Natural Dye Applications In Luxury Versus Mass-Market Textiles
SEP 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Natural Dye Evolution and Objectives
Natural dye utilization in textiles has evolved significantly over millennia, from ancient civilizations' rudimentary extraction methods to today's sophisticated applications. Archaeological evidence suggests natural dyeing practices dating back to 6,000 BCE in China and 4,000 BCE in Egypt, where plant, insect, and mineral sources provided the foundation for textile coloration. The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal shift with the introduction of synthetic dyes in 1856, when William Henry Perkin accidentally discovered mauveine, initiating a rapid decline in natural dye usage.
The 21st century has witnessed a renaissance in natural dyeing, driven by increasing environmental consciousness and sustainability concerns. This resurgence reflects growing awareness of synthetic dyes' ecological impact, including water pollution, toxic chemical usage, and non-biodegradable waste generation. The luxury textile sector has particularly embraced this trend, positioning natural dyes as premium features that align with evolving consumer values around sustainability and authenticity.
Current technological advancements focus on addressing historical limitations of natural dyes, including color consistency, fastness properties, and scalability challenges. Research institutions and innovative textile companies are developing enhanced extraction methods, mordanting techniques, and standardization protocols to improve performance metrics while maintaining ecological benefits. These developments aim to bridge the gap between traditional craftsmanship and modern industrial requirements.
The primary objective in natural dye technology development is establishing viable pathways for broader commercial adoption across market segments. For luxury textiles, this means perfecting techniques that deliver exceptional color richness, uniqueness, and heritage value while maintaining production exclusivity. Conversely, mass-market applications require significant innovations in cost efficiency, process standardization, and supply chain optimization to compete with synthetic alternatives.
Another critical goal involves comprehensive documentation and preservation of traditional dyeing knowledge, which faces extinction as artisanal practices decline globally. This cultural preservation effort runs parallel to scientific advancement, creating a unique intersection of heritage conservation and technological innovation. Research institutions are increasingly collaborating with traditional craftspeople to codify centuries-old techniques while enhancing them with modern scientific understanding.
Looking forward, the field aims to develop hybrid approaches that combine natural dye benefits with technological efficiency. This includes bio-engineered dye sources, precision agriculture for dye plants, automated extraction systems, and digital color matching technologies. The ultimate vision encompasses creating sustainable, scalable natural dyeing processes that can serve both luxury and mass-market segments while significantly reducing the textile industry's environmental footprint.
The 21st century has witnessed a renaissance in natural dyeing, driven by increasing environmental consciousness and sustainability concerns. This resurgence reflects growing awareness of synthetic dyes' ecological impact, including water pollution, toxic chemical usage, and non-biodegradable waste generation. The luxury textile sector has particularly embraced this trend, positioning natural dyes as premium features that align with evolving consumer values around sustainability and authenticity.
Current technological advancements focus on addressing historical limitations of natural dyes, including color consistency, fastness properties, and scalability challenges. Research institutions and innovative textile companies are developing enhanced extraction methods, mordanting techniques, and standardization protocols to improve performance metrics while maintaining ecological benefits. These developments aim to bridge the gap between traditional craftsmanship and modern industrial requirements.
The primary objective in natural dye technology development is establishing viable pathways for broader commercial adoption across market segments. For luxury textiles, this means perfecting techniques that deliver exceptional color richness, uniqueness, and heritage value while maintaining production exclusivity. Conversely, mass-market applications require significant innovations in cost efficiency, process standardization, and supply chain optimization to compete with synthetic alternatives.
Another critical goal involves comprehensive documentation and preservation of traditional dyeing knowledge, which faces extinction as artisanal practices decline globally. This cultural preservation effort runs parallel to scientific advancement, creating a unique intersection of heritage conservation and technological innovation. Research institutions are increasingly collaborating with traditional craftspeople to codify centuries-old techniques while enhancing them with modern scientific understanding.
