How Battery Acid Concentrations Affect Energy Conversion in Cells
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Battery Acid Evolution
The evolution of battery acid concentrations has played a crucial role in the development of more efficient and powerful energy storage systems. Initially, lead-acid batteries utilized dilute sulfuric acid solutions, typically ranging from 20% to 30% concentration. This early formulation provided a balance between reactivity and stability but limited the overall energy density of the cells.
As research progressed, scientists discovered that increasing the acid concentration could significantly enhance the battery's performance. By the mid-20th century, battery manufacturers began experimenting with higher concentrations, pushing the limits to 35-40%. This shift resulted in improved energy density and faster charge-discharge cycles, making batteries more suitable for a wider range of applications.
The 1970s and 1980s saw further advancements in acid concentration optimization. Researchers found that fine-tuning the acid concentration based on specific battery designs and intended uses could yield substantial benefits. For instance, deep-cycle batteries used in renewable energy systems began utilizing acid concentrations of up to 50%, while starter batteries for automobiles maintained lower concentrations to balance power output and longevity.
The advent of valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) batteries in the late 20th century marked another milestone in battery acid evolution. These sealed batteries used highly concentrated electrolytes, often in gel or absorbed glass mat (AGM) form, with acid concentrations reaching 65% or higher. This innovation not only increased energy density but also improved safety and reduced maintenance requirements.
Recent years have seen a focus on optimizing acid concentrations for specific applications and environmental conditions. For example, researchers have developed temperature-adaptive electrolytes that can adjust their concentration based on ambient conditions, ensuring optimal performance across a wide range of temperatures. Additionally, the integration of advanced additives and electrolyte modifiers has allowed for further fine-tuning of acid properties, enhancing both performance and longevity.
The ongoing evolution of battery acid concentrations continues to drive improvements in energy conversion efficiency. Current research is exploring the potential of ultra-high concentration electrolytes, with some experimental designs pushing beyond 70% concentration. These advanced formulations promise even greater energy densities and faster charge rates, potentially revolutionizing the capabilities of lead-acid batteries in high-performance applications.
As research progressed, scientists discovered that increasing the acid concentration could significantly enhance the battery's performance. By the mid-20th century, battery manufacturers began experimenting with higher concentrations, pushing the limits to 35-40%. This shift resulted in improved energy density and faster charge-discharge cycles, making batteries more suitable for a wider range of applications.
The 1970s and 1980s saw further advancements in acid concentration optimization. Researchers found that fine-tuning the acid concentration based on specific battery designs and intended uses could yield substantial benefits. For instance, deep-cycle batteries used in renewable energy systems began utilizing acid concentrations of up to 50%, while starter batteries for automobiles maintained lower concentrations to balance power output and longevity.
The advent of valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) batteries in the late 20th century marked another milestone in battery acid evolution. These sealed batteries used highly concentrated electrolytes, often in gel or absorbed glass mat (AGM) form, with acid concentrations reaching 65% or higher. This innovation not only increased energy density but also improved safety and reduced maintenance requirements.
Recent years have seen a focus on optimizing acid concentrations for specific applications and environmental conditions. For example, researchers have developed temperature-adaptive electrolytes that can adjust their concentration based on ambient conditions, ensuring optimal performance across a wide range of temperatures. Additionally, the integration of advanced additives and electrolyte modifiers has allowed for further fine-tuning of acid properties, enhancing both performance and longevity.
The ongoing evolution of battery acid concentrations continues to drive improvements in energy conversion efficiency. Current research is exploring the potential of ultra-high concentration electrolytes, with some experimental designs pushing beyond 70% concentration. These advanced formulations promise even greater energy densities and faster charge rates, potentially revolutionizing the capabilities of lead-acid batteries in high-performance applications.
Energy Conversion Demand
The demand for efficient energy conversion in battery cells has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the growing need for portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems. This surge in demand is primarily fueled by the global shift towards sustainable energy solutions and the rapid advancement of technology-dependent sectors.
In the automotive industry, the push for electric vehicles has created a significant market for high-performance batteries with improved energy conversion capabilities. Major automakers are investing heavily in research and development to enhance battery technology, focusing on increasing energy density and conversion efficiency. This trend is expected to continue as governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations and offer incentives for electric vehicle adoption.
The consumer electronics sector also plays a crucial role in driving the demand for enhanced energy conversion in battery cells. With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices, consumers are increasingly seeking longer battery life and faster charging capabilities. This has led manufacturers to explore innovative battery technologies and optimize energy conversion processes to meet these demands.
