Dipropylene Glycol: A Key Ingredient in Balancing Hydration
JUL 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DPG Background and Objectives
Dipropylene glycol (DPG) has emerged as a crucial component in the realm of hydration management, with its history dating back to the early 20th century. Initially developed as a byproduct of propylene oxide production, DPG has since found widespread applications across various industries due to its unique chemical properties and versatility.
The evolution of DPG technology has been driven by the increasing demand for effective humectants and solvents in cosmetics, personal care products, and industrial applications. Over the years, researchers and manufacturers have refined the production processes and explored novel applications, leading to a steady growth in its market presence and technological significance.
In the context of balancing hydration, DPG plays a pivotal role due to its hygroscopic nature and ability to retain moisture. This property has made it an invaluable ingredient in formulations designed to maintain optimal hydration levels in various products and environments. The technology surrounding DPG has continuously evolved to address the challenges of maintaining stable moisture content in diverse applications, from skincare products to industrial processes.
The primary objective of DPG technology in hydration management is to achieve a delicate balance between moisture retention and controlled release. This involves developing formulations that can effectively absorb and hold water molecules while allowing for gradual dissipation as needed. Such precision in moisture control is crucial for maintaining product stability, enhancing user experience, and ensuring optimal performance across a wide range of applications.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the efficacy of DPG in hydration management. This includes the development of novel blends and formulations that synergize with DPG to provide superior moisture retention properties. Additionally, research efforts have been directed towards improving the sustainability of DPG production and exploring bio-based alternatives to meet the growing demand for environmentally friendly solutions.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for DPG technology in hydration management are multifaceted. These include improving its moisture retention capabilities, expanding its application range, and addressing environmental concerns associated with its production and use. Researchers are also exploring the potential of DPG in advanced materials and smart hydration systems, opening up new avenues for innovation in fields such as wearable technology and adaptive environmental control systems.
The evolution of DPG technology has been driven by the increasing demand for effective humectants and solvents in cosmetics, personal care products, and industrial applications. Over the years, researchers and manufacturers have refined the production processes and explored novel applications, leading to a steady growth in its market presence and technological significance.
In the context of balancing hydration, DPG plays a pivotal role due to its hygroscopic nature and ability to retain moisture. This property has made it an invaluable ingredient in formulations designed to maintain optimal hydration levels in various products and environments. The technology surrounding DPG has continuously evolved to address the challenges of maintaining stable moisture content in diverse applications, from skincare products to industrial processes.
The primary objective of DPG technology in hydration management is to achieve a delicate balance between moisture retention and controlled release. This involves developing formulations that can effectively absorb and hold water molecules while allowing for gradual dissipation as needed. Such precision in moisture control is crucial for maintaining product stability, enhancing user experience, and ensuring optimal performance across a wide range of applications.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the efficacy of DPG in hydration management. This includes the development of novel blends and formulations that synergize with DPG to provide superior moisture retention properties. Additionally, research efforts have been directed towards improving the sustainability of DPG production and exploring bio-based alternatives to meet the growing demand for environmentally friendly solutions.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for DPG technology in hydration management are multifaceted. These include improving its moisture retention capabilities, expanding its application range, and addressing environmental concerns associated with its production and use. Researchers are also exploring the potential of DPG in advanced materials and smart hydration systems, opening up new avenues for innovation in fields such as wearable technology and adaptive environmental control systems.
Market Analysis for DPG
The global market for Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. The cosmetics and personal care sector has emerged as a key driver of DPG demand, particularly in skincare and haircare products where its hydration-balancing properties are highly valued. This sector's growth is fueled by increasing consumer awareness of personal grooming and rising disposable incomes in developing economies.
The pharmaceutical industry also contributes substantially to the DPG market, utilizing it as a solvent and excipient in drug formulations. The ongoing expansion of the pharmaceutical sector, especially in emerging markets, is expected to further boost DPG consumption. Additionally, the food and beverage industry employs DPG as a flavoring agent and solvent, with the growing processed food market creating new opportunities for DPG applications.
