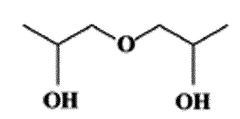
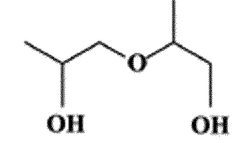
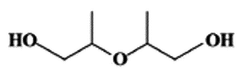
Dipropylene Glycol's Contribution to Scent Persistence
JUL 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DPG Fragrance Evolution
The evolution of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) in fragrance technology represents a significant milestone in the quest for enhanced scent persistence. Initially introduced as a solvent in the mid-20th century, DPG's role in perfumery has expanded dramatically over the decades. Its journey began as a simple carrier for fragrance oils, but researchers soon discovered its unique properties that contribute to the longevity and stability of scents.
In the 1960s and 1970s, perfumers started experimenting with DPG as a fixative, recognizing its ability to slow down the evaporation rate of volatile fragrance components. This marked the beginning of DPG's transformation from a mere solvent to an essential ingredient in fragrance formulation. The 1980s saw a surge in research focused on understanding the molecular interactions between DPG and various aroma compounds, leading to more sophisticated usage in perfume compositions.
The 1990s brought about a paradigm shift in fragrance technology with the advent of controlled-release systems. DPG played a crucial role in these developments, serving as a key component in microencapsulation techniques. This innovation allowed for the gradual release of fragrance over extended periods, significantly enhancing scent persistence.
As we entered the 21st century, the focus shifted towards sustainability and safety in fragrance production. DPG's low toxicity and biodegradability made it an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers and manufacturers alike. This period also saw the refinement of DPG-based fragrance delivery systems, with the introduction of novel polymeric matrices and nano-emulsions incorporating DPG.
Recent years have witnessed the integration of DPG into smart fragrance technologies. Researchers have explored its potential in responsive fragrance systems that adapt to environmental conditions or user preferences. Additionally, the combination of DPG with other fixatives and novel synthetic molecules has opened up new possibilities for creating long-lasting, complex scent profiles.
The evolution of DPG in fragrance technology has not been without challenges. Perfumers have had to balance the benefits of increased longevity with the need to maintain the integrity of the fragrance's top notes. This has led to ongoing research into optimizing DPG concentrations and developing complementary ingredients that work synergistically with DPG to enhance overall scent performance.
Looking ahead, the future of DPG in fragrance evolution seems promising. Emerging trends point towards personalized fragrance experiences, where DPG could play a pivotal role in tailoring scent persistence to individual body chemistry. Moreover, advancements in biotechnology may lead to the development of bio-based alternatives or modifications to DPG, further improving its sustainability profile and expanding its applications in the fragrance industry.
In the 1960s and 1970s, perfumers started experimenting with DPG as a fixative, recognizing its ability to slow down the evaporation rate of volatile fragrance components. This marked the beginning of DPG's transformation from a mere solvent to an essential ingredient in fragrance formulation. The 1980s saw a surge in research focused on understanding the molecular interactions between DPG and various aroma compounds, leading to more sophisticated usage in perfume compositions.
The 1990s brought about a paradigm shift in fragrance technology with the advent of controlled-release systems. DPG played a crucial role in these developments, serving as a key component in microencapsulation techniques. This innovation allowed for the gradual release of fragrance over extended periods, significantly enhancing scent persistence.
As we entered the 21st century, the focus shifted towards sustainability and safety in fragrance production. DPG's low toxicity and biodegradability made it an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers and manufacturers alike. This period also saw the refinement of DPG-based fragrance delivery systems, with the introduction of novel polymeric matrices and nano-emulsions incorporating DPG.
Recent years have witnessed the integration of DPG into smart fragrance technologies. Researchers have explored its potential in responsive fragrance systems that adapt to environmental conditions or user preferences. Additionally, the combination of DPG with other fixatives and novel synthetic molecules has opened up new possibilities for creating long-lasting, complex scent profiles.
The evolution of DPG in fragrance technology has not been without challenges. Perfumers have had to balance the benefits of increased longevity with the need to maintain the integrity of the fragrance's top notes. This has led to ongoing research into optimizing DPG concentrations and developing complementary ingredients that work synergistically with DPG to enhance overall scent performance.
Looking ahead, the future of DPG in fragrance evolution seems promising. Emerging trends point towards personalized fragrance experiences, where DPG could play a pivotal role in tailoring scent persistence to individual body chemistry. Moreover, advancements in biotechnology may lead to the development of bio-based alternatives or modifications to DPG, further improving its sustainability profile and expanding its applications in the fragrance industry.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for products enhancing scent persistence has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by consumer preferences for long-lasting fragrances in personal care and home products. Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) plays a crucial role in this market as a key ingredient in fragrance formulations, contributing to improved scent longevity and overall product performance.