Renewable energy storage systems represent another significant area of growth for battery technology. As solar and wind power generation becomes more widespread, the need for efficient and reliable energy storage solutions has become paramount. Grid-scale battery systems require high-performance cells with excellent energy conversion properties to effectively store and distribute power, ensuring a stable and sustainable energy supply.
The industrial sector, including manufacturing and logistics, is also contributing to the increased demand for improved energy conversion in battery cells. The adoption of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and other battery-powered equipment in warehouses and production facilities has created a need for long-lasting, high-performance batteries that can operate continuously in demanding environments.
Furthermore, the telecommunications industry is driving demand for advanced battery solutions to power remote cell towers and backup systems. As 5G networks continue to expand, the need for reliable and efficient energy storage and conversion becomes even more critical to ensure uninterrupted service.
The growing focus on sustainability and environmental concerns has also influenced the demand for improved energy conversion in battery cells. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and production processes to reduce the environmental impact of battery production and disposal while maintaining or enhancing energy conversion efficiency.
As these various sectors continue to evolve and expand, the demand for advanced battery technologies with superior energy conversion capabilities is expected to grow exponentially in the coming years. This trend is likely to drive further innovation and investment in battery research and development, ultimately leading to more efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions across multiple industries.
In the automotive industry, the push for electric vehicles has created a significant market for high-performance batteries with improved energy conversion capabilities. Major automakers are investing heavily in research and development to enhance battery technology, focusing on increasing energy density and conversion efficiency. This trend is expected to continue as governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations and offer incentives for electric vehicle adoption.
The consumer electronics sector also plays a crucial role in driving the demand for enhanced energy conversion in battery cells. With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices, consumers are increasingly seeking longer battery life and faster charging capabilities. This has led manufacturers to explore innovative battery technologies and optimize energy conversion processes to meet these demands.
Renewable energy storage systems represent another significant area of growth for battery technology. As solar and wind power generation becomes more widespread, the need for efficient and reliable energy storage solutions has become paramount. Grid-scale battery systems require high-performance cells with excellent energy conversion properties to effectively store and distribute power, ensuring a stable and sustainable energy supply.
The industrial sector, including manufacturing and logistics, is also contributing to the increased demand for improved energy conversion in battery cells. The adoption of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and other battery-powered equipment in warehouses and production facilities has created a need for long-lasting, high-performance batteries that can operate continuously in demanding environments.
Furthermore, the telecommunications industry is driving demand for advanced battery solutions to power remote cell towers and backup systems. As 5G networks continue to expand, the need for reliable and efficient energy storage and conversion becomes even more critical to ensure uninterrupted service.
The growing focus on sustainability and environmental concerns has also influenced the demand for improved energy conversion in battery cells. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and production processes to reduce the environmental impact of battery production and disposal while maintaining or enhancing energy conversion efficiency.
As these various sectors continue to evolve and expand, the demand for advanced battery technologies with superior energy conversion capabilities is expected to grow exponentially in the coming years. This trend is likely to drive further innovation and investment in battery research and development, ultimately leading to more efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions across multiple industries.
