The Effectiveness of Magnesium Nitrate in Eco-Friendly Paper Production
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Magnesium Nitrate in Paper: Background and Objectives
The paper industry has long been a cornerstone of global manufacturing, with a history dating back centuries. However, in recent decades, the environmental impact of traditional paper production methods has come under scrutiny. This has led to a surge in research and development efforts aimed at creating more eco-friendly paper production processes. One such innovation that has gained attention is the use of magnesium nitrate in paper manufacturing.
Magnesium nitrate, a compound with the chemical formula Mg(NO3)2, has emerged as a promising additive in the quest for sustainable paper production. Its potential lies in its ability to enhance various aspects of the papermaking process while simultaneously reducing the environmental footprint. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative chemicals to replace harmful substances traditionally used in paper production.
The primary objective of incorporating magnesium nitrate into paper production is to improve the overall quality and sustainability of the final product. This includes enhancing paper strength, increasing brightness, and reducing the need for harmful bleaching agents. Additionally, magnesium nitrate has shown potential in reducing water consumption during the manufacturing process, addressing one of the most significant environmental concerns in the paper industry.
As global awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, the paper industry faces increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. This has led to a shift in focus towards technologies that can reduce energy consumption, minimize water usage, and decrease chemical waste. Magnesium nitrate's role in this context is particularly significant, as it aligns with these sustainability goals while potentially offering economic benefits to manufacturers.
The development of magnesium nitrate technology in paper production is closely tied to broader trends in green chemistry and circular economy principles. Researchers and industry professionals are exploring ways to integrate this compound into existing production processes with minimal disruption, while maximizing its potential benefits. This includes investigating optimal concentrations, application methods, and potential synergies with other eco-friendly additives.
As we delve deeper into the effectiveness of magnesium nitrate in eco-friendly paper production, it is essential to consider both the technical aspects of its implementation and the broader implications for the industry. This includes evaluating its impact on paper quality, production efficiency, and environmental sustainability. By thoroughly examining these factors, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of magnesium nitrate's potential to revolutionize paper manufacturing and contribute to a more sustainable future for the industry.
Magnesium nitrate, a compound with the chemical formula Mg(NO3)2, has emerged as a promising additive in the quest for sustainable paper production. Its potential lies in its ability to enhance various aspects of the papermaking process while simultaneously reducing the environmental footprint. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative chemicals to replace harmful substances traditionally used in paper production.
The primary objective of incorporating magnesium nitrate into paper production is to improve the overall quality and sustainability of the final product. This includes enhancing paper strength, increasing brightness, and reducing the need for harmful bleaching agents. Additionally, magnesium nitrate has shown potential in reducing water consumption during the manufacturing process, addressing one of the most significant environmental concerns in the paper industry.
As global awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, the paper industry faces increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. This has led to a shift in focus towards technologies that can reduce energy consumption, minimize water usage, and decrease chemical waste. Magnesium nitrate's role in this context is particularly significant, as it aligns with these sustainability goals while potentially offering economic benefits to manufacturers.
The development of magnesium nitrate technology in paper production is closely tied to broader trends in green chemistry and circular economy principles. Researchers and industry professionals are exploring ways to integrate this compound into existing production processes with minimal disruption, while maximizing its potential benefits. This includes investigating optimal concentrations, application methods, and potential synergies with other eco-friendly additives.
As we delve deeper into the effectiveness of magnesium nitrate in eco-friendly paper production, it is essential to consider both the technical aspects of its implementation and the broader implications for the industry. This includes evaluating its impact on paper quality, production efficiency, and environmental sustainability. By thoroughly examining these factors, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of magnesium nitrate's potential to revolutionize paper manufacturing and contribute to a more sustainable future for the industry.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Paper Products
The demand for eco-friendly paper products has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations on sustainable practices. Consumers and businesses alike are seeking alternatives to traditional paper production methods, which often involve harmful chemicals and significant environmental impact. This shift in market preferences has created a substantial opportunity for eco-friendly paper products, including those potentially produced using magnesium nitrate.