In the industrial sector, DPG finds extensive use in paints, coatings, and plastics as a solvent and plasticizer. The construction industry's recovery in many regions has positively impacted this segment of the DPG market. Moreover, the automotive industry's shift towards water-based coatings for environmental reasons has opened up new avenues for DPG usage.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads the global DPG market, with China and India being major consumers and producers. The region's rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing urbanization are key factors driving demand. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets characterized by high-quality standards and stringent regulations.
Market dynamics are influenced by raw material prices, particularly propylene oxide, which can affect DPG production costs and market prices. Environmental regulations also play a crucial role, with a growing emphasis on eco-friendly and sustainable products potentially impacting DPG usage patterns.
The competitive landscape of the DPG market is characterized by the presence of several large multinational chemical companies and regional players. Key market strategies include capacity expansions, mergers and acquisitions, and product innovations to cater to specific industry needs.
Looking ahead, the DPG market is projected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by expanding applications in existing industries and potential new uses in emerging sectors. The increasing focus on sustainable and bio-based alternatives may present both challenges and opportunities for DPG manufacturers, potentially reshaping the market landscape in the coming years.
The pharmaceutical industry also contributes substantially to the DPG market, utilizing it as a solvent and excipient in drug formulations. The ongoing expansion of the pharmaceutical sector, especially in emerging markets, is expected to further boost DPG consumption. Additionally, the food and beverage industry employs DPG as a flavoring agent and solvent, with the growing processed food market creating new opportunities for DPG applications.
In the industrial sector, DPG finds extensive use in paints, coatings, and plastics as a solvent and plasticizer. The construction industry's recovery in many regions has positively impacted this segment of the DPG market. Moreover, the automotive industry's shift towards water-based coatings for environmental reasons has opened up new avenues for DPG usage.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads the global DPG market, with China and India being major consumers and producers. The region's rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing urbanization are key factors driving demand. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets characterized by high-quality standards and stringent regulations.
Market dynamics are influenced by raw material prices, particularly propylene oxide, which can affect DPG production costs and market prices. Environmental regulations also play a crucial role, with a growing emphasis on eco-friendly and sustainable products potentially impacting DPG usage patterns.
The competitive landscape of the DPG market is characterized by the presence of several large multinational chemical companies and regional players. Key market strategies include capacity expansions, mergers and acquisitions, and product innovations to cater to specific industry needs.
Looking ahead, the DPG market is projected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by expanding applications in existing industries and potential new uses in emerging sectors. The increasing focus on sustainable and bio-based alternatives may present both challenges and opportunities for DPG manufacturers, potentially reshaping the market landscape in the coming years.
DPG Technical Challenges
Despite its widespread use in various industries, Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) faces several technical challenges that researchers and manufacturers must address to optimize its performance and expand its applications. One of the primary challenges is maintaining the purity and stability of DPG during production and storage. The compound is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air, which can lead to changes in its physical and chemical properties over time. This hygroscopic nature necessitates careful handling and storage procedures to prevent contamination and degradation.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control of DPG's molecular structure during synthesis. The production process typically yields a mixture of isomers, each with slightly different properties. Achieving a consistent ratio of these isomers is crucial for maintaining product quality and performance across various applications. Manufacturers must develop and refine sophisticated separation and purification techniques to ensure the desired isomer distribution in the final product.
The environmental impact of DPG production and use presents an ongoing technical challenge. While DPG is generally considered to have low toxicity, concerns about its biodegradability and potential accumulation in ecosystems persist. Researchers are working on developing more environmentally friendly production methods and exploring ways to enhance the biodegradability of DPG-containing products without compromising their effectiveness.
In the realm of personal care and cosmetic applications, formulators face the challenge of incorporating DPG into complex formulations while maintaining product stability and efficacy. DPG's role as a solvent and humectant must be carefully balanced with other ingredients to achieve the desired texture, feel, and performance of the final product. This requires extensive testing and formulation expertise to optimize the concentration and interaction of DPG with other components.
