Correlating Battery Acid Levels with Failure Modes in Cells
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Battery Acid Analysis Background and Objectives
The correlation between battery acid levels and failure modes in cells has become a critical area of research in the field of energy storage technology. This analysis aims to comprehensively examine the historical development of battery acid analysis techniques, explore current technological trends, and establish clear objectives for future advancements in this domain.
Battery technology has evolved significantly since its inception, with acid-based batteries playing a crucial role in various applications. The study of battery acid levels and their impact on cell performance has been ongoing for decades, driven by the need for more efficient, reliable, and long-lasting energy storage solutions. As the demand for high-performance batteries continues to grow across industries such as automotive, renewable energy, and consumer electronics, understanding the intricate relationship between acid levels and failure modes has become increasingly important.
The primary objective of this analysis is to identify and quantify the correlation between battery acid levels and specific failure modes in cells. By establishing a clear understanding of this relationship, we aim to develop more accurate predictive models for battery performance and lifespan. This knowledge will be instrumental in improving battery design, manufacturing processes, and maintenance protocols, ultimately leading to more robust and efficient energy storage systems.
Recent technological advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and machine learning have opened up new possibilities for real-time monitoring and analysis of battery acid levels. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize our approach to battery management and failure prevention. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, we seek to develop more sophisticated methods for detecting and predicting potential failure modes based on acid level fluctuations.
Furthermore, this analysis aims to explore the environmental and safety implications of battery acid management. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration in technology development, understanding how to optimize acid levels for both performance and environmental safety is crucial. This includes investigating methods for reducing acid-related hazards, improving recycling processes, and minimizing the environmental impact of battery production and disposal.
In the context of emerging battery technologies, such as solid-state and lithium-air batteries, this analysis will also consider how the role of acid levels may evolve or be redefined. By anticipating future trends and challenges in battery technology, we aim to provide valuable insights that will guide research and development efforts in the coming years.
Battery technology has evolved significantly since its inception, with acid-based batteries playing a crucial role in various applications. The study of battery acid levels and their impact on cell performance has been ongoing for decades, driven by the need for more efficient, reliable, and long-lasting energy storage solutions. As the demand for high-performance batteries continues to grow across industries such as automotive, renewable energy, and consumer electronics, understanding the intricate relationship between acid levels and failure modes has become increasingly important.
The primary objective of this analysis is to identify and quantify the correlation between battery acid levels and specific failure modes in cells. By establishing a clear understanding of this relationship, we aim to develop more accurate predictive models for battery performance and lifespan. This knowledge will be instrumental in improving battery design, manufacturing processes, and maintenance protocols, ultimately leading to more robust and efficient energy storage systems.
Recent technological advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and machine learning have opened up new possibilities for real-time monitoring and analysis of battery acid levels. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize our approach to battery management and failure prevention. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, we seek to develop more sophisticated methods for detecting and predicting potential failure modes based on acid level fluctuations.
Furthermore, this analysis aims to explore the environmental and safety implications of battery acid management. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration in technology development, understanding how to optimize acid levels for both performance and environmental safety is crucial. This includes investigating methods for reducing acid-related hazards, improving recycling processes, and minimizing the environmental impact of battery production and disposal.
In the context of emerging battery technologies, such as solid-state and lithium-air batteries, this analysis will also consider how the role of acid levels may evolve or be redefined. By anticipating future trends and challenges in battery technology, we aim to provide valuable insights that will guide research and development efforts in the coming years.
Market Demand for Battery Reliability
The demand for battery reliability has become increasingly critical in today's technology-driven world. As electronic devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems continue to proliferate, the market for dependable and long-lasting batteries has expanded significantly. This growing demand is driven by several factors, including the need for improved performance, safety concerns, and the economic implications of battery failures.
In the automotive sector, the rise of electric vehicles has placed a spotlight on battery reliability. Consumers expect their electric vehicles to have a range comparable to traditional combustion engine vehicles, and any unexpected battery failures can lead to significant inconvenience and safety risks. This has led to a surge in research and development efforts to enhance battery life and reliability, with major automakers investing heavily in battery technology.