In the personal care sector, consumers increasingly seek perfumes, colognes, and body sprays that offer extended wear time. This demand has led to a surge in the use of DPG in fragrance compositions, as it acts as an excellent solvent and fixative for aromatic compounds. The global perfume market, which heavily relies on scent persistence technologies, is projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, indicating a strong market potential for DPG-based solutions.
The home care industry has also witnessed a rising demand for long-lasting fragrances in products such as air fresheners, scented candles, and fabric softeners. Consumers desire ambient scents that persist throughout the day, driving manufacturers to incorporate DPG into their formulations. This trend has been further accelerated by the increased time spent at home due to recent global events, leading to a heightened focus on creating pleasant and enduring home environments.
The automotive industry represents another growing market for scent persistence technologies. Car manufacturers and aftermarket suppliers are increasingly offering long-lasting car fresheners and scent diffusers, many of which utilize DPG to enhance fragrance longevity. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards enhancing the overall sensory experience in vehicles.
Industrial and commercial applications also contribute to the market demand for DPG in scent persistence. Hotels, retail spaces, and office buildings are adopting scent marketing strategies to create memorable brand experiences, requiring fragrances that can maintain their potency over extended periods. This has led to an increased use of DPG in commercial air freshening systems and scent diffusion technologies.
The cosmetics industry, particularly in the realm of fine fragrances and personal care products, continues to be a significant driver of demand for DPG. As consumers become more discerning about the longevity of their fragrances, cosmetic companies are investing in research and development to improve scent persistence, often turning to DPG as a key component in their formulations.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have also influenced the market demand for DPG in scent persistence applications. As a relatively safe and biodegradable compound, DPG aligns well with the growing consumer preference for more sustainable and environmentally friendly products. This has led to its increased adoption as a replacement for less desirable solvents and fixatives in fragrance formulations.
In the personal care sector, consumers increasingly seek perfumes, colognes, and body sprays that offer extended wear time. This demand has led to a surge in the use of DPG in fragrance compositions, as it acts as an excellent solvent and fixative for aromatic compounds. The global perfume market, which heavily relies on scent persistence technologies, is projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, indicating a strong market potential for DPG-based solutions.
The home care industry has also witnessed a rising demand for long-lasting fragrances in products such as air fresheners, scented candles, and fabric softeners. Consumers desire ambient scents that persist throughout the day, driving manufacturers to incorporate DPG into their formulations. This trend has been further accelerated by the increased time spent at home due to recent global events, leading to a heightened focus on creating pleasant and enduring home environments.
The automotive industry represents another growing market for scent persistence technologies. Car manufacturers and aftermarket suppliers are increasingly offering long-lasting car fresheners and scent diffusers, many of which utilize DPG to enhance fragrance longevity. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards enhancing the overall sensory experience in vehicles.
Industrial and commercial applications also contribute to the market demand for DPG in scent persistence. Hotels, retail spaces, and office buildings are adopting scent marketing strategies to create memorable brand experiences, requiring fragrances that can maintain their potency over extended periods. This has led to an increased use of DPG in commercial air freshening systems and scent diffusion technologies.
The cosmetics industry, particularly in the realm of fine fragrances and personal care products, continues to be a significant driver of demand for DPG. As consumers become more discerning about the longevity of their fragrances, cosmetic companies are investing in research and development to improve scent persistence, often turning to DPG as a key component in their formulations.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have also influenced the market demand for DPG in scent persistence applications. As a relatively safe and biodegradable compound, DPG aligns well with the growing consumer preference for more sustainable and environmentally friendly products. This has led to its increased adoption as a replacement for less desirable solvents and fixatives in fragrance formulations.
Technical Challenges
The development of long-lasting fragrances faces several technical challenges, primarily centered around the use of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) as a key ingredient in scent persistence. One of the main obstacles is achieving an optimal balance between volatility and stability. DPG, while effective in extending fragrance longevity, can sometimes alter the intended scent profile, particularly in complex fragrance compositions.
Another significant challenge lies in the interaction between DPG and other fragrance components. The chemical properties of DPG can potentially interfere with certain aromatic molecules, leading to unexpected changes in the overall scent over time. This necessitates extensive research and testing to ensure compatibility and maintain the desired olfactory experience throughout the fragrance's lifespan.