Acid Concentration Challenges
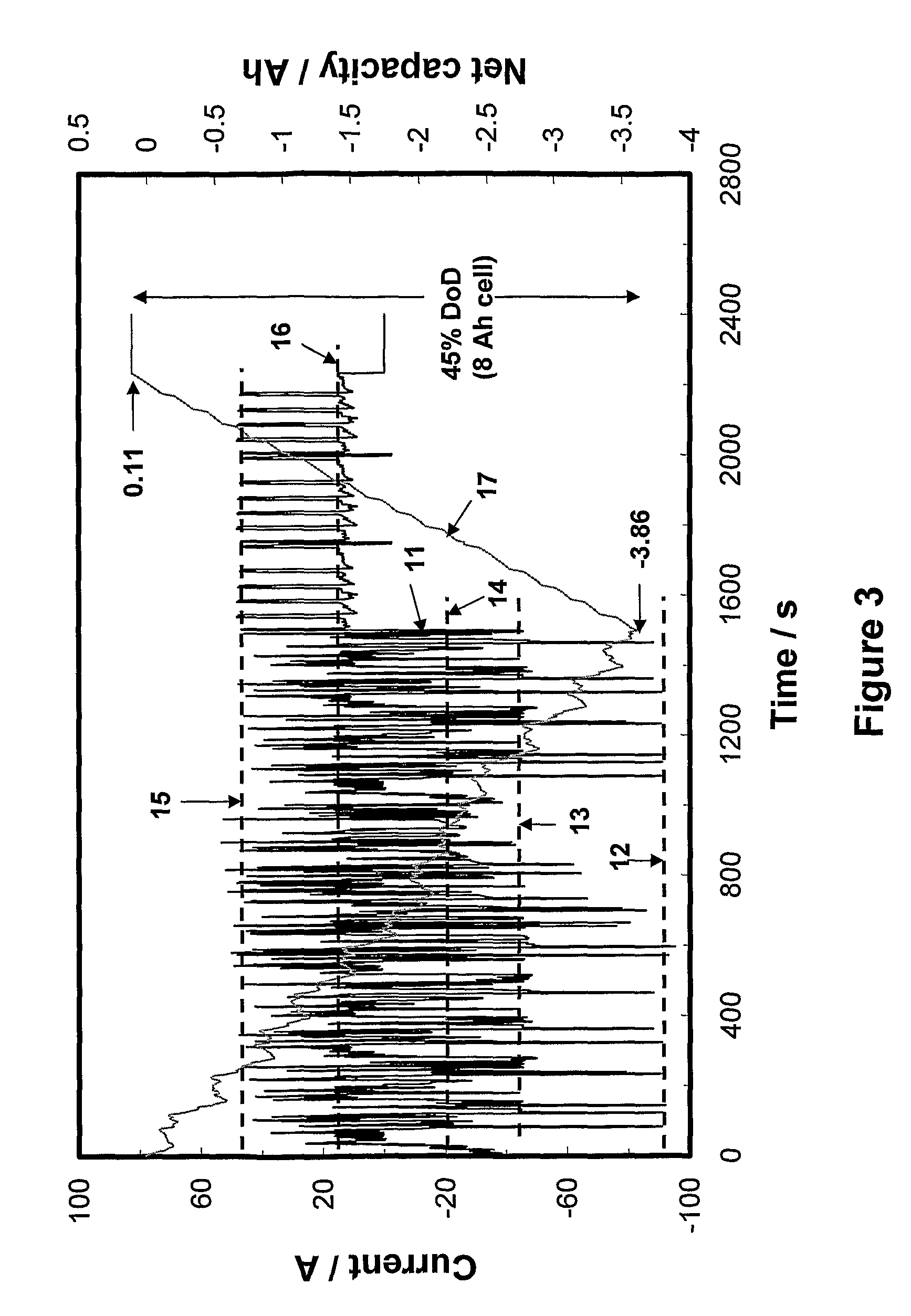
The concentration of acid in battery cells plays a crucial role in energy conversion efficiency and overall battery performance. One of the primary challenges in this domain is maintaining the optimal acid concentration throughout the battery's lifecycle. As batteries discharge and recharge, the acid concentration fluctuates, leading to potential issues such as sulfation, capacity loss, and reduced efficiency.
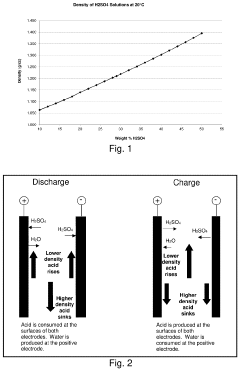
A significant challenge lies in managing the stratification of acid within the battery. During charging, the acid tends to concentrate at the bottom of the cell, creating an uneven distribution. This stratification can lead to localized areas of high acidity, potentially causing accelerated corrosion of battery components and reducing the overall lifespan of the battery.
Another critical challenge is the impact of temperature on acid concentration. Higher temperatures can cause increased evaporation of the electrolyte, leading to a more concentrated acid solution. This can accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, potentially improving short-term performance but at the cost of long-term durability. Conversely, lower temperatures can result in decreased acid concentration, reducing the battery's ability to deliver power effectively.
The precise control of acid concentration is further complicated by the varying demands placed on batteries in different applications. For instance, deep-cycle batteries used in renewable energy storage systems experience different acid concentration fluctuations compared to starter batteries in automobiles. Developing solutions that can adapt to these diverse usage patterns while maintaining optimal acid concentration remains a significant challenge.