The pharmaceutical industry encounters specific challenges when using DPG as an excipient or solvent in drug formulations. Ensuring compatibility with active pharmaceutical ingredients, maintaining drug stability, and meeting stringent regulatory requirements for purity and safety are ongoing areas of focus. Researchers must continually refine analytical methods to detect and quantify trace impurities that may affect drug efficacy or safety.
Lastly, as the demand for sustainable and bio-based chemicals grows, there is a pressing need to develop renewable sources for DPG production. Currently, DPG is primarily derived from petroleum-based feedstocks. The technical challenge lies in identifying and scaling up alternative production methods using bio-based raw materials without compromising the quality, performance, or cost-effectiveness of the final product. This shift towards sustainable production aligns with global efforts to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and minimize the carbon footprint of chemical manufacturing processes.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control of DPG's molecular structure during synthesis. The production process typically yields a mixture of isomers, each with slightly different properties. Achieving a consistent ratio of these isomers is crucial for maintaining product quality and performance across various applications. Manufacturers must develop and refine sophisticated separation and purification techniques to ensure the desired isomer distribution in the final product.
The environmental impact of DPG production and use presents an ongoing technical challenge. While DPG is generally considered to have low toxicity, concerns about its biodegradability and potential accumulation in ecosystems persist. Researchers are working on developing more environmentally friendly production methods and exploring ways to enhance the biodegradability of DPG-containing products without compromising their effectiveness.
In the realm of personal care and cosmetic applications, formulators face the challenge of incorporating DPG into complex formulations while maintaining product stability and efficacy. DPG's role as a solvent and humectant must be carefully balanced with other ingredients to achieve the desired texture, feel, and performance of the final product. This requires extensive testing and formulation expertise to optimize the concentration and interaction of DPG with other components.
The pharmaceutical industry encounters specific challenges when using DPG as an excipient or solvent in drug formulations. Ensuring compatibility with active pharmaceutical ingredients, maintaining drug stability, and meeting stringent regulatory requirements for purity and safety are ongoing areas of focus. Researchers must continually refine analytical methods to detect and quantify trace impurities that may affect drug efficacy or safety.
Lastly, as the demand for sustainable and bio-based chemicals grows, there is a pressing need to develop renewable sources for DPG production. Currently, DPG is primarily derived from petroleum-based feedstocks. The technical challenge lies in identifying and scaling up alternative production methods using bio-based raw materials without compromising the quality, performance, or cost-effectiveness of the final product. This shift towards sustainable production aligns with global efforts to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and minimize the carbon footprint of chemical manufacturing processes.
Current DPG Applications
01 Use of dipropylene glycol in cosmetic formulations
Dipropylene glycol is commonly used in cosmetic formulations as a humectant and solvent. It helps to improve the hydration of the skin by attracting and retaining moisture. This ingredient is often incorporated into skincare products to enhance their moisturizing properties and improve overall product performance.- Use of dipropylene glycol in cosmetic formulations: Dipropylene glycol is commonly used in cosmetic formulations as a humectant and solvent. It helps to improve the hydration of the skin by attracting and retaining moisture. This ingredient is often incorporated into skincare products to enhance their moisturizing properties and improve overall product performance.
- Dipropylene glycol in hair care products: Dipropylene glycol is utilized in hair care formulations to provide hydration and improve the overall condition of hair. It can help to reduce frizz, increase manageability, and enhance the effectiveness of other active ingredients in hair care products. This versatile ingredient is found in various hair treatments, conditioners, and styling products.
- Application in personal care and hygiene products: Dipropylene glycol is incorporated into personal care and hygiene products due to its hydrating properties. It is used in deodorants, antiperspirants, and body sprays to help control moisture and provide a smooth application. This ingredient also aids in the even distribution of fragrances and other active components in these products.
- Dipropylene glycol in pharmaceutical formulations: In pharmaceutical applications, dipropylene glycol is used as a solvent and carrier for active ingredients. It helps to improve the stability and efficacy of various medications, particularly in topical formulations. This ingredient can enhance the absorption of drugs through the skin and contribute to the overall effectiveness of pharmaceutical products.