The global eco-friendly paper market has shown robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion. Key factors contributing to this growth include increasing corporate sustainability initiatives, government regulations promoting environmentally friendly practices, and consumer demand for green products. Industries such as packaging, printing, and stationery are particularly interested in adopting eco-friendly paper solutions to meet their sustainability goals and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
In the packaging sector, there is a notable trend towards replacing plastic materials with biodegradable paper alternatives. This transition is especially prominent in the food and beverage industry, where concerns about plastic pollution have led to a surge in demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions. The retail sector is also embracing eco-friendly paper products for shopping bags and product packaging, responding to consumer preferences and regulatory pressures.
The printing industry, facing challenges from digital media, is finding new opportunities in eco-friendly paper products. Many businesses are opting for sustainably produced paper for their marketing materials, reports, and other printed documents as part of their corporate social responsibility efforts. This trend is particularly strong among companies targeting environmentally conscious consumers or operating in sectors with high environmental scrutiny.
Educational institutions and office environments are also significant contributors to the growing demand for eco-friendly paper products. Schools and universities are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, including the use of recycled and eco-friendly paper for textbooks, notebooks, and administrative purposes. Similarly, offices are transitioning to eco-friendly paper options for their day-to-day operations, driven by both environmental concerns and potential cost savings associated with more efficient paper production methods.
The market demand for eco-friendly paper products extends beyond traditional paper applications. Innovative uses in fields such as construction (e.g., eco-friendly wallpapers) and textiles (e.g., paper-based fabrics) are emerging, further expanding the potential market for sustainably produced paper. These new applications highlight the versatility of eco-friendly paper and its potential to replace less sustainable materials in various industries.
The global eco-friendly paper market has shown robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion. Key factors contributing to this growth include increasing corporate sustainability initiatives, government regulations promoting environmentally friendly practices, and consumer demand for green products. Industries such as packaging, printing, and stationery are particularly interested in adopting eco-friendly paper solutions to meet their sustainability goals and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
In the packaging sector, there is a notable trend towards replacing plastic materials with biodegradable paper alternatives. This transition is especially prominent in the food and beverage industry, where concerns about plastic pollution have led to a surge in demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions. The retail sector is also embracing eco-friendly paper products for shopping bags and product packaging, responding to consumer preferences and regulatory pressures.
The printing industry, facing challenges from digital media, is finding new opportunities in eco-friendly paper products. Many businesses are opting for sustainably produced paper for their marketing materials, reports, and other printed documents as part of their corporate social responsibility efforts. This trend is particularly strong among companies targeting environmentally conscious consumers or operating in sectors with high environmental scrutiny.
Educational institutions and office environments are also significant contributors to the growing demand for eco-friendly paper products. Schools and universities are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, including the use of recycled and eco-friendly paper for textbooks, notebooks, and administrative purposes. Similarly, offices are transitioning to eco-friendly paper options for their day-to-day operations, driven by both environmental concerns and potential cost savings associated with more efficient paper production methods.
The market demand for eco-friendly paper products extends beyond traditional paper applications. Innovative uses in fields such as construction (e.g., eco-friendly wallpapers) and textiles (e.g., paper-based fabrics) are emerging, further expanding the potential market for sustainably produced paper. These new applications highlight the versatility of eco-friendly paper and its potential to replace less sustainable materials in various industries.
Current Challenges in Green Paper Manufacturing
The paper industry faces significant challenges in its pursuit of eco-friendly production methods. Traditional paper manufacturing processes are resource-intensive, consuming vast amounts of water, energy, and chemicals, while generating substantial waste and emissions. One of the primary hurdles is the reduction of water usage, as conventional papermaking requires large volumes of water for pulping, washing, and processing. This not only strains local water resources but also leads to the generation of contaminated wastewater that requires extensive treatment.
Energy consumption presents another major challenge. The paper production process, particularly in the drying phase, demands considerable thermal and electrical energy. Many mills still rely on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and increasing the carbon footprint of paper products. The industry is under pressure to transition to renewable energy sources and implement more energy-efficient technologies.
Chemical usage in paper production poses environmental and health concerns. Bleaching agents, such as chlorine-based compounds, have been traditionally used to achieve the desired whiteness in paper. However, these chemicals can produce harmful byproducts, including dioxins and other organochlorines, which are persistent environmental pollutants. The challenge lies in finding effective, eco-friendly alternatives that maintain paper quality while minimizing environmental impact.