Measuring and monitoring acid concentration accurately in real-time presents another hurdle. Traditional methods often require manual testing, which can be time-consuming and may not provide continuous data. The development of advanced sensors and monitoring systems that can provide real-time, accurate measurements of acid concentration without compromising the battery's integrity is an ongoing area of research and development.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in managing acid concentrations. The disposal and recycling of batteries with high acid content require careful handling to prevent environmental contamination. Developing more environmentally friendly electrolytes or finding ways to neutralize acid safely during the recycling process are important considerations in addressing this challenge.
A significant challenge lies in managing the stratification of acid within the battery. During charging, the acid tends to concentrate at the bottom of the cell, creating an uneven distribution. This stratification can lead to localized areas of high acidity, potentially causing accelerated corrosion of battery components and reducing the overall lifespan of the battery.
Another critical challenge is the impact of temperature on acid concentration. Higher temperatures can cause increased evaporation of the electrolyte, leading to a more concentrated acid solution. This can accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, potentially improving short-term performance but at the cost of long-term durability. Conversely, lower temperatures can result in decreased acid concentration, reducing the battery's ability to deliver power effectively.
The precise control of acid concentration is further complicated by the varying demands placed on batteries in different applications. For instance, deep-cycle batteries used in renewable energy storage systems experience different acid concentration fluctuations compared to starter batteries in automobiles. Developing solutions that can adapt to these diverse usage patterns while maintaining optimal acid concentration remains a significant challenge.
Measuring and monitoring acid concentration accurately in real-time presents another hurdle. Traditional methods often require manual testing, which can be time-consuming and may not provide continuous data. The development of advanced sensors and monitoring systems that can provide real-time, accurate measurements of acid concentration without compromising the battery's integrity is an ongoing area of research and development.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in managing acid concentrations. The disposal and recycling of batteries with high acid content require careful handling to prevent environmental contamination. Developing more environmentally friendly electrolytes or finding ways to neutralize acid safely during the recycling process are important considerations in addressing this challenge.
Current Acid Solutions
01 Battery cell structure and design
Innovations in battery cell structure and design focus on improving energy conversion efficiency and overall performance. This includes advancements in electrode materials, cell geometry, and internal component arrangements to optimize energy density and power output.- Battery cell structure and design: Innovations in battery cell structure and design focus on improving energy conversion efficiency and overall performance. This includes advancements in electrode materials, cell geometry, and internal component arrangements to optimize energy density and power output.
- Energy conversion mechanisms: Development of novel energy conversion mechanisms within battery cells, including improved electrochemical processes, enhanced ion transport, and innovative charge/discharge cycles. These advancements aim to increase the efficiency of converting chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa.
- Thermal management and energy efficiency: Implementation of thermal management systems and energy-efficient designs in battery cells to optimize performance and longevity. This includes heat dissipation techniques, temperature control mechanisms, and strategies to minimize energy losses during conversion processes.
- Advanced materials for energy conversion: Utilization of advanced materials in battery cell components to enhance energy conversion capabilities. This includes the development of novel electrode materials, electrolytes, and separators that improve conductivity, stability, and overall energy conversion efficiency.
- Integration of energy harvesting technologies: Incorporation of energy harvesting technologies into battery cell systems to supplement energy conversion and storage. This may include the integration of solar cells, piezoelectric elements, or other energy harvesting mechanisms to improve overall energy efficiency and extend battery life.
02 Energy conversion mechanisms
Research into novel energy conversion mechanisms within battery cells aims to enhance the efficiency of converting chemical energy into electrical energy. This involves exploring new electrochemical reactions, catalysts, and charge transfer processes to improve overall battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal management in battery cells
Effective thermal management is crucial for maintaining optimal battery performance and longevity. Innovations in this area focus on heat dissipation techniques, temperature control systems, and materials that enhance thermal conductivity within the battery cell.Expand Specific Solutions04 Battery management systems
Advanced battery management systems are being developed to optimize energy conversion and utilization in battery cells. These systems incorporate intelligent monitoring, control algorithms, and predictive maintenance features to enhance overall battery efficiency and lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel materials for energy conversion
Research into new materials for battery components aims to improve energy conversion efficiency. This includes exploring advanced electrode materials, electrolytes, and separators that can enhance charge storage capacity, conductivity, and overall battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Battery Manufacturers
The battery acid concentration technology market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the expanding electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors. The global market size for advanced battery technologies is projected to reach billions of dollars in the coming years. While the basic principles of battery acid concentration are well-established, ongoing research and development efforts by key players like Tianneng Battery Group, GS Yuasa, and Panasonic are focused on improving energy density, efficiency, and longevity. These companies, along with others like Robert Bosch and NEC, are investing heavily in R&D to optimize acid concentrations and electrode materials for enhanced performance. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with automotive and grid storage solutions seeing rapid advancements, while some niche industrial applications are still in earlier stages of development.