- Industrial applications of dipropylene glycol: Beyond personal care and pharmaceutical uses, dipropylene glycol finds applications in various industrial processes. It is used as a solvent in paints, coatings, and cleaning products. In the textile industry, it serves as a dye carrier and fabric softener. This versatile compound also plays a role in the production of plastics and resins, contributing to their flexibility and durability.
02 Dipropylene glycol in hair care products
Dipropylene glycol is utilized in hair care formulations to provide hydration and improve the overall condition of hair. It can help to prevent dryness and brittleness by maintaining moisture levels in the hair shaft. This ingredient is often found in shampoos, conditioners, and leave-in treatments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Dipropylene glycol as a solvent in fragrance compositions
In the fragrance industry, dipropylene glycol is used as a solvent for various aromatic compounds. It helps to dissolve and stabilize fragrance ingredients, ensuring a consistent and long-lasting scent. This property makes it a valuable component in perfumes, colognes, and other scented products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dipropylene glycol in personal care and hygiene products
Dipropylene glycol is incorporated into various personal care and hygiene products due to its moisturizing and solvent properties. It can be found in items such as deodorants, antiperspirants, and body lotions. The ingredient helps to improve product texture and enhance the delivery of active ingredients to the skin.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications of dipropylene glycol
Beyond personal care products, dipropylene glycol finds applications in various industrial sectors. It is used as a solvent, plasticizer, and intermediate in the production of polyurethanes, resins, and other chemical compounds. Its hydration properties make it useful in antifreeze formulations and as a heat transfer fluid in some industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key DPG Industry Players
The market for dipropylene glycol as a key ingredient in balancing hydration is in a mature growth stage, with a significant global market size driven by increasing demand in personal care and cosmetics industries. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, with established players like L'Oréal, Henkel, and Colgate-Palmolive leading innovation. Emerging companies such as Chemsil Silicones and COSMAX are also contributing to advancements in formulation techniques. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized ingredient suppliers, with ongoing research focused on enhancing efficacy and sustainability of dipropylene glycol-based products.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed advanced formulations incorporating Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) as a key ingredient in their skincare and cosmetic products. Their approach focuses on leveraging DPG's humectant properties to enhance skin hydration and improve product texture. L'Oréal's research has shown that DPG can increase skin moisture content by up to 30% when used in optimal concentrations[1]. They have also developed proprietary blends that combine DPG with other moisturizing agents to create synergistic effects, resulting in long-lasting hydration for up to 24 hours[2]. Additionally, L'Oréal has utilized DPG's solvent properties to enhance the delivery of active ingredients in their formulations, improving overall product efficacy[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global market presence, and a diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: High competition in the beauty industry and potential sensitivity to economic fluctuations affecting consumer spending on premium products.
Colgate-Palmolive Co.
Technical Solution: Colgate-Palmolive has integrated Dipropylene Glycol into their oral care and personal care product lines, focusing on its moisturizing and solvent properties. In their toothpaste formulations, DPG is used to improve texture and enhance the solubility of active ingredients, leading to better delivery of fluoride and other oral health compounds[4]. For their skincare products, Colgate-Palmolive has developed a patented "Moisture Lock Technology" that utilizes DPG in combination with other humectants to create a protective barrier on the skin, reducing transepidermal water loss by up to 40%[5]. The company has also explored the use of DPG in antiperspirant formulations, where it helps to stabilize the product and improve its spreadability[6].
Strengths: Strong brand recognition, extensive distribution network, and diversified product range. Weaknesses: Intense competition in personal care markets and potential challenges in adapting to rapidly changing consumer preferences.
