Analytical Methods For Natural Dye Identification And Batch Control
SEP 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Natural Dye Analysis Background and Objectives
Natural dyes have been utilized for coloring textiles, foods, and various materials for thousands of years, with evidence dating back to Neolithic periods. These dyes, derived from plants, insects, minerals, and fungi, represent one of humanity's earliest technological achievements. The transition from natural to synthetic dyes during the Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift in manufacturing processes, yet recent decades have witnessed a resurgence of interest in natural dyes due to growing environmental concerns and consumer demand for sustainable products.
The analytical study of natural dyes sits at the intersection of chemistry, archaeology, conservation science, and textile engineering. Traditional identification methods relied heavily on visual assessment and simple chemical tests, which often proved insufficient for precise characterization. Modern analytical approaches have evolved to address these limitations, incorporating sophisticated instrumental techniques that enable more accurate identification and quantification of natural colorants.
Current market trends indicate increasing demand for natural dyes across multiple industries, including textiles, cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals. This growth is primarily driven by consumer preference for eco-friendly products, stricter regulations on synthetic chemicals, and the unique aesthetic qualities that natural dyes provide. However, the widespread commercial adoption of natural dyes faces significant challenges related to standardization, quality control, and batch-to-batch consistency.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate existing analytical methods for natural dye identification and batch control, with particular emphasis on techniques that can be implemented in industrial settings. We aim to assess the capabilities, limitations, and practical applications of various analytical approaches, ranging from traditional wet chemistry to advanced spectroscopic and chromatographic methods.
Additionally, this research seeks to identify emerging technologies and methodological innovations that could enhance the precision, efficiency, and accessibility of natural dye analysis. By establishing robust analytical protocols, we intend to address the critical challenges of standardization and quality assurance that currently hinder the broader industrial adoption of natural colorants.
The ultimate goal is to develop a framework for reliable natural dye identification and batch control that balances analytical rigor with practical implementation considerations. Such a framework would support the sustainable growth of natural dye industries while ensuring consistent product quality that meets modern manufacturing standards and consumer expectations.
The analytical study of natural dyes sits at the intersection of chemistry, archaeology, conservation science, and textile engineering. Traditional identification methods relied heavily on visual assessment and simple chemical tests, which often proved insufficient for precise characterization. Modern analytical approaches have evolved to address these limitations, incorporating sophisticated instrumental techniques that enable more accurate identification and quantification of natural colorants.
Current market trends indicate increasing demand for natural dyes across multiple industries, including textiles, cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals. This growth is primarily driven by consumer preference for eco-friendly products, stricter regulations on synthetic chemicals, and the unique aesthetic qualities that natural dyes provide. However, the widespread commercial adoption of natural dyes faces significant challenges related to standardization, quality control, and batch-to-batch consistency.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate existing analytical methods for natural dye identification and batch control, with particular emphasis on techniques that can be implemented in industrial settings. We aim to assess the capabilities, limitations, and practical applications of various analytical approaches, ranging from traditional wet chemistry to advanced spectroscopic and chromatographic methods.
Additionally, this research seeks to identify emerging technologies and methodological innovations that could enhance the precision, efficiency, and accessibility of natural dye analysis. By establishing robust analytical protocols, we intend to address the critical challenges of standardization and quality assurance that currently hinder the broader industrial adoption of natural colorants.
The ultimate goal is to develop a framework for reliable natural dye identification and batch control that balances analytical rigor with practical implementation considerations. Such a framework would support the sustainable growth of natural dye industries while ensuring consistent product quality that meets modern manufacturing standards and consumer expectations.
Market Demand for Natural Dye Authentication
The global market for natural dye authentication has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. The textile industry, historically one of the largest consumers of dyes, has seen a paradigm shift towards natural alternatives due to environmental concerns associated with synthetic dyes. This transition has created a substantial market need for reliable authentication methods to verify the genuineness of natural dyes.
