Electrostatic Shielding with Borosilicate Glass
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Borosilicate Glass ES Background and Objectives
Electrostatic shielding has been a critical concern in various industries, particularly in electronics, aerospace, and scientific research. The quest for effective shielding materials has led to the exploration of numerous substances, with borosilicate glass emerging as a promising candidate in recent years. This research aims to investigate the potential of borosilicate glass in electrostatic shielding applications, addressing the growing need for advanced materials in high-precision environments.
The evolution of electrostatic shielding technology has been driven by the increasing miniaturization and sensitivity of electronic components. Traditional metallic shields, while effective, often introduce weight and space constraints that are undesirable in many modern applications. Borosilicate glass, known for its excellent thermal and chemical properties, has attracted attention due to its unique electrical characteristics and potential for integration into complex systems.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively evaluate the electrostatic shielding capabilities of borosilicate glass. This includes analyzing its fundamental properties, such as dielectric strength, surface resistivity, and charge dissipation rates. Additionally, the study aims to explore various modifications and treatments that could enhance the glass's shielding effectiveness, potentially opening new avenues for its application in sensitive electronic environments.
Another key goal is to investigate the feasibility of incorporating borosilicate glass into existing shielding designs, assessing its compatibility with other materials and its impact on overall system performance. This includes examining potential fabrication techniques that could allow for the creation of complex shielding structures using borosilicate glass, such as multi-layered composites or micro-engineered surfaces.
Furthermore, this research seeks to understand the long-term stability and reliability of borosilicate glass in electrostatic shielding applications. This involves studying its behavior under various environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity changes, and exposure to radiation. The findings will be crucial in determining the glass's suitability for use in demanding applications such as space technology or high-energy physics experiments.
By exploring these aspects, the research aims to contribute to the broader field of electrostatic shielding, potentially offering new solutions to longstanding challenges in electromagnetic compatibility and interference reduction. The outcomes of this study could have far-reaching implications for industries ranging from consumer electronics to advanced scientific instrumentation, paving the way for more efficient, compact, and effective shielding solutions.
The evolution of electrostatic shielding technology has been driven by the increasing miniaturization and sensitivity of electronic components. Traditional metallic shields, while effective, often introduce weight and space constraints that are undesirable in many modern applications. Borosilicate glass, known for its excellent thermal and chemical properties, has attracted attention due to its unique electrical characteristics and potential for integration into complex systems.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively evaluate the electrostatic shielding capabilities of borosilicate glass. This includes analyzing its fundamental properties, such as dielectric strength, surface resistivity, and charge dissipation rates. Additionally, the study aims to explore various modifications and treatments that could enhance the glass's shielding effectiveness, potentially opening new avenues for its application in sensitive electronic environments.
Another key goal is to investigate the feasibility of incorporating borosilicate glass into existing shielding designs, assessing its compatibility with other materials and its impact on overall system performance. This includes examining potential fabrication techniques that could allow for the creation of complex shielding structures using borosilicate glass, such as multi-layered composites or micro-engineered surfaces.
Furthermore, this research seeks to understand the long-term stability and reliability of borosilicate glass in electrostatic shielding applications. This involves studying its behavior under various environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity changes, and exposure to radiation. The findings will be crucial in determining the glass's suitability for use in demanding applications such as space technology or high-energy physics experiments.
By exploring these aspects, the research aims to contribute to the broader field of electrostatic shielding, potentially offering new solutions to longstanding challenges in electromagnetic compatibility and interference reduction. The outcomes of this study could have far-reaching implications for industries ranging from consumer electronics to advanced scientific instrumentation, paving the way for more efficient, compact, and effective shielding solutions.
Market Demand for ES Solutions
The market demand for electrostatic shielding (ES) solutions has been steadily growing across various industries, driven by the increasing need for protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electrostatic discharge (ESD). As electronic devices become more compact and sensitive, the importance of effective shielding solutions has become paramount. Borosilicate glass, known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and thermal resistance, has emerged as a promising material for ES applications.
In the consumer electronics sector, the demand for ES solutions is particularly strong. With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, manufacturers are seeking innovative ways to protect sensitive components from electromagnetic interference. The global smartphone market alone, which is expected to reach 1.5 billion units by 2025, represents a significant opportunity for ES solutions incorporating borosilicate glass.