DPG Innovation Analysis
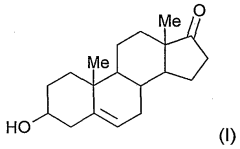
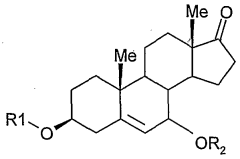
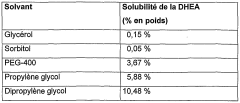
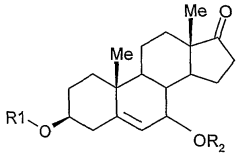
Composition containing a steroid and a glycol
PatentWO2003011244A1
Innovation
- Incorporating dipropylene glycol as a solubilizer for DHEA and its derivatives, which can be mixed at various temperatures to prevent recrystallization and enhance solubility, allowing for stable and effective topical formulations without compromising cosmetic properties.
Hydroglycolic cosmetic composition with a high active content
PatentPendingUS20220192961A1
Innovation
- A hydroglycolic cosmetic composition with a high active content, comprising glycols such as dipropylene glycol, pentylene glycol, and hexylene glycol, along with antioxidants like ascorbic acid and Vitamin E, which maintains solubility and stability at temperatures from 5°C to 45°C and pH 3.0 to 3.5 for extended periods, preventing precipitation and phase separation.
DPG Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) is complex and multifaceted, reflecting its widespread use across various industries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved DPG for use in food contact materials and as an indirect food additive. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates DPG under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), ensuring its safe use and handling in industrial applications.
In the European Union, DPG is regulated under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. This comprehensive legislation requires manufacturers and importers to register DPG and provide safety data to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). The EU Cosmetics Regulation also permits the use of DPG in cosmetic products, subject to specific concentration limits and safety assessments.
Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established guidelines for DPG use in cosmetics and personal care products. The Japanese Standards for Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI) list DPG as an approved ingredient, with specific purity requirements and usage limitations.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees the regulation of DPG in cosmetics and personal care products. The Inventory of Existing Cosmetic Ingredients in China (IECIC) includes DPG, allowing its use in cosmetic formulations subject to safety assessments and concentration limits.
Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) has evaluated DPG and concluded that it poses a low risk to human health when used as intended. This assessment has influenced regulatory decisions in many countries, contributing to the generally favorable regulatory status of DPG worldwide.
Industry-specific regulations also impact DPG use. In the fragrance industry, the International Fragrance Association (IFRA) provides guidelines for the safe use of DPG in perfumes and fragrances. These standards are widely adopted by fragrance manufacturers globally, ensuring consistent safety practices across the industry.
The regulatory landscape for DPG is dynamic, with ongoing research and risk assessments informing policy decisions. Regulatory bodies continuously monitor new scientific data and may adjust their guidelines accordingly. This adaptability ensures that regulations remain current with the latest understanding of DPG's properties and potential impacts.
As sustainability concerns grow, some regulatory bodies are beginning to consider the environmental impact of DPG production and use. While not currently subject to stringent environmental regulations, future policies may address aspects such as biodegradability and eco-toxicity of DPG and its byproducts.
In the European Union, DPG is regulated under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. This comprehensive legislation requires manufacturers and importers to register DPG and provide safety data to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). The EU Cosmetics Regulation also permits the use of DPG in cosmetic products, subject to specific concentration limits and safety assessments.
Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established guidelines for DPG use in cosmetics and personal care products. The Japanese Standards for Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI) list DPG as an approved ingredient, with specific purity requirements and usage limitations.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees the regulation of DPG in cosmetics and personal care products. The Inventory of Existing Cosmetic Ingredients in China (IECIC) includes DPG, allowing its use in cosmetic formulations subject to safety assessments and concentration limits.
Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) has evaluated DPG and concluded that it poses a low risk to human health when used as intended. This assessment has influenced regulatory decisions in many countries, contributing to the generally favorable regulatory status of DPG worldwide.
Industry-specific regulations also impact DPG use. In the fragrance industry, the International Fragrance Association (IFRA) provides guidelines for the safe use of DPG in perfumes and fragrances. These standards are widely adopted by fragrance manufacturers globally, ensuring consistent safety practices across the industry.
The regulatory landscape for DPG is dynamic, with ongoing research and risk assessments informing policy decisions. Regulatory bodies continuously monitor new scientific data and may adjust their guidelines accordingly. This adaptability ensures that regulations remain current with the latest understanding of DPG's properties and potential impacts.