Consumer preferences have evolved dramatically, with a growing segment willing to pay premium prices for products colored with authenticated natural dyes. Market research indicates that the natural dye market is expanding at approximately twice the rate of the overall dye industry, reflecting this shift in consumer values. Particularly in high-end fashion, home textiles, and organic product lines, the demand for verified natural dye usage has become a significant market differentiator.
Regulatory frameworks across multiple regions have also contributed to market demand for authentication methods. The European Union's REACH regulations, Japan's stringent chemical substance control laws, and increasing restrictions in North America have all created compliance requirements that favor natural dyes. These regulatory pressures have transformed authentication from a marketing advantage to a compliance necessity in many markets.
The food and cosmetic industries represent rapidly growing segments for natural dye authentication. With clean label movements gaining momentum globally, manufacturers are replacing synthetic colorants with natural alternatives, creating urgent need for reliable identification and quality control methods. This cross-industry demand has expanded the market for analytical authentication technologies beyond traditional textile applications.
Supply chain transparency has emerged as another critical market driver. Brands facing increasing scrutiny from consumers and watchdog organizations are implementing traceability measures throughout their production processes. Authentication of natural dyes forms a key component of these transparency initiatives, allowing companies to substantiate sustainability claims and avoid accusations of greenwashing.
The premium segment of the market shows particular interest in authentication technologies that can identify specific botanical sources and traditional production methods. This capability allows luxury brands to verify and market the cultural heritage aspects of their products, connecting consumers with traditional craftsmanship and regional production techniques.
Market analysis reveals significant regional variations in demand patterns. While European markets prioritize ecological sustainability aspects of natural dyes, Asian markets often emphasize traditional cultural connections and health benefits. North American markets show growing interest in both aspects, with particular emphasis on supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing verification.
Consumer preferences have evolved dramatically, with a growing segment willing to pay premium prices for products colored with authenticated natural dyes. Market research indicates that the natural dye market is expanding at approximately twice the rate of the overall dye industry, reflecting this shift in consumer values. Particularly in high-end fashion, home textiles, and organic product lines, the demand for verified natural dye usage has become a significant market differentiator.
Regulatory frameworks across multiple regions have also contributed to market demand for authentication methods. The European Union's REACH regulations, Japan's stringent chemical substance control laws, and increasing restrictions in North America have all created compliance requirements that favor natural dyes. These regulatory pressures have transformed authentication from a marketing advantage to a compliance necessity in many markets.
The food and cosmetic industries represent rapidly growing segments for natural dye authentication. With clean label movements gaining momentum globally, manufacturers are replacing synthetic colorants with natural alternatives, creating urgent need for reliable identification and quality control methods. This cross-industry demand has expanded the market for analytical authentication technologies beyond traditional textile applications.
Supply chain transparency has emerged as another critical market driver. Brands facing increasing scrutiny from consumers and watchdog organizations are implementing traceability measures throughout their production processes. Authentication of natural dyes forms a key component of these transparency initiatives, allowing companies to substantiate sustainability claims and avoid accusations of greenwashing.
The premium segment of the market shows particular interest in authentication technologies that can identify specific botanical sources and traditional production methods. This capability allows luxury brands to verify and market the cultural heritage aspects of their products, connecting consumers with traditional craftsmanship and regional production techniques.
Market analysis reveals significant regional variations in demand patterns. While European markets prioritize ecological sustainability aspects of natural dyes, Asian markets often emphasize traditional cultural connections and health benefits. North American markets show growing interest in both aspects, with particular emphasis on supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing verification.
Current Analytical Challenges in Natural Dye Identification
Despite significant advancements in analytical techniques, the identification and quality control of natural dyes continue to present substantial challenges for researchers and industry professionals. The complex chemical composition of natural dyes, which often contain multiple chromophores and auxiliary compounds, makes precise identification particularly difficult. Unlike synthetic dyes with well-defined chemical structures, natural dyes exhibit considerable batch-to-batch variation due to factors such as geographical origin, harvesting season, extraction methods, and storage conditions.