Waste management is another critical issue. The paper industry generates significant amounts of solid waste, including sludge from wastewater treatment and rejected fibers. Disposing of this waste in landfills is unsustainable and contributes to environmental degradation. The industry must develop innovative ways to reduce, reuse, or recycle these waste materials.
Deforestation and sustainable sourcing of raw materials remain ongoing challenges. While many companies have adopted responsible forestry practices, the demand for virgin wood pulp continues to put pressure on forest ecosystems. Balancing the need for high-quality fiber with forest conservation efforts requires continuous innovation in sourcing strategies and the development of alternative fiber sources.
The paper industry also faces the challenge of reducing its overall carbon emissions. This encompasses not only direct emissions from manufacturing processes but also those associated with transportation and the entire supply chain. Implementing carbon capture technologies and optimizing logistics are areas that require significant investment and technological advancement.
Lastly, meeting consumer expectations for eco-friendly products while maintaining cost-effectiveness is a delicate balance. Green paper manufacturing often involves higher production costs, which can be challenging to reconcile with market demands for affordable products. The industry must innovate to develop cost-effective, sustainable processes that do not compromise on quality or environmental standards.
Energy consumption presents another major challenge. The paper production process, particularly in the drying phase, demands considerable thermal and electrical energy. Many mills still rely on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and increasing the carbon footprint of paper products. The industry is under pressure to transition to renewable energy sources and implement more energy-efficient technologies.
Chemical usage in paper production poses environmental and health concerns. Bleaching agents, such as chlorine-based compounds, have been traditionally used to achieve the desired whiteness in paper. However, these chemicals can produce harmful byproducts, including dioxins and other organochlorines, which are persistent environmental pollutants. The challenge lies in finding effective, eco-friendly alternatives that maintain paper quality while minimizing environmental impact.
Waste management is another critical issue. The paper industry generates significant amounts of solid waste, including sludge from wastewater treatment and rejected fibers. Disposing of this waste in landfills is unsustainable and contributes to environmental degradation. The industry must develop innovative ways to reduce, reuse, or recycle these waste materials.
Deforestation and sustainable sourcing of raw materials remain ongoing challenges. While many companies have adopted responsible forestry practices, the demand for virgin wood pulp continues to put pressure on forest ecosystems. Balancing the need for high-quality fiber with forest conservation efforts requires continuous innovation in sourcing strategies and the development of alternative fiber sources.
The paper industry also faces the challenge of reducing its overall carbon emissions. This encompasses not only direct emissions from manufacturing processes but also those associated with transportation and the entire supply chain. Implementing carbon capture technologies and optimizing logistics are areas that require significant investment and technological advancement.
Lastly, meeting consumer expectations for eco-friendly products while maintaining cost-effectiveness is a delicate balance. Green paper manufacturing often involves higher production costs, which can be challenging to reconcile with market demands for affordable products. The industry must innovate to develop cost-effective, sustainable processes that do not compromise on quality or environmental standards.
Magnesium Nitrate Application Methods in Paper Production
01 Agricultural applications
Magnesium nitrate is effective in agricultural applications, particularly as a fertilizer. It provides essential nutrients to plants, improving crop yield and quality. The compound is easily absorbed by plants, making it an efficient source of both magnesium and nitrogen for various crops.- Agricultural applications of magnesium nitrate: Magnesium nitrate is effective in agricultural applications, particularly as a fertilizer. It provides essential nutrients to plants, improving crop yield and quality. The compound is easily absorbed by plants and can help address magnesium deficiencies in soil.
- Use in water treatment and purification: Magnesium nitrate demonstrates effectiveness in water treatment processes. It can be used for removing contaminants, adjusting water hardness, and as a coagulant aid in wastewater treatment. The compound's properties make it suitable for various water purification applications.
- Industrial and chemical applications: In industrial settings, magnesium nitrate proves effective in various chemical processes. It is used in the production of catalysts, as a raw material in the manufacture of other magnesium compounds, and in the synthesis of certain organic compounds. Its effectiveness in these applications is due to its chemical properties and reactivity.
- Fire retardant and flame-resistant applications: Magnesium nitrate is effective as a fire retardant and flame-resistant agent. It can be incorporated into various materials to enhance their fire-resistant properties. The compound's ability to release nitrogen when heated contributes to its effectiveness in suppressing flames and reducing fire spread.