The automotive industry is another key driver of demand for ES solutions. As vehicles become more electrified and incorporate advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), the need for effective shielding against EMI has intensified. The global automotive electronics market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8% from 2021 to 2026, further fueling the demand for ES solutions.
In the aerospace and defense sectors, where equipment reliability is critical, the demand for high-performance ES solutions is substantial. Borosilicate glass-based shielding could find applications in avionics, communication systems, and radar equipment. The global aerospace and defense market is expected to recover and grow post-pandemic, presenting opportunities for advanced ES solutions.
The healthcare industry, particularly in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment, requires robust ES solutions to ensure accurate and interference-free operation. With the global medical devices market projected to reach $600 billion by 2023, the demand for ES solutions in this sector is set to increase significantly.
Industrial automation and control systems also contribute to the growing demand for ES solutions. As factories become smarter and more connected, the need to protect sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference becomes crucial. The global industrial automation market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.3% from 2020 to 2027, indicating a strong potential for ES solutions.
The telecommunications industry, especially with the ongoing rollout of 5G networks, presents another significant market for ES solutions. The higher frequencies used in 5G technology require more effective shielding to maintain signal integrity and prevent interference. This sector's growth is expected to drive innovation in ES solutions, potentially leveraging the properties of borosilicate glass.
In the consumer electronics sector, the demand for ES solutions is particularly strong. With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, manufacturers are seeking innovative ways to protect sensitive components from electromagnetic interference. The global smartphone market alone, which is expected to reach 1.5 billion units by 2025, represents a significant opportunity for ES solutions incorporating borosilicate glass.
The automotive industry is another key driver of demand for ES solutions. As vehicles become more electrified and incorporate advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), the need for effective shielding against EMI has intensified. The global automotive electronics market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8% from 2021 to 2026, further fueling the demand for ES solutions.
In the aerospace and defense sectors, where equipment reliability is critical, the demand for high-performance ES solutions is substantial. Borosilicate glass-based shielding could find applications in avionics, communication systems, and radar equipment. The global aerospace and defense market is expected to recover and grow post-pandemic, presenting opportunities for advanced ES solutions.
The healthcare industry, particularly in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment, requires robust ES solutions to ensure accurate and interference-free operation. With the global medical devices market projected to reach $600 billion by 2023, the demand for ES solutions in this sector is set to increase significantly.
Industrial automation and control systems also contribute to the growing demand for ES solutions. As factories become smarter and more connected, the need to protect sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference becomes crucial. The global industrial automation market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.3% from 2020 to 2027, indicating a strong potential for ES solutions.
The telecommunications industry, especially with the ongoing rollout of 5G networks, presents another significant market for ES solutions. The higher frequencies used in 5G technology require more effective shielding to maintain signal integrity and prevent interference. This sector's growth is expected to drive innovation in ES solutions, potentially leveraging the properties of borosilicate glass.
ES Challenges with Borosilicate Glass
Electrostatic shielding with borosilicate glass presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers must overcome. One of the primary difficulties lies in the inherent properties of borosilicate glass itself. While borosilicate glass offers excellent thermal and chemical resistance, its electrical properties are not ideal for effective electrostatic shielding.
The relatively low electrical conductivity of borosilicate glass limits its ability to dissipate static charges efficiently. This characteristic makes it challenging to create a uniform and reliable electrostatic shield using borosilicate glass alone. As a result, researchers must explore innovative methods to enhance the glass's conductive properties without compromising its other beneficial attributes.
Another challenge is the integration of conductive materials with borosilicate glass to improve its shielding capabilities. Techniques such as thin-film deposition or surface modification are often employed, but achieving a seamless and durable bond between the glass and conductive layers can be problematic. The difference in thermal expansion coefficients between the glass and conductive materials can lead to delamination or cracking under thermal stress.
The transparency of borosilicate glass, while advantageous in many applications, poses a unique challenge for electrostatic shielding. Maintaining optical clarity while incorporating conductive elements for shielding is a delicate balance that requires careful material selection and processing techniques. This is particularly crucial in applications where visual transparency is essential, such as in display technologies or scientific instruments.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness present additional hurdles in the development of electrostatic shielding solutions using borosilicate glass. Creating large-scale, uniform shielding surfaces with consistent performance across the entire area is technically demanding and can be expensive. This challenge is compounded by the need for specialized equipment and processes to modify or coat the glass effectively.