Traditional analytical methods such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and UV-visible spectroscopy provide limited information and often fail to distinguish between closely related dye compounds or detect minor components that may significantly impact color properties. These techniques lack the sensitivity and specificity required for comprehensive characterization of natural dye profiles.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has emerged as a more powerful tool, but still faces limitations when analyzing complex natural dye mixtures. Peak overlap, matrix effects, and the lack of comprehensive reference standards for natural dye compounds hamper accurate identification. Additionally, the diverse polarities of compounds within natural dyes often necessitate multiple separation conditions, complicating analysis protocols.
Mass spectrometry techniques offer enhanced sensitivity but encounter challenges with ionization efficiency variations among different dye components. Structural isomers, which are common in natural dye compounds, may produce identical mass spectra, leading to ambiguous identifications. Furthermore, the fragmentation patterns of natural dye molecules can be complex and difficult to interpret without extensive reference databases.
Non-destructive techniques such as reflectance spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging show promise for in-situ analysis but suffer from limited specificity when distinguishing between similar dyes or identifying minor components. These methods are also highly sensitive to substrate effects, making standardization across different materials challenging.
The development of reliable reference materials represents another significant challenge. The natural variability of dye sources means that creating standardized references that account for all possible variations is extremely difficult. This lack of comprehensive standards hampers method validation and quality control procedures.
Data interpretation presents further complications, as the complex spectral or chromatographic profiles generated by natural dyes require sophisticated chemometric approaches. Current algorithms may struggle to account for the inherent variability of natural products, leading to inconsistent results across different analytical platforms or laboratories.
Traditional analytical methods such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and UV-visible spectroscopy provide limited information and often fail to distinguish between closely related dye compounds or detect minor components that may significantly impact color properties. These techniques lack the sensitivity and specificity required for comprehensive characterization of natural dye profiles.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has emerged as a more powerful tool, but still faces limitations when analyzing complex natural dye mixtures. Peak overlap, matrix effects, and the lack of comprehensive reference standards for natural dye compounds hamper accurate identification. Additionally, the diverse polarities of compounds within natural dyes often necessitate multiple separation conditions, complicating analysis protocols.
Mass spectrometry techniques offer enhanced sensitivity but encounter challenges with ionization efficiency variations among different dye components. Structural isomers, which are common in natural dye compounds, may produce identical mass spectra, leading to ambiguous identifications. Furthermore, the fragmentation patterns of natural dye molecules can be complex and difficult to interpret without extensive reference databases.
Non-destructive techniques such as reflectance spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging show promise for in-situ analysis but suffer from limited specificity when distinguishing between similar dyes or identifying minor components. These methods are also highly sensitive to substrate effects, making standardization across different materials challenging.
The development of reliable reference materials represents another significant challenge. The natural variability of dye sources means that creating standardized references that account for all possible variations is extremely difficult. This lack of comprehensive standards hampers method validation and quality control procedures.
Data interpretation presents further complications, as the complex spectral or chromatographic profiles generated by natural dyes require sophisticated chemometric approaches. Current algorithms may struggle to account for the inherent variability of natural products, leading to inconsistent results across different analytical platforms or laboratories.
Established Methods for Natural Dye Characterization
01 Analytical methods for batch quality control
Various analytical methods are employed for batch quality control in manufacturing processes. These methods involve the use of specialized equipment and techniques to monitor and ensure the consistency and quality of products across different batches. The analytical approaches include spectroscopic analysis, chromatography, and other testing methodologies that can identify variations in batch composition, helping manufacturers maintain product standards and regulatory compliance.- Analytical methods for batch quality control: Various analytical methods are employed to ensure batch quality control in manufacturing processes. These methods involve the use of specialized equipment and techniques to identify and measure critical parameters that affect product quality. By implementing robust analytical methods, manufacturers can maintain consistency across batches, detect deviations early, and ensure compliance with quality standards. These approaches often integrate automated testing systems that can rapidly analyze samples and provide real-time data for process control decisions.