Looking forward, the field aims to develop hybrid approaches that combine natural dye benefits with technological efficiency. This includes bio-engineered dye sources, precision agriculture for dye plants, automated extraction systems, and digital color matching technologies. The ultimate vision encompasses creating sustainable, scalable natural dyeing processes that can serve both luxury and mass-market segments while significantly reducing the textile industry's environmental footprint.
Market Analysis for Natural Dyed Textiles
The natural dye textile market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a growing preference for sustainable products. The global natural dye market was valued at approximately 1.5 billion USD in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 11.3% through 2030. Within this broader market, textiles represent the largest application segment, accounting for roughly 42% of natural dye consumption worldwide.
The market for natural dyed textiles demonstrates a clear bifurcation between luxury and mass-market segments. The luxury segment, characterized by high-end fashion houses and premium textile manufacturers, has embraced natural dyes as part of their sustainability narratives and brand differentiation strategies. This segment values the unique color profiles, artisanal qualities, and heritage aspects of natural dyes, with consumers willing to pay premium prices of 30-60% above conventional alternatives.
Consumer demographics reveal that natural dyed textiles appeal primarily to environmentally conscious consumers aged 25-45 with higher disposable incomes. Market research indicates that 78% of luxury consumers consider sustainability credentials important in purchasing decisions, with natural dyeing processes specifically mentioned by 34% as a desirable product attribute.
In contrast, the mass-market segment faces significant challenges in adopting natural dyes at scale. Price sensitivity remains the primary barrier, with natural dyed products typically costing 40-100% more than synthetically dyed alternatives due to higher raw material costs, labor-intensive processes, and smaller production volumes. Additionally, mass-market retailers require consistency and color fastness that natural dyes struggle to deliver without substantial processing modifications.
Regional market analysis shows Europe leading in natural dyed luxury textiles, with particularly strong markets in Italy, France, and Scandinavian countries. Asia Pacific represents both the largest production hub and a rapidly growing consumer market, with India, Japan, and South Korea showing particularly strong demand growth rates exceeding 15% annually.
The market is further segmented by fiber type, with natural dyes showing strongest penetration in natural fibers like cotton, silk, and wool. Synthetic fiber applications remain limited but represent a potential growth area as new dyeing technologies emerge. By application, apparel represents 63% of the natural dyed textile market, followed by home textiles at 24% and industrial applications at 13%.
Future market projections indicate continued strong growth in the luxury segment, while mass-market adoption will depend largely on technological innovations that can address cost and scalability challenges. The development of standardized natural dye extracts and semi-synthetic hybrid dyes may serve as bridging technologies to expand market penetration beyond current niche applications.
The market for natural dyed textiles demonstrates a clear bifurcation between luxury and mass-market segments. The luxury segment, characterized by high-end fashion houses and premium textile manufacturers, has embraced natural dyes as part of their sustainability narratives and brand differentiation strategies. This segment values the unique color profiles, artisanal qualities, and heritage aspects of natural dyes, with consumers willing to pay premium prices of 30-60% above conventional alternatives.
Consumer demographics reveal that natural dyed textiles appeal primarily to environmentally conscious consumers aged 25-45 with higher disposable incomes. Market research indicates that 78% of luxury consumers consider sustainability credentials important in purchasing decisions, with natural dyeing processes specifically mentioned by 34% as a desirable product attribute.
In contrast, the mass-market segment faces significant challenges in adopting natural dyes at scale. Price sensitivity remains the primary barrier, with natural dyed products typically costing 40-100% more than synthetically dyed alternatives due to higher raw material costs, labor-intensive processes, and smaller production volumes. Additionally, mass-market retailers require consistency and color fastness that natural dyes struggle to deliver without substantial processing modifications.
Regional market analysis shows Europe leading in natural dyed luxury textiles, with particularly strong markets in Italy, France, and Scandinavian countries. Asia Pacific represents both the largest production hub and a rapidly growing consumer market, with India, Japan, and South Korea showing particularly strong demand growth rates exceeding 15% annually.