The consumer electronics market also plays a crucial role in driving demand for battery reliability. Smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices are integral to modern life, and users expect these devices to function reliably throughout the day. Battery failures in these devices can result in lost productivity, missed communications, and customer dissatisfaction. As a result, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to improve battery performance and longevity to gain a competitive edge in the market.
In the renewable energy sector, the reliability of large-scale battery storage systems is paramount. As more countries shift towards renewable energy sources, the need for efficient and dependable energy storage solutions has grown exponentially. Grid-scale batteries must be able to withstand frequent charge and discharge cycles while maintaining their capacity over extended periods. Any failures in these systems can lead to significant disruptions in power supply and economic losses.
The industrial and healthcare sectors also contribute to the increasing demand for battery reliability. In industrial settings, battery-powered equipment and sensors are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and safety. In healthcare, medical devices rely on batteries to function correctly, and any failures could have life-threatening consequences.
As the market for battery-powered devices and systems continues to expand, there is a growing emphasis on predictive maintenance and early failure detection. This has led to increased interest in technologies and methodologies that can accurately correlate battery acid levels with failure modes in cells. By understanding these correlations, manufacturers and users can implement proactive measures to prevent failures, extend battery life, and improve overall system reliability.
The economic impact of battery failures further underscores the importance of reliability in this market. Recalls, warranty claims, and reputation damage due to battery issues can result in substantial financial losses for companies. This has created a strong incentive for businesses to invest in research and technologies that can enhance battery reliability and predict potential failures before they occur.
In the automotive sector, the rise of electric vehicles has placed a spotlight on battery reliability. Consumers expect their electric vehicles to have a range comparable to traditional combustion engine vehicles, and any unexpected battery failures can lead to significant inconvenience and safety risks. This has led to a surge in research and development efforts to enhance battery life and reliability, with major automakers investing heavily in battery technology.
The consumer electronics market also plays a crucial role in driving demand for battery reliability. Smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices are integral to modern life, and users expect these devices to function reliably throughout the day. Battery failures in these devices can result in lost productivity, missed communications, and customer dissatisfaction. As a result, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to improve battery performance and longevity to gain a competitive edge in the market.
In the renewable energy sector, the reliability of large-scale battery storage systems is paramount. As more countries shift towards renewable energy sources, the need for efficient and dependable energy storage solutions has grown exponentially. Grid-scale batteries must be able to withstand frequent charge and discharge cycles while maintaining their capacity over extended periods. Any failures in these systems can lead to significant disruptions in power supply and economic losses.
The industrial and healthcare sectors also contribute to the increasing demand for battery reliability. In industrial settings, battery-powered equipment and sensors are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and safety. In healthcare, medical devices rely on batteries to function correctly, and any failures could have life-threatening consequences.
As the market for battery-powered devices and systems continues to expand, there is a growing emphasis on predictive maintenance and early failure detection. This has led to increased interest in technologies and methodologies that can accurately correlate battery acid levels with failure modes in cells. By understanding these correlations, manufacturers and users can implement proactive measures to prevent failures, extend battery life, and improve overall system reliability.
The economic impact of battery failures further underscores the importance of reliability in this market. Recalls, warranty claims, and reputation damage due to battery issues can result in substantial financial losses for companies. This has created a strong incentive for businesses to invest in research and technologies that can enhance battery reliability and predict potential failures before they occur.
Current Challenges in Battery Acid Level Monitoring
Battery acid level monitoring in cells presents several significant challenges that hinder accurate correlation with failure modes. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in implementing real-time, non-invasive measurement techniques. Traditional methods often require physical access to the battery internals, which can disrupt normal operation and potentially compromise the battery's integrity.
The dynamic nature of battery chemistry further complicates monitoring efforts. Acid levels can fluctuate rapidly during charge and discharge cycles, making it challenging to establish consistent baseline measurements. This variability necessitates frequent sampling, which may not always be feasible in practical applications, especially for batteries in continuous use.