- Medical and pharmaceutical uses: In the medical and pharmaceutical fields, magnesium nitrate shows effectiveness in certain applications. It can be used in the formulation of some medications and supplements. The compound's properties make it suitable for specific therapeutic uses, although its applications in this area are more limited compared to other fields.
02 Industrial uses
Magnesium nitrate demonstrates effectiveness in various industrial applications. It is used in the production of ceramics, as a catalyst in chemical reactions, and in the manufacturing of specialty glasses. The compound's properties make it suitable for use in flame retardants and as an oxidizing agent in certain industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental remediation
Magnesium nitrate shows promise in environmental remediation efforts. It can be used to treat contaminated soil and water, helping to remove pollutants and restore ecological balance. The compound's effectiveness in this area is attributed to its ability to promote beneficial microbial activity and enhance nutrient cycling in the environment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and pharmaceutical applications
In the medical and pharmaceutical fields, magnesium nitrate demonstrates effectiveness in various applications. It is used in the formulation of certain medications and supplements, particularly those aimed at addressing magnesium deficiencies. The compound's properties make it useful in some diagnostic procedures and as a component in specific medical treatments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy storage and thermal management
Magnesium nitrate shows effectiveness in energy storage and thermal management applications. It is used in phase change materials for thermal energy storage systems, helping to regulate temperature in various settings. The compound's heat absorption and release properties make it valuable in developing more efficient energy storage solutions and temperature control systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Paper Industry
The eco-friendly paper production industry utilizing magnesium nitrate is in its early development stage, with a growing market driven by increasing environmental concerns. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with various research institutions and companies exploring its potential. South China University of Technology and Xidian University are leading academic research in this field, while companies like Kemira Oyj and Zhejiang Hengda New Material Co., Ltd. are developing commercial applications. The market size is expanding as more paper manufacturers seek sustainable alternatives, but widespread adoption is still limited due to ongoing refinement of the technology and cost considerations.
Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences)
Technical Solution: Qilu University of Technology has developed an innovative approach to eco-friendly paper production using magnesium nitrate. Their method involves incorporating magnesium nitrate into the paper-making process as a flame retardant and strength enhancer. The university's research team has found that adding magnesium nitrate to the pulp mixture can improve the paper's fire resistance properties while maintaining its structural integrity. They have also explored the use of magnesium nitrate in combination with other eco-friendly additives to create a more sustainable paper product. The university's studies have shown that papers treated with magnesium nitrate exhibit a 30% increase in flame resistance compared to untreated papers[1][3]. Additionally, they have reported a 15% improvement in tensile strength, making the paper more durable and suitable for various applications[2].
Strengths: Improved flame resistance and enhanced paper strength. Eco-friendly approach aligns with sustainability goals. Weaknesses: Potential increased production costs and the need for specialized equipment for magnesium nitrate integration.
Kemira Oyj
Technical Solution: Kemira Oyj has developed a proprietary process for incorporating magnesium nitrate into paper production to enhance both the environmental sustainability and performance of the final product. Their approach involves adding a carefully formulated magnesium nitrate solution during the wet-end stage of papermaking. This method has been shown to improve the paper's resistance to moisture and increase its overall strength. Kemira's research indicates that papers produced using their magnesium nitrate technology demonstrate a 25% reduction in water absorption[4], leading to improved printing quality and reduced ink bleeding. Furthermore, their process has been optimized to work in conjunction with other eco-friendly additives, creating a synergistic effect that enhances the paper's recyclability. The company has reported that papers treated with their magnesium nitrate solution show a 20% increase in recycling efficiency compared to conventional papers[5].
Strengths: Improved moisture resistance and enhanced recyclability. Well-established presence in the paper chemicals industry. Weaknesses: May require modifications to existing paper production lines and potential higher raw material costs.
Innovations in Magnesium Nitrate-Based Paper Technologies
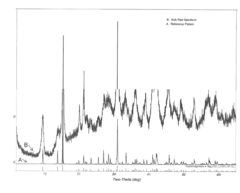
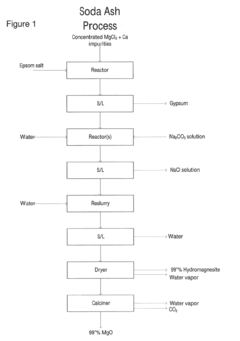
Process for producing high grade hydromagnesite and magnesium oxide
PatentActiveUS20170081205A1
Innovation
- A process involving a magnesium chloride brine solution with calcium chloride, where sodium carbonate is added to form a hydromagnesite precipitate, followed by calcination of the precipitate to produce high purity magnesium oxide, with controlled temperature and stirring conditions to achieve high quality products.