- Data management systems for batch control: Advanced data management systems are essential for effective batch control in manufacturing environments. These systems collect, store, and analyze data from various production stages to ensure batch consistency and traceability. They enable real-time monitoring of process parameters, facilitate quick identification of deviations, and support decision-making through data visualization tools. By implementing comprehensive data management solutions, manufacturers can improve batch-to-batch consistency, reduce variability, and maintain detailed records for regulatory compliance.
- Automated identification and testing systems: Automated identification and testing systems play a crucial role in modern batch control processes. These systems utilize advanced technologies such as machine vision, barcode scanning, and RFID to accurately identify materials and products throughout the manufacturing process. Integrated testing equipment performs automated analyses at critical control points, reducing human error and increasing throughput. By implementing these automated systems, manufacturers can achieve higher accuracy in batch identification, improve testing consistency, and enhance overall quality control efficiency.
- Statistical methods for batch analysis: Statistical methods are fundamental to effective batch analysis and control in manufacturing processes. These approaches include statistical process control (SPC), design of experiments (DOE), and multivariate analysis techniques that help identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in batch data. By applying statistical methods, manufacturers can establish control limits, detect process shifts early, and make data-driven decisions to optimize batch quality. These techniques also support root cause analysis when deviations occur, enabling continuous improvement of manufacturing processes.
- Integration of analytical methods with manufacturing execution systems: The integration of analytical methods with manufacturing execution systems (MES) creates a comprehensive approach to batch control. This integration enables seamless data flow between laboratory information management systems (LIMS), quality control processes, and production systems. Real-time analytical results can trigger automated adjustments to process parameters, ensuring batch quality is maintained throughout production. By connecting analytical methods directly with manufacturing systems, companies can achieve greater process control, reduce time to release batches, and improve overall manufacturing efficiency.
02 Automated systems for batch monitoring and control
Automated systems have been developed to enhance batch monitoring and control processes. These systems utilize sensors, data acquisition tools, and control algorithms to continuously monitor production parameters and make real-time adjustments. By automating the identification and control of critical process variables, manufacturers can achieve greater consistency between batches, reduce human error, and improve overall production efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Data management solutions for analytical testing
Specialized data management solutions have been created to handle the large volumes of data generated during analytical testing of product batches. These solutions include database systems, data processing algorithms, and visualization tools that help in organizing, analyzing, and interpreting test results. Effective data management enables better tracking of batch-to-batch variations, facilitates regulatory compliance documentation, and supports quality decision-making processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced identification techniques for batch analysis
Advanced identification techniques have been developed for more precise batch analysis. These include molecular fingerprinting, spectral analysis, and machine learning-based pattern recognition systems that can detect subtle differences between batches. By employing these sophisticated identification methods, manufacturers can better understand product characteristics, identify potential quality issues earlier, and ensure consistency across production runs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of analytical methods with manufacturing processes
Integration approaches connect analytical testing directly with manufacturing processes to create more responsive production systems. These integrated solutions enable real-time analysis and feedback during production, allowing for immediate process adjustments based on analytical results. By closing the loop between testing and manufacturing, companies can implement continuous improvement strategies, reduce waste, and optimize production parameters for consistent batch quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Natural Dye Analytics
The natural dye identification market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable textile solutions. The analytical methods sector is expanding as industries seek reliable authentication and quality control for natural dyes. Academic institutions dominate research, with Donghua University, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, and Jiangnan University leading technological innovation in China, while the University of Groningen provides European expertise. Commercial players like DyStar Colours and Bio-Rad Laboratories contribute analytical instrumentation and standardization methods. The technology is maturing with advanced chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques, but challenges remain in standardization across diverse natural sources. Integration of traditional knowledge with modern analytical approaches is creating new opportunities for batch control systems that ensure consistency in natural dye production.
