The Evolution of Dolby Vision in Home Video Productions
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dolby Vision Background and Objectives
Dolby Vision, a cutting-edge High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology, has revolutionized the home video production landscape since its introduction in 2014. This advanced imaging format, developed by Dolby Laboratories, aims to deliver an unparalleled viewing experience by significantly enhancing picture quality, color depth, and contrast ratio.
The primary objective of Dolby Vision is to faithfully reproduce the filmmaker's creative intent, ensuring that viewers at home can experience content as close to the original vision as possible. This technology addresses the limitations of traditional video formats by expanding the color gamut, increasing brightness levels, and preserving detail in both the darkest and brightest areas of the image.
Dolby Vision's evolution in home video productions can be traced back to the growing demand for more immersive and lifelike visual experiences. As display technologies advanced, consumers began to expect higher quality content that could fully utilize the capabilities of their new devices. This market pressure drove the development of HDR technologies, with Dolby Vision emerging as a leading solution.
The technology's background is rooted in Dolby's extensive experience in audio and video processing. Building upon their success in surround sound and noise reduction, Dolby leveraged their expertise to tackle the challenges of video reproduction. By collaborating with filmmakers, content creators, and device manufacturers, Dolby aimed to create a comprehensive ecosystem that could support this advanced HDR format from production to playback.
One of the key objectives of Dolby Vision was to establish a standardized approach to HDR content creation and delivery. This involved developing tools and workflows that would allow content creators to grade their material in Dolby Vision, ensuring consistency across different display devices and viewing environments. The technology also aimed to be backward compatible, allowing for graceful degradation on non-HDR displays while still providing an optimal experience on supported devices.
As the home entertainment landscape continued to evolve, Dolby Vision adapted to meet the changing needs of the industry. The technology expanded beyond traditional broadcast and physical media to encompass streaming platforms, mobile devices, and gaming consoles. This versatility has been crucial in maintaining Dolby Vision's relevance and driving its adoption across various content delivery channels.
Throughout its evolution, Dolby Vision has consistently pushed the boundaries of what is possible in home video production. By setting new standards for image quality and providing content creators with powerful tools to realize their artistic vision, Dolby Vision has played a significant role in shaping the future of home entertainment. Its ongoing development continues to focus on enhancing the viewer experience while addressing the technical challenges posed by emerging display technologies and content distribution methods.
The primary objective of Dolby Vision is to faithfully reproduce the filmmaker's creative intent, ensuring that viewers at home can experience content as close to the original vision as possible. This technology addresses the limitations of traditional video formats by expanding the color gamut, increasing brightness levels, and preserving detail in both the darkest and brightest areas of the image.
Dolby Vision's evolution in home video productions can be traced back to the growing demand for more immersive and lifelike visual experiences. As display technologies advanced, consumers began to expect higher quality content that could fully utilize the capabilities of their new devices. This market pressure drove the development of HDR technologies, with Dolby Vision emerging as a leading solution.
The technology's background is rooted in Dolby's extensive experience in audio and video processing. Building upon their success in surround sound and noise reduction, Dolby leveraged their expertise to tackle the challenges of video reproduction. By collaborating with filmmakers, content creators, and device manufacturers, Dolby aimed to create a comprehensive ecosystem that could support this advanced HDR format from production to playback.
One of the key objectives of Dolby Vision was to establish a standardized approach to HDR content creation and delivery. This involved developing tools and workflows that would allow content creators to grade their material in Dolby Vision, ensuring consistency across different display devices and viewing environments. The technology also aimed to be backward compatible, allowing for graceful degradation on non-HDR displays while still providing an optimal experience on supported devices.
As the home entertainment landscape continued to evolve, Dolby Vision adapted to meet the changing needs of the industry. The technology expanded beyond traditional broadcast and physical media to encompass streaming platforms, mobile devices, and gaming consoles. This versatility has been crucial in maintaining Dolby Vision's relevance and driving its adoption across various content delivery channels.
