T wave inversion in the context of renal insufficiency-related cardiac changes
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
T Wave Inversion Background and Objectives
T wave inversion is a significant electrocardiographic finding that has garnered increasing attention in the context of renal insufficiency-related cardiac changes. This phenomenon, characterized by the reversal of the normal T wave polarity in one or more leads of an electrocardiogram (ECG), has been observed with higher frequency in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
The historical background of T wave inversion research dates back to the early 20th century when Willem Einthoven first described the components of the ECG. However, its specific association with renal insufficiency has only been extensively studied in recent decades. As the prevalence of CKD continues to rise globally, understanding the cardiac manifestations of renal dysfunction has become increasingly crucial.
T wave inversion in the setting of renal insufficiency presents a unique challenge to clinicians and researchers alike. It represents a complex interplay between electrolyte imbalances, uremic toxins, and structural changes in the myocardium that are common in patients with impaired renal function. The presence of T wave inversion in this population has been associated with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events and mortality.
The primary objective of research in this field is to elucidate the underlying mechanisms that lead to T wave inversion in patients with renal insufficiency. This includes investigating the roles of electrolyte disturbances, particularly potassium and calcium imbalances, which are common in CKD patients and can significantly affect cardiac repolarization.
Another key goal is to determine the prognostic value of T wave inversion in this specific patient population. While T wave inversion is generally considered a marker of myocardial ischemia or structural heart disease, its interpretation in the context of renal insufficiency requires careful consideration of the unique pathophysiological changes associated with kidney dysfunction.
Furthermore, research aims to establish standardized criteria for interpreting T wave inversions in patients with renal insufficiency, as the current guidelines may not fully account for the specific ECG changes seen in this group. This standardization is crucial for improving diagnostic accuracy and guiding appropriate management strategies.
Lastly, there is a growing interest in exploring potential therapeutic interventions that could mitigate the development or progression of T wave inversions in patients with renal insufficiency. This includes investigating the effects of optimal dialysis strategies, electrolyte management, and novel pharmacological approaches on cardiac electrical activity and structural remodeling.
The historical background of T wave inversion research dates back to the early 20th century when Willem Einthoven first described the components of the ECG. However, its specific association with renal insufficiency has only been extensively studied in recent decades. As the prevalence of CKD continues to rise globally, understanding the cardiac manifestations of renal dysfunction has become increasingly crucial.
T wave inversion in the setting of renal insufficiency presents a unique challenge to clinicians and researchers alike. It represents a complex interplay between electrolyte imbalances, uremic toxins, and structural changes in the myocardium that are common in patients with impaired renal function. The presence of T wave inversion in this population has been associated with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events and mortality.
The primary objective of research in this field is to elucidate the underlying mechanisms that lead to T wave inversion in patients with renal insufficiency. This includes investigating the roles of electrolyte disturbances, particularly potassium and calcium imbalances, which are common in CKD patients and can significantly affect cardiac repolarization.
Another key goal is to determine the prognostic value of T wave inversion in this specific patient population. While T wave inversion is generally considered a marker of myocardial ischemia or structural heart disease, its interpretation in the context of renal insufficiency requires careful consideration of the unique pathophysiological changes associated with kidney dysfunction.
Furthermore, research aims to establish standardized criteria for interpreting T wave inversions in patients with renal insufficiency, as the current guidelines may not fully account for the specific ECG changes seen in this group. This standardization is crucial for improving diagnostic accuracy and guiding appropriate management strategies.
Lastly, there is a growing interest in exploring potential therapeutic interventions that could mitigate the development or progression of T wave inversions in patients with renal insufficiency. This includes investigating the effects of optimal dialysis strategies, electrolyte management, and novel pharmacological approaches on cardiac electrical activity and structural remodeling.
Clinical Significance in Renal Insufficiency
T wave inversion in the context of renal insufficiency-related cardiac changes holds significant clinical importance in the management and prognosis of patients with kidney disease. This electrocardiographic finding serves as a crucial indicator of underlying cardiac abnormalities and potential cardiovascular complications associated with renal dysfunction.