Environmental factors also play a role in the challenges faced by electrostatic shielding with borosilicate glass. Humidity, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to various chemicals can affect the long-term stability and performance of the shielding. Developing solutions that maintain their effectiveness under diverse environmental conditions is crucial for widespread adoption.
Lastly, the complexity of electrostatic fields and their interaction with composite materials like coated borosilicate glass necessitates advanced modeling and testing methodologies. Accurately predicting and measuring the shielding effectiveness of these materials in real-world applications requires sophisticated simulation tools and experimental setups, which can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
The relatively low electrical conductivity of borosilicate glass limits its ability to dissipate static charges efficiently. This characteristic makes it challenging to create a uniform and reliable electrostatic shield using borosilicate glass alone. As a result, researchers must explore innovative methods to enhance the glass's conductive properties without compromising its other beneficial attributes.
Another challenge is the integration of conductive materials with borosilicate glass to improve its shielding capabilities. Techniques such as thin-film deposition or surface modification are often employed, but achieving a seamless and durable bond between the glass and conductive layers can be problematic. The difference in thermal expansion coefficients between the glass and conductive materials can lead to delamination or cracking under thermal stress.
The transparency of borosilicate glass, while advantageous in many applications, poses a unique challenge for electrostatic shielding. Maintaining optical clarity while incorporating conductive elements for shielding is a delicate balance that requires careful material selection and processing techniques. This is particularly crucial in applications where visual transparency is essential, such as in display technologies or scientific instruments.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness present additional hurdles in the development of electrostatic shielding solutions using borosilicate glass. Creating large-scale, uniform shielding surfaces with consistent performance across the entire area is technically demanding and can be expensive. This challenge is compounded by the need for specialized equipment and processes to modify or coat the glass effectively.
Environmental factors also play a role in the challenges faced by electrostatic shielding with borosilicate glass. Humidity, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to various chemicals can affect the long-term stability and performance of the shielding. Developing solutions that maintain their effectiveness under diverse environmental conditions is crucial for widespread adoption.
Lastly, the complexity of electrostatic fields and their interaction with composite materials like coated borosilicate glass necessitates advanced modeling and testing methodologies. Accurately predicting and measuring the shielding effectiveness of these materials in real-world applications requires sophisticated simulation tools and experimental setups, which can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Current ES Solutions with Borosilicate Glass
01 Composition and properties of borosilicate glass for electrostatic shielding
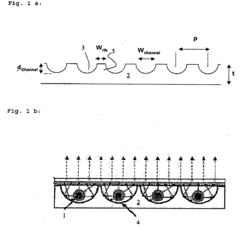
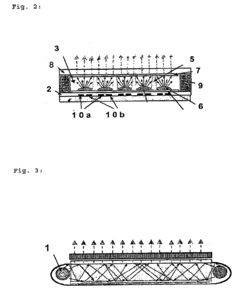
Borosilicate glass is used for electrostatic shielding due to its unique composition and properties. It typically contains boron oxide, which enhances its electrical insulation capabilities. The glass also exhibits low thermal expansion, high chemical resistance, and good transparency, making it suitable for various shielding applications.- Composition of borosilicate glass for electrostatic shielding: Borosilicate glass compositions are developed specifically for electrostatic shielding applications. These compositions typically include boron oxide, silicon dioxide, and other additives to enhance the glass's electrical properties and durability. The specific formulation is tailored to provide optimal electrostatic shielding while maintaining the desirable characteristics of borosilicate glass, such as thermal resistance and chemical stability.
- Surface treatment of borosilicate glass for improved shielding: Various surface treatment methods are applied to borosilicate glass to enhance its electrostatic shielding capabilities. These treatments may include coating the glass with conductive materials, creating micro or nanostructures on the surface, or incorporating specific ions into the glass surface. Such treatments aim to increase the glass's ability to dissipate or block electrostatic charges without compromising its optical properties.
- Borosilicate glass in electronic device shielding: Borosilicate glass is utilized in various electronic devices for electrostatic shielding purposes. This application includes using the glass as a protective cover for displays, sensors, or other sensitive components. The glass is often integrated into the device design to provide a transparent yet effective barrier against electrostatic interference, ensuring the proper functioning of electronic components while maintaining visibility and touch sensitivity where required.