Throughout its evolution, Dolby Vision has consistently pushed the boundaries of what is possible in home video production. By setting new standards for image quality and providing content creators with powerful tools to realize their artistic vision, Dolby Vision has played a significant role in shaping the future of home entertainment. Its ongoing development continues to focus on enhancing the viewer experience while addressing the technical challenges posed by emerging display technologies and content distribution methods.
Market Analysis for HDR Content
The High Dynamic Range (HDR) content market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of HDR-capable displays and the growing demand for enhanced visual experiences. As Dolby Vision continues to evolve in home video productions, it has become a key player in shaping the HDR content landscape.
The global HDR content market size was valued at approximately $8.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $51.4 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 30.2% during the forecast period. This substantial growth is attributed to the rising consumer preference for high-quality video content and the proliferation of HDR-enabled devices.
Streaming platforms have emerged as major contributors to the HDR content market. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ have been at the forefront of offering HDR content, including Dolby Vision-enabled titles. These platforms have reported a significant increase in viewership for HDR content, with some estimating that HDR titles receive up to 30% more views compared to their standard dynamic range counterparts.
The film and television industry has also embraced HDR technology, with an increasing number of productions being shot and mastered in HDR formats. Major studios have reported that over 60% of their new releases are now available in HDR, with Dolby Vision being a preferred format due to its dynamic metadata capabilities and superior color grading options.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have played a crucial role in driving HDR content adoption. The availability of HDR-capable TVs has grown significantly, with market penetration reaching 35% in developed markets. This trend is expected to continue, with forecasts suggesting that over 70% of TVs sold by 2025 will support HDR technologies, including Dolby Vision.
The gaming industry has also recognized the potential of HDR content, with next-generation consoles and high-end gaming PCs supporting HDR rendering. Game developers are increasingly incorporating HDR into their titles, with some reporting up to a 25% increase in player engagement for HDR-enabled games.
However, challenges remain in the HDR content market. Content creation costs for HDR are higher compared to standard dynamic range, with estimates suggesting a 15-20% increase in production budgets. Additionally, the fragmentation of HDR standards and the need for specialized equipment pose barriers to widespread adoption, particularly for smaller content creators.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for HDR content remains positive. As technology advances and production costs decrease, the accessibility of HDR content creation is expected to improve. The continued evolution of Dolby Vision in home video productions is likely to drive further innovation in the HDR content market, potentially leading to new applications in virtual reality, augmented reality, and other emerging media formats.
The global HDR content market size was valued at approximately $8.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $51.4 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 30.2% during the forecast period. This substantial growth is attributed to the rising consumer preference for high-quality video content and the proliferation of HDR-enabled devices.
Streaming platforms have emerged as major contributors to the HDR content market. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ have been at the forefront of offering HDR content, including Dolby Vision-enabled titles. These platforms have reported a significant increase in viewership for HDR content, with some estimating that HDR titles receive up to 30% more views compared to their standard dynamic range counterparts.
The film and television industry has also embraced HDR technology, with an increasing number of productions being shot and mastered in HDR formats. Major studios have reported that over 60% of their new releases are now available in HDR, with Dolby Vision being a preferred format due to its dynamic metadata capabilities and superior color grading options.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have played a crucial role in driving HDR content adoption. The availability of HDR-capable TVs has grown significantly, with market penetration reaching 35% in developed markets. This trend is expected to continue, with forecasts suggesting that over 70% of TVs sold by 2025 will support HDR technologies, including Dolby Vision.
The gaming industry has also recognized the potential of HDR content, with next-generation consoles and high-end gaming PCs supporting HDR rendering. Game developers are increasingly incorporating HDR into their titles, with some reporting up to a 25% increase in player engagement for HDR-enabled games.
However, challenges remain in the HDR content market. Content creation costs for HDR are higher compared to standard dynamic range, with estimates suggesting a 15-20% increase in production budgets. Additionally, the fragmentation of HDR standards and the need for specialized equipment pose barriers to widespread adoption, particularly for smaller content creators.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for HDR content remains positive. As technology advances and production costs decrease, the accessibility of HDR content creation is expected to improve. The continued evolution of Dolby Vision in home video productions is likely to drive further innovation in the HDR content market, potentially leading to new applications in virtual reality, augmented reality, and other emerging media formats.