In patients with renal insufficiency, T wave inversion often reflects the complex interplay between electrolyte imbalances, uremic toxins, and structural changes in the myocardium. The presence of inverted T waves may signify left ventricular hypertrophy, a common consequence of chronic kidney disease due to increased afterload and volume overload. This structural adaptation can lead to altered repolarization patterns, manifesting as T wave inversions on the ECG.
Furthermore, T wave inversion in renal insufficiency patients may indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction, which are more prevalent in this population due to accelerated atherosclerosis and vascular calcification. The recognition of these ECG changes is crucial for early detection and management of coronary artery disease, potentially reducing morbidity and mortality rates among renal patients.
Electrolyte disturbances, particularly hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia, commonly observed in renal insufficiency, can also contribute to T wave inversions. These electrolyte imbalances affect the cardiac action potential and repolarization process, leading to characteristic ECG changes. Identifying T wave inversions in this context may prompt immediate correction of electrolyte abnormalities, preventing life-threatening arrhythmias.
The clinical significance of T wave inversion extends to risk stratification in renal insufficiency patients. Studies have shown that the presence and extent of T wave inversions correlate with increased cardiovascular events and mortality in this population. This information can guide clinicians in tailoring treatment strategies, including more aggressive cardiovascular risk factor management and closer monitoring.
In the context of renal transplantation, T wave inversions may serve as an early marker of allograft rejection or dysfunction. Regular ECG monitoring in transplant recipients can aid in the timely detection of cardiac complications and guide immunosuppressive therapy adjustments.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of T wave inversions in renal insufficiency patients provides valuable insights into the progression of cardiac involvement. Serial ECG assessments can track changes in T wave morphology, offering a non-invasive method to monitor cardiac status and evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
In patients with renal insufficiency, T wave inversion often reflects the complex interplay between electrolyte imbalances, uremic toxins, and structural changes in the myocardium. The presence of inverted T waves may signify left ventricular hypertrophy, a common consequence of chronic kidney disease due to increased afterload and volume overload. This structural adaptation can lead to altered repolarization patterns, manifesting as T wave inversions on the ECG.
Furthermore, T wave inversion in renal insufficiency patients may indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction, which are more prevalent in this population due to accelerated atherosclerosis and vascular calcification. The recognition of these ECG changes is crucial for early detection and management of coronary artery disease, potentially reducing morbidity and mortality rates among renal patients.
Electrolyte disturbances, particularly hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia, commonly observed in renal insufficiency, can also contribute to T wave inversions. These electrolyte imbalances affect the cardiac action potential and repolarization process, leading to characteristic ECG changes. Identifying T wave inversions in this context may prompt immediate correction of electrolyte abnormalities, preventing life-threatening arrhythmias.
The clinical significance of T wave inversion extends to risk stratification in renal insufficiency patients. Studies have shown that the presence and extent of T wave inversions correlate with increased cardiovascular events and mortality in this population. This information can guide clinicians in tailoring treatment strategies, including more aggressive cardiovascular risk factor management and closer monitoring.
In the context of renal transplantation, T wave inversions may serve as an early marker of allograft rejection or dysfunction. Regular ECG monitoring in transplant recipients can aid in the timely detection of cardiac complications and guide immunosuppressive therapy adjustments.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of T wave inversions in renal insufficiency patients provides valuable insights into the progression of cardiac involvement. Serial ECG assessments can track changes in T wave morphology, offering a non-invasive method to monitor cardiac status and evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
Current Challenges in T Wave Analysis
T wave inversion analysis in the context of renal insufficiency-related cardiac changes presents several significant challenges for researchers and clinicians. One of the primary difficulties lies in distinguishing between pathological T wave inversions caused by renal insufficiency and those resulting from other cardiac conditions. The complex interplay between renal dysfunction and cardiac electrophysiology often leads to ambiguous ECG readings, making accurate interpretation a formidable task.
Another major challenge is the variability in T wave morphology among patients with renal insufficiency. The degree of T wave inversion can differ significantly based on the severity of renal dysfunction, comorbidities, and individual patient factors. This heterogeneity complicates the development of standardized criteria for T wave analysis in this specific patient population.
The dynamic nature of T wave changes in renal insufficiency patients further compounds the difficulty of analysis. As renal function fluctuates, so too can the appearance of T waves on ECG, necessitating frequent monitoring and reassessment. This temporal variability makes it challenging to establish consistent baseline measurements and track meaningful changes over time.
