PHEV market penetration strategies in emerging economies
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PHEV Technology Evolution
The evolution of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) technology has been marked by significant advancements over the past two decades. Initially, PHEVs were introduced as a bridge between conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and fully electric vehicles, offering a compromise between range anxiety and emission reduction.
In the early 2000s, the first generation of PHEVs featured relatively small battery capacities, typically allowing for 10-20 miles of all-electric range. These vehicles primarily relied on nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which were heavier and less energy-dense compared to modern alternatives. The electric motors in these early models were often underpowered, serving mainly as assist motors rather than primary propulsion units.
As battery technology progressed, the mid-2010s saw a shift towards lithium-ion batteries, which significantly improved energy density and reduced weight. This transition enabled manufacturers to increase all-electric ranges to 30-50 miles without compromising vehicle performance or interior space. Concurrently, advancements in power electronics and motor technology led to more efficient and powerful electric drivetrains.
The late 2010s and early 2020s witnessed further refinements in PHEV technology. Battery management systems became more sophisticated, optimizing charge and discharge cycles to extend battery life and improve overall efficiency. Integration of regenerative braking systems also improved, capturing more energy during deceleration and further enhancing efficiency.
Recent developments have focused on increasing the electric-only range of PHEVs, with some models now offering up to 100 miles of all-electric driving. This has been achieved through continued improvements in battery chemistry, including the adoption of silicon-based anodes and solid-state electrolytes, which promise higher energy densities and faster charging capabilities.
In emerging economies, the evolution of PHEV technology has been influenced by unique market conditions and infrastructure challenges. Manufacturers have adapted their strategies to develop more affordable PHEV models with smaller battery capacities, focusing on urban commuting needs. Additionally, there has been an emphasis on developing robust powertrains capable of withstanding diverse road conditions and extreme climates often found in these markets.
Looking forward, the trajectory of PHEV technology in emerging economies is likely to focus on cost reduction and localization of production. This may involve the development of region-specific battery chemistries that utilize locally available materials, as well as the optimization of hybrid powertrains for local driving conditions and fuel qualities. As these markets continue to grow, we can expect to see increased investment in PHEV technology tailored to the specific needs and constraints of emerging economies.
In the early 2000s, the first generation of PHEVs featured relatively small battery capacities, typically allowing for 10-20 miles of all-electric range. These vehicles primarily relied on nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which were heavier and less energy-dense compared to modern alternatives. The electric motors in these early models were often underpowered, serving mainly as assist motors rather than primary propulsion units.
As battery technology progressed, the mid-2010s saw a shift towards lithium-ion batteries, which significantly improved energy density and reduced weight. This transition enabled manufacturers to increase all-electric ranges to 30-50 miles without compromising vehicle performance or interior space. Concurrently, advancements in power electronics and motor technology led to more efficient and powerful electric drivetrains.
The late 2010s and early 2020s witnessed further refinements in PHEV technology. Battery management systems became more sophisticated, optimizing charge and discharge cycles to extend battery life and improve overall efficiency. Integration of regenerative braking systems also improved, capturing more energy during deceleration and further enhancing efficiency.
Recent developments have focused on increasing the electric-only range of PHEVs, with some models now offering up to 100 miles of all-electric driving. This has been achieved through continued improvements in battery chemistry, including the adoption of silicon-based anodes and solid-state electrolytes, which promise higher energy densities and faster charging capabilities.
In emerging economies, the evolution of PHEV technology has been influenced by unique market conditions and infrastructure challenges. Manufacturers have adapted their strategies to develop more affordable PHEV models with smaller battery capacities, focusing on urban commuting needs. Additionally, there has been an emphasis on developing robust powertrains capable of withstanding diverse road conditions and extreme climates often found in these markets.
Looking forward, the trajectory of PHEV technology in emerging economies is likely to focus on cost reduction and localization of production. This may involve the development of region-specific battery chemistries that utilize locally available materials, as well as the optimization of hybrid powertrains for local driving conditions and fuel qualities. As these markets continue to grow, we can expect to see increased investment in PHEV technology tailored to the specific needs and constraints of emerging economies.
PHEV Market Potential
The market potential for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) in emerging economies presents a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges. These markets, characterized by rapid economic growth and increasing urbanization, offer fertile ground for PHEV adoption. However, the potential is tempered by unique local conditions that must be carefully considered.
Emerging economies are experiencing a surge in vehicle ownership as disposable incomes rise. This trend, coupled with growing environmental awareness and government initiatives to reduce emissions, creates a favorable environment for PHEV market expansion. The appeal of PHEVs lies in their ability to bridge the gap between conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and fully electric vehicles, offering a compromise that addresses range anxiety while still providing significant environmental benefits.
The market size for PHEVs in emerging economies is expected to grow substantially over the next decade. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing fuel prices, stricter emission regulations, and improving charging infrastructure. Additionally, as battery technology advances and production costs decrease, PHEVs are becoming more affordable and attractive to a broader consumer base.
However, the market potential varies significantly across different emerging economies. Factors such as government policies, energy mix, and consumer preferences play crucial roles in shaping the PHEV market landscape. For instance, countries with supportive government policies, including tax incentives and subsidies, are likely to see faster PHEV adoption rates. Conversely, markets with limited charging infrastructure or heavily subsidized fossil fuels may face slower growth.
The consumer segment in emerging economies presents unique characteristics that influence PHEV market potential. Urban middle-class consumers, in particular, represent a key target demographic. This group often combines environmental consciousness with the desire for technologically advanced vehicles. However, price sensitivity remains a significant factor, necessitating strategies that balance cost with perceived value.