Dolby Vision Technical Challenges
Dolby Vision, while revolutionary in its approach to enhancing video quality, faces several technical challenges in its implementation for home video productions. One of the primary hurdles is the complexity of the HDR metadata required for Dolby Vision. This metadata, which includes frame-by-frame instructions for optimizing brightness, color, and contrast, demands significant processing power and storage capacity. As a result, encoding and decoding Dolby Vision content can be computationally intensive, potentially leading to increased production costs and longer processing times.
Another challenge lies in the backward compatibility of Dolby Vision with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays. While Dolby Vision is designed to be backwards compatible, ensuring that the content looks optimal on both HDR and SDR screens can be a delicate balancing act. This often requires careful color grading and mastering to maintain the creator's artistic intent across different display technologies.
The adoption of Dolby Vision in home video productions also faces obstacles related to content delivery. The increased data requirements for Dolby Vision streams can strain bandwidth limitations, particularly in regions with less developed internet infrastructure. This challenge extends to physical media as well, where the additional data needed for Dolby Vision may impact storage capacity on Blu-ray discs or other formats.
Furthermore, the implementation of Dolby Vision in consumer devices presents its own set of challenges. Display manufacturers must integrate specific hardware and software capabilities to fully support Dolby Vision, which can increase the cost of televisions and other playback devices. This cost factor can slow down widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
Interoperability between different HDR formats also poses a significant challenge. With competing standards like HDR10+ in the market, content creators and device manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of formats and ensure compatibility across various platforms. This fragmentation in the HDR ecosystem can lead to confusion for consumers and additional complexity in the production pipeline.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of Dolby Vision technology itself presents ongoing challenges. As the standard evolves to incorporate new features and improvements, maintaining consistency across different versions of Dolby Vision-enabled content and devices becomes increasingly complex. This continuous evolution requires regular updates to both content and hardware, potentially creating compatibility issues and necessitating ongoing investment from all stakeholders in the Dolby Vision ecosystem.
Another challenge lies in the backward compatibility of Dolby Vision with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays. While Dolby Vision is designed to be backwards compatible, ensuring that the content looks optimal on both HDR and SDR screens can be a delicate balancing act. This often requires careful color grading and mastering to maintain the creator's artistic intent across different display technologies.
The adoption of Dolby Vision in home video productions also faces obstacles related to content delivery. The increased data requirements for Dolby Vision streams can strain bandwidth limitations, particularly in regions with less developed internet infrastructure. This challenge extends to physical media as well, where the additional data needed for Dolby Vision may impact storage capacity on Blu-ray discs or other formats.
Furthermore, the implementation of Dolby Vision in consumer devices presents its own set of challenges. Display manufacturers must integrate specific hardware and software capabilities to fully support Dolby Vision, which can increase the cost of televisions and other playback devices. This cost factor can slow down widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
Interoperability between different HDR formats also poses a significant challenge. With competing standards like HDR10+ in the market, content creators and device manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of formats and ensure compatibility across various platforms. This fragmentation in the HDR ecosystem can lead to confusion for consumers and additional complexity in the production pipeline.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of Dolby Vision technology itself presents ongoing challenges. As the standard evolves to incorporate new features and improvements, maintaining consistency across different versions of Dolby Vision-enabled content and devices becomes increasingly complex. This continuous evolution requires regular updates to both content and hardware, potentially creating compatibility issues and necessitating ongoing investment from all stakeholders in the Dolby Vision ecosystem.
Current Dolby Vision Implementation
01 High Dynamic Range (HDR) Technology
Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance image quality by expanding the range of both contrast and color. This results in brighter highlights, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut, providing a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience.- High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology: Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance image quality by expanding the range of both contrast and color. This results in brighter highlights, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut, providing a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience.
- Dynamic metadata optimization: Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata to optimize the image on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This allows for precise control over brightness, contrast, and color, ensuring that each scene is displayed at its best quality.
