Solvent-Free Stabilization Techniques For Plant-Based Dyes
SEP 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Plant-Based Dye Technology Background and Objectives
Plant-based dyes represent one of humanity's earliest technological innovations, dating back to prehistoric times when natural colorants were extracted from plants for textile decoration, art, and cultural expression. Throughout history, these dyes were traditionally stabilized using mordants like alum, iron, or copper salts, which helped bind colorants to fibers. However, the industrial revolution in the 19th century led to the development of synthetic dyes, which gradually displaced natural alternatives due to their consistency, color range, and stability advantages.
In recent decades, there has been a significant resurgence of interest in plant-based dyes driven by growing environmental concerns, consumer demand for sustainable products, and stricter regulations on synthetic chemical usage. This revival has highlighted a critical technological gap: conventional stabilization methods for plant-based dyes typically rely on chemical solvents that present environmental and health concerns, contradicting the inherent sustainability of the natural colorants themselves.
The technological evolution in this field has progressed from traditional water-based extraction with mordants to more sophisticated approaches involving various solvents. Current research is increasingly focused on developing solvent-free stabilization techniques that maintain or enhance color fastness while eliminating harmful chemical components. This represents a paradigm shift in natural dye technology, aligning with circular economy principles and sustainable manufacturing practices.
The primary objective of solvent-free stabilization technology for plant-based dyes is to develop environmentally benign methods that deliver commercial-grade performance in terms of color stability, fastness, and longevity. This includes exploring innovative approaches such as supercritical CO2 processing, plasma treatment, enzymatic processes, and advanced biomaterial encapsulation techniques that can effectively stabilize natural chromophores without conventional solvents.
Secondary objectives include standardizing extraction and application protocols to ensure consistency across production batches, developing scalable technologies suitable for industrial implementation, and creating comprehensive databases of plant sources and their corresponding colorant properties. These efforts aim to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern scientific understanding of natural dye chemistry.
The technological trajectory points toward integrated systems that combine sustainable sourcing of plant materials, zero-waste processing methods, and advanced stabilization techniques that eliminate the need for harmful solvents while delivering performance comparable to synthetic alternatives. Success in this domain could revolutionize multiple industries including textiles, cosmetics, food coloring, and sustainable packaging, while significantly reducing environmental impact across global supply chains.
In recent decades, there has been a significant resurgence of interest in plant-based dyes driven by growing environmental concerns, consumer demand for sustainable products, and stricter regulations on synthetic chemical usage. This revival has highlighted a critical technological gap: conventional stabilization methods for plant-based dyes typically rely on chemical solvents that present environmental and health concerns, contradicting the inherent sustainability of the natural colorants themselves.
The technological evolution in this field has progressed from traditional water-based extraction with mordants to more sophisticated approaches involving various solvents. Current research is increasingly focused on developing solvent-free stabilization techniques that maintain or enhance color fastness while eliminating harmful chemical components. This represents a paradigm shift in natural dye technology, aligning with circular economy principles and sustainable manufacturing practices.
The primary objective of solvent-free stabilization technology for plant-based dyes is to develop environmentally benign methods that deliver commercial-grade performance in terms of color stability, fastness, and longevity. This includes exploring innovative approaches such as supercritical CO2 processing, plasma treatment, enzymatic processes, and advanced biomaterial encapsulation techniques that can effectively stabilize natural chromophores without conventional solvents.
Secondary objectives include standardizing extraction and application protocols to ensure consistency across production batches, developing scalable technologies suitable for industrial implementation, and creating comprehensive databases of plant sources and their corresponding colorant properties. These efforts aim to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern scientific understanding of natural dye chemistry.