Moreover, the influence of electrolyte imbalances, particularly potassium and calcium disturbances common in renal insufficiency, adds another layer of complexity to T wave analysis. These electrolyte shifts can dramatically alter T wave morphology, potentially masking or mimicking pathological changes and confounding interpretation.
The lack of large-scale, longitudinal studies specifically examining T wave inversions in renal insufficiency patients represents a significant gap in current knowledge. This deficiency hampers the development of robust, evidence-based guidelines for ECG interpretation in this context, leaving clinicians to rely heavily on individual expertise and limited data sets.
Technical limitations in ECG recording and analysis systems also pose challenges. Many existing algorithms for automated T wave analysis are not optimized for the unique ECG patterns seen in renal insufficiency, potentially leading to inaccurate readings or missed abnormalities. The need for more sophisticated, context-aware analysis tools is evident but remains unmet.
Lastly, the multifactorial nature of cardiac changes in renal insufficiency complicates the isolation of T wave inversion as a specific diagnostic or prognostic marker. Distinguishing the clinical significance of T wave inversions from other ECG abnormalities and non-ECG indicators of cardiac dysfunction requires a comprehensive approach that is often difficult to implement in practice.
Another major challenge is the variability in T wave morphology among patients with renal insufficiency. The degree of T wave inversion can differ significantly based on the severity of renal dysfunction, comorbidities, and individual patient factors. This heterogeneity complicates the development of standardized criteria for T wave analysis in this specific patient population.
The dynamic nature of T wave changes in renal insufficiency patients further compounds the difficulty of analysis. As renal function fluctuates, so too can the appearance of T waves on ECG, necessitating frequent monitoring and reassessment. This temporal variability makes it challenging to establish consistent baseline measurements and track meaningful changes over time.
Moreover, the influence of electrolyte imbalances, particularly potassium and calcium disturbances common in renal insufficiency, adds another layer of complexity to T wave analysis. These electrolyte shifts can dramatically alter T wave morphology, potentially masking or mimicking pathological changes and confounding interpretation.
The lack of large-scale, longitudinal studies specifically examining T wave inversions in renal insufficiency patients represents a significant gap in current knowledge. This deficiency hampers the development of robust, evidence-based guidelines for ECG interpretation in this context, leaving clinicians to rely heavily on individual expertise and limited data sets.
Technical limitations in ECG recording and analysis systems also pose challenges. Many existing algorithms for automated T wave analysis are not optimized for the unique ECG patterns seen in renal insufficiency, potentially leading to inaccurate readings or missed abnormalities. The need for more sophisticated, context-aware analysis tools is evident but remains unmet.
Lastly, the multifactorial nature of cardiac changes in renal insufficiency complicates the isolation of T wave inversion as a specific diagnostic or prognostic marker. Distinguishing the clinical significance of T wave inversions from other ECG abnormalities and non-ECG indicators of cardiac dysfunction requires a comprehensive approach that is often difficult to implement in practice.
Existing T Wave Inversion Detection Methods
01 Detection and analysis of T wave inversion
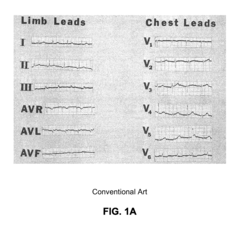
T wave inversion is a significant indicator in electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis. Advanced algorithms and methods are developed to accurately detect and analyze T wave inversions, which can be crucial in diagnosing various cardiac conditions. These techniques often involve signal processing, machine learning, and pattern recognition to identify abnormal T wave morphologies.- Detection and analysis of T wave inversion: T wave inversion is a significant indicator in electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis. Advanced algorithms and methods are developed to accurately detect and analyze T wave inversions, which can be crucial in diagnosing various cardiac conditions. These techniques often involve signal processing, machine learning, and pattern recognition to identify abnormal T wave morphologies.
- Correlation of T wave inversion with cardiac pathologies: Research focuses on establishing correlations between T wave inversions and specific cardiac pathologies. Studies investigate the relationship between inverted T waves and conditions such as ischemia, cardiomyopathy, and electrolyte imbalances. This knowledge aids in improving diagnostic accuracy and risk stratification in patients with suspected heart diseases.