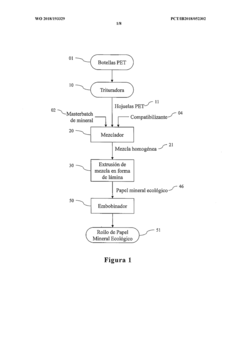
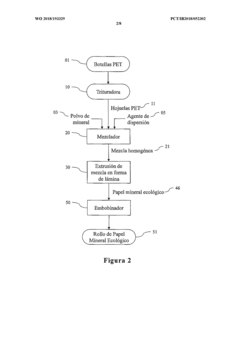
Ecological mineral paper made of recycled plastic and method for producing same
PatentWO2018193329A1
Innovation
- The development of eco-friendly synthetic mineral paper utilizing recycled plastics, specifically PET bottle waste, combined with naturally available minerals like calcium carbonate, talc, or mica, and a polymeric matrix, which provides enhanced properties such as moisture impermeability, tear resistance, and antimicrobial characteristics, through a process involving grinding, mixing, and extrusion techniques.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Magnesium Nitrate Use
The environmental impact assessment of magnesium nitrate use in eco-friendly paper production is a critical aspect of evaluating its effectiveness and sustainability. Magnesium nitrate, while offering potential benefits in paper manufacturing, requires careful consideration of its ecological footprint throughout its lifecycle.
In the production phase, the synthesis of magnesium nitrate involves the reaction of magnesium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide with nitric acid. This process consumes energy and resources, potentially contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. However, compared to traditional paper production methods, the use of magnesium nitrate may lead to reduced energy consumption during the papermaking process, partially offsetting its production-related environmental impact.
The application of magnesium nitrate in paper production can significantly reduce the amount of water required, as it enhances water retention in the paper fibers. This water-saving effect is particularly beneficial in regions facing water scarcity issues. Additionally, the improved water retention properties result in faster drying times, further reducing energy consumption in the drying phase of paper production.
One of the primary environmental advantages of using magnesium nitrate is its potential to reduce the use of harmful chemicals in paper production. Traditional methods often rely on chlorine-based bleaching agents, which can lead to the formation of toxic byproducts such as dioxins. Magnesium nitrate-based processes can help minimize or eliminate the need for these harmful chemicals, resulting in cleaner effluents and reduced environmental contamination.
However, the introduction of magnesium nitrate into the paper production process may lead to increased nitrogen content in wastewater. If not properly managed, this could contribute to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Implementing effective wastewater treatment systems is crucial to mitigate this potential negative impact.
The end-of-life considerations for paper products produced with magnesium nitrate are generally positive. These papers are typically more biodegradable than those produced with traditional methods, as they contain fewer synthetic additives. This characteristic can lead to reduced environmental impact in landfills and improved recyclability.
In terms of resource conservation, the use of magnesium nitrate can potentially increase the efficiency of raw material utilization in paper production. By improving fiber bonding and paper strength, it may allow for the use of lower-grade or recycled fibers without compromising product quality. This could lead to reduced pressure on virgin forest resources and promote a more circular economy in the paper industry.
While the environmental benefits of magnesium nitrate in paper production are significant, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand its net environmental impact. These assessments should consider factors such as raw material sourcing, energy consumption, water usage, emissions, and waste generation across the entire production and use cycle.
In the production phase, the synthesis of magnesium nitrate involves the reaction of magnesium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide with nitric acid. This process consumes energy and resources, potentially contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. However, compared to traditional paper production methods, the use of magnesium nitrate may lead to reduced energy consumption during the papermaking process, partially offsetting its production-related environmental impact.
The application of magnesium nitrate in paper production can significantly reduce the amount of water required, as it enhances water retention in the paper fibers. This water-saving effect is particularly beneficial in regions facing water scarcity issues. Additionally, the improved water retention properties result in faster drying times, further reducing energy consumption in the drying phase of paper production.