The technological trajectory points toward integrated systems that combine sustainable sourcing of plant materials, zero-waste processing methods, and advanced stabilization techniques that eliminate the need for harmful solvents while delivering performance comparable to synthetic alternatives. Success in this domain could revolutionize multiple industries including textiles, cosmetics, food coloring, and sustainable packaging, while significantly reducing environmental impact across global supply chains.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Colorants
The global market for sustainable colorants is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a shift towards eco-friendly products across industries. Plant-based dyes represent a rapidly expanding segment within this market, with an estimated market value of $3.5 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 8.2%. This growth trajectory is particularly notable in the textile, food and beverage, cosmetics, and packaging industries.
Consumer preferences are increasingly favoring natural products with transparent supply chains and minimal environmental impact. According to recent market surveys, 67% of global consumers consider sustainability as an important factor in their purchasing decisions, with this percentage rising to 73% among millennials and Gen Z demographics. This shift in consumer behavior has created substantial market opportunities for plant-based dyes that can offer performance comparable to synthetic alternatives.
The textile industry remains the largest application sector for plant-based dyes, accounting for approximately 45% of the market share. This is followed by food and beverage applications at 28%, cosmetics at 15%, and packaging at 8%. Regional analysis indicates that Europe leads the sustainable colorants market with a 35% share, followed by North America (28%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (12%). The Asia-Pacific region, however, is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing industrialization coupled with stricter environmental regulations.
Key market drivers include stringent environmental regulations limiting the use of synthetic dyes, growing consumer awareness about health hazards associated with synthetic colorants, and corporate sustainability initiatives. The EU's REACH regulations and similar frameworks in other regions have accelerated the transition towards natural alternatives. Additionally, major brands across industries are setting ambitious sustainability targets, further stimulating demand for plant-based colorants.
Market challenges primarily revolve around performance limitations of current plant-based dyes, including color consistency, stability, and fastness properties. The higher cost of production compared to synthetic alternatives remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Current price premiums for plant-based dyes range from 30-150% above synthetic counterparts, depending on the specific application and performance requirements.
Emerging market opportunities include the development of novel stabilization techniques that can enhance the performance of plant-based dyes without relying on chemical solvents. Innovations in this area could potentially unlock new market segments and applications where synthetic dyes currently dominate due to superior technical performance. The premium segment of various industries shows particular promise, with consumers willing to pay 15-25% more for products featuring natural, sustainable colorants.
Consumer preferences are increasingly favoring natural products with transparent supply chains and minimal environmental impact. According to recent market surveys, 67% of global consumers consider sustainability as an important factor in their purchasing decisions, with this percentage rising to 73% among millennials and Gen Z demographics. This shift in consumer behavior has created substantial market opportunities for plant-based dyes that can offer performance comparable to synthetic alternatives.
The textile industry remains the largest application sector for plant-based dyes, accounting for approximately 45% of the market share. This is followed by food and beverage applications at 28%, cosmetics at 15%, and packaging at 8%. Regional analysis indicates that Europe leads the sustainable colorants market with a 35% share, followed by North America (28%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (12%). The Asia-Pacific region, however, is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing industrialization coupled with stricter environmental regulations.
Key market drivers include stringent environmental regulations limiting the use of synthetic dyes, growing consumer awareness about health hazards associated with synthetic colorants, and corporate sustainability initiatives. The EU's REACH regulations and similar frameworks in other regions have accelerated the transition towards natural alternatives. Additionally, major brands across industries are setting ambitious sustainability targets, further stimulating demand for plant-based colorants.
Market challenges primarily revolve around performance limitations of current plant-based dyes, including color consistency, stability, and fastness properties. The higher cost of production compared to synthetic alternatives remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Current price premiums for plant-based dyes range from 30-150% above synthetic counterparts, depending on the specific application and performance requirements.
Emerging market opportunities include the development of novel stabilization techniques that can enhance the performance of plant-based dyes without relying on chemical solvents. Innovations in this area could potentially unlock new market segments and applications where synthetic dyes currently dominate due to superior technical performance. The premium segment of various industries shows particular promise, with consumers willing to pay 15-25% more for products featuring natural, sustainable colorants.