University of Groningen
Technical Solution: The University of Groningen has developed advanced analytical methods for natural dye identification focusing on high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) combined with liquid chromatography (LC) and innovative sample preparation techniques. Their approach employs a multi-analytical strategy that includes soft ionization techniques such as electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) to preserve molecular information during analysis. The university's research team has pioneered the use of principal component analysis (PCA) and other chemometric tools to differentiate between closely related dye sources based on minor component distributions and degradation markers. Their methodology includes specialized extraction protocols using mild hydrolysis conditions that preserve glycosidic bonds in dye molecules, allowing for more accurate source identification. For batch control applications, they've developed a statistical quality control framework that establishes acceptance parameters based on natural variation in botanical sources while identifying outliers that indicate process deviations. Their analytical approach can detect adulterations at levels as low as 2% in mixed dye preparations.
Strengths: Cutting-edge mass spectrometry techniques; sophisticated chemometric data analysis; preservation of molecular structural information; detection of subtle differences between similar dye sources. Weaknesses: Requires expensive analytical instrumentation; complex data interpretation requiring specialized expertise; methods may be challenging to implement in industrial settings without significant adaptation.
China National Silk Museum
Technical Solution: The China National Silk Museum has developed specialized analytical methods for identifying natural dyes in historical textiles and archaeological specimens. Their approach integrates non-destructive and micro-destructive techniques including fiber optic reflectance spectroscopy (FORS), Raman spectroscopy, and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and mass spectrometry (UHPLC-DAD-MS). The museum's methodology is particularly notable for its minimal sample requirements, often requiring less than 0.1mg of material, making it suitable for precious historical artifacts. Their analytical protocol includes a systematic workflow that begins with non-destructive imaging and spectroscopic screening, followed by targeted micro-sampling only when necessary. For batch control in conservation treatments and reproductions, they've established a reference collection of over 200 historically accurate natural dyes prepared using traditional methods documented in ancient Chinese texts. This collection serves as analytical standards for authentication and reproduction work. The museum has also developed specialized extraction protocols optimized for aged and degraded dyes in archaeological textiles.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in historical and archaeological specimens; minimal sample requirements; integration of non-destructive and micro-destructive techniques; extensive reference collection of historically prepared dyes. Weaknesses: Methods optimized for historical samples may be less applicable to modern industrial quality control; specialized equipment requirements; time-intensive analytical procedures not suited for high-throughput applications.
Critical Technologies in Dye Fingerprinting
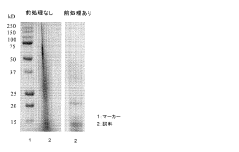
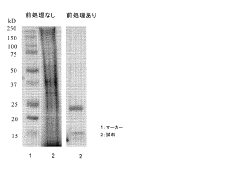
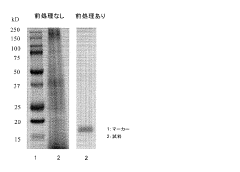
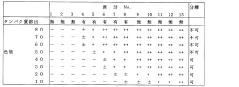
Method of analyzing protein in natural acid dye
PatentActiveJP2015014589A
Innovation
- A method involving gel filtration and ultrafiltration pretreatments using crosslinked polysaccharides and agarose derivatives with specific pH and salt concentrations, followed by protein analysis using methods like Bradford and SDS-Page, to separate dye components and enable precise protein analysis.
Method for determining synthetic dyes and natural carmine dye
PatentPendingRU2022118566A
Innovation
- Development of a comprehensive analytical method that simultaneously determines both synthetic dyes and natural carmine dye in a single process.
- Utilization of chromatographic comparison between analyzed components and standard coloring additives for accurate dye identification.