Fleet markets, including taxis and corporate fleets, also offer substantial potential for PHEV adoption in emerging economies. These segments can benefit from the lower operating costs of PHEVs, especially in urban environments with frequent stop-and-go traffic. Government and public sector fleets may lead the way in PHEV adoption, setting examples and creating initial demand to support market growth.
The long-term market potential for PHEVs in emerging economies is closely tied to the development of supporting infrastructure and technology. As charging networks expand and battery technology improves, the value proposition of PHEVs will strengthen. Moreover, the potential for PHEVs to integrate with smart grid systems and contribute to energy stability in regions with developing power infrastructure adds another dimension to their market appeal.
Emerging economies are experiencing a surge in vehicle ownership as disposable incomes rise. This trend, coupled with growing environmental awareness and government initiatives to reduce emissions, creates a favorable environment for PHEV market expansion. The appeal of PHEVs lies in their ability to bridge the gap between conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and fully electric vehicles, offering a compromise that addresses range anxiety while still providing significant environmental benefits.
The market size for PHEVs in emerging economies is expected to grow substantially over the next decade. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing fuel prices, stricter emission regulations, and improving charging infrastructure. Additionally, as battery technology advances and production costs decrease, PHEVs are becoming more affordable and attractive to a broader consumer base.
However, the market potential varies significantly across different emerging economies. Factors such as government policies, energy mix, and consumer preferences play crucial roles in shaping the PHEV market landscape. For instance, countries with supportive government policies, including tax incentives and subsidies, are likely to see faster PHEV adoption rates. Conversely, markets with limited charging infrastructure or heavily subsidized fossil fuels may face slower growth.
The consumer segment in emerging economies presents unique characteristics that influence PHEV market potential. Urban middle-class consumers, in particular, represent a key target demographic. This group often combines environmental consciousness with the desire for technologically advanced vehicles. However, price sensitivity remains a significant factor, necessitating strategies that balance cost with perceived value.
Fleet markets, including taxis and corporate fleets, also offer substantial potential for PHEV adoption in emerging economies. These segments can benefit from the lower operating costs of PHEVs, especially in urban environments with frequent stop-and-go traffic. Government and public sector fleets may lead the way in PHEV adoption, setting examples and creating initial demand to support market growth.
The long-term market potential for PHEVs in emerging economies is closely tied to the development of supporting infrastructure and technology. As charging networks expand and battery technology improves, the value proposition of PHEVs will strengthen. Moreover, the potential for PHEVs to integrate with smart grid systems and contribute to energy stability in regions with developing power infrastructure adds another dimension to their market appeal.
Technical Barriers
The adoption of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) in emerging economies faces several significant technical barriers that hinder widespread market penetration. One of the primary challenges is the lack of adequate charging infrastructure. Many emerging economies struggle with unreliable power grids and limited electricity distribution networks, particularly in rural areas. This deficiency makes it difficult for potential PHEV owners to charge their vehicles conveniently and reliably, reducing the appeal of these vehicles.
Another technical barrier is the high initial cost of PHEVs compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. The advanced technology and components used in PHEVs, such as high-capacity batteries and sophisticated power management systems, contribute to their elevated price points. This cost disparity is particularly pronounced in emerging economies where price sensitivity is often a crucial factor in consumer purchasing decisions.
The complexity of PHEV technology also presents a significant challenge. Many emerging economies lack the technical expertise and specialized knowledge required for the maintenance and repair of these advanced vehicles. This shortage of skilled technicians and specialized service centers can lead to higher maintenance costs and longer downtimes, deterring potential buyers and fleet operators from adopting PHEVs.
Battery technology limitations further compound the technical barriers. Current battery technologies used in PHEVs may not be optimized for the diverse and often extreme climate conditions found in many emerging economies. Issues such as reduced battery life in high-temperature environments or decreased performance in cold climates can negatively impact the overall efficiency and reliability of PHEVs in these markets.
The integration of PHEVs with existing power grids poses another technical challenge. Many emerging economies' power systems are not equipped to handle the additional load that widespread PHEV adoption would create. The lack of smart grid technologies and load management systems can lead to grid instability and potential blackouts, especially during peak charging times.
Furthermore, the absence of standardized charging protocols and connectors across different PHEV models and manufacturers creates compatibility issues. This lack of standardization can lead to confusion among consumers and increased costs for infrastructure development, as charging stations need to accommodate multiple standards.
Lastly, the limited range of PHEVs in all-electric mode may not meet the needs of consumers in emerging economies where long-distance travel is common due to geographical factors. The perception of range anxiety, coupled with the lack of widespread fast-charging infrastructure, can significantly impede the adoption of PHEVs in these markets.
Another technical barrier is the high initial cost of PHEVs compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. The advanced technology and components used in PHEVs, such as high-capacity batteries and sophisticated power management systems, contribute to their elevated price points. This cost disparity is particularly pronounced in emerging economies where price sensitivity is often a crucial factor in consumer purchasing decisions.
The complexity of PHEV technology also presents a significant challenge. Many emerging economies lack the technical expertise and specialized knowledge required for the maintenance and repair of these advanced vehicles. This shortage of skilled technicians and specialized service centers can lead to higher maintenance costs and longer downtimes, deterring potential buyers and fleet operators from adopting PHEVs.
Battery technology limitations further compound the technical barriers. Current battery technologies used in PHEVs may not be optimized for the diverse and often extreme climate conditions found in many emerging economies. Issues such as reduced battery life in high-temperature environments or decreased performance in cold climates can negatively impact the overall efficiency and reliability of PHEVs in these markets.