The market is further segmented by fiber type, with natural dyes showing strongest penetration in natural fibers like cotton, silk, and wool. Synthetic fiber applications remain limited but represent a potential growth area as new dyeing technologies emerge. By application, apparel represents 63% of the natural dyed textile market, followed by home textiles at 24% and industrial applications at 13%.
Future market projections indicate continued strong growth in the luxury segment, while mass-market adoption will depend largely on technological innovations that can address cost and scalability challenges. The development of standardized natural dye extracts and semi-synthetic hybrid dyes may serve as bridging technologies to expand market penetration beyond current niche applications.
Natural Dye Technology Landscape
Natural dye technology has evolved significantly over the past decades, transitioning from traditional artisanal practices to more sophisticated applications that meet modern industrial requirements. The landscape of natural dye technology encompasses a diverse range of botanical, animal, and mineral sources, each offering unique coloration properties and sustainability benefits compared to synthetic alternatives.
The current natural dye technology landscape is characterized by a growing integration of traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches. Extraction methodologies have advanced from basic soaking and boiling techniques to more efficient methods including ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and enzyme-assisted processes that significantly improve yield and color consistency while reducing processing time and resource consumption.
Mordanting technologies have similarly progressed, with innovations focusing on replacing toxic metal mordants with more environmentally friendly alternatives such as tannins, proteins, and bio-mordants derived from waste materials. These developments address critical sustainability concerns while maintaining or enhancing color fastness properties essential for commercial applications.
Color standardization represents a crucial advancement in the natural dye technology landscape. Digital color matching systems, spectrophotometric analysis, and computational color prediction models now enable manufacturers to achieve consistent coloration across production batches—a historical limitation that previously restricted natural dyes to artisanal markets.
Application technologies have diversified to accommodate various textile substrates and production scales. Continuous dyeing processes, pad-dry-cure methods, and digital printing with natural colorants have emerged as viable alternatives to traditional batch dyeing, particularly relevant for the mass-market segment seeking to incorporate natural dyes into existing production infrastructure.
Waste management and circular economy approaches are increasingly integrated into natural dye technology systems. Innovations include the extraction of dyes from agricultural and food processing waste streams, development of closed-loop water systems, and the creation of biodegradable dyeing auxiliaries that minimize environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
The luxury and mass-market segments exhibit divergent technological approaches. Luxury brands typically emphasize heritage techniques, geographical indication, and artisanal processes that preserve cultural significance while creating product differentiation. Conversely, mass-market applications focus on scalability, cost-efficiency, and integration with existing industrial infrastructure, often resulting in hybrid systems that combine natural dye components with conventional processing technologies.
Research institutions and innovative startups are driving technological advancement through interdisciplinary approaches combining biotechnology, green chemistry, and materials science to address persistent challenges in natural dyeing, particularly regarding color consistency, fastness properties, and economic viability at industrial scales.
The current natural dye technology landscape is characterized by a growing integration of traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches. Extraction methodologies have advanced from basic soaking and boiling techniques to more efficient methods including ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and enzyme-assisted processes that significantly improve yield and color consistency while reducing processing time and resource consumption.
Mordanting technologies have similarly progressed, with innovations focusing on replacing toxic metal mordants with more environmentally friendly alternatives such as tannins, proteins, and bio-mordants derived from waste materials. These developments address critical sustainability concerns while maintaining or enhancing color fastness properties essential for commercial applications.
Color standardization represents a crucial advancement in the natural dye technology landscape. Digital color matching systems, spectrophotometric analysis, and computational color prediction models now enable manufacturers to achieve consistent coloration across production batches—a historical limitation that previously restricted natural dyes to artisanal markets.
Application technologies have diversified to accommodate various textile substrates and production scales. Continuous dyeing processes, pad-dry-cure methods, and digital printing with natural colorants have emerged as viable alternatives to traditional batch dyeing, particularly relevant for the mass-market segment seeking to incorporate natural dyes into existing production infrastructure.