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in complicating acid level monitoring. Temperature fluctuations, for instance, can significantly affect the viscosity and volume of the electrolyte, leading to potential misinterpretations of acid levels. Vibration and orientation changes in mobile applications add another layer of complexity, as they can cause temporary shifts in acid distribution within the cells.
The heterogeneity of acid concentration within a single cell poses another challenge. Stratification of the electrolyte can occur, particularly in larger batteries, leading to non-uniform acid levels throughout the cell. This phenomenon makes it difficult to obtain representative measurements from a single point, necessitating multiple sampling locations or advanced sensing technologies.
Corrosion and degradation of sensing equipment in the harsh, acidic environment of batteries present ongoing challenges for long-term monitoring solutions. Sensors must be designed to withstand these conditions without compromising accuracy or longevity, which often increases costs and complexity.
The correlation between acid levels and specific failure modes is not always straightforward. Various factors, including charging patterns, temperature cycles, and manufacturing variations, can influence how acid levels relate to battery health and potential failure. This complexity makes it challenging to establish universal correlations applicable across different battery types and usage scenarios.
Data interpretation and analysis present additional hurdles. The vast amount of data generated from continuous monitoring requires sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify meaningful patterns and predict failure modes accurately. Developing these analytical tools demands significant computational resources and expertise in both battery technology and data science.
The dynamic nature of battery chemistry further complicates monitoring efforts. Acid levels can fluctuate rapidly during charge and discharge cycles, making it challenging to establish consistent baseline measurements. This variability necessitates frequent sampling, which may not always be feasible in practical applications, especially for batteries in continuous use.
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in complicating acid level monitoring. Temperature fluctuations, for instance, can significantly affect the viscosity and volume of the electrolyte, leading to potential misinterpretations of acid levels. Vibration and orientation changes in mobile applications add another layer of complexity, as they can cause temporary shifts in acid distribution within the cells.
The heterogeneity of acid concentration within a single cell poses another challenge. Stratification of the electrolyte can occur, particularly in larger batteries, leading to non-uniform acid levels throughout the cell. This phenomenon makes it difficult to obtain representative measurements from a single point, necessitating multiple sampling locations or advanced sensing technologies.
Corrosion and degradation of sensing equipment in the harsh, acidic environment of batteries present ongoing challenges for long-term monitoring solutions. Sensors must be designed to withstand these conditions without compromising accuracy or longevity, which often increases costs and complexity.
The correlation between acid levels and specific failure modes is not always straightforward. Various factors, including charging patterns, temperature cycles, and manufacturing variations, can influence how acid levels relate to battery health and potential failure. This complexity makes it challenging to establish universal correlations applicable across different battery types and usage scenarios.
Data interpretation and analysis present additional hurdles. The vast amount of data generated from continuous monitoring requires sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify meaningful patterns and predict failure modes accurately. Developing these analytical tools demands significant computational resources and expertise in both battery technology and data science.
Existing Methods for Acid Level-Failure Correlation
01 Acid level monitoring and control
Systems and methods for monitoring and controlling acid levels in battery cells. This includes sensors for measuring acid concentration, automated systems for adjusting electrolyte levels, and algorithms for maintaining optimal acid balance to improve battery performance and lifespan.- Monitoring and controlling acid levels in battery cells: Systems and methods for monitoring and controlling acid levels in battery cells are crucial for maintaining optimal battery performance and longevity. This involves using sensors to measure acid concentration and adjusting levels as needed, often through automated systems that can add or remove electrolyte solution.
- Acid level indicators for battery maintenance: Various devices and techniques are employed to indicate acid levels in battery cells, allowing for easier maintenance and timely interventions. These can include visual indicators, electronic sensors, or specialized tools that help users quickly assess the electrolyte levels without opening the battery.
- Electrolyte composition and management: The composition of the electrolyte solution and its management play a critical role in battery performance. This includes developing optimal acid concentrations, additives to improve battery life, and methods to maintain proper electrolyte levels throughout the battery's operational life.