- Manufacturing processes for electrostatic shielding borosilicate glass: Specialized manufacturing processes are developed to produce borosilicate glass with enhanced electrostatic shielding properties. These processes may involve precise control of the glass composition during melting, specific forming techniques, and post-processing treatments. The manufacturing methods are designed to ensure uniform distribution of shielding properties throughout the glass and to maintain the glass's structural integrity and optical clarity.
- Testing and characterization of electrostatic shielding in borosilicate glass: Methods for testing and characterizing the electrostatic shielding effectiveness of borosilicate glass are developed. These include techniques for measuring the glass's electrical properties, its ability to dissipate or block electrostatic charges, and its performance under various environmental conditions. Standardized testing procedures are established to ensure consistent evaluation of the glass's shielding capabilities across different applications and manufacturing batches.
02 Surface treatment techniques for enhancing electrostatic shielding
Various surface treatment techniques are applied to borosilicate glass to improve its electrostatic shielding properties. These may include coating with conductive materials, ion implantation, or chemical etching. Such treatments can significantly enhance the glass's ability to dissipate or block electrostatic charges.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of borosilicate glass in electronic devices for shielding
Borosilicate glass is incorporated into electronic devices as an electrostatic shielding component. It can be used in display screens, sensor housings, or as protective covers for sensitive electronic components. The integration often involves specialized manufacturing processes to ensure optimal shielding performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Composite materials combining borosilicate glass for enhanced shielding
Composite materials that incorporate borosilicate glass are developed to provide superior electrostatic shielding. These composites may combine the glass with other materials such as polymers or metals to create layered structures or matrix composites with improved shielding effectiveness and additional beneficial properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and measurement methods for electrostatic shielding efficiency
Specialized testing and measurement techniques are employed to evaluate the electrostatic shielding efficiency of borosilicate glass. These methods may include charge decay measurements, surface resistivity tests, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding effectiveness assessments. Such testing ensures the reliability and performance of the glass in shielding applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ES and Glass Industry
The research on electrostatic shielding with borosilicate glass is in a developing stage, with growing market potential due to increasing applications in electronics, aerospace, and medical industries. The global borosilicate glass market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and demand for high-performance materials. Companies like SCHOTT AG, Corning, Inc., and AGC, Inc. are leading players in this field, leveraging their extensive experience in glass manufacturing and R&D capabilities. Emerging players such as Hunan Kibing Pharmaceutical Material Technology Co., Ltd. and Zhangzhou Kibing Glass Co., Ltd. are also making strides in specialized applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical sector. The technology's maturity varies across different applications, with ongoing research focused on enhancing shielding effectiveness and material properties.
SCHOTT AG
Technical Solution: SCHOTT AG has developed advanced borosilicate glass compositions with enhanced electrostatic shielding properties. Their research focuses on optimizing the chemical composition and surface treatment of borosilicate glass to improve its electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection capabilities. SCHOTT's proprietary CONTURAN® coating technology is applied to borosilicate glass substrates, creating a transparent conductive layer that effectively dissipates static charges[1]. This innovative approach combines the inherent benefits of borosilicate glass, such as high thermal and chemical resistance, with improved electrostatic shielding performance. SCHOTT has also explored the integration of nanoparticles into the glass matrix to further enhance its electrostatic properties without compromising optical transparency[3].
Strengths: Expertise in specialized glass manufacturing, established coating technologies, and a strong R&D foundation. Weaknesses: Potential high production costs and limited scalability for mass-market applications.
Corning, Inc.
Technical Solution: Corning's research on electrostatic shielding with borosilicate glass focuses on developing multi-functional glass compositions. Their approach involves incorporating conductive elements into the glass structure to create an intrinsic shielding effect. Corning has patented a method for producing borosilicate glass with embedded conductive nanofibers, which form a three-dimensional network within the glass matrix[2]. This unique structure provides effective electrostatic shielding while maintaining the glass's optical and mechanical properties. Additionally, Corning has explored surface modification techniques, such as ion exchange processes, to create a thin, conductive layer on the glass surface without altering its bulk properties[4]. Their research also extends to the development of glass-ceramic composites that combine the benefits of borosilicate glass with enhanced electrostatic shielding capabilities.