- Quantitative determination of natural carmine dye content within mixed coloring agents through peak release time analysis.
Sustainability Impact of Natural Dye Authentication
The adoption of reliable analytical methods for natural dye identification and batch control significantly enhances sustainability across multiple dimensions. By accurately authenticating natural dyes, industries can ensure genuine eco-friendly materials are being utilized, directly reducing the environmental footprint compared to synthetic alternatives. Natural dyes typically require less energy during production, generate fewer toxic byproducts, and are biodegradable, making their proper identification crucial for true environmental benefits.
Authentication systems enable transparent supply chains, allowing consumers and manufacturers to verify the ecological credentials of their products. This transparency creates market incentives for sustainable practices and discourages greenwashing, where products falsely claim environmental benefits. When consumers can trust natural dye claims through scientific verification, they are more willing to pay premium prices for genuinely sustainable products.
From a resource management perspective, accurate identification methods help preserve traditional knowledge and protect biodiversity. Many natural dyes derive from plants with cultural significance to indigenous communities. Authentication systems can help ensure fair compensation for these communities when their traditional knowledge is commercialized, supporting social sustainability alongside environmental benefits.
The economic dimension of sustainability also benefits from reliable authentication. By establishing consistent quality control measures, manufacturers can develop standardized natural dye products that meet industrial requirements. This standardization helps overcome one of the major barriers to widespread natural dye adoption—batch-to-batch variation—making sustainable alternatives more viable for commercial applications.
Water conservation represents another significant sustainability impact. Synthetic dye production and application typically consume vast quantities of water and generate contaminated effluent. Authenticated natural dyes often require less water throughout their lifecycle and produce less harmful wastewater, reducing pressure on freshwater resources in manufacturing regions.
Carbon footprint reduction is achievable through proper natural dye authentication. When verification systems confirm locally-sourced natural dyes, they enable shorter supply chains with reduced transportation emissions. Additionally, many natural dye plants sequester carbon during growth, potentially offering carbon offset benefits when cultivation is expanded to meet industrial demand.
Looking forward, the development of more sophisticated, accessible authentication technologies could accelerate the transition from synthetic to natural dyes across multiple industries, creating cascading sustainability benefits throughout global supply chains and consumer markets.
Authentication systems enable transparent supply chains, allowing consumers and manufacturers to verify the ecological credentials of their products. This transparency creates market incentives for sustainable practices and discourages greenwashing, where products falsely claim environmental benefits. When consumers can trust natural dye claims through scientific verification, they are more willing to pay premium prices for genuinely sustainable products.
From a resource management perspective, accurate identification methods help preserve traditional knowledge and protect biodiversity. Many natural dyes derive from plants with cultural significance to indigenous communities. Authentication systems can help ensure fair compensation for these communities when their traditional knowledge is commercialized, supporting social sustainability alongside environmental benefits.
The economic dimension of sustainability also benefits from reliable authentication. By establishing consistent quality control measures, manufacturers can develop standardized natural dye products that meet industrial requirements. This standardization helps overcome one of the major barriers to widespread natural dye adoption—batch-to-batch variation—making sustainable alternatives more viable for commercial applications.
Water conservation represents another significant sustainability impact. Synthetic dye production and application typically consume vast quantities of water and generate contaminated effluent. Authenticated natural dyes often require less water throughout their lifecycle and produce less harmful wastewater, reducing pressure on freshwater resources in manufacturing regions.
Carbon footprint reduction is achievable through proper natural dye authentication. When verification systems confirm locally-sourced natural dyes, they enable shorter supply chains with reduced transportation emissions. Additionally, many natural dye plants sequester carbon during growth, potentially offering carbon offset benefits when cultivation is expanded to meet industrial demand.
Looking forward, the development of more sophisticated, accessible authentication technologies could accelerate the transition from synthetic to natural dyes across multiple industries, creating cascading sustainability benefits throughout global supply chains and consumer markets.