- Color mapping and gamut expansion: The technology incorporates advanced color mapping and gamut expansion techniques to reproduce a wider range of colors more accurately. This results in more vibrant and true-to-life images, with smoother color gradients and reduced banding artifacts.
- Display-specific calibration: Dolby Vision includes display-specific calibration capabilities, allowing the content to be optimized for the specific characteristics of each display device. This ensures that the image quality is maintained across different screens and viewing environments.
- Content creation and mastering tools: The technology provides content creators with advanced tools for mastering and grading content in Dolby Vision. These tools enable precise control over the image quality during the production process, ensuring that the creator's intent is preserved and accurately reproduced on compatible displays.
02 Dynamic Metadata Processing
Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata processing to optimize image quality on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This allows for precise control over brightness, contrast, and color, ensuring that each image is displayed at its best possible quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Color Mapping and Gamut Expansion
The technology incorporates advanced color mapping and gamut expansion techniques to reproduce a wider range of colors more accurately. This results in more vibrant and true-to-life images, with smoother color gradients and reduced banding artifacts.Expand Specific Solutions04 Display-Specific Optimization
Dolby Vision adapts its output to the specific capabilities of each display device, ensuring optimal image quality across a wide range of screens. This includes adjusting for factors such as peak brightness, black levels, and color gamut to maximize the visual experience on any compatible display.Expand Specific Solutions05 Content Creation and Mastering Tools
The technology provides content creators with advanced tools for mastering and grading content in Dolby Vision. These tools enable precise control over the final image quality, allowing creators to ensure their artistic vision is accurately represented across different display technologies and viewing environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HDR Technology
The evolution of Dolby Vision in home video productions is characterized by a competitive landscape in a rapidly maturing market. As the technology advances from early adoption to mainstream implementation, key players like Dolby Laboratories, Sony, and Microsoft are driving innovation. The market size is expanding significantly, with increasing consumer demand for high-quality home entertainment experiences. Technologically, Dolby Vision is reaching a high level of maturity, with companies like Koninklijke Philips, Toshiba, and Sharp contributing to its development and integration across various devices and platforms. This progression is reshaping the home video industry, pushing boundaries in visual quality and content delivery.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Laboratories has been at the forefront of Dolby Vision technology evolution for home video productions. Their approach involves dynamic metadata that optimizes each frame or scene for the specific display capabilities[1]. This allows for enhanced contrast, brighter highlights, and a wider color gamut. Dolby Vision IQ, their latest innovation, uses ambient light sensors to automatically adjust HDR performance based on the viewing environment[2]. They've also developed Dolby Vision for Gaming, which brings the technology to interactive media, offering real-time HDR optimization for game consoles and PCs[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading HDR technology, wide adoption in consumer electronics, continuous innovation. Weaknesses: Licensing costs for manufacturers, requires compatible hardware and content.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has been a key player in the evolution of HDR technologies, including Dolby Vision. They've developed their own HDR10+ format, which competes with Dolby Vision but shares similar principles of dynamic metadata[4]. For Dolby Vision compatibility, Philips has integrated the technology into their high-end OLED and LCD TVs, offering consumers access to this premium HDR format[5]. Their approach focuses on enhancing picture quality through advanced local dimming techniques and high peak brightness capabilities, which complement Dolby Vision content[6].
Strengths: Strong presence in consumer electronics, development of competing HDR technologies. Weaknesses: Divided focus between multiple HDR formats may dilute efforts.
Core Dolby Vision Innovations
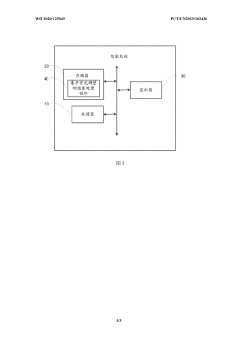
Image processing method employing backlight adjustment, smart television, and storage medium
PatentWO2020125049A1
Innovation
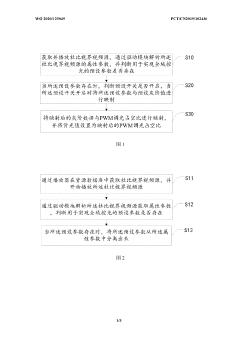
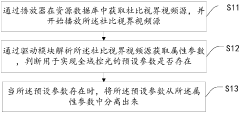
- By analyzing the attribute parameters of the Dolby Vision video source, it is determined whether the preset parameters exist, and the backlight value is adjusted according to the preset switch and grayscale value mapping to achieve smooth transition of backlight changes and dynamically adjust the backlight effect.