Waste management and circular economy approaches are increasingly integrated into natural dye technology systems. Innovations include the extraction of dyes from agricultural and food processing waste streams, development of closed-loop water systems, and the creation of biodegradable dyeing auxiliaries that minimize environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
The luxury and mass-market segments exhibit divergent technological approaches. Luxury brands typically emphasize heritage techniques, geographical indication, and artisanal processes that preserve cultural significance while creating product differentiation. Conversely, mass-market applications focus on scalability, cost-efficiency, and integration with existing industrial infrastructure, often resulting in hybrid systems that combine natural dye components with conventional processing technologies.
Research institutions and innovative startups are driving technological advancement through interdisciplinary approaches combining biotechnology, green chemistry, and materials science to address persistent challenges in natural dyeing, particularly regarding color consistency, fastness properties, and economic viability at industrial scales.
Current Natural Dyeing Methodologies
01 Plant-derived natural dyes
Natural dyes extracted from various plant sources can be used as environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic dyes. These plant-derived colorants are obtained from different parts of plants including roots, leaves, flowers, and fruits. They offer biodegradable and renewable coloring solutions for textiles, food, cosmetics, and other applications with reduced environmental impact and toxicity compared to synthetic alternatives.- Plant-derived natural dyes: Natural dyes extracted from various plant sources can be used as environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic dyes. These plant-derived colorants are obtained from different parts of plants including roots, leaves, flowers, and fruits. They offer biodegradable and renewable coloring solutions for textiles, food, cosmetics, and other applications, with reduced environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives.
- Extraction and processing methods for natural dyes: Various extraction and processing techniques are employed to obtain natural dyes from their sources. These methods include aqueous extraction, solvent extraction, enzymatic extraction, and ultrasonic-assisted extraction. The processing techniques aim to improve the yield, purity, and stability of the natural colorants while preserving their beneficial properties and minimizing environmental impact during production.
- Application of natural dyes in textiles: Natural dyes can be effectively applied to various textile materials including cotton, wool, silk, and synthetic fibers. The application processes often involve mordanting techniques to improve color fastness and durability. These natural colorants provide unique aesthetic qualities, including distinctive hues and color variations that synthetic dyes cannot replicate, while also offering potential health benefits due to their non-toxic nature.
- Stabilization and enhancement of natural dyes: Various methods are employed to enhance the stability, color intensity, and fastness properties of natural dyes. These include the use of mordants, fixatives, and other additives that help bind the dye to the substrate. Advanced formulation techniques can improve the light fastness, wash fastness, and overall durability of natural dyes, addressing common limitations compared to synthetic alternatives.
- Novel applications and innovations in natural dyes: Recent innovations have expanded the applications of natural dyes beyond traditional uses. These include functional natural dyes with antimicrobial, UV-protective, or medicinal properties, as well as applications in food coloring, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and advanced materials. Novel formulations and combinations with other natural or synthetic materials have created new possibilities for sustainable coloration across various industries.