Current Challenges in Natural Dye Stabilization
Despite the growing interest in plant-based dyes as sustainable alternatives to synthetic colorants, their widespread adoption faces significant technical barriers. The primary challenge lies in the inherent instability of natural chromophores when exposed to environmental factors. Plant-based dyes typically demonstrate poor light fastness, with visible color degradation occurring after minimal UV exposure. This photodegradation results from the breakdown of conjugated systems within the chromophore structure, fundamentally altering their light absorption properties.
Thermal stability presents another major obstacle, as many plant-derived colorants undergo significant color shifts when subjected to processing temperatures common in industrial applications. This thermal sensitivity severely limits their integration into existing manufacturing processes that require heat treatment phases.
pH sensitivity further complicates the application of natural dyes, with many exhibiting dramatic color changes across the pH spectrum. This characteristic, while potentially useful for specialized applications like pH indicators, creates significant challenges for maintaining consistent coloration in products exposed to varying environmental conditions or cleaning agents.
Water solubility, while advantageous for application processes, becomes problematic for product longevity. Most plant-based chromophores readily dissolve in water, leading to color bleeding and fading during washing or exposure to humidity. This water sensitivity significantly restricts their use in textiles, packaging, and other applications where moisture resistance is essential.
Microbial degradation represents a less discussed but equally important challenge. The organic nature of plant-based colorants makes them susceptible to bacterial and fungal attack, potentially leading to discoloration and the production of undesirable byproducts during storage or use.
Current stabilization approaches predominantly rely on mordants and chemical fixatives, many of which introduce toxicity concerns that contradict the sustainability benefits of natural dyes. Traditional mordanting techniques using metal salts can introduce heavy metals into wastewater streams, while synthetic binding agents often contain formaldehyde or other harmful compounds.
The absence of standardized evaluation protocols for natural dye stability further complicates development efforts. Unlike synthetic colorants, which benefit from established testing methodologies, natural dye assessment remains inconsistent across research groups, making comparative analysis challenging and slowing technological advancement.
The development of solvent-free stabilization techniques is further hindered by the extreme diversity of plant-based chromophores, each with unique chemical structures and stability profiles. This heterogeneity necessitates customized approaches rather than universal solutions, significantly increasing research and development complexity.
Thermal stability presents another major obstacle, as many plant-derived colorants undergo significant color shifts when subjected to processing temperatures common in industrial applications. This thermal sensitivity severely limits their integration into existing manufacturing processes that require heat treatment phases.
pH sensitivity further complicates the application of natural dyes, with many exhibiting dramatic color changes across the pH spectrum. This characteristic, while potentially useful for specialized applications like pH indicators, creates significant challenges for maintaining consistent coloration in products exposed to varying environmental conditions or cleaning agents.
Water solubility, while advantageous for application processes, becomes problematic for product longevity. Most plant-based chromophores readily dissolve in water, leading to color bleeding and fading during washing or exposure to humidity. This water sensitivity significantly restricts their use in textiles, packaging, and other applications where moisture resistance is essential.
Microbial degradation represents a less discussed but equally important challenge. The organic nature of plant-based colorants makes them susceptible to bacterial and fungal attack, potentially leading to discoloration and the production of undesirable byproducts during storage or use.
Current stabilization approaches predominantly rely on mordants and chemical fixatives, many of which introduce toxicity concerns that contradict the sustainability benefits of natural dyes. Traditional mordanting techniques using metal salts can introduce heavy metals into wastewater streams, while synthetic binding agents often contain formaldehyde or other harmful compounds.
The absence of standardized evaluation protocols for natural dye stability further complicates development efforts. Unlike synthetic colorants, which benefit from established testing methodologies, natural dye assessment remains inconsistent across research groups, making comparative analysis challenging and slowing technological advancement.
The development of solvent-free stabilization techniques is further hindered by the extreme diversity of plant-based chromophores, each with unique chemical structures and stability profiles. This heterogeneity necessitates customized approaches rather than universal solutions, significantly increasing research and development complexity.