Image processing method based on backlight adjustment, smart television and storage medium
PatentActiveCN109640155A
Innovation
- By analyzing the attribute parameters of the Dolby Vision video source, it is determined whether the preset parameters exist, and mapped according to the preset switch and grayscale value, and the PWM dimming duty cycle is adjusted to set the backlight value to achieve smooth transition changes in the backlight.
Content Creation Workflow
The content creation workflow for Dolby Vision in home video productions has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to the changing landscape of digital cinematography and post-production techniques. Initially, the process was complex and required specialized equipment, limiting its adoption to high-end productions. However, as technology advanced, the workflow became more streamlined and accessible to a broader range of content creators.
In the early stages of Dolby Vision implementation, the workflow typically began with capturing footage using high dynamic range (HDR) cameras capable of recording a wide color gamut. This raw footage would then undergo a meticulous color grading process using specialized software and hardware that could interpret and manipulate the expanded color and brightness information.
As the technology matured, Dolby introduced more user-friendly tools and plugins for popular post-production software suites. This integration allowed colorists and editors to work with Dolby Vision content within familiar environments, significantly reducing the learning curve and increasing efficiency. The introduction of these tools also enabled smaller production houses and independent creators to incorporate Dolby Vision into their workflows.
One of the key advancements in the content creation workflow was the development of simultaneous HDR and SDR grading capabilities. This innovation allowed creators to produce both Dolby Vision and standard dynamic range versions of their content in a single pass, saving time and ensuring consistency across different display technologies.
The evolution of metadata management has been another crucial aspect of the Dolby Vision workflow. Initially, metadata creation was a manual and time-consuming process. However, automated tools for generating and embedding Dolby Vision metadata have streamlined this part of the workflow, ensuring that the final content can be accurately displayed on compatible devices.
Recent developments have focused on real-time Dolby Vision processing, enabling live broadcast and streaming applications. This has expanded the technology's use beyond traditional film and television production into live sports, events, and interactive content creation.
The democratization of Dolby Vision technology has also led to the emergence of consumer-grade tools and mobile applications that can capture and process Dolby Vision content. This expansion has blurred the lines between professional and prosumer content creation, opening up new possibilities for user-generated HDR content.
As the content creation workflow continues to evolve, there is an increasing emphasis on cloud-based solutions and remote collaboration tools. These advancements allow for more flexible and distributed production processes, enabling teams to work on Dolby Vision content from various locations while maintaining the high standards required for HDR delivery.
In the early stages of Dolby Vision implementation, the workflow typically began with capturing footage using high dynamic range (HDR) cameras capable of recording a wide color gamut. This raw footage would then undergo a meticulous color grading process using specialized software and hardware that could interpret and manipulate the expanded color and brightness information.
As the technology matured, Dolby introduced more user-friendly tools and plugins for popular post-production software suites. This integration allowed colorists and editors to work with Dolby Vision content within familiar environments, significantly reducing the learning curve and increasing efficiency. The introduction of these tools also enabled smaller production houses and independent creators to incorporate Dolby Vision into their workflows.
One of the key advancements in the content creation workflow was the development of simultaneous HDR and SDR grading capabilities. This innovation allowed creators to produce both Dolby Vision and standard dynamic range versions of their content in a single pass, saving time and ensuring consistency across different display technologies.
The evolution of metadata management has been another crucial aspect of the Dolby Vision workflow. Initially, metadata creation was a manual and time-consuming process. However, automated tools for generating and embedding Dolby Vision metadata have streamlined this part of the workflow, ensuring that the final content can be accurately displayed on compatible devices.