One of the primary environmental advantages of using magnesium nitrate is its potential to reduce the use of harmful chemicals in paper production. Traditional methods often rely on chlorine-based bleaching agents, which can lead to the formation of toxic byproducts such as dioxins. Magnesium nitrate-based processes can help minimize or eliminate the need for these harmful chemicals, resulting in cleaner effluents and reduced environmental contamination.
However, the introduction of magnesium nitrate into the paper production process may lead to increased nitrogen content in wastewater. If not properly managed, this could contribute to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Implementing effective wastewater treatment systems is crucial to mitigate this potential negative impact.
The end-of-life considerations for paper products produced with magnesium nitrate are generally positive. These papers are typically more biodegradable than those produced with traditional methods, as they contain fewer synthetic additives. This characteristic can lead to reduced environmental impact in landfills and improved recyclability.
In terms of resource conservation, the use of magnesium nitrate can potentially increase the efficiency of raw material utilization in paper production. By improving fiber bonding and paper strength, it may allow for the use of lower-grade or recycled fibers without compromising product quality. This could lead to reduced pressure on virgin forest resources and promote a more circular economy in the paper industry.
While the environmental benefits of magnesium nitrate in paper production are significant, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand its net environmental impact. These assessments should consider factors such as raw material sourcing, energy consumption, water usage, emissions, and waste generation across the entire production and use cycle.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Use in Paper Production
The regulatory framework for chemical use in paper production is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the adoption of eco-friendly practices, including the use of magnesium nitrate. At the global level, organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide guidelines and recommendations for sustainable industrial practices, which influence national policies.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemical use in paper production through various acts and programs. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requires manufacturers to report new chemical substances and provides the EPA with authority to regulate their use. The Clean Water Act and the Clean Air Act also impose strict regulations on effluents and emissions from paper mills, indirectly affecting the choice of chemicals used in production processes.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment from risks posed by chemicals. This regulation has far-reaching implications for the paper industry, as it requires manufacturers to register and assess the safety of chemicals used in their processes, including those like magnesium nitrate.
In Asia, countries such as China and Japan have been strengthening their chemical regulations. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both require rigorous safety assessments and reporting for new chemicals used in industrial processes, including paper production.
The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) provide certification schemes that include guidelines on chemical use in paper production. While these are voluntary standards, they have gained significant traction in the industry and often influence regulatory decisions.
Specific to magnesium nitrate, its use in paper production is subject to regulations governing fertilizers and industrial chemicals. In the EU, it falls under the Fertilising Products Regulation (EU) 2019/1009, which sets rules for making fertilizing products available on the EU market. In the US, it is regulated under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) when used for agricultural purposes.
As the paper industry moves towards more eco-friendly practices, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on promoting the use of less harmful chemicals. This trend is likely to favor the adoption of substances like magnesium nitrate, which have lower environmental impacts compared to traditional chemicals used in paper production. However, manufacturers must navigate a complex web of regulations to ensure compliance across different markets and jurisdictions.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemical use in paper production through various acts and programs. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requires manufacturers to report new chemical substances and provides the EPA with authority to regulate their use. The Clean Water Act and the Clean Air Act also impose strict regulations on effluents and emissions from paper mills, indirectly affecting the choice of chemicals used in production processes.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment from risks posed by chemicals. This regulation has far-reaching implications for the paper industry, as it requires manufacturers to register and assess the safety of chemicals used in their processes, including those like magnesium nitrate.
In Asia, countries such as China and Japan have been strengthening their chemical regulations. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both require rigorous safety assessments and reporting for new chemicals used in industrial processes, including paper production.
The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) provide certification schemes that include guidelines on chemical use in paper production. While these are voluntary standards, they have gained significant traction in the industry and often influence regulatory decisions.
Specific to magnesium nitrate, its use in paper production is subject to regulations governing fertilizers and industrial chemicals. In the EU, it falls under the Fertilising Products Regulation (EU) 2019/1009, which sets rules for making fertilizing products available on the EU market. In the US, it is regulated under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) when used for agricultural purposes.
As the paper industry moves towards more eco-friendly practices, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on promoting the use of less harmful chemicals. This trend is likely to favor the adoption of substances like magnesium nitrate, which have lower environmental impacts compared to traditional chemicals used in paper production. However, manufacturers must navigate a complex web of regulations to ensure compliance across different markets and jurisdictions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!