Quality Control Standards and Certification Frameworks
The establishment of robust quality control standards and certification frameworks is essential for the natural dye industry to ensure consistency, authenticity, and safety. Currently, several international organizations have developed standards specifically for natural dye identification and batch control. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has implemented ISO 20128, which outlines the testing methods for determining the colorfastness of natural dyes. Similarly, the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC) has established Test Method 200, focusing on the identification and quantification of natural colorants in textiles.
These standards typically specify acceptable ranges for key parameters such as color consistency, pH levels, heavy metal content, and light fastness. For instance, the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) mandates that natural dyes must not contain more than 20 ppm of heavy metals and must achieve a minimum rating of 3-4 on the Blue Wool Scale for light fastness. These quantifiable metrics enable manufacturers to maintain consistent quality across production batches.
Certification frameworks have also emerged to validate compliance with these standards. The Natural Dye Certification Program (NDCP) provides a comprehensive assessment of natural dye products, evaluating both the analytical methods used for identification and the consistency of batch production. Similarly, the Ecological and Toxicological Association of Dyes and Organic Pigments Manufacturers (ETAD) offers certification specifically focused on the ecological and toxicological aspects of natural dyes.
Regional certification bodies have developed specialized frameworks tailored to local natural dye traditions. In India, the Crafts Council of India has established the Natural Dye Certification Scheme, which incorporates traditional knowledge while ensuring modern quality standards. Japan's Eco Mark certification includes specific provisions for natural dyes used in textiles, emphasizing both environmental sustainability and batch consistency.
The implementation of these standards and certifications requires sophisticated analytical methods. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) fingerprinting has become the gold standard for natural dye identification in certification processes. Spectrophotometric analysis is commonly used to verify color consistency between batches, with acceptable Delta E values typically set at ≤2.0 for premium certifications.
Future developments in quality control standards are likely to incorporate more advanced analytical techniques, such as hyperspectral imaging and portable spectroscopy devices, enabling real-time batch monitoring. Additionally, blockchain technology is being explored to create transparent certification systems that can track natural dyes from source to final product, enhancing traceability and authenticity verification throughout the supply chain.
These standards typically specify acceptable ranges for key parameters such as color consistency, pH levels, heavy metal content, and light fastness. For instance, the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) mandates that natural dyes must not contain more than 20 ppm of heavy metals and must achieve a minimum rating of 3-4 on the Blue Wool Scale for light fastness. These quantifiable metrics enable manufacturers to maintain consistent quality across production batches.
Certification frameworks have also emerged to validate compliance with these standards. The Natural Dye Certification Program (NDCP) provides a comprehensive assessment of natural dye products, evaluating both the analytical methods used for identification and the consistency of batch production. Similarly, the Ecological and Toxicological Association of Dyes and Organic Pigments Manufacturers (ETAD) offers certification specifically focused on the ecological and toxicological aspects of natural dyes.
Regional certification bodies have developed specialized frameworks tailored to local natural dye traditions. In India, the Crafts Council of India has established the Natural Dye Certification Scheme, which incorporates traditional knowledge while ensuring modern quality standards. Japan's Eco Mark certification includes specific provisions for natural dyes used in textiles, emphasizing both environmental sustainability and batch consistency.
The implementation of these standards and certifications requires sophisticated analytical methods. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) fingerprinting has become the gold standard for natural dye identification in certification processes. Spectrophotometric analysis is commonly used to verify color consistency between batches, with acceptable Delta E values typically set at ≤2.0 for premium certifications.
Future developments in quality control standards are likely to incorporate more advanced analytical techniques, such as hyperspectral imaging and portable spectroscopy devices, enabling real-time batch monitoring. Additionally, blockchain technology is being explored to create transparent certification systems that can track natural dyes from source to final product, enhancing traceability and authenticity verification throughout the supply chain.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!