- Wearable devices for continuous T wave monitoring: Innovative wearable devices are being developed to enable continuous monitoring of T waves outside clinical settings. These devices incorporate miniaturized ECG sensors and advanced data processing capabilities to detect T wave inversions in real-time. This technology allows for early detection of cardiac abnormalities and improved patient care through remote monitoring.
- Artificial intelligence in T wave inversion interpretation: Artificial intelligence and deep learning techniques are increasingly applied to interpret T wave inversions more accurately. These AI-powered systems can analyze large datasets of ECG recordings to identify subtle patterns and variations in T wave morphology. This approach enhances the sensitivity and specificity of T wave inversion detection, potentially reducing misdiagnoses.
- T wave inversion in specific patient populations: Research is conducted on T wave inversion characteristics in specific patient populations, such as athletes, elderly individuals, and those with genetic predispositions to cardiac disorders. These studies aim to establish normal variants and differentiate them from pathological T wave inversions, leading to more personalized and accurate cardiac assessments.
02 T wave inversion in cardiac risk assessment
T wave inversion plays a vital role in assessing cardiac risk. Research focuses on correlating T wave inversions with specific cardiac pathologies and developing risk stratification models. These models consider factors such as the location, depth, and duration of T wave inversions to predict potential cardiac events and guide treatment decisions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wearable devices for continuous T wave monitoring
Innovative wearable devices are being developed to continuously monitor T waves and detect inversions in real-time. These devices integrate miniaturized ECG sensors with advanced signal processing capabilities, allowing for long-term monitoring outside clinical settings. They aim to provide early warning of cardiac abnormalities and improve patient outcomes through timely interventions.Expand Specific Solutions04 AI and machine learning in T wave inversion analysis
Artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques are increasingly applied to analyze T wave inversions. These approaches enhance the accuracy and speed of T wave inversion detection, reduce false positives, and uncover subtle patterns that may be indicative of specific cardiac conditions. AI-driven systems can process large volumes of ECG data to identify trends and predict outcomes related to T wave abnormalities.Expand Specific Solutions05 T wave inversion in specific patient populations
Research is conducted on T wave inversion characteristics in specific patient populations, such as athletes, elderly individuals, or those with particular genetic predispositions. These studies aim to establish normal variants and differentiate them from pathological T wave inversions. Understanding population-specific T wave patterns helps in tailoring diagnostic criteria and improving the accuracy of cardiac assessments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Researchers and Institutions
The research on T wave inversion in renal insufficiency-related cardiac changes is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential due to the increasing prevalence of kidney diseases. The technology is still evolving, with various companies and institutions contributing to its advancement. Key players like Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Siemens Healthcare are leveraging their expertise in cardiac monitoring and imaging to explore this field. Academic institutions such as Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Shanghai Jiao Tong University are also conducting significant research. The market is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers and emerging biotech firms, indicating a competitive landscape with opportunities for innovation and collaboration.
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Inc.
Technical Solution: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center has developed a novel approach to analyzing T wave inversion in renal patients using advanced imaging techniques combined with ECG data. Their method employs cardiac MRI to assess structural changes in the heart and correlates these findings with ECG abnormalities, including T wave inversion[2]. The research team has created a predictive model that incorporates biomarkers of renal function, electrolyte levels, and cardiac imaging data to assess the risk of adverse cardiac events in patients with renal insufficiency[4]. This multi-modal approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between renal dysfunction and cardiac electrical abnormalities, potentially leading to more targeted interventions.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining imaging and ECG data; potential for highly personalized risk assessment. Weaknesses: Requires access to advanced imaging technology; may be resource-intensive and not suitable for all clinical settings.
Medtronic, Inc.
Technical Solution: Medtronic has developed advanced ECG algorithms for detecting T wave inversion in patients with renal insufficiency. Their approach combines machine learning techniques with traditional signal processing to improve accuracy. The system analyzes multiple ECG leads simultaneously, considering temporal and spatial relationships between T waves across different leads[1]. It also incorporates patient-specific factors like electrolyte levels and medication history to contextualize T wave changes. Medtronic's solution includes real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing for early detection of cardiac changes in dialysis patients[3]. The technology has been integrated into their cardiac monitoring devices and dialysis machines, providing a comprehensive approach to managing cardiac risks in renal patients.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach integrating multiple data sources; real-time monitoring capabilities; large installed base of devices. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment; potential for false positives in complex cases.