Existing Solvent-Free Stabilization Approaches
01 Chemical stabilization methods for plant-based dyes
Various chemical treatments can be applied to plant-based dyes to enhance their stability. These include the use of mordants, pH adjusters, and chemical fixatives that form bonds with the dye molecules to prevent degradation. Metal salts such as aluminum, iron, and copper compounds are commonly used as mordants to create stable complexes with natural dyes. Additionally, certain polymers and resins can encapsulate dye molecules, protecting them from environmental factors that cause fading.- Chemical stabilization methods for plant-based dyes: Various chemical treatments can be applied to plant-based dyes to enhance their stability. These include the use of mordants, pH adjusters, and chemical fixatives that form bonds with the dye molecules to prevent degradation. Metal salts such as aluminum, iron, and copper compounds are commonly used as mordants to create stable complexes with natural dyes, improving their fastness properties and resistance to environmental factors.
- Encapsulation and microencapsulation techniques: Encapsulation technologies protect plant-based dyes from external factors that cause degradation. By enclosing dye molecules within protective matrices or microcapsules, these techniques shield the colorants from light, oxygen, moisture, and pH changes. Various encapsulating materials including natural polymers, synthetic polymers, and inorganic materials can be used to create protective barriers around the dye molecules, extending their shelf life and application stability.
- Natural additives and bio-based stabilizers: Natural additives derived from plants and other biological sources can enhance the stability of plant-based dyes. These include antioxidants, UV absorbers, and natural fixatives that prevent color fading and degradation. Tannins, flavonoids, and other polyphenolic compounds from plant extracts can act as co-pigments that form complexes with dye molecules, improving their resistance to light and washing. These bio-based stabilizers offer environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic stabilizers.
- Process optimization for dye extraction and application: Optimized extraction and application processes significantly impact the stability of plant-based dyes. Controlled temperature, time, and solvent selection during extraction can preserve the integrity of color compounds. Similarly, application methods such as controlled pH environments, appropriate substrate preparation, and optimized drying conditions can enhance dye fixation and longevity. These process improvements help maintain the original properties of natural colorants and extend their useful life in various applications.
- Composite formulations with synthetic stabilizers: Combining plant-based dyes with synthetic stabilizers creates hybrid systems that benefit from both natural coloration and enhanced stability. These composite formulations may include UV absorbers, antioxidants, chelating agents, and polymer binders that protect the dye molecules from degradation factors. The synergistic effect between natural dyes and synthetic additives results in improved color fastness, light stability, and resistance to washing while maintaining the eco-friendly appeal of plant-derived colorants.
02 Antioxidant additives for dye preservation
Incorporating antioxidants into plant-based dye formulations significantly improves their stability by preventing oxidative degradation. Natural antioxidants such as vitamin E, ascorbic acid, and plant extracts rich in polyphenols can neutralize free radicals that would otherwise break down dye molecules. These additives extend the color life of natural dyes when exposed to light, heat, and air, making them more viable for commercial applications in textiles, cosmetics, and food products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Microencapsulation and nanotechnology for dye protection
Advanced techniques such as microencapsulation and nanotechnology offer innovative approaches to stabilizing plant-based dyes. By encapsulating dye molecules within microscopic shells or binding them to nanoparticles, these methods create physical barriers against environmental degradation factors. The controlled release properties of these systems can also extend the functional lifespan of the dyes. These technologies have shown particular promise in improving light fastness, wash fastness, and overall durability of natural colorants.Expand Specific Solutions04 Enzymatic treatments for dye fixation
Enzymatic processes can be employed to enhance the stability of plant-based dyes through controlled oxidation or polymerization reactions. Enzymes such as laccases, peroxidases, and tyrosinases catalyze reactions that create stronger bonds between dye molecules and substrates. These biocatalytic approaches offer environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional chemical treatments while potentially improving color depth and fastness properties. The specificity of enzymatic reactions also allows for more precise control over the stabilization process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Natural binding agents and sustainable stabilizers
Plant-derived binding agents and stabilizers provide eco-friendly solutions for enhancing the durability of natural dyes. Materials such as tannins, alginates, gums, and mucilages extracted from plants can function as effective fixatives. These natural polymers form hydrogen bonds and other interactions with dye molecules, improving their resistance to washing, light exposure, and environmental stressors. Additionally, certain plant extracts contain compounds that synergistically enhance the stability of other plant-based dyes when used in combination.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Natural Colorant Development
The solvent-free stabilization of plant-based dyes market is in an early growth phase, with increasing demand driven by sustainability trends in the textile and food industries. The global market size is expanding as consumers seek eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic colorants. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players include BASF Corp. and Archroma IP GmbH, who have established robust R&D capabilities in sustainable dye technologies. Clariant International and Eastman Chemical are advancing innovative stabilization methods, while academic institutions like Wuhan Textile University and Donghua University contribute significant research. Companies like Bayer AG and Novartis are exploring crossover applications from their pharmaceutical expertise into natural colorant stabilization, indicating growing cross-industry interest in this emerging technology space.