Tianneng Battery Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Tianneng has focused on optimizing acid concentrations through advanced manufacturing processes and materials. They have developed a proprietary "Nano-Grid Technology" that increases the surface area of battery plates, allowing for more efficient chemical reactions and improved energy conversion. Their research indicates that this technology can increase battery capacity by up to 30% while maintaining stable acid concentrations[7]. Tianneng has also implemented an automated electrolyte filling system that ensures precise acid levels during production, reducing variations in battery performance[8].
Strengths: Innovative nano-grid technology, increased battery capacity, and precise manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: Potential scalability issues and higher production costs.
Daramic LLC
Technical Solution: Daramic, as a leading separator manufacturer, has developed advanced separator technologies that directly impact acid concentration management in batteries. Their "HD Technology" incorporates a unique pore structure that optimizes acid distribution and retention, leading to improved energy conversion efficiency. Daramic's separators have been shown to reduce acid stratification by up to 40%, resulting in more uniform acid concentrations throughout the battery[9]. They have also introduced a novel surface treatment process that enhances wettability, ensuring better electrolyte distribution and reducing the risk of dry spots that can impair battery performance[10].
Strengths: Specialized separator technology, reduced acid stratification, and improved electrolyte distribution. Weaknesses: Limited to separator components and dependent on battery manufacturers for implementation.
Concentration Innovations
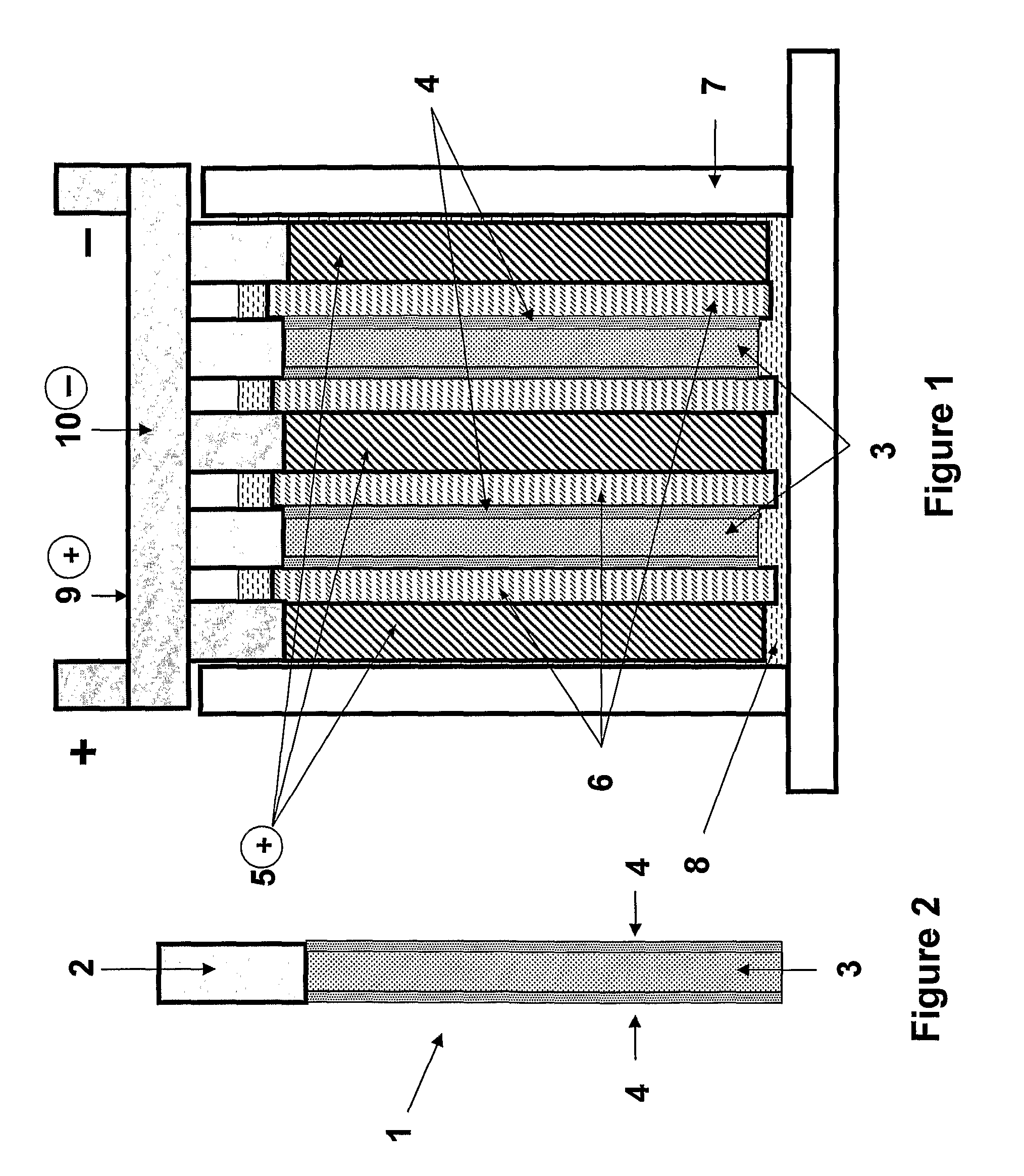
Energy storage device
PatentActiveUS20100203362A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a charging ability-increasing additive in the positive battery electrode material, such as conductive carbon materials or tin dioxide, and optimizing electrolyte concentration and plate conductivity to balance the performance of both plates, along with using capacitor electrode materials to share high-rate operations.
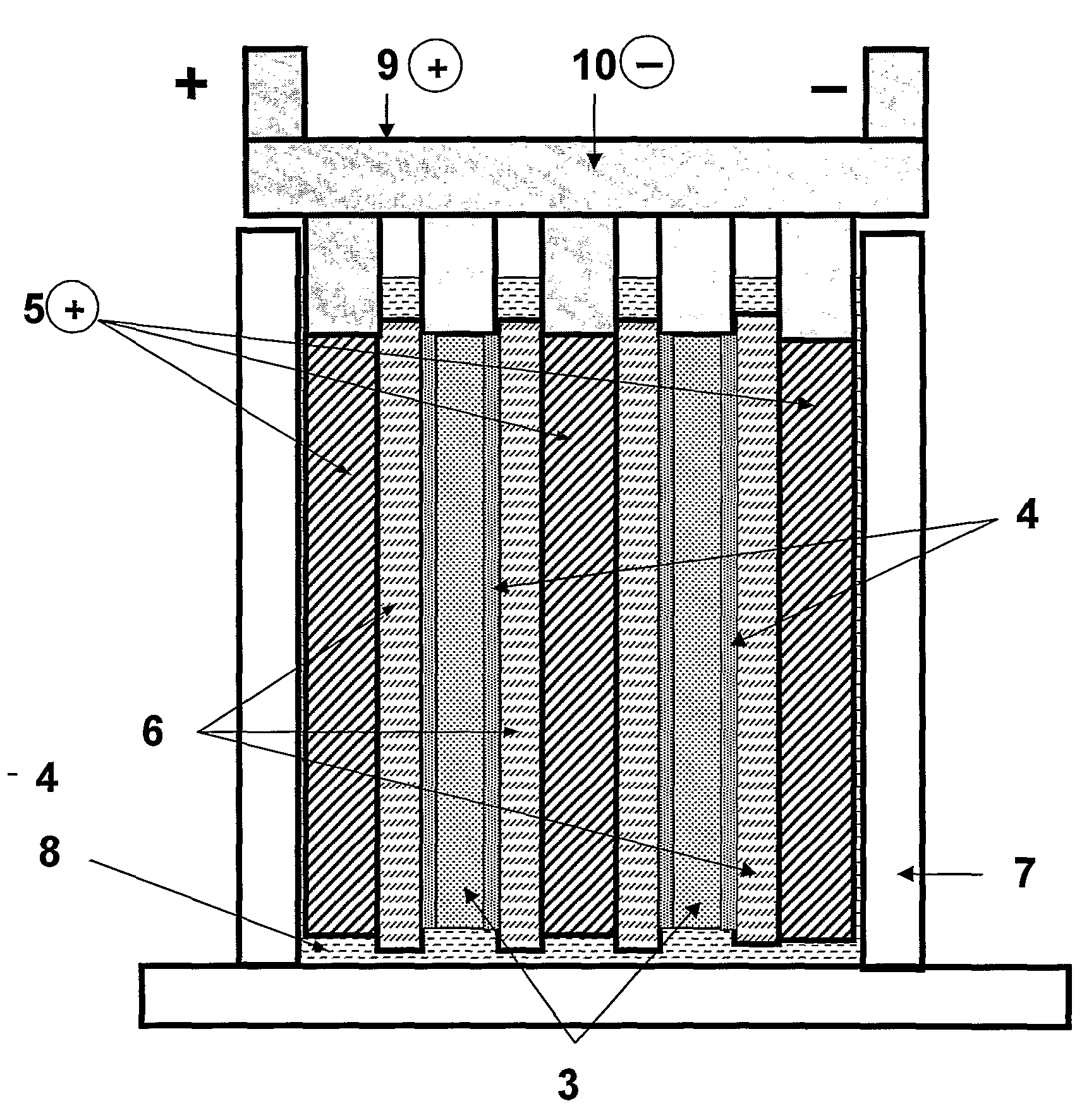
Acid stratification mitigation, electrolytes, devices, and methods related thereto
PatentActiveUS20240222702A1