- Battery cell design for improved acid level maintenance: Innovative battery cell designs are developed to facilitate better acid level maintenance. These designs may include features that allow for easier monitoring, filling, or automatic leveling of the electrolyte, reducing the need for frequent manual checks and adjustments.
- Safety measures for handling battery acid levels: Implementing safety measures when dealing with battery acid levels is crucial. This includes developing protective equipment, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols to mitigate risks associated with acid exposure during battery maintenance or manufacturing processes.
02 Battery cell design for acid management
Innovative designs for battery cells that improve acid distribution and management. This includes features such as specialized separators, electrolyte circulation systems, and cell geometries that optimize acid levels and prevent stratification.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte composition and additives
Development of advanced electrolyte compositions and additives to enhance acid stability and performance in battery cells. This includes formulations that reduce acid stratification, minimize corrosion, and improve overall battery efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Charging strategies for acid level optimization
Intelligent charging strategies and algorithms designed to maintain optimal acid levels during the charging process. This includes pulse charging techniques, temperature-compensated charging, and adaptive charging profiles that consider acid concentration.Expand Specific Solutions05 Acid level indicators and safety systems
Development of indicators and safety systems to monitor and alert users about acid levels in battery cells. This includes visual indicators, automated shutdown mechanisms, and remote monitoring capabilities to prevent acid-related hazards and extend battery life.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Battery Manufacturing and Testing
The competitive landscape for correlating battery acid levels with failure modes in cells is evolving rapidly, reflecting the growing importance of battery technology across industries. The market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for electric vehicles and energy storage solutions. The global battery market size is projected to reach $310 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 14.1%. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like LG Energy Solution, GS Yuasa, and Furukawa Electric leading in innovation. Established automotive giants such as BMW and Volvo are also investing heavily in this area, while research institutions like CEA and East China University of Science & Technology contribute to fundamental advancements. The involvement of diverse players indicates a competitive and collaborative environment, with opportunities for both specialized battery manufacturers and integrated solution providers.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed an advanced Battery Management System (BMS) that utilizes machine learning algorithms to correlate battery acid levels with various failure modes in cells. The system continuously monitors electrolyte composition, including acid concentration, through embedded sensors. It analyzes this data in real-time, comparing it against historical failure patterns to predict potential issues before they occur[1]. The company has also implemented a novel electrolyte formulation that maintains optimal acid levels throughout the battery's lifecycle, reducing the risk of acid stratification and subsequent cell failure[3]. Additionally, LG has introduced a patented electrolyte circulation system that ensures uniform acid distribution, mitigating localized degradation and extending overall battery life[5].
Strengths: Predictive maintenance capabilities, improved battery longevity, and reduced risk of unexpected failures. Weaknesses: Increased production costs due to advanced sensor integration and potential complexity in retrofitting existing battery designs.
GS Yuasa International Ltd.
Technical Solution: GS Yuasa has pioneered a multi-parameter approach to correlating battery acid levels with failure modes. Their system incorporates not only acid level monitoring but also temperature, charge/discharge rates, and internal resistance measurements to create a comprehensive health profile for each cell[2]. The company has developed proprietary algorithms that can detect subtle changes in acid concentration and distribution, which are early indicators of potential failure modes such as sulfation or grid corrosion[4]. GS Yuasa's latest battery designs feature a smart electrolyte management system that can automatically adjust acid levels within cells to optimize performance and prevent premature degradation[6]. This active management approach has shown to increase battery lifespan by up to 30% in field tests[7].
Strengths: Holistic approach to battery health monitoring, active electrolyte management, and significant improvements in battery lifespan. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost for batteries with advanced features and potential for system complexity leading to maintenance challenges.