The integration of PHEVs with existing power grids poses another technical challenge. Many emerging economies' power systems are not equipped to handle the additional load that widespread PHEV adoption would create. The lack of smart grid technologies and load management systems can lead to grid instability and potential blackouts, especially during peak charging times.
Furthermore, the absence of standardized charging protocols and connectors across different PHEV models and manufacturers creates compatibility issues. This lack of standardization can lead to confusion among consumers and increased costs for infrastructure development, as charging stations need to accommodate multiple standards.
Lastly, the limited range of PHEVs in all-electric mode may not meet the needs of consumers in emerging economies where long-distance travel is common due to geographical factors. The perception of range anxiety, coupled with the lack of widespread fast-charging infrastructure, can significantly impede the adoption of PHEVs in these markets.
Current PHEV Solutions
01 Market analysis and penetration strategies for PHEVs
This category focuses on analyzing the PHEV market and developing strategies to increase market penetration. It includes studying consumer behavior, identifying market trends, and creating marketing plans to promote PHEV adoption. The research also covers pricing strategies, incentives, and other factors that influence consumer decisions to purchase PHEVs.- Market analysis and consumer behavior: Understanding market trends and consumer behavior is crucial for PHEV market penetration. This includes analyzing factors such as consumer preferences, purchasing patterns, and adoption rates. Market research helps identify barriers to adoption and opportunities for growth in the PHEV sector.
- Charging infrastructure development: Expanding and improving charging infrastructure is essential for increasing PHEV market penetration. This involves developing a network of charging stations, implementing smart grid technologies, and enhancing the efficiency of charging systems to support widespread PHEV adoption.
- Government policies and incentives: Government policies and incentives play a significant role in promoting PHEV market penetration. This includes tax credits, subsidies, and regulations that encourage the production and purchase of PHEVs, as well as policies that support the development of supporting infrastructure.
- Technological advancements in PHEV design: Continuous improvements in PHEV technology contribute to increased market penetration. This includes advancements in battery technology, powertrain efficiency, and vehicle range, as well as the integration of smart features and connectivity solutions to enhance the overall PHEV experience.
- Integration with renewable energy sources: Integrating PHEVs with renewable energy sources can enhance their appeal and market penetration. This involves developing systems that allow PHEVs to utilize clean energy for charging, as well as exploring vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies that enable PHEVs to contribute to grid stability and energy management.
02 Charging infrastructure development for PHEVs
This area addresses the development and expansion of charging infrastructure to support PHEV market penetration. It includes planning and implementing charging stations, integrating smart grid technologies, and improving the accessibility and convenience of charging for PHEV owners. The research also covers innovative charging solutions and their impact on PHEV adoption rates.Expand Specific Solutions03 PHEV powertrain and battery technology advancements
This category focuses on technological improvements in PHEV powertrains and battery systems to enhance performance, efficiency, and range. It includes research on advanced battery chemistries, power management systems, and hybrid drivetrain configurations. These advancements aim to make PHEVs more attractive to consumers and increase their market penetration.Expand Specific Solutions04 Government policies and incentives for PHEV adoption
This area examines the role of government policies and incentives in promoting PHEV market penetration. It includes research on tax credits, subsidies, emissions regulations, and other policy measures that encourage PHEV adoption. The studies also analyze the effectiveness of various incentive programs and their impact on PHEV sales and market share.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of PHEVs with smart grid and renewable energy systems
This category explores the integration of PHEVs with smart grid technologies and renewable energy systems to enhance their appeal and market penetration. It includes research on vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies, demand response programs, and the use of PHEVs as distributed energy resources. The studies also examine how these integrations can provide additional value to PHEV owners and utilities, potentially increasing adoption rates.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PHEV Manufacturers
The PHEV market in emerging economies is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established automakers and new entrants. Companies like Guangzhou Automobile Group, Zhejiang Geely, and Chery Automobile are actively developing PHEV technologies, while international players such as Ford and Honda are also vying for market share. The technology maturity varies, with some firms like SAIC GM Wuling and Changan Automobile making significant strides in PHEV development. Universities and research institutes, including Beijing University of Technology and Jilin University, are contributing to technological advancements, indicating a collaborative ecosystem for innovation in this sector.
Zhejiang Geely Holding Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Geely has developed a comprehensive PHEV market penetration strategy for emerging economies, focusing on affordable luxury and advanced technology. Their approach includes: 1) Developing cost-effective PHEV powertrains tailored for emerging markets [1]. 2) Leveraging their multi-brand portfolio (including Volvo and Lynk & Co) to offer PHEVs across various price points [2]. 3) Establishing local production facilities in target markets to reduce costs and adapt to local preferences [3]. 4) Implementing a "glocalization" strategy, combining global technology with localized design and features [4]. 5) Partnering with local energy providers to develop charging infrastructure and promote PHEV adoption [5].
Strengths: Strong brand portfolio, cost-effective technology, local production capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in adapting to diverse regulatory environments in different emerging markets.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford's PHEV market penetration strategy for emerging economies focuses on adaptability and localization. Key elements include: 1) Developing modular PHEV platforms that can be easily adapted to various vehicle types and local preferences [6]. 2) Implementing a "Power of Choice" strategy, offering multiple powertrain options including PHEVs to cater to diverse market needs [7]. 3) Collaborating with local partners for production and distribution to reduce costs and increase market access [8]. 4) Investing in battery technology research to improve performance and reduce costs, making PHEVs more attractive in price-sensitive markets [9]. 5) Developing smart charging solutions and partnering with local utilities to address infrastructure challenges in emerging markets [10].
Strengths: Global experience, adaptable technology platforms, strong R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential brand perception challenges in some emerging markets compared to local manufacturers.