Innovation
- Introducing an acid-soluble and acid-stable polymer with high molecular weight into the electrolyte to increase viscosity, which resists convective flows and reduces acid stratification by partially immobilizing the acid, thereby enhancing battery performance.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of battery acid concentrations in energy conversion cells is a critical consideration in the development and deployment of battery technologies. The primary environmental concerns stem from the production, use, and disposal of batteries containing acidic electrolytes.
During battery manufacturing, the production of acid electrolytes involves chemical processes that can generate harmful emissions and waste products. Higher acid concentrations typically require more intensive manufacturing processes, potentially increasing the environmental footprint of battery production. Additionally, the extraction and processing of raw materials for high-concentration electrolytes may lead to increased mining activities and associated ecological disruptions.
In the operational phase, batteries with higher acid concentrations generally exhibit improved energy conversion efficiency, which can lead to longer battery life and reduced waste generation over time. However, this benefit must be balanced against the increased potential for environmental damage in case of leaks or improper disposal. Highly concentrated battery acids pose a greater risk to soil and water ecosystems if released into the environment.
The disposal and recycling of batteries present significant environmental challenges. Higher acid concentrations complicate the recycling process, requiring more sophisticated and energy-intensive methods to safely neutralize and recover materials. This can result in increased energy consumption and potential emissions during the recycling phase. Conversely, the improved energy density of high-concentration batteries may reduce the overall volume of battery waste, potentially mitigating some environmental impacts associated with transportation and storage of spent batteries.
Efforts to address these environmental concerns include the development of less hazardous electrolyte formulations, improved battery casing designs to prevent leaks, and advanced recycling technologies. Some researchers are exploring bio-based or neutral pH electrolytes as alternatives to traditional acidic solutions, aiming to reduce the environmental risks associated with battery production and disposal.