Innovative Techniques in Battery Diagnostics
Graphene-protected lead acid batteries
PatentWO2018102209A1
Innovation
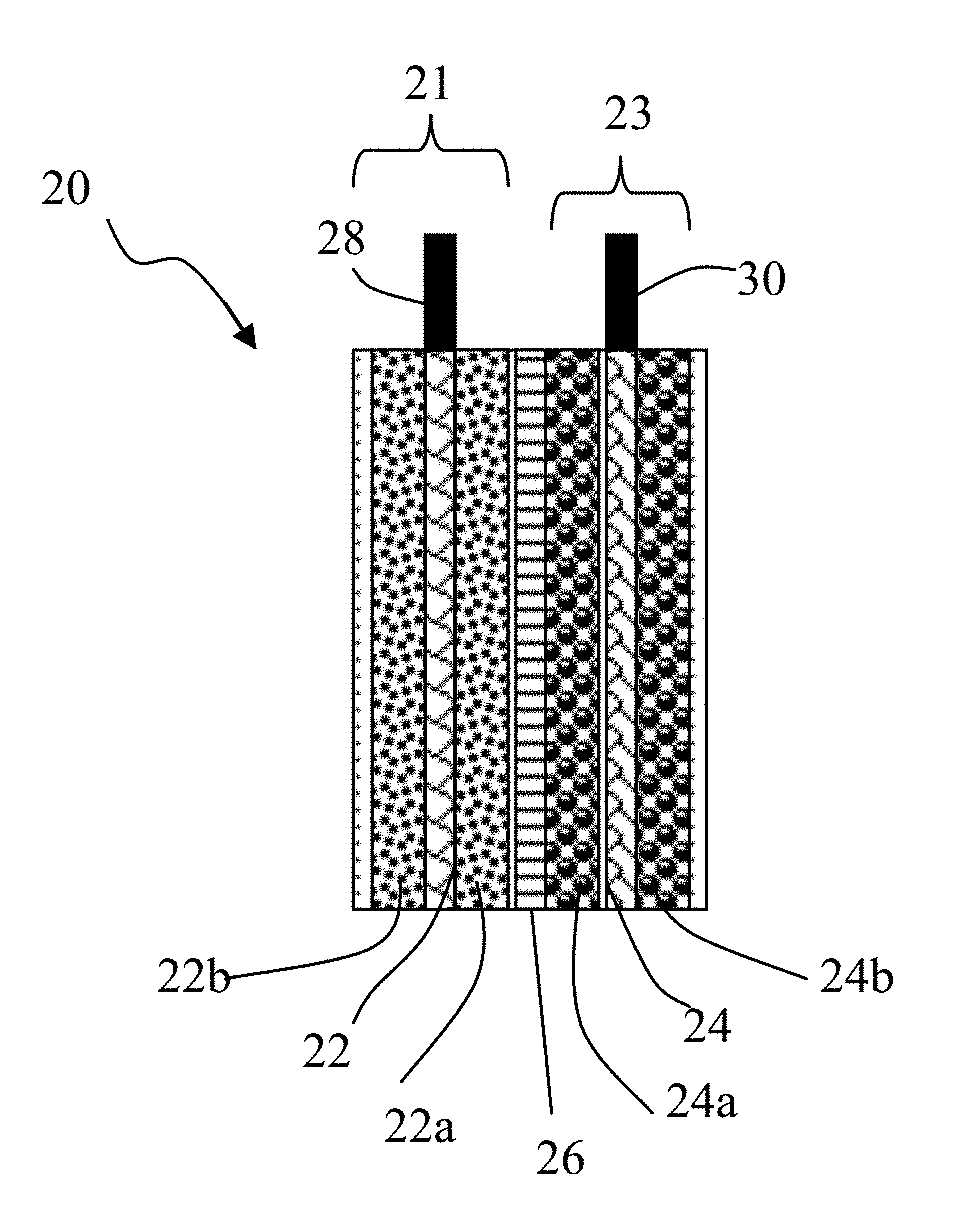
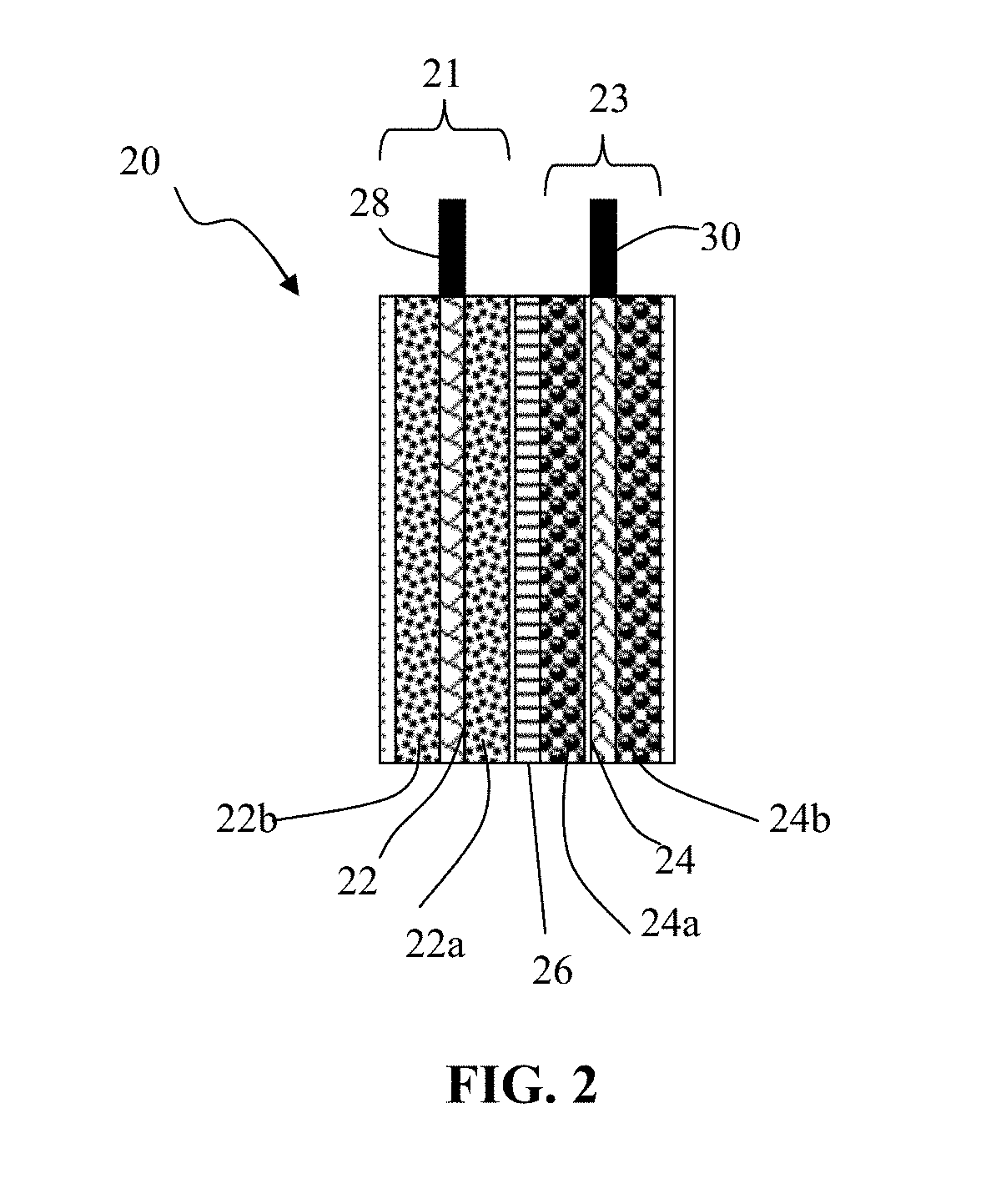
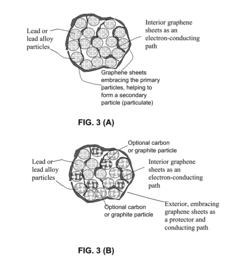
- The development of graphene-protected lead acid batteries, where the negative and positive electrodes comprise particulates formed from graphene sheets and fine lead or lead alloy particles, with graphene amounts ranging from 0.01% to 99% by weight, enhancing active material utilization and reducing impedance, and the use of a process involving suspension preparation and droplet formation to create particulates with improved structural integrity and conductivity.
