significant role in shaping consumer behavior. These may include preferential parking, access to high-occupancy vehicle lanes, and reduced toll fees. Such incentives appeal to consumers' desire for convenience and can be particularly effective in urban areas where traffic congestion is a major concern.
Consumer awareness and understanding of available incentives are critical factors in their effectiveness. Research has shown that many consumers are not fully aware of the incentives available to them, which can limit the impact of these programs. Improved communication and education strategies are necessary to maximize the influence of government incentives on consumer behavior.
The long-term sustainability of incentive programs is another important consideration. As PHEVs become more mainstream, there is a risk that consumers may become overly reliant on incentives, potentially leading to market distortions. Gradual phase-out strategies for incentives can help mitigate this risk while still encouraging adoption.
Cultural and social factors also influence the effectiveness of government incentives on PHEV adoption. In some regions, environmental consciousness and social status associated with owning a PHEV may amplify the impact of incentives. Conversely, in areas where traditional automotive culture is deeply ingrained, incentives may need to be coupled with broader cultural shift initiatives to be truly effective.
In conclusion, government incentives have a significant and multifaceted impact on consumer behavior regarding PHEV adoption. While financial incentives are generally effective, their impact varies across consumer segments and regions. Non-financial incentives, consumer awareness, and cultural factors all play important roles in shaping adoption patterns. A comprehensive understanding of these dynamics is essential for designing effective policies to promote PHEV adoption and achieve broader sustainability goals in the transportation sector.
Financial incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies, have been shown to have a substantial impact on consumer decision-making processes. These incentives effectively reduce the upfront costs of PHEVs, making them more competitive with conventional vehicles. Studies have consistently demonstrated a positive correlation between the availability of financial incentives and PHEV sales, with regions offering more generous incentives typically experiencing higher adoption rates.
However, the effectiveness of financial incentives is not uniform across all consumer segments. High-income consumers, who are often early adopters of new technologies, may be less sensitive to financial incentives compared to middle-income consumers. This suggests that targeted incentive programs may be more effective in promoting widespread PHEV adoption.
Non-financial incentives also play a significant role in shaping consumer behavior. These may include preferential parking, access to high-occupancy vehicle lanes, and reduced toll fees. Such incentives appeal to consumers' desire for convenience and can be particularly effective in urban areas where traffic congestion is a major concern.
Consumer awareness and understanding of available incentives are critical factors in their effectiveness. Research has shown that many consumers are not fully aware of the incentives available to them, which can limit the impact of these programs. Improved communication and education strategies are necessary to maximize the influence of government incentives on consumer behavior.
The long-term sustainability of incentive programs is another important consideration. As PHEVs become more mainstream, there is a risk that consumers may become overly reliant on incentives, potentially leading to market distortions. Gradual phase-out strategies for incentives can help mitigate this risk while still encouraging adoption.
Cultural and social factors also influence the effectiveness of government incentives on PHEV adoption. In some regions, environmental consciousness and social status associated with owning a PHEV may amplify the impact of incentives. Conversely, in areas where traditional automotive culture is deeply ingrained, incentives may need to be coupled with broader cultural shift initiatives to be truly effective.
In conclusion, government incentives have a significant and multifaceted impact on consumer behavior regarding PHEV adoption. While financial incentives are generally effective, their impact varies across consumer segments and regions. Non-financial incentives, consumer awareness, and cultural factors all play important roles in shaping adoption patterns. A comprehensive understanding of these dynamics is essential for designing effective policies to promote PHEV adoption and achieve broader sustainability goals in the transportation sector.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!