02 Extraction and processing methods for natural dyes
Various extraction and processing techniques are employed to obtain natural dyes from their sources. These methods include aqueous extraction, solvent extraction, enzymatic extraction, and ultrasonic-assisted extraction. The processing techniques aim to improve the yield, purity, and stability of the natural colorants while preserving their beneficial properties. Optimization of these methods enhances the commercial viability of natural dyes for industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mordants and fixatives for natural dyes
Mordants and fixatives are used to improve the colorfastness and binding properties of natural dyes to various substrates. These substances, which can be metallic salts or bio-mordants, create bonds between the dye molecules and the substrate, enhancing color stability, wash resistance, and light fastness. The selection of appropriate mordants significantly affects the final color shade and durability of the dyed material.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of natural dyes in textiles and fashion
Natural dyes are increasingly being used in the textile and fashion industry as sustainable alternatives. These dyes can be applied to various fibers including cotton, wool, silk, and other natural fibers through different dyeing techniques. The growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products has led to innovations in natural dyeing processes that are compatible with industrial-scale production while maintaining environmental benefits.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel formulations and stabilization of natural dyes
Innovative formulations and stabilization techniques have been developed to overcome the limitations of natural dyes such as poor stability, limited color range, and inconsistent performance. These advancements include microencapsulation, nanoformulations, and the use of antioxidants and UV stabilizers. Such technologies enhance the shelf life, color intensity, and application range of natural dyes, making them more competitive with synthetic alternatives in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Luxury Brands
The natural dye market in textiles exhibits a growing yet fragmented competitive landscape, currently in a transitional phase from niche to mainstream adoption. The global market is expanding steadily, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable products in both luxury and mass-market segments. Technologically, natural dyes remain at varying maturity levels, with companies like Modern Meadow, Kolon Industries, and Kuraray leading innovation in bio-based colorants and sustainable textile processing. Academic institutions including Soochow University and Zhejiang Sci-Tech University are advancing research in extraction methods and color stability. Traditional manufacturers such as Zhejiang Jishan Printing & Dyeing are adapting to incorporate natural dye technologies, while newer entrants like Rheom Materials are developing novel biomaterial approaches that integrate naturally-derived colorants into next-generation textiles.
Modern Meadow, Inc.
Technical Solution: Modern Meadow has developed a revolutionary approach to natural dyeing through their bio-fabricated materials technology. Their platform combines biotechnology with material science to create programmable natural colorants that can be precisely engineered for specific applications. For luxury textiles, Modern Meadow has developed Bio-Alloy™ technology that integrates natural dye compounds with protein structures at the molecular level, creating exceptionally stable colors with unique visual characteristics impossible to achieve with traditional dyeing methods. Their process eliminates the need for conventional mordants by creating covalent bonds between the colorant molecules and the textile substrate. For mass-market applications, they've developed scalable fermentation-based production of natural dye compounds that can be standardized and produced at industrial scale, addressing the consistency and supply challenges typically associated with plant-derived colorants. Their closed-loop manufacturing system reduces water usage by approximately 80% compared to conventional natural dyeing processes while eliminating wastewater discharge.
Strengths: Highly innovative biotechnology approach; exceptional color stability without traditional mordants; dramatically reduced environmental impact; precise color control and consistency. Weaknesses: Relatively new technology with limited commercial implementation; higher initial costs than conventional dyeing; currently limited to specific fiber types and applications.
Zhejiang Jishan Printing & Dyeing Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Zhejiang Jishan has developed an innovative natural dye application system specifically designed for both luxury and mass-market textiles. Their technology utilizes plant-based colorants extracted through environmentally friendly processes that minimize chemical usage. The company has pioneered a proprietary mordanting technique that enhances color fastness of natural dyes to meet industrial standards, addressing one of the key limitations in natural dyeing. Their system incorporates ultrasonic-assisted dyeing methods that improve dye penetration and reduce water consumption by approximately 40% compared to conventional natural dyeing processes. For luxury markets, they've developed specialized extraction methods that preserve the unique color variations and subtle hues characteristic of natural dyes, while their mass-market applications focus on standardization and cost efficiency through automated dyeing processes and color matching systems.
Strengths: Superior environmental profile with reduced chemical and water usage; scalable processes suitable for both luxury and mass production; proprietary mordanting techniques that improve color fastness. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to synthetic dyes; limited color palette compared to synthetic alternatives; requires specialized equipment for optimal results.
Key Innovations in Natural Dye Extraction
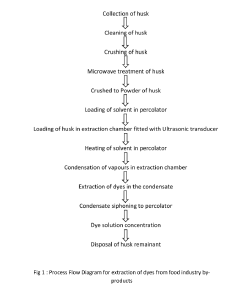
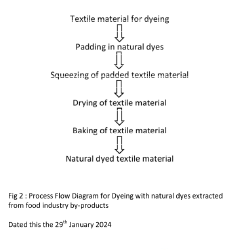
Natural dyeing of textiles with natural dyes extracted from food industry by products
PatentPendingIN202421005821A
Innovation
- A novel process using microwave-assisted Soxhlet sonic extraction to extract dyes from pulse husks, followed by the pad dry bake method for dyeing textiles without chemicals, employing mordants like alum and natural substances, and utilizing an indigenously manufactured extraction machine.