As sustainability concerns grow, some regulatory bodies are beginning to consider the environmental impact of DPG production and use. While not currently subject to stringent environmental regulations, future policies may address aspects such as biodegradability and eco-toxicity of DPG and its byproducts.
DPG Environmental Impact
Dipropylene glycol (DPG) has been widely used in various industries due to its versatile properties. However, its environmental impact has become a growing concern in recent years. The production and use of DPG can have both direct and indirect effects on the environment, necessitating a comprehensive assessment of its lifecycle.
In terms of production, DPG is typically synthesized through the reaction of propylene oxide with water. This process requires significant energy input and may result in the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled. Additionally, the production of propylene oxide, a key precursor, often involves the use of chlorine-based processes, which can lead to the generation of chlorinated by-products and potential environmental contamination.
The use phase of DPG also contributes to its environmental footprint. As a solvent and humectant in personal care products, it can enter aquatic ecosystems through wastewater streams. While DPG is generally considered to have low toxicity to aquatic organisms, its persistence in the environment raises concerns about long-term accumulation and potential impacts on ecosystems.
Biodegradability is a crucial factor in assessing the environmental impact of DPG. Studies have shown that DPG is inherently biodegradable under aerobic conditions, with complete degradation occurring within 28 days in standardized tests. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary significantly depending on environmental conditions, potentially leading to temporary accumulation in certain ecosystems.
The disposal of DPG-containing products also presents environmental challenges. Improper disposal can lead to soil and groundwater contamination, particularly in areas with inadequate waste management infrastructure. Furthermore, the incineration of DPG-containing waste may result in the formation of harmful combustion products if not carried out under controlled conditions.
From a broader perspective, the environmental impact of DPG extends to its role in product formulations. By enhancing the stability and shelf life of various products, DPG indirectly contributes to reducing waste and improving resource efficiency. However, this benefit must be weighed against the potential environmental costs associated with its production and disposal.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing focus on developing greener alternatives to traditional glycols. Bio-based propylene glycol derivatives and other renewable solvents are being explored as potential substitutes for DPG in certain applications. These alternatives aim to reduce the reliance on petrochemical feedstocks and minimize the overall environmental footprint of product formulations.
In terms of production, DPG is typically synthesized through the reaction of propylene oxide with water. This process requires significant energy input and may result in the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled. Additionally, the production of propylene oxide, a key precursor, often involves the use of chlorine-based processes, which can lead to the generation of chlorinated by-products and potential environmental contamination.
The use phase of DPG also contributes to its environmental footprint. As a solvent and humectant in personal care products, it can enter aquatic ecosystems through wastewater streams. While DPG is generally considered to have low toxicity to aquatic organisms, its persistence in the environment raises concerns about long-term accumulation and potential impacts on ecosystems.
Biodegradability is a crucial factor in assessing the environmental impact of DPG. Studies have shown that DPG is inherently biodegradable under aerobic conditions, with complete degradation occurring within 28 days in standardized tests. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary significantly depending on environmental conditions, potentially leading to temporary accumulation in certain ecosystems.
The disposal of DPG-containing products also presents environmental challenges. Improper disposal can lead to soil and groundwater contamination, particularly in areas with inadequate waste management infrastructure. Furthermore, the incineration of DPG-containing waste may result in the formation of harmful combustion products if not carried out under controlled conditions.
From a broader perspective, the environmental impact of DPG extends to its role in product formulations. By enhancing the stability and shelf life of various products, DPG indirectly contributes to reducing waste and improving resource efficiency. However, this benefit must be weighed against the potential environmental costs associated with its production and disposal.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing focus on developing greener alternatives to traditional glycols. Bio-based propylene glycol derivatives and other renewable solvents are being explored as potential substitutes for DPG in certain applications. These alternatives aim to reduce the reliance on petrochemical feedstocks and minimize the overall environmental footprint of product formulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!