PHEV Core Innovations
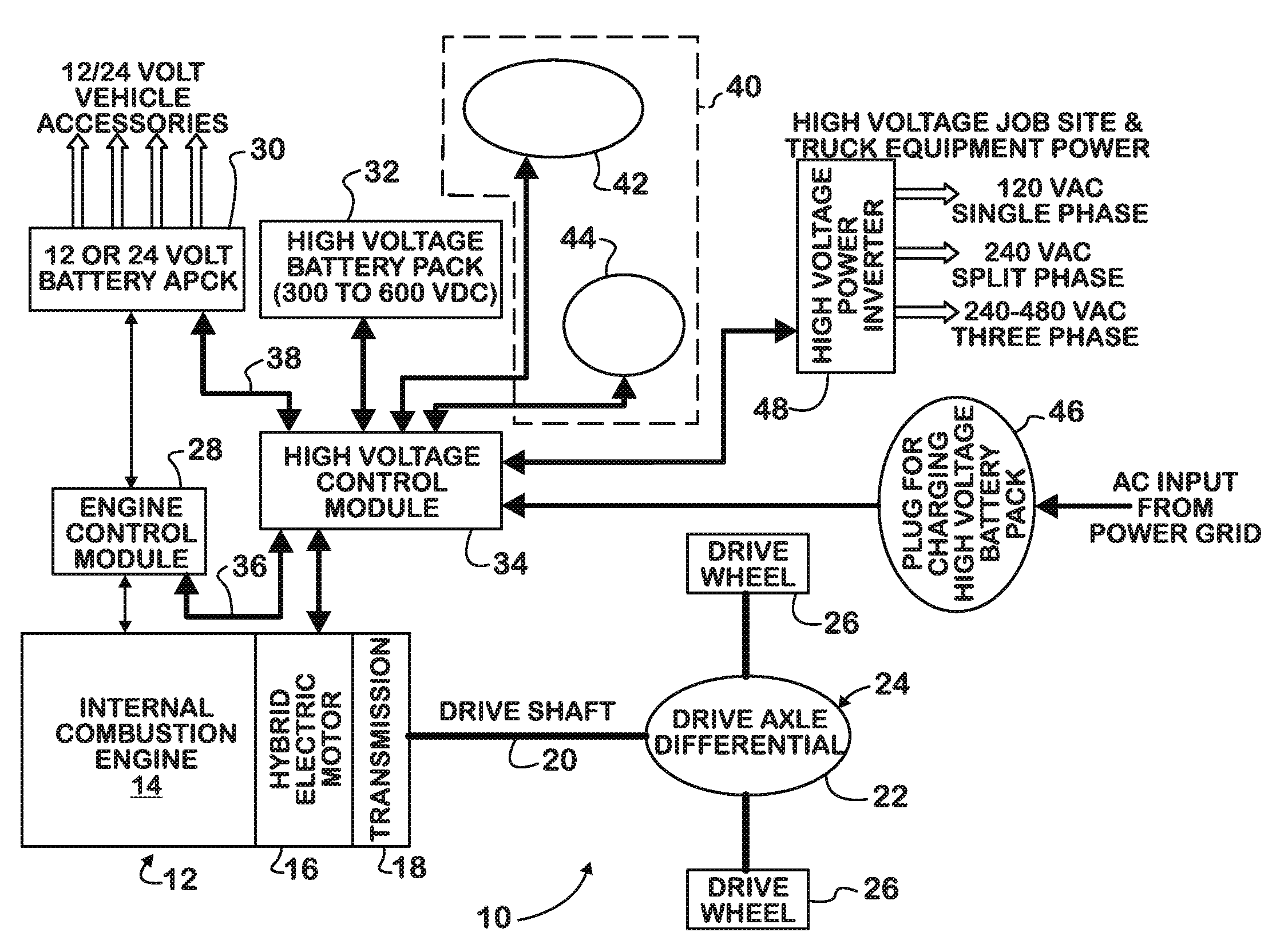
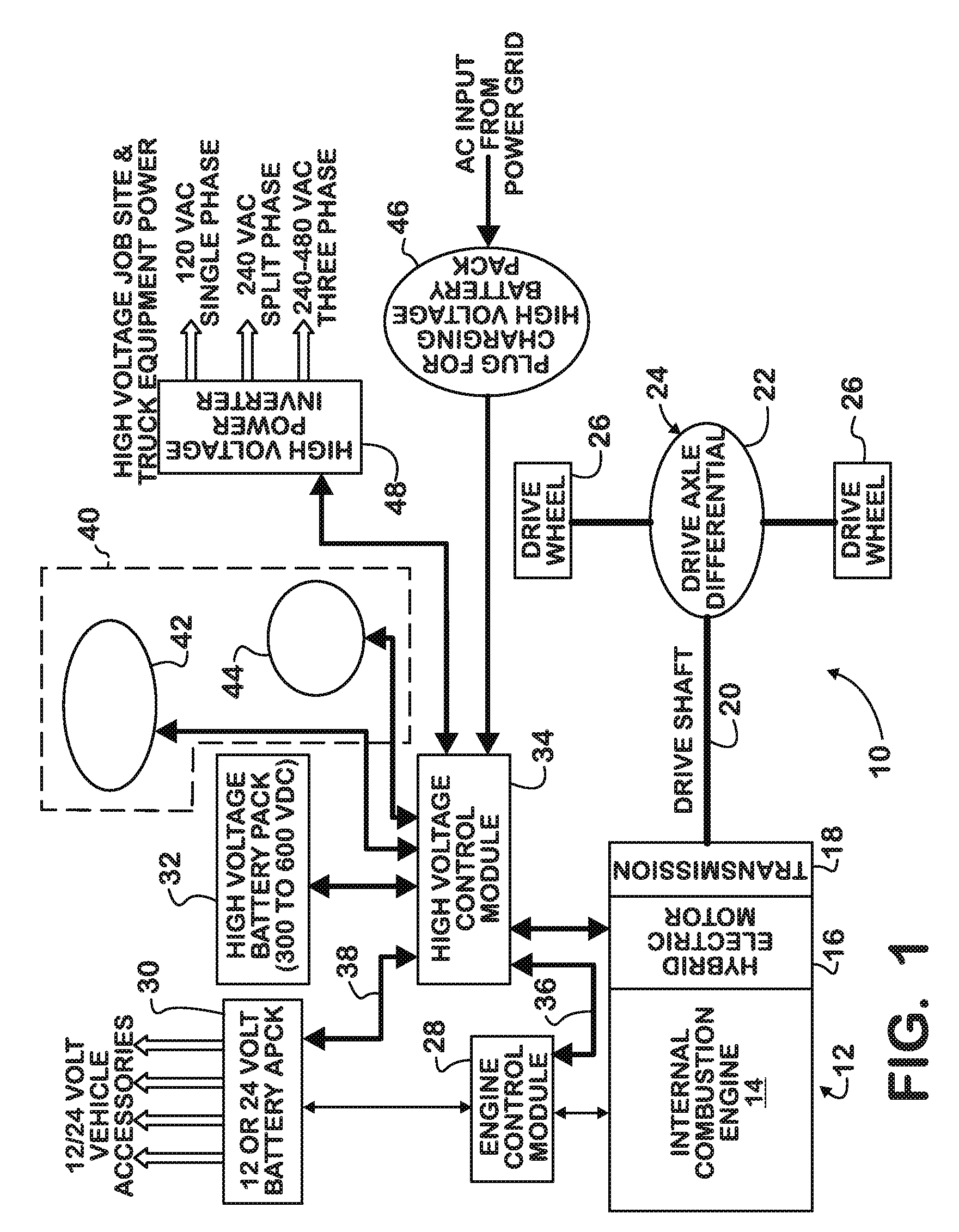
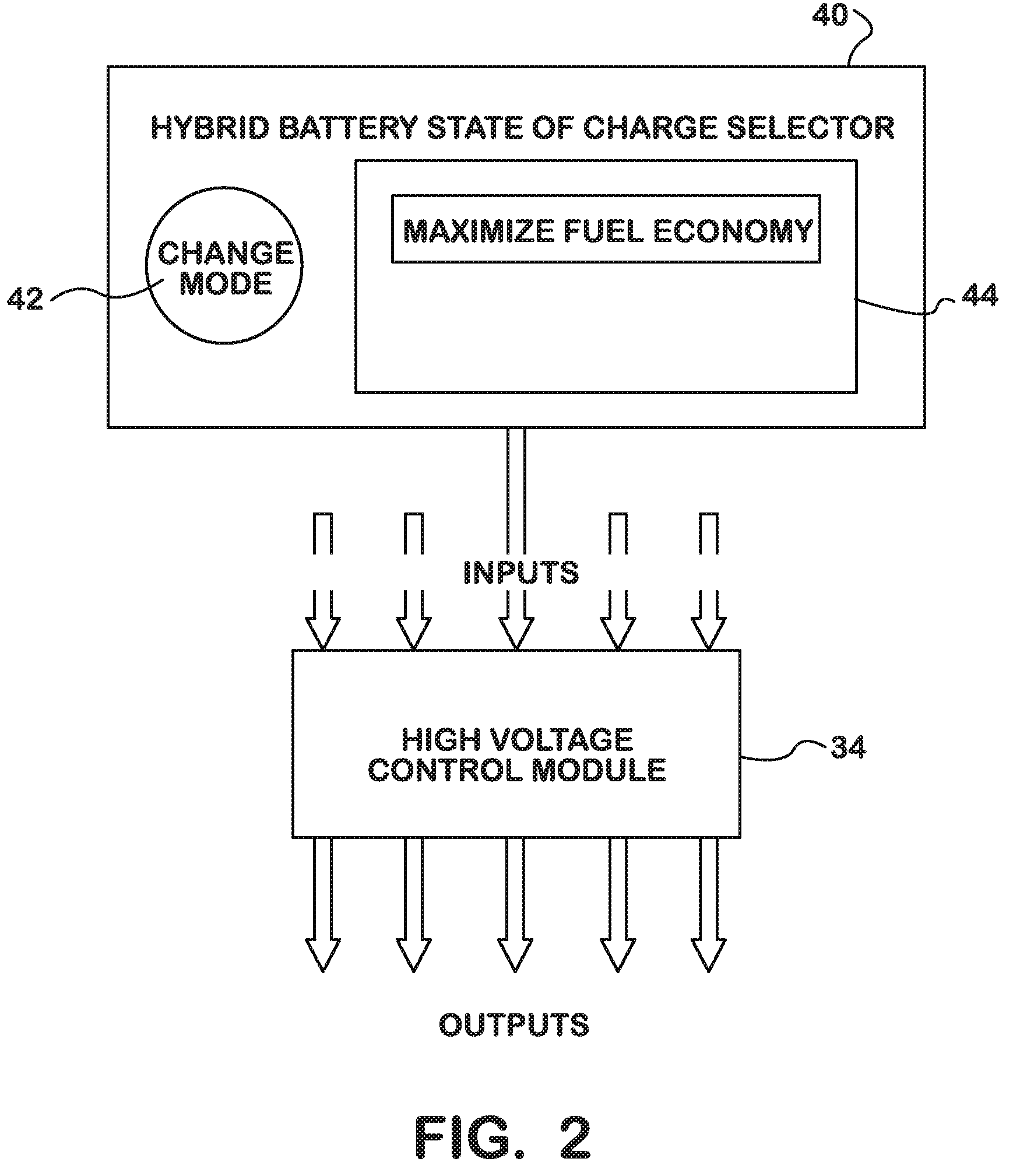
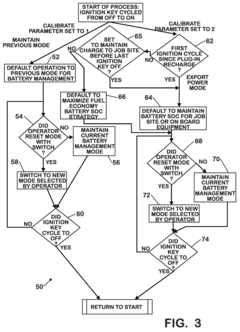
Battery pack management strategy in a hybrid electric motor vehicle
PatentInactiveUS20090248228A1
Innovation
- A software algorithm that allows operators to choose between 'Maximize Fuel Economy' and 'Maintain Charge To Job Site' strategies, with a calibratable parameter determining the default strategy selection each time the vehicle is started, and a momentary contact switch for manual override, enabling operators to select how battery energy is used.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle model reference adaptive optimal energy management method
PatentInactiveCN111959490A
Innovation
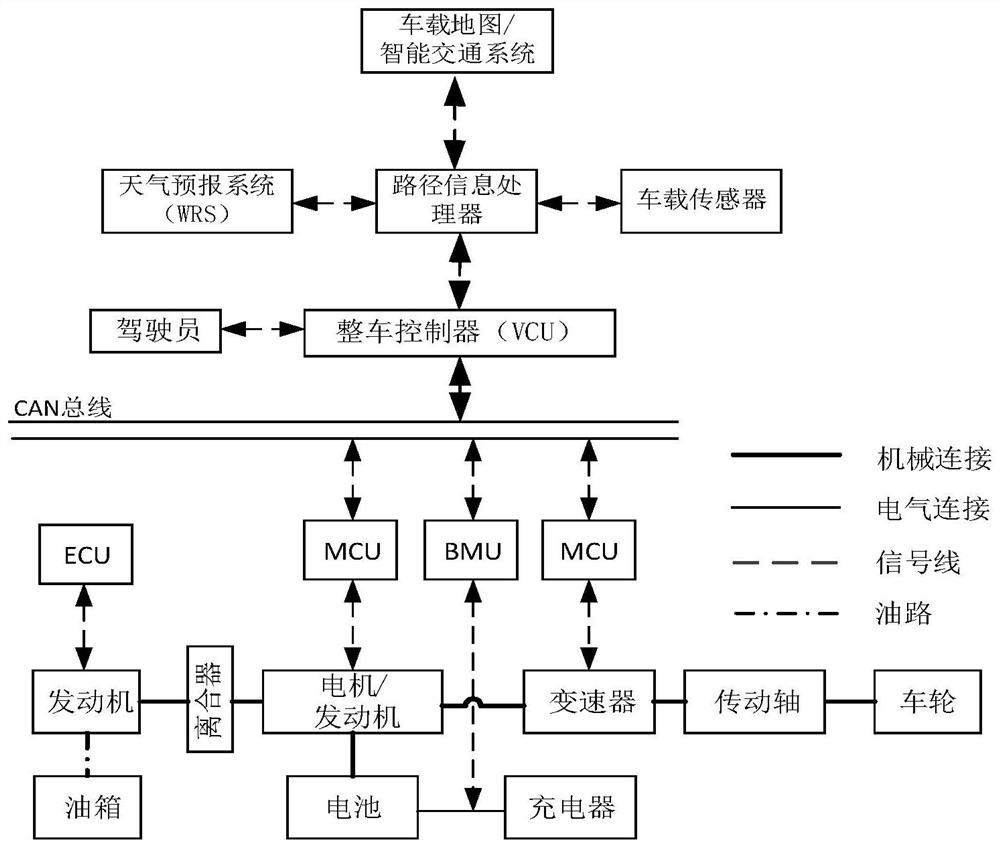
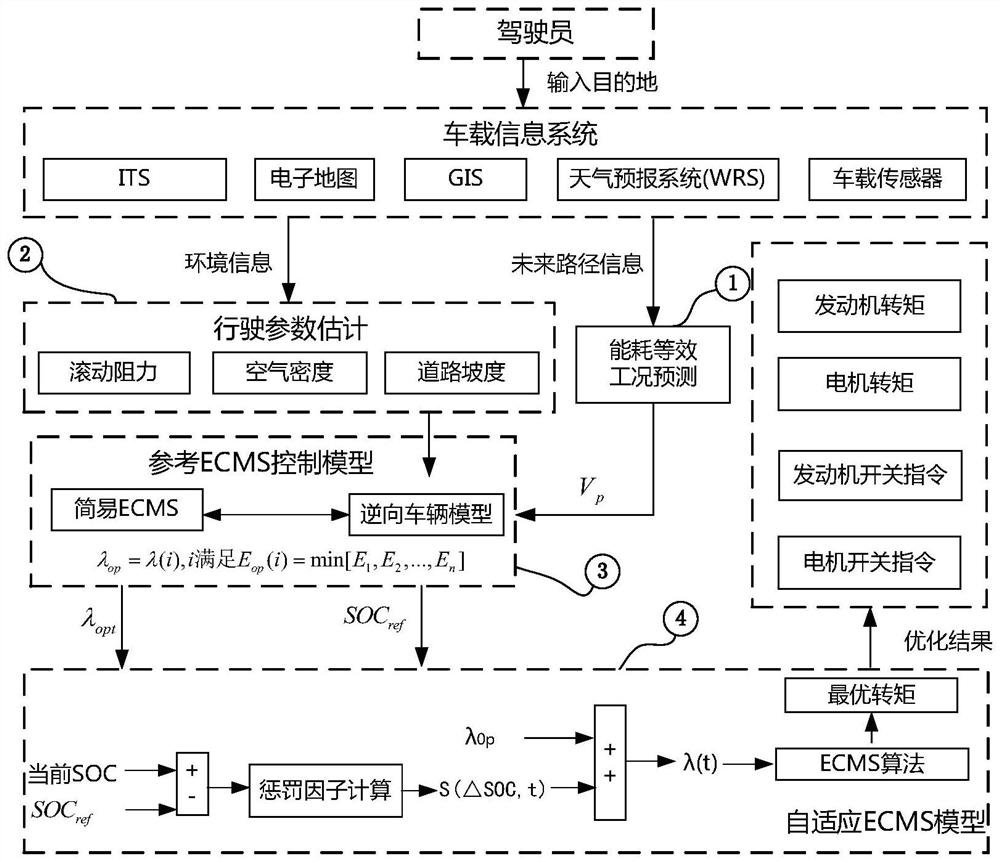
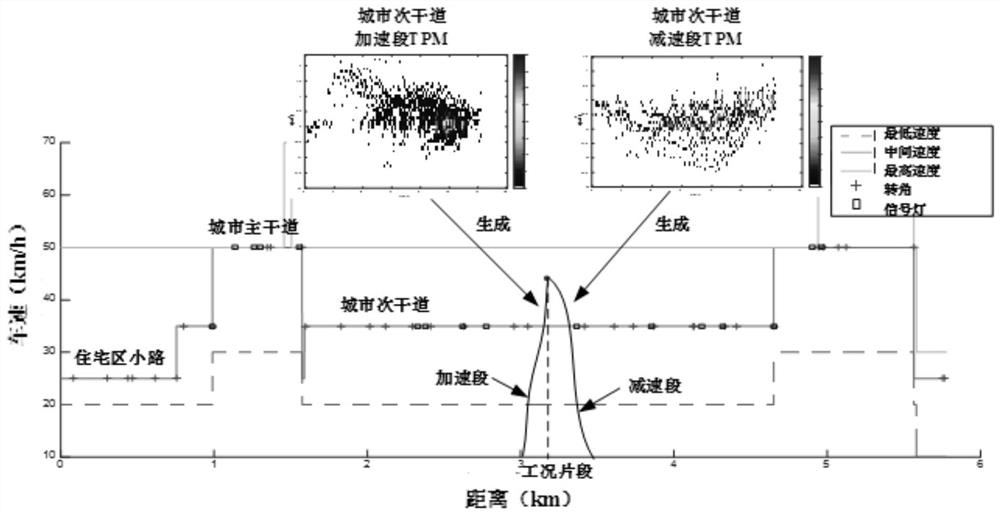
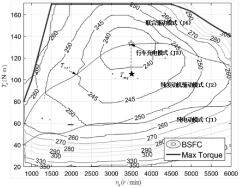