Production method for finished garment dyeing using natural fruit dye
PatentWO2019227765A1
Innovation
- Fruits with high pigment content are used as natural dyes. Through a dyeing process without adding chemical additives and dyes, the traditional washing and dehydration sequence is changed. A dyeing vat with a large channel nozzle and a protective wrapping cloth are used for uniform dyeing to ensure that the finished garments are dyed. color fastness and dimensional stability.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of natural dyes in textile applications reveals significant differences between luxury and mass-market implementations. Natural dyes generally demonstrate lower environmental toxicity compared to synthetic alternatives, with reduced chemical runoff and decreased water pollution. Luxury textile producers typically employ more sustainable water management systems during the dyeing process, often recycling up to 80% of water used, while mass-market manufacturers may recycle only 20-30% due to cost constraints.
Carbon footprint analyses indicate that small-batch natural dyeing methods used in luxury textiles produce approximately 40% less greenhouse gas emissions compared to industrial-scale synthetic dyeing operations. However, land use considerations present a complex challenge - natural dye cultivation requires substantial agricultural space, potentially competing with food production or contributing to deforestation if not properly managed.
The cultivation practices for natural dye sources vary dramatically between market segments. Luxury brands increasingly invest in regenerative agriculture methods that enhance soil health and biodiversity, often establishing direct relationships with farmers to ensure sustainable harvesting. Conversely, mass-market adoption of natural dyes frequently relies on conventional farming methods with higher pesticide usage and less attention to ecosystem preservation.
Waste management represents another critical environmental factor. Luxury textile producers typically generate less waste per unit through precise application techniques and often implement closed-loop systems where dyeing byproducts are repurposed. Mass-market operations, driven by efficiency demands, generate significantly more waste material that frequently enters landfills or waterways.
Energy consumption patterns differ substantially between segments. Artisanal dyeing methods employed in luxury textiles typically use 30-50% less energy than industrial processes, though this advantage diminishes at scale. Some innovative mass-market manufacturers have begun implementing solar-powered dyeing facilities to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining production volumes.
Biodegradability assessments reveal that naturally dyed textiles from both market segments decompose more readily than synthetically dyed alternatives, though luxury products often achieve superior results due to their avoidance of synthetic mordants and fixatives that can persist in the environment. This advantage becomes particularly significant when considering textile waste management and end-of-life product scenarios in the circular economy framework.
Carbon footprint analyses indicate that small-batch natural dyeing methods used in luxury textiles produce approximately 40% less greenhouse gas emissions compared to industrial-scale synthetic dyeing operations. However, land use considerations present a complex challenge - natural dye cultivation requires substantial agricultural space, potentially competing with food production or contributing to deforestation if not properly managed.
The cultivation practices for natural dye sources vary dramatically between market segments. Luxury brands increasingly invest in regenerative agriculture methods that enhance soil health and biodiversity, often establishing direct relationships with farmers to ensure sustainable harvesting. Conversely, mass-market adoption of natural dyes frequently relies on conventional farming methods with higher pesticide usage and less attention to ecosystem preservation.
Waste management represents another critical environmental factor. Luxury textile producers typically generate less waste per unit through precise application techniques and often implement closed-loop systems where dyeing byproducts are repurposed. Mass-market operations, driven by efficiency demands, generate significantly more waste material that frequently enters landfills or waterways.
Energy consumption patterns differ substantially between segments. Artisanal dyeing methods employed in luxury textiles typically use 30-50% less energy than industrial processes, though this advantage diminishes at scale. Some innovative mass-market manufacturers have begun implementing solar-powered dyeing facilities to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining production volumes.