Strengths: Strong materials science expertise, extensive patent portfolio, and established manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up production of complex glass compositions.
Innovations in Borosilicate Glass ES
UV-radiation absorbing glass with high chemical resistance, especially for a fluorescent lamp, and methods of making and using same
PatentInactiveUS20040266603A1
Innovation
- A borosilicate glass with a composition of 67-74% SiO2, 5-10% B2O3, 3-10% Al2O3, and specific amounts of TiO2, Fe2O3, and other oxides, refined without chlorides or Sb2O3, achieving high hydrolytic resistance and a sharp UV absorption edge without discoloration or solarization.
Test cell for a noble gas polarizer
PatentInactiveEP1192476A2
Innovation
- A glass sample cell design featuring flat, plane windows fused into a cylindrical borosilicate glass body, capable of withstanding high pressures, with non-magnetic and alkali-resistant sealing, and ethylene propylene sealing rings to minimize polarization loss, ensuring a parallel light path and reduced lens effects.
Environmental Impact of ES Glass Production
The production of electrostatic shielding (ES) glass using borosilicate materials has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process involves energy-intensive melting of raw materials, including silica, boron oxide, and various metal oxides, at temperatures exceeding 1500°C. This high-temperature fusion process contributes to substantial carbon emissions, particularly when fossil fuels are used as the primary energy source. Additionally, the extraction and processing of raw materials, especially boron compounds, can lead to habitat disruption and soil degradation in mining areas.
Water consumption is another critical environmental factor in ES glass production. The manufacturing process requires large volumes of water for cooling, cleaning, and processing, potentially straining local water resources in areas of production. Moreover, wastewater from the production process may contain trace amounts of heavy metals and other pollutants, necessitating proper treatment before discharge to prevent water pollution.
The use of chemical additives in the glass formulation, while essential for achieving the desired electrostatic properties, introduces potential environmental risks. Some of these additives may be toxic or persistent in the environment, requiring careful handling and disposal protocols to minimize ecological impact. Furthermore, the production of ES glass generates air emissions, including particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can contribute to local air quality issues if not properly controlled.
On a positive note, the durability and recyclability of borosilicate ES glass offer some environmental benefits. The long lifespan of ES glass products reduces the need for frequent replacement, thereby conserving resources in the long term. Additionally, borosilicate glass is fully recyclable, allowing for the potential development of closed-loop recycling systems that could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of ES glass production.
The manufacturing facilities themselves also have environmental implications, including land use changes and potential impacts on local ecosystems. However, modern production techniques and environmental management systems can help mitigate these effects through efficient resource use, waste reduction strategies, and habitat restoration efforts.
As the demand for ES glass in various applications continues to grow, addressing these environmental challenges becomes increasingly important. Industry efforts to adopt cleaner production technologies, such as electric melting furnaces powered by renewable energy sources, could substantially reduce the carbon footprint of ES glass manufacturing. Furthermore, innovations in raw material sourcing, water recycling systems, and emissions control technologies are crucial for enhancing the overall sustainability of ES glass production.
Water consumption is another critical environmental factor in ES glass production. The manufacturing process requires large volumes of water for cooling, cleaning, and processing, potentially straining local water resources in areas of production. Moreover, wastewater from the production process may contain trace amounts of heavy metals and other pollutants, necessitating proper treatment before discharge to prevent water pollution.
The use of chemical additives in the glass formulation, while essential for achieving the desired electrostatic properties, introduces potential environmental risks. Some of these additives may be toxic or persistent in the environment, requiring careful handling and disposal protocols to minimize ecological impact. Furthermore, the production of ES glass generates air emissions, including particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can contribute to local air quality issues if not properly controlled.
On a positive note, the durability and recyclability of borosilicate ES glass offer some environmental benefits. The long lifespan of ES glass products reduces the need for frequent replacement, thereby conserving resources in the long term. Additionally, borosilicate glass is fully recyclable, allowing for the potential development of closed-loop recycling systems that could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of ES glass production.
The manufacturing facilities themselves also have environmental implications, including land use changes and potential impacts on local ecosystems. However, modern production techniques and environmental management systems can help mitigate these effects through efficient resource use, waste reduction strategies, and habitat restoration efforts.