Innovative Approaches in ECG Signal Processing
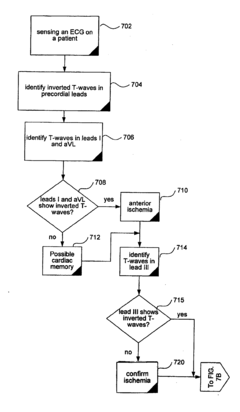
Differentiating Ischemic From Non-Ischemic T-Wave Inversion
PatentInactiveUS20070129640A1
Innovation
- A method and system that calculate the direction of the T-wave vector from electrocardiographic data to diagnose ischemia (vector between 75° and 200°) and cardiac memory (vector between 0° and -90°) to distinguish between the two conditions.
Impact on Renal Disease Management
The impact of T wave inversion in the context of renal insufficiency-related cardiac changes on renal disease management is significant and multifaceted. This electrocardiographic finding has important implications for patient care, treatment strategies, and overall disease prognosis.
T wave inversion, when observed in patients with renal insufficiency, serves as a crucial indicator of underlying cardiac abnormalities. It prompts healthcare providers to conduct more thorough cardiovascular assessments, potentially leading to earlier detection of cardiac complications associated with renal disease. This early identification allows for timely interventions and adjustments in treatment plans, potentially slowing the progression of both renal and cardiac dysfunction.
The presence of T wave inversion in this context may influence the choice and dosing of medications used in renal disease management. Certain drugs commonly prescribed for renal insufficiency may need to be adjusted or avoided due to their potential impact on cardiac function. For instance, some antihypertensive medications or diuretics might require careful consideration to prevent exacerbation of cardiac issues.
Furthermore, the detection of T wave inversion may necessitate more frequent cardiac monitoring in renal patients. This increased surveillance can help in tracking the progression of cardiac changes and guide decisions regarding the timing and nature of interventions, such as dialysis initiation or adjustment of fluid management strategies.
The management of anemia, a common complication in renal insufficiency, may also be influenced by the presence of T wave inversion. The correction of anemia in these patients might require a more cautious approach, balancing the need for improved oxygen delivery with the risk of cardiac stress.
From a diagnostic perspective, the presence of T wave inversion in renal patients may complicate the interpretation of other cardiac tests. This can lead to the need for more advanced cardiac imaging techniques or invasive procedures to accurately assess cardiac function and structure in these patients.
In terms of long-term management, the presence of T wave inversion may influence decisions regarding kidney transplantation. Patients with this ECG finding might require more extensive cardiac evaluation and potentially cardiac interventions before being considered suitable candidates for transplantation.
Lastly, the recognition of T wave inversion in renal patients underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to care. It necessitates closer collaboration between nephrologists, cardiologists, and other specialists to provide comprehensive management that addresses both renal and cardiac aspects of the patient's condition.
T wave inversion, when observed in patients with renal insufficiency, serves as a crucial indicator of underlying cardiac abnormalities. It prompts healthcare providers to conduct more thorough cardiovascular assessments, potentially leading to earlier detection of cardiac complications associated with renal disease. This early identification allows for timely interventions and adjustments in treatment plans, potentially slowing the progression of both renal and cardiac dysfunction.
The presence of T wave inversion in this context may influence the choice and dosing of medications used in renal disease management. Certain drugs commonly prescribed for renal insufficiency may need to be adjusted or avoided due to their potential impact on cardiac function. For instance, some antihypertensive medications or diuretics might require careful consideration to prevent exacerbation of cardiac issues.
Furthermore, the detection of T wave inversion may necessitate more frequent cardiac monitoring in renal patients. This increased surveillance can help in tracking the progression of cardiac changes and guide decisions regarding the timing and nature of interventions, such as dialysis initiation or adjustment of fluid management strategies.
The management of anemia, a common complication in renal insufficiency, may also be influenced by the presence of T wave inversion. The correction of anemia in these patients might require a more cautious approach, balancing the need for improved oxygen delivery with the risk of cardiac stress.