Recent developments have focused on real-time Dolby Vision processing, enabling live broadcast and streaming applications. This has expanded the technology's use beyond traditional film and television production into live sports, events, and interactive content creation.
The democratization of Dolby Vision technology has also led to the emergence of consumer-grade tools and mobile applications that can capture and process Dolby Vision content. This expansion has blurred the lines between professional and prosumer content creation, opening up new possibilities for user-generated HDR content.
As the content creation workflow continues to evolve, there is an increasing emphasis on cloud-based solutions and remote collaboration tools. These advancements allow for more flexible and distributed production processes, enabling teams to work on Dolby Vision content from various locations while maintaining the high standards required for HDR delivery.
Consumer Display Technology Trends
The consumer display technology landscape has undergone significant transformations in recent years, with Dolby Vision playing a pivotal role in shaping home video experiences. This high dynamic range (HDR) imaging technology has become increasingly prevalent in consumer-grade displays, driving advancements in picture quality and color accuracy.
One of the most notable trends is the widespread adoption of OLED and QLED technologies in high-end televisions and monitors. These display types offer superior contrast ratios and color reproduction, providing an ideal canvas for Dolby Vision content. The technology's ability to optimize brightness, contrast, and color on a scene-by-scene basis has become a key selling point for premium displays.
Another significant trend is the increasing affordability of 4K and 8K resolution displays. As manufacturing processes improve and economies of scale come into play, consumers can access higher resolution screens at more accessible price points. This trend has created a fertile ground for Dolby Vision to showcase its capabilities, as the technology can leverage the increased pixel density to deliver more nuanced and detailed images.
The rise of streaming services has also influenced consumer display technology trends. With major platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ offering Dolby Vision content, there's a growing demand for compatible displays in homes. This has led to a broader integration of Dolby Vision support across various price tiers of televisions and monitors.
Mobile devices have not been left behind in this evolution. High-end smartphones and tablets now frequently feature Dolby Vision-capable displays, extending the technology's reach beyond traditional living room setups. This trend reflects the increasing importance of mobile platforms for video consumption and gaming.
Gaming consoles and PCs have also embraced Dolby Vision, with the latest generation of hardware supporting the technology. This has led to a convergence of display technologies across different entertainment mediums, providing a more consistent visual experience for consumers across their devices.
As consumer awareness of display technologies grows, there's an increasing emphasis on calibration and accuracy. Dolby Vision's automated tone mapping and dynamic metadata have become valuable features for consumers seeking a "director's intent" viewing experience without the need for manual adjustments.
One of the most notable trends is the widespread adoption of OLED and QLED technologies in high-end televisions and monitors. These display types offer superior contrast ratios and color reproduction, providing an ideal canvas for Dolby Vision content. The technology's ability to optimize brightness, contrast, and color on a scene-by-scene basis has become a key selling point for premium displays.
Another significant trend is the increasing affordability of 4K and 8K resolution displays. As manufacturing processes improve and economies of scale come into play, consumers can access higher resolution screens at more accessible price points. This trend has created a fertile ground for Dolby Vision to showcase its capabilities, as the technology can leverage the increased pixel density to deliver more nuanced and detailed images.
The rise of streaming services has also influenced consumer display technology trends. With major platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ offering Dolby Vision content, there's a growing demand for compatible displays in homes. This has led to a broader integration of Dolby Vision support across various price tiers of televisions and monitors.
Mobile devices have not been left behind in this evolution. High-end smartphones and tablets now frequently feature Dolby Vision-capable displays, extending the technology's reach beyond traditional living room setups. This trend reflects the increasing importance of mobile platforms for video consumption and gaming.
Gaming consoles and PCs have also embraced Dolby Vision, with the latest generation of hardware supporting the technology. This has led to a convergence of display technologies across different entertainment mediums, providing a more consistent visual experience for consumers across their devices.
As consumer awareness of display technologies grows, there's an increasing emphasis on calibration and accuracy. Dolby Vision's automated tone mapping and dynamic metadata have become valuable features for consumers seeking a "director's intent" viewing experience without the need for manual adjustments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!