Archroma IP GmbH
Technical Solution: Archroma has developed the EarthColors® technology, a groundbreaking solvent-free approach to stabilizing plant-based dyes. Their process transforms agricultural waste and non-edible plant parts into high-performance colorants without using conventional chemical solvents. The technology employs a proprietary bio-enzymatic extraction process where specific enzymes break down plant cell walls to release colorant compounds in an aqueous medium. Archroma's innovation includes a patented "NatureFix" system that uses plant-derived polyphenols and proteins as natural mordants, creating stable bonds between the dye molecules and textile fibers. Their process incorporates cyclodextrin-based encapsulation technology that forms molecular inclusion complexes with the dye compounds, significantly enhancing light fastness and wash durability. Additionally, Archroma utilizes ultrasonic energy during processing to improve dye penetration and fixation without thermal degradation, preserving the natural vibrancy of plant-based colorants while achieving industrial performance standards.
Strengths: Fully traceable supply chain from waste to final product; excellent sustainability profile with reduced water and energy consumption; comparable performance to synthetic dyes in many applications. Weaknesses: Higher production costs than conventional synthetic dyes; limited color palette compared to synthetic alternatives; requires specialized processing equipment for optimal results.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has pioneered the "EcoFix" technology platform for solvent-free stabilization of plant-based dyes. This innovative approach utilizes supercritical CO2 as a processing medium instead of conventional organic solvents, creating a completely solvent-free environment for dye extraction and stabilization. Their process incorporates proprietary biopolymer matrices derived from renewable resources that encapsulate and protect plant chromophores from oxidative degradation. BASF's technology employs a combination of modified cyclodextrins and plant-derived polyphenols that form inclusion complexes with colorant molecules, significantly enhancing their stability against UV radiation and washing. The company has also developed a novel cross-linking technique using enzymatic catalysis that creates stable bonds between natural dyes and textile fibers without chemical solvents. This multi-layered approach results in plant-based colorants with industrial-grade performance characteristics while maintaining environmental sustainability throughout the production process.
Strengths: Exceptional color stability compared to traditional natural dye processing; scalable industrial production capabilities; comprehensive sustainability profile with reduced water consumption. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment costs for manufacturing infrastructure; more complex processing parameters requiring precise control; slightly narrower application temperature range than solvent-stabilized alternatives.
Critical Patents in Plant-Based Dye Technology
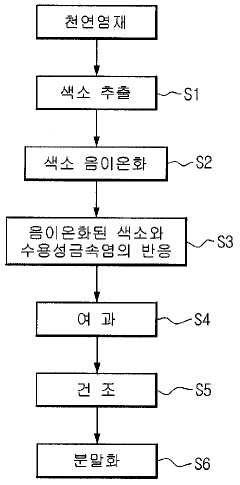
Method of manufacturing natural dye stabilized and natural dye manufactured by the same
PatentInactiveKR1020100049423A
Innovation
- Anionizing natural dyes with an alkaline agent and reacting them with water-soluble metal salts to form stabilized metal complex salts, followed by filtration, drying, and mixing with dispersants to enhance stability and dispersibility.