From a diagnostic perspective, the presence of T wave inversion in renal patients may complicate the interpretation of other cardiac tests. This can lead to the need for more advanced cardiac imaging techniques or invasive procedures to accurately assess cardiac function and structure in these patients.
In terms of long-term management, the presence of T wave inversion may influence decisions regarding kidney transplantation. Patients with this ECG finding might require more extensive cardiac evaluation and potentially cardiac interventions before being considered suitable candidates for transplantation.
Lastly, the recognition of T wave inversion in renal patients underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to care. It necessitates closer collaboration between nephrologists, cardiologists, and other specialists to provide comprehensive management that addresses both renal and cardiac aspects of the patient's condition.
Ethical Considerations in Cardiac Diagnostics
The ethical considerations in cardiac diagnostics, particularly in the context of T wave inversion research related to renal insufficiency-induced cardiac changes, are multifaceted and require careful attention. These considerations encompass patient autonomy, informed consent, privacy, and the responsible use of medical data.
One primary ethical concern is ensuring that patients fully understand the implications of participating in such research. Given the complexity of cardiac diagnostics and the potential risks associated with renal insufficiency, it is crucial to provide clear, comprehensive information to patients. This includes explaining the purpose of the research, potential benefits, and any risks involved in the diagnostic procedures.
Privacy and data protection are paramount in cardiac diagnostics research. With the increasing use of electronic health records and big data analytics, researchers must implement robust safeguards to protect patient information. This includes anonymizing data, securing storage systems, and limiting access to sensitive information only to authorized personnel.
The principle of justice in research ethics demands that the benefits and burdens of research be distributed fairly. In the context of T wave inversion studies, this means ensuring that patient selection is based on scientific criteria rather than convenience or bias. It also involves considering how the research outcomes might benefit or impact different patient populations, particularly those with renal insufficiency.
Researchers must also grapple with the ethical implications of incidental findings. During cardiac diagnostics, unrelated health issues may be discovered. Protocols must be in place to address how such findings are communicated to patients and what follow-up care is provided.
The use of advanced diagnostic technologies raises questions about resource allocation and access to care. Ethical considerations include how to balance the use of sophisticated, potentially costly diagnostic tools with the need to provide equitable healthcare access to all patients, including those with limited resources.
Lastly, there is an ethical obligation to ensure the scientific integrity of the research. This includes using appropriate methodologies, avoiding conflicts of interest, and transparently reporting results, including negative findings. The responsible conduct of research is crucial for maintaining public trust and advancing medical knowledge in a way that truly benefits patients with cardiac and renal conditions.
One primary ethical concern is ensuring that patients fully understand the implications of participating in such research. Given the complexity of cardiac diagnostics and the potential risks associated with renal insufficiency, it is crucial to provide clear, comprehensive information to patients. This includes explaining the purpose of the research, potential benefits, and any risks involved in the diagnostic procedures.
Privacy and data protection are paramount in cardiac diagnostics research. With the increasing use of electronic health records and big data analytics, researchers must implement robust safeguards to protect patient information. This includes anonymizing data, securing storage systems, and limiting access to sensitive information only to authorized personnel.
The principle of justice in research ethics demands that the benefits and burdens of research be distributed fairly. In the context of T wave inversion studies, this means ensuring that patient selection is based on scientific criteria rather than convenience or bias. It also involves considering how the research outcomes might benefit or impact different patient populations, particularly those with renal insufficiency.
Researchers must also grapple with the ethical implications of incidental findings. During cardiac diagnostics, unrelated health issues may be discovered. Protocols must be in place to address how such findings are communicated to patients and what follow-up care is provided.
The use of advanced diagnostic technologies raises questions about resource allocation and access to care. Ethical considerations include how to balance the use of sophisticated, potentially costly diagnostic tools with the need to provide equitable healthcare access to all patients, including those with limited resources.
Lastly, there is an ethical obligation to ensure the scientific integrity of the research. This includes using appropriate methodologies, avoiding conflicts of interest, and transparently reporting results, including negative findings. The responsible conduct of research is crucial for maintaining public trust and advancing medical knowledge in a way that truly benefits patients with cardiac and renal conditions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!