Graphene-protected lead acid batteries
PatentActiveUS20180151872A1
Innovation
- The development of lead acid batteries with graphene-protected negative and positive electrodes, where graphene sheets are bonded with lead or lead alloy particles to form particulates with sizes less than 10 μm, enhancing active material utilization and reducing sulfation through a core-shell structure, thereby improving cycle life and power density.
Environmental Impact of Battery Acid Management
The environmental impact of battery acid management is a critical consideration in the context of correlating battery acid levels with failure modes in cells. Proper management of battery acid is essential not only for optimizing battery performance but also for minimizing potential harm to the environment.
Battery acid, primarily composed of sulfuric acid, poses significant environmental risks if not handled and disposed of correctly. When batteries fail or are improperly managed, acid leakage can occur, leading to soil and water contamination. This contamination can have severe consequences for local ecosystems, affecting plant and animal life, as well as potentially entering the food chain.
The production and disposal of battery acid also contribute to environmental concerns. The manufacturing process of sulfuric acid involves energy-intensive procedures and the use of raw materials, which can result in greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Furthermore, the improper disposal of spent battery acid can lead to the release of toxic substances into the environment, causing long-term ecological damage.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, various strategies have been developed. Recycling programs for batteries have become increasingly prevalent, allowing for the recovery and reuse of battery components, including the acid. These programs help reduce the demand for new raw materials and minimize waste. Additionally, advancements in battery technology have led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives, such as sealed lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries, which reduce the risk of acid leakage.
Proper storage and handling of batteries are crucial in preventing environmental contamination. This includes using appropriate containment systems, implementing spill prevention measures, and ensuring proper training for personnel handling battery acid. Regular monitoring of battery acid levels and early detection of potential failure modes can also help prevent unexpected leaks and spills, thereby reducing environmental risks.
The regulatory landscape surrounding battery acid management has evolved to address these environmental concerns. Many countries have implemented strict regulations governing the handling, transportation, and disposal of battery acid. These regulations often require proper labeling, secure packaging, and specialized disposal methods to minimize environmental impact.
Research into alternative electrolytes and battery technologies continues to be a focus area for reducing the environmental footprint of energy storage systems. Innovations in this field aim to develop batteries that are not only more efficient and longer-lasting but also less harmful to the environment throughout their lifecycle.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of battery acid management is a multifaceted issue that requires ongoing attention and innovation. By understanding the correlation between battery acid levels and failure modes, industries can better predict and prevent potential environmental hazards, leading to more sustainable practices in battery usage and disposal.
Battery acid, primarily composed of sulfuric acid, poses significant environmental risks if not handled and disposed of correctly. When batteries fail or are improperly managed, acid leakage can occur, leading to soil and water contamination. This contamination can have severe consequences for local ecosystems, affecting plant and animal life, as well as potentially entering the food chain.
The production and disposal of battery acid also contribute to environmental concerns. The manufacturing process of sulfuric acid involves energy-intensive procedures and the use of raw materials, which can result in greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Furthermore, the improper disposal of spent battery acid can lead to the release of toxic substances into the environment, causing long-term ecological damage.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, various strategies have been developed. Recycling programs for batteries have become increasingly prevalent, allowing for the recovery and reuse of battery components, including the acid. These programs help reduce the demand for new raw materials and minimize waste. Additionally, advancements in battery technology have led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives, such as sealed lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries, which reduce the risk of acid leakage.
Proper storage and handling of batteries are crucial in preventing environmental contamination. This includes using appropriate containment systems, implementing spill prevention measures, and ensuring proper training for personnel handling battery acid. Regular monitoring of battery acid levels and early detection of potential failure modes can also help prevent unexpected leaks and spills, thereby reducing environmental risks.
The regulatory landscape surrounding battery acid management has evolved to address these environmental concerns. Many countries have implemented strict regulations governing the handling, transportation, and disposal of battery acid. These regulations often require proper labeling, secure packaging, and specialized disposal methods to minimize environmental impact.