The regulatory landscape surrounding battery technologies is evolving to address these environmental impacts. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for the handling, transportation, and disposal of batteries containing hazardous materials. These regulations often mandate proper labeling, safe storage practices, and responsible recycling procedures to minimize environmental risks.
In conclusion, while higher battery acid concentrations can offer improved energy conversion efficiency, they also present increased environmental challenges throughout the battery lifecycle. Balancing these factors is crucial for the sustainable development of battery technologies, requiring ongoing research into safer materials, improved manufacturing processes, and more efficient recycling methods.
During battery manufacturing, the production of acid electrolytes involves chemical processes that can generate harmful emissions and waste products. Higher acid concentrations typically require more intensive manufacturing processes, potentially increasing the environmental footprint of battery production. Additionally, the extraction and processing of raw materials for high-concentration electrolytes may lead to increased mining activities and associated ecological disruptions.
In the operational phase, batteries with higher acid concentrations generally exhibit improved energy conversion efficiency, which can lead to longer battery life and reduced waste generation over time. However, this benefit must be balanced against the increased potential for environmental damage in case of leaks or improper disposal. Highly concentrated battery acids pose a greater risk to soil and water ecosystems if released into the environment.
The disposal and recycling of batteries present significant environmental challenges. Higher acid concentrations complicate the recycling process, requiring more sophisticated and energy-intensive methods to safely neutralize and recover materials. This can result in increased energy consumption and potential emissions during the recycling phase. Conversely, the improved energy density of high-concentration batteries may reduce the overall volume of battery waste, potentially mitigating some environmental impacts associated with transportation and storage of spent batteries.