- Obtain future route information through intelligent transportation and vehicle navigation systems, generate energy consumption equivalent prediction conditions, combine traditional threshold values and ECMS algorithms to establish a reference simple ECMS model, and optimize the algorithm to obtain the optimal equivalent factor and reference SOCref, and Corrections are made during actual driving to achieve adaptive control and optimal distribution of fuel consumption.
Infrastructure Challenges
Infrastructure challenges pose significant barriers to the widespread adoption of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) in emerging economies. The lack of adequate charging infrastructure is a primary concern, as it directly impacts the convenience and practicality of PHEV ownership. Many emerging economies struggle with limited power grid capacity and reliability, which can hinder the deployment of charging stations and affect the overall charging experience for PHEV users.
The distribution of charging stations is often uneven, with a concentration in urban areas and limited availability in rural regions. This disparity creates range anxiety among potential PHEV buyers, particularly for those who need to travel long distances or reside in less developed areas. Additionally, the installation of home charging units can be challenging due to inadequate electrical systems in residential buildings, especially in older urban areas or informal settlements.
Another critical infrastructure challenge is the need for standardization of charging protocols and payment systems. The absence of unified standards across different PHEV manufacturers and charging station operators can lead to compatibility issues and user frustration. This lack of interoperability may discourage potential PHEV adopters who fear being locked into a specific ecosystem or facing difficulties when traveling between regions.
The cost of establishing and maintaining charging infrastructure is also a significant hurdle for emerging economies. Limited public and private investment in charging networks can slow down the expansion of necessary infrastructure. Moreover, the allocation of resources between developing traditional fuel infrastructure and building new charging stations presents a complex balancing act for policymakers and energy companies.
Grid stability and power quality are additional concerns in many emerging markets. The increased electricity demand from widespread PHEV adoption could strain existing power systems, potentially leading to blackouts or voltage fluctuations. This necessitates substantial investments in grid modernization and smart charging technologies to manage peak loads effectively.
Lastly, the lack of skilled technicians and maintenance personnel for PHEV-related infrastructure poses a challenge. Emerging economies may face difficulties in training and retaining a workforce capable of installing, maintaining, and repairing charging stations and related equipment. This skills gap can lead to prolonged downtime for charging infrastructure and reduced reliability, further impacting PHEV adoption rates.
Addressing these infrastructure challenges requires a coordinated effort from governments, private sector entities, and international organizations. Strategies such as public-private partnerships, targeted incentives for infrastructure development, and knowledge transfer programs can help overcome these barriers and facilitate the growth of PHEV markets in emerging economies.