Stabilization method of leuco type dye
PatentActiveJP2019176802A
Innovation
- The addition of sulfite and a nonionic surfactant, particularly polyoxyethylene lauryl ether, stabilizes the chromogenic substrate solution by suppressing non-enzymatic oxidation and color development.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of solvent-free stabilization techniques for plant-based dyes reveals significant ecological advantages compared to conventional dyeing methods. Traditional dyeing processes typically consume large volumes of water and utilize harmful chemicals, resulting in substantial wastewater contamination. In contrast, solvent-free approaches dramatically reduce water usage by up to 90% in some applications, minimizing the discharge of toxic effluents into aquatic ecosystems.
Carbon footprint analyses demonstrate that solvent-free stabilization techniques generally produce 40-60% fewer greenhouse gas emissions than conventional methods. This reduction stems primarily from decreased energy requirements for heating solvents and treating contaminated wastewater. The elimination of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) commonly found in solvent-based processes further enhances air quality around manufacturing facilities.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) of plant-based dyes utilizing solvent-free stabilization show promising sustainability metrics. These techniques typically reduce overall environmental impact by 30-45% across categories including eutrophication potential, acidification, and ecotoxicity. The biodegradability of both the dyes and stabilization components ensures minimal persistent environmental contamination, with most compounds breaking down within 3-6 months under natural conditions.
Resource efficiency represents another critical environmental advantage. Solvent-free methods typically require 25-35% less raw material input per unit of dyed product. The elimination of petroleum-derived solvents reduces dependence on non-renewable resources, while the plant-based nature of the dyes themselves creates potential for closed-loop material cycles when agricultural waste streams serve as dye sources.
Waste management challenges are substantially reduced with solvent-free approaches. The absence of contaminated solvents eliminates hazardous waste disposal requirements that typically accompany conventional dyeing operations. Solid waste byproducts from these processes are generally compostable or suitable for energy recovery, creating opportunities for zero-waste manufacturing systems.
Regulatory compliance is increasingly favoring solvent-free technologies as environmental legislation tightens globally. The European Union's REACH regulations, California's Proposition 65, and similar frameworks in Asia are progressively restricting solvent use in consumer products. Manufacturers adopting solvent-free stabilization for plant-based dyes gain competitive advantages through reduced compliance costs and avoidance of potential future restrictions.
Carbon footprint analyses demonstrate that solvent-free stabilization techniques generally produce 40-60% fewer greenhouse gas emissions than conventional methods. This reduction stems primarily from decreased energy requirements for heating solvents and treating contaminated wastewater. The elimination of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) commonly found in solvent-based processes further enhances air quality around manufacturing facilities.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) of plant-based dyes utilizing solvent-free stabilization show promising sustainability metrics. These techniques typically reduce overall environmental impact by 30-45% across categories including eutrophication potential, acidification, and ecotoxicity. The biodegradability of both the dyes and stabilization components ensures minimal persistent environmental contamination, with most compounds breaking down within 3-6 months under natural conditions.
Resource efficiency represents another critical environmental advantage. Solvent-free methods typically require 25-35% less raw material input per unit of dyed product. The elimination of petroleum-derived solvents reduces dependence on non-renewable resources, while the plant-based nature of the dyes themselves creates potential for closed-loop material cycles when agricultural waste streams serve as dye sources.
Waste management challenges are substantially reduced with solvent-free approaches. The absence of contaminated solvents eliminates hazardous waste disposal requirements that typically accompany conventional dyeing operations. Solid waste byproducts from these processes are generally compostable or suitable for energy recovery, creating opportunities for zero-waste manufacturing systems.