Efforts to address these environmental concerns include the development of less hazardous electrolyte formulations, improved battery casing designs to prevent leaks, and advanced recycling technologies. Some researchers are exploring bio-based or neutral pH electrolytes as alternatives to traditional acidic solutions, aiming to reduce the environmental risks associated with battery production and disposal.
The regulatory landscape surrounding battery technologies is evolving to address these environmental impacts. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for the handling, transportation, and disposal of batteries containing hazardous materials. These regulations often mandate proper labeling, safe storage practices, and responsible recycling procedures to minimize environmental risks.
In conclusion, while higher battery acid concentrations can offer improved energy conversion efficiency, they also present increased environmental challenges throughout the battery lifecycle. Balancing these factors is crucial for the sustainable development of battery technologies, requiring ongoing research into safer materials, improved manufacturing processes, and more efficient recycling methods.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations play a crucial role in managing the risks associated with battery acid concentrations and their impact on energy conversion in cells. These regulations are designed to protect workers, consumers, and the environment from potential hazards related to battery manufacturing, handling, and disposal.
In the manufacturing process, strict guidelines are in place to ensure proper handling and storage of battery acids. Workers are required to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including acid-resistant gloves, goggles, and protective clothing. Ventilation systems must be installed to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes, and emergency eyewash stations and showers must be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Transportation of batteries and battery acids is subject to stringent regulations. The United Nations has established a classification system for dangerous goods, with battery acids falling under Class 8 (Corrosive Substances). Specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements must be met to ensure safe transport. Vehicles carrying these materials must be equipped with appropriate safety features and follow designated routes to minimize risks to populated areas.
For consumer safety, regulations mandate clear labeling of battery products, including warnings about potential hazards and proper handling instructions. Manufacturers are required to provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) detailing the composition, hazards, and emergency procedures associated with their products. Additionally, regulations often specify maximum allowable acid concentrations in consumer batteries to reduce the risk of injury in case of leakage or accidental exposure.
Environmental regulations address the disposal and recycling of batteries to prevent soil and water contamination. Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, requiring manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, including proper disposal and recycling. Specific guidelines exist for the neutralization and treatment of battery acids before disposal, and specialized facilities are required for recycling lead-acid batteries.
In research and development settings, additional safety protocols are necessary when experimenting with varying acid concentrations to optimize energy conversion. Laboratories must adhere to strict containment measures, waste management procedures, and emergency response plans. Regular safety audits and training programs are mandated to ensure compliance with these regulations.
As technology advances and new battery chemistries emerge, safety regulations continue to evolve. Regulatory bodies work closely with industry experts and researchers to update standards and guidelines, addressing new risks and incorporating lessons learned from incidents. This ongoing process ensures that safety measures keep pace with technological developments in battery technology and energy conversion efficiency.
In the manufacturing process, strict guidelines are in place to ensure proper handling and storage of battery acids. Workers are required to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including acid-resistant gloves, goggles, and protective clothing. Ventilation systems must be installed to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes, and emergency eyewash stations and showers must be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Transportation of batteries and battery acids is subject to stringent regulations. The United Nations has established a classification system for dangerous goods, with battery acids falling under Class 8 (Corrosive Substances). Specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements must be met to ensure safe transport. Vehicles carrying these materials must be equipped with appropriate safety features and follow designated routes to minimize risks to populated areas.
For consumer safety, regulations mandate clear labeling of battery products, including warnings about potential hazards and proper handling instructions. Manufacturers are required to provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) detailing the composition, hazards, and emergency procedures associated with their products. Additionally, regulations often specify maximum allowable acid concentrations in consumer batteries to reduce the risk of injury in case of leakage or accidental exposure.
Environmental regulations address the disposal and recycling of batteries to prevent soil and water contamination. Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, requiring manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, including proper disposal and recycling. Specific guidelines exist for the neutralization and treatment of battery acids before disposal, and specialized facilities are required for recycling lead-acid batteries.
In research and development settings, additional safety protocols are necessary when experimenting with varying acid concentrations to optimize energy conversion. Laboratories must adhere to strict containment measures, waste management procedures, and emergency response plans. Regular safety audits and training programs are mandated to ensure compliance with these regulations.
As technology advances and new battery chemistries emerge, safety regulations continue to evolve. Regulatory bodies work closely with industry experts and researchers to update standards and guidelines, addressing new risks and incorporating lessons learned from incidents. This ongoing process ensures that safety measures keep pace with technological developments in battery technology and energy conversion efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!