The distribution of charging stations is often uneven, with a concentration in urban areas and limited availability in rural regions. This disparity creates range anxiety among potential PHEV buyers, particularly for those who need to travel long distances or reside in less developed areas. Additionally, the installation of home charging units can be challenging due to inadequate electrical systems in residential buildings, especially in older urban areas or informal settlements.
Another critical infrastructure challenge is the need for standardization of charging protocols and payment systems. The absence of unified standards across different PHEV manufacturers and charging station operators can lead to compatibility issues and user frustration. This lack of interoperability may discourage potential PHEV adopters who fear being locked into a specific ecosystem or facing difficulties when traveling between regions.
The cost of establishing and maintaining charging infrastructure is also a significant hurdle for emerging economies. Limited public and private investment in charging networks can slow down the expansion of necessary infrastructure. Moreover, the allocation of resources between developing traditional fuel infrastructure and building new charging stations presents a complex balancing act for policymakers and energy companies.
Grid stability and power quality are additional concerns in many emerging markets. The increased electricity demand from widespread PHEV adoption could strain existing power systems, potentially leading to blackouts or voltage fluctuations. This necessitates substantial investments in grid modernization and smart charging technologies to manage peak loads effectively.
Lastly, the lack of skilled technicians and maintenance personnel for PHEV-related infrastructure poses a challenge. Emerging economies may face difficulties in training and retaining a workforce capable of installing, maintaining, and repairing charging stations and related equipment. This skills gap can lead to prolonged downtime for charging infrastructure and reduced reliability, further impacting PHEV adoption rates.
Addressing these infrastructure challenges requires a coordinated effort from governments, private sector entities, and international organizations. Strategies such as public-private partnerships, targeted incentives for infrastructure development, and knowledge transfer programs can help overcome these barriers and facilitate the growth of PHEV markets in emerging economies.
Policy Incentives
Policy incentives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) in emerging economies. These incentives are designed to overcome the initial barriers to market penetration, such as higher upfront costs and limited infrastructure.
Financial incentives are often at the forefront of policy measures. Many emerging economies offer purchase subsidies or tax rebates to reduce the initial cost of PHEVs. For instance, some countries provide direct cash incentives to buyers, while others offer reduced import duties or registration fees for these vehicles. These financial incentives help bridge the price gap between PHEVs and conventional vehicles, making them more attractive to consumers.
Tax-based incentives are another common approach. Governments may implement reduced or zero-rated vehicle excise duties, lower annual road taxes, or exemptions from congestion charges for PHEVs. These ongoing financial benefits can significantly reduce the total cost of ownership over the vehicle's lifetime, enhancing the long-term value proposition for consumers.
Infrastructure development incentives are equally important. Governments often provide grants or tax breaks for the installation of charging stations, both in public spaces and private residences. Some countries mandate a certain percentage of parking spaces in new buildings to be equipped with charging facilities. These measures address the "range anxiety" concerns and make PHEVs more practical for everyday use.
Non-financial incentives also play a significant role. These may include preferential lane access, free or discounted parking in city centers, and extended access to low-emission zones. Such privileges can be particularly appealing in congested urban areas of emerging economies, where traffic and parking are major concerns.
Policy frameworks often include targets for government and public sector fleets to incorporate a certain percentage of PHEVs. This not only creates a stable demand for manufacturers but also increases visibility and public acceptance of these vehicles.
Research and development incentives are crucial for long-term market development. Governments may offer grants, tax credits, or collaborative programs to encourage local innovation in PHEV technology. This can help build domestic capabilities and potentially reduce costs through localized production.
However, it's important to note that policy incentives in emerging economies must be carefully balanced with fiscal constraints. Sustainable, long-term policies that gradually shift from direct subsidies to market-based mechanisms are often more effective in creating a self-sustaining PHEV market.
Financial incentives are often at the forefront of policy measures. Many emerging economies offer purchase subsidies or tax rebates to reduce the initial cost of PHEVs. For instance, some countries provide direct cash incentives to buyers, while others offer reduced import duties or registration fees for these vehicles. These financial incentives help bridge the price gap between PHEVs and conventional vehicles, making them more attractive to consumers.
Tax-based incentives are another common approach. Governments may implement reduced or zero-rated vehicle excise duties, lower annual road taxes, or exemptions from congestion charges for PHEVs. These ongoing financial benefits can significantly reduce the total cost of ownership over the vehicle's lifetime, enhancing the long-term value proposition for consumers.
Infrastructure development incentives are equally important. Governments often provide grants or tax breaks for the installation of charging stations, both in public spaces and private residences. Some countries mandate a certain percentage of parking spaces in new buildings to be equipped with charging facilities. These measures address the "range anxiety" concerns and make PHEVs more practical for everyday use.
Non-financial incentives also play a significant role. These may include preferential lane access, free or discounted parking in city centers, and extended access to low-emission zones. Such privileges can be particularly appealing in congested urban areas of emerging economies, where traffic and parking are major concerns.
Policy frameworks often include targets for government and public sector fleets to incorporate a certain percentage of PHEVs. This not only creates a stable demand for manufacturers but also increases visibility and public acceptance of these vehicles.
Research and development incentives are crucial for long-term market development. Governments may offer grants, tax credits, or collaborative programs to encourage local innovation in PHEV technology. This can help build domestic capabilities and potentially reduce costs through localized production.
However, it's important to note that policy incentives in emerging economies must be carefully balanced with fiscal constraints. Sustainable, long-term policies that gradually shift from direct subsidies to market-based mechanisms are often more effective in creating a self-sustaining PHEV market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!