Regulatory compliance is increasingly favoring solvent-free technologies as environmental legislation tightens globally. The European Union's REACH regulations, California's Proposition 65, and similar frameworks in Asia are progressively restricting solvent use in consumer products. Manufacturers adopting solvent-free stabilization for plant-based dyes gain competitive advantages through reduced compliance costs and avoidance of potential future restrictions.
Regulatory Framework for Natural Colorants
The regulatory landscape for natural colorants, particularly plant-based dyes, has evolved significantly in response to growing consumer demand for clean-label products. Regulatory frameworks vary globally, creating a complex environment for manufacturers implementing solvent-free stabilization techniques for plant-based dyes.
In the United States, the FDA regulates colorants under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, classifying them as either "certified" (synthetic) or "exempt from certification" (natural). Plant-based dyes fall under the latter category, with specific limitations on application and concentration. The FDA's approach to solvent-free stabilization techniques remains evolving, with increasing scrutiny on processing aids and stabilizers used in natural colorant preparations.
The European Union operates under the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines, with natural colorants regulated under the E-number system (E160-E180 for plant-based colors). The EU has implemented stricter regulations regarding extraction methods, favoring solvent-free techniques that align with clean-label trends. Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 specifically addresses food additives, including natural colorants, with amendments focusing on sustainable processing methods.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks show considerable variation. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare maintains a positive list system for food additives, including plant-based colorants, with specific provisions for traditional plant extracts. China's National Medical Products Administration has recently updated regulations to encourage environmentally friendly extraction methods, including solvent-free techniques for natural dyes.
Certification schemes have emerged as significant market drivers for natural colorants. Organic certification bodies like USDA Organic, EU Organic, and COSMOS for cosmetics have established specific guidelines for processing methods, explicitly favoring solvent-free extraction techniques. These certifications often require documentation of the entire supply chain, including stabilization processes.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a shift toward harmonization of standards for natural colorants. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed technical specifications for natural ingredients, including plant-based dyes, addressing extraction methods and stabilization techniques. The Codex Alimentarius Commission continues to work on international standards for natural colorants that may influence future regulatory frameworks.
Compliance challenges for manufacturers implementing solvent-free stabilization techniques include documentation requirements, stability testing protocols, and labeling regulations. Many jurisdictions require extensive stability data demonstrating that alternative stabilization methods maintain color integrity throughout product shelf life without compromising safety or quality.
In the United States, the FDA regulates colorants under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, classifying them as either "certified" (synthetic) or "exempt from certification" (natural). Plant-based dyes fall under the latter category, with specific limitations on application and concentration. The FDA's approach to solvent-free stabilization techniques remains evolving, with increasing scrutiny on processing aids and stabilizers used in natural colorant preparations.
The European Union operates under the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines, with natural colorants regulated under the E-number system (E160-E180 for plant-based colors). The EU has implemented stricter regulations regarding extraction methods, favoring solvent-free techniques that align with clean-label trends. Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 specifically addresses food additives, including natural colorants, with amendments focusing on sustainable processing methods.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks show considerable variation. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare maintains a positive list system for food additives, including plant-based colorants, with specific provisions for traditional plant extracts. China's National Medical Products Administration has recently updated regulations to encourage environmentally friendly extraction methods, including solvent-free techniques for natural dyes.
Certification schemes have emerged as significant market drivers for natural colorants. Organic certification bodies like USDA Organic, EU Organic, and COSMOS for cosmetics have established specific guidelines for processing methods, explicitly favoring solvent-free extraction techniques. These certifications often require documentation of the entire supply chain, including stabilization processes.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a shift toward harmonization of standards for natural colorants. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed technical specifications for natural ingredients, including plant-based dyes, addressing extraction methods and stabilization techniques. The Codex Alimentarius Commission continues to work on international standards for natural colorants that may influence future regulatory frameworks.
Compliance challenges for manufacturers implementing solvent-free stabilization techniques include documentation requirements, stability testing protocols, and labeling regulations. Many jurisdictions require extensive stability data demonstrating that alternative stabilization methods maintain color integrity throughout product shelf life without compromising safety or quality.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!