As the demand for ES glass in various applications continues to grow, addressing these environmental challenges becomes increasingly important. Industry efforts to adopt cleaner production technologies, such as electric melting furnaces powered by renewable energy sources, could substantially reduce the carbon footprint of ES glass manufacturing. Furthermore, innovations in raw material sourcing, water recycling systems, and emissions control technologies are crucial for enhancing the overall sustainability of ES glass production.
ES Glass Standards and Certifications
Electrostatic shielding with borosilicate glass is subject to various standards and certifications to ensure its effectiveness and safety in different applications. These standards provide guidelines for manufacturing, testing, and implementing electrostatic shielding solutions using borosilicate glass.
One of the primary standards governing electrostatic shielding materials is IEC 61340, which addresses the protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena. This standard includes specific requirements for materials used in electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection, including borosilicate glass. Manufacturers must adhere to these guidelines to ensure their products meet the necessary performance criteria for effective electrostatic shielding.
The ASTM D257 standard is another crucial certification for borosilicate glass used in electrostatic shielding applications. This standard outlines the methods for measuring the DC resistance or conductance of insulating materials, including glass. Borosilicate glass manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with this standard to validate the material's electrical properties and its suitability for electrostatic shielding purposes.
In the aerospace and defense industries, MIL-STD-461 is a key standard that addresses electromagnetic interference (EMI) characteristics of equipment and systems. While not specific to borosilicate glass, this standard influences the requirements for electrostatic shielding materials used in military and aerospace applications, where borosilicate glass may be employed.
The ISO 14644 standard, which focuses on cleanroom environments, also impacts the use of borosilicate glass in electrostatic shielding applications. This standard sets requirements for air cleanliness and particle contamination, which are critical factors in environments where electrostatic discharge can be particularly problematic.
For medical applications, the IEC 60601 series of standards governs the safety and performance of medical electrical equipment. These standards include requirements for electrostatic discharge protection, which may involve the use of borosilicate glass in certain medical devices or equipment.
Certification processes for borosilicate glass used in electrostatic shielding typically involve rigorous testing procedures. These may include surface resistivity measurements, volume resistivity tests, and electrostatic decay time assessments. The results of these tests must meet or exceed the specified standards to achieve certification.
It's important to note that standards and certifications may vary depending on the specific application and geographic region. Manufacturers and users of borosilicate glass for electrostatic shielding must stay informed about the latest updates to relevant standards and ensure ongoing compliance to maintain the effectiveness and reliability of their electrostatic shielding solutions.
One of the primary standards governing electrostatic shielding materials is IEC 61340, which addresses the protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena. This standard includes specific requirements for materials used in electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection, including borosilicate glass. Manufacturers must adhere to these guidelines to ensure their products meet the necessary performance criteria for effective electrostatic shielding.
The ASTM D257 standard is another crucial certification for borosilicate glass used in electrostatic shielding applications. This standard outlines the methods for measuring the DC resistance or conductance of insulating materials, including glass. Borosilicate glass manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with this standard to validate the material's electrical properties and its suitability for electrostatic shielding purposes.
In the aerospace and defense industries, MIL-STD-461 is a key standard that addresses electromagnetic interference (EMI) characteristics of equipment and systems. While not specific to borosilicate glass, this standard influences the requirements for electrostatic shielding materials used in military and aerospace applications, where borosilicate glass may be employed.
The ISO 14644 standard, which focuses on cleanroom environments, also impacts the use of borosilicate glass in electrostatic shielding applications. This standard sets requirements for air cleanliness and particle contamination, which are critical factors in environments where electrostatic discharge can be particularly problematic.
For medical applications, the IEC 60601 series of standards governs the safety and performance of medical electrical equipment. These standards include requirements for electrostatic discharge protection, which may involve the use of borosilicate glass in certain medical devices or equipment.
Certification processes for borosilicate glass used in electrostatic shielding typically involve rigorous testing procedures. These may include surface resistivity measurements, volume resistivity tests, and electrostatic decay time assessments. The results of these tests must meet or exceed the specified standards to achieve certification.
It's important to note that standards and certifications may vary depending on the specific application and geographic region. Manufacturers and users of borosilicate glass for electrostatic shielding must stay informed about the latest updates to relevant standards and ensure ongoing compliance to maintain the effectiveness and reliability of their electrostatic shielding solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!