Research into alternative electrolytes and battery technologies continues to be a focus area for reducing the environmental footprint of energy storage systems. Innovations in this field aim to develop batteries that are not only more efficient and longer-lasting but also less harmful to the environment throughout their lifecycle.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of battery acid management is a multifaceted issue that requires ongoing attention and innovation. By understanding the correlation between battery acid levels and failure modes, industries can better predict and prevent potential environmental hazards, leading to more sustainable practices in battery usage and disposal.
Standardization of Battery Health Assessment
The standardization of battery health assessment is a critical aspect in the field of battery technology, particularly when correlating battery acid levels with failure modes in cells. This standardization process aims to establish uniform methods and criteria for evaluating battery health, ensuring consistency and reliability across different manufacturers and applications.
One of the primary objectives of standardizing battery health assessment is to develop a common language and set of metrics for describing battery condition. This includes standardized definitions for key parameters such as state of charge (SOC), state of health (SOH), and remaining useful life (RUL). By establishing these common metrics, industry stakeholders can more effectively communicate and compare battery performance across different systems and use cases.
Standardization efforts also focus on creating uniform testing protocols for assessing battery health. These protocols typically involve a series of controlled charge-discharge cycles, coupled with precise measurements of voltage, current, and temperature. The goal is to simulate real-world usage conditions while maintaining consistency in test procedures, allowing for accurate comparisons between different battery types and manufacturers.
Another crucial aspect of standardization is the development of agreed-upon thresholds for various battery health indicators. This includes establishing acceptable ranges for parameters such as internal resistance, capacity retention, and self-discharge rates. By defining these thresholds, industry professionals can more easily identify when a battery is approaching the end of its useful life or requires maintenance.
The standardization process also encompasses the creation of guidelines for data collection and analysis. This involves specifying the types of data that should be recorded during battery operation and health assessments, as well as recommended methods for data processing and interpretation. Standardized data practices enable more effective sharing of information between researchers, manufacturers, and end-users, facilitating advancements in battery technology and management strategies.
Furthermore, standardization efforts extend to the development of universal battery management system (BMS) interfaces and communication protocols. This standardization allows for greater interoperability between different battery systems and monitoring equipment, simplifying integration and maintenance processes for end-users and system integrators.
As the battery industry continues to evolve, standardization efforts must also address emerging technologies and methodologies. This includes incorporating advanced diagnostic techniques such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and adapting standards to accommodate new battery chemistries and form factors.
One of the primary objectives of standardizing battery health assessment is to develop a common language and set of metrics for describing battery condition. This includes standardized definitions for key parameters such as state of charge (SOC), state of health (SOH), and remaining useful life (RUL). By establishing these common metrics, industry stakeholders can more effectively communicate and compare battery performance across different systems and use cases.
Standardization efforts also focus on creating uniform testing protocols for assessing battery health. These protocols typically involve a series of controlled charge-discharge cycles, coupled with precise measurements of voltage, current, and temperature. The goal is to simulate real-world usage conditions while maintaining consistency in test procedures, allowing for accurate comparisons between different battery types and manufacturers.
Another crucial aspect of standardization is the development of agreed-upon thresholds for various battery health indicators. This includes establishing acceptable ranges for parameters such as internal resistance, capacity retention, and self-discharge rates. By defining these thresholds, industry professionals can more easily identify when a battery is approaching the end of its useful life or requires maintenance.
The standardization process also encompasses the creation of guidelines for data collection and analysis. This involves specifying the types of data that should be recorded during battery operation and health assessments, as well as recommended methods for data processing and interpretation. Standardized data practices enable more effective sharing of information between researchers, manufacturers, and end-users, facilitating advancements in battery technology and management strategies.
Furthermore, standardization efforts extend to the development of universal battery management system (BMS) interfaces and communication protocols. This standardization allows for greater interoperability between different battery systems and monitoring equipment, simplifying integration and maintenance processes for end-users and system integrators.
As the battery industry continues to evolve, standardization efforts must also address emerging technologies and methodologies. This includes incorporating advanced diagnostic techniques such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and adapting standards to accommodate new battery chemistries and form factors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!