Biodegradability assessments reveal that naturally dyed textiles from both market segments decompose more readily than synthetically dyed alternatives, though luxury products often achieve superior results due to their avoidance of synthetic mordants and fixatives that can persist in the environment. This advantage becomes particularly significant when considering textile waste management and end-of-life product scenarios in the circular economy framework.
Supply Chain Considerations
The supply chain for natural dyes presents distinct challenges and opportunities when comparing luxury and mass-market textile applications. Luxury brands typically operate with smaller production volumes, allowing for more specialized sourcing relationships with natural dye producers. These relationships often involve direct partnerships with artisanal communities or specialized suppliers who can provide consistent, high-quality natural colorants with documented provenance—a critical factor for luxury brand storytelling and authenticity claims.
In contrast, mass-market textile production requires significantly larger dye quantities, creating substantial scaling challenges for natural dye implementation. The inconsistency in natural raw materials presents a fundamental supply chain obstacle, as seasonal variations in plant harvests can affect color consistency across large production runs. This variability is less problematic in luxury contexts where limited editions or slight color variations may actually enhance product uniqueness and exclusivity.
Geographical considerations also heavily influence natural dye supply chains. Many traditional natural dye sources are concentrated in specific regions—indigo from India, cochineal from Peru, madder from Turkey—creating complex international supply networks. Luxury brands often leverage these geographical connections in their marketing narratives, while mass-market producers must navigate the logistical complexities of sourcing from multiple global locations to meet volume requirements.
Certification and traceability systems represent another critical supply chain component. Luxury brands increasingly implement sophisticated tracking mechanisms to verify natural dye authenticity and ethical sourcing practices. Mass-market applications typically require more standardized certification approaches that can be implemented at scale, such as GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) certification for natural dye processes.
Storage and shelf-life considerations further differentiate the supply chains. Natural dyes often have shorter shelf lives than synthetic alternatives, requiring more frequent production cycles and specialized storage conditions. Luxury producers can more easily accommodate these requirements within their smaller-batch production models, while mass-market manufacturers must develop more extensive preservation and inventory management systems.
Cost structures throughout the supply chain vary dramatically between segments. Luxury brands can absorb the premium costs of natural dyes through their higher product pricing, while mass-market applications require significant supply chain optimization to make natural dyes economically viable. This often involves developing hybrid approaches that combine natural dyes with compatible synthetic fixatives or processing aids to reduce overall costs while maintaining sustainability credentials.
In contrast, mass-market textile production requires significantly larger dye quantities, creating substantial scaling challenges for natural dye implementation. The inconsistency in natural raw materials presents a fundamental supply chain obstacle, as seasonal variations in plant harvests can affect color consistency across large production runs. This variability is less problematic in luxury contexts where limited editions or slight color variations may actually enhance product uniqueness and exclusivity.
Geographical considerations also heavily influence natural dye supply chains. Many traditional natural dye sources are concentrated in specific regions—indigo from India, cochineal from Peru, madder from Turkey—creating complex international supply networks. Luxury brands often leverage these geographical connections in their marketing narratives, while mass-market producers must navigate the logistical complexities of sourcing from multiple global locations to meet volume requirements.
Certification and traceability systems represent another critical supply chain component. Luxury brands increasingly implement sophisticated tracking mechanisms to verify natural dye authenticity and ethical sourcing practices. Mass-market applications typically require more standardized certification approaches that can be implemented at scale, such as GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) certification for natural dye processes.
Storage and shelf-life considerations further differentiate the supply chains. Natural dyes often have shorter shelf lives than synthetic alternatives, requiring more frequent production cycles and specialized storage conditions. Luxury producers can more easily accommodate these requirements within their smaller-batch production models, while mass-market manufacturers must develop more extensive preservation and inventory management systems.
Cost structures throughout the supply chain vary dramatically between segments. Luxury brands can absorb the premium costs of natural dyes through their higher product pricing, while mass-market applications require significant supply chain optimization to make natural dyes economically viable. This often involves developing hybrid approaches that combine natural dyes with compatible synthetic fixatives or processing aids to reduce overall costs while maintaining sustainability credentials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!