The environmental impact of DPG usage also presents a technical hurdle. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the fragrance industry, finding eco-friendly alternatives or reducing DPG concentrations without compromising scent persistence is a pressing concern. This challenge requires innovative approaches to formulation and possibly the development of new, more sustainable fixative agents.
Stability across various environmental conditions poses another technical difficulty. Fragrances containing DPG must maintain their integrity and performance under different temperatures, humidity levels, and exposure to light. Ensuring consistent scent persistence across these variables demands sophisticated encapsulation techniques and advanced delivery systems.
The regulatory landscape surrounding DPG usage adds complexity to its application in fragrance formulations. Varying global regulations on chemical ingredients in personal care products necessitate the development of region-specific formulations, which can be technically challenging and resource-intensive.
Scalability in production is another technical challenge. As demand for long-lasting fragrances grows, manufacturers must optimize DPG integration processes for large-scale production without compromising quality or consistency. This involves refining mixing techniques, temperature control, and quality assurance measures.
Lastly, the pursuit of enhanced scent persistence through DPG must be balanced with consumer preferences for natural and clean label products. Developing formulations that leverage DPG's benefits while meeting these market demands requires innovative approaches to ingredient sourcing and formulation transparency.
Another significant challenge lies in the interaction between DPG and other fragrance components. The chemical properties of DPG can potentially interfere with certain aromatic molecules, leading to unexpected changes in the overall scent over time. This necessitates extensive research and testing to ensure compatibility and maintain the desired olfactory experience throughout the fragrance's lifespan.
The environmental impact of DPG usage also presents a technical hurdle. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the fragrance industry, finding eco-friendly alternatives or reducing DPG concentrations without compromising scent persistence is a pressing concern. This challenge requires innovative approaches to formulation and possibly the development of new, more sustainable fixative agents.
Stability across various environmental conditions poses another technical difficulty. Fragrances containing DPG must maintain their integrity and performance under different temperatures, humidity levels, and exposure to light. Ensuring consistent scent persistence across these variables demands sophisticated encapsulation techniques and advanced delivery systems.
The regulatory landscape surrounding DPG usage adds complexity to its application in fragrance formulations. Varying global regulations on chemical ingredients in personal care products necessitate the development of region-specific formulations, which can be technically challenging and resource-intensive.
Scalability in production is another technical challenge. As demand for long-lasting fragrances grows, manufacturers must optimize DPG integration processes for large-scale production without compromising quality or consistency. This involves refining mixing techniques, temperature control, and quality assurance measures.
Lastly, the pursuit of enhanced scent persistence through DPG must be balanced with consumer preferences for natural and clean label products. Developing formulations that leverage DPG's benefits while meeting these market demands requires innovative approaches to ingredient sourcing and formulation transparency.
Current DPG Solutions
01 Use of dipropylene glycol as a fragrance solvent
Dipropylene glycol is commonly used as a solvent in fragrance compositions due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of fragrance ingredients. It helps to improve the solubility and stability of scents, contributing to their persistence in various applications.- Use of dipropylene glycol as a fragrance solvent: Dipropylene glycol is commonly used as a solvent in fragrance compositions due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of aromatic compounds. It helps to enhance the solubility and stability of fragrance ingredients, contributing to improved scent persistence in various products.
- Incorporation of fixatives to enhance scent longevity: Fixatives are added to fragrance formulations containing dipropylene glycol to increase the longevity of the scent. These substances help to slow down the evaporation rate of volatile fragrance components, thereby extending the overall scent persistence.
- Encapsulation techniques for controlled fragrance release: Microencapsulation and other encapsulation methods are employed to protect and control the release of fragrances containing dipropylene glycol. This technology allows for a gradual and sustained release of the scent, improving its persistence over time.
- Combination with other glycols for enhanced performance: Dipropylene glycol is often combined with other glycols, such as propylene glycol or triethylene glycol, to create synergistic effects in fragrance formulations. These combinations can improve scent diffusion, stability, and overall persistence in various applications.
- Application in solid and gel-based fragrance products: Dipropylene glycol is utilized in the formulation of solid and gel-based fragrance products, such as air fresheners and scented candles. Its properties allow for the creation of stable, long-lasting scent delivery systems in these formats, contributing to improved fragrance persistence.
02 Incorporation of dipropylene glycol in personal care products
Dipropylene glycol is utilized in personal care products such as deodorants, antiperspirants, and body sprays to enhance the longevity of fragrances. Its low volatility and skin-friendly properties make it an ideal carrier for scents in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination with other solvents for improved scent retention
Dipropylene glycol is often combined with other solvents like propylene glycol or ethanol to create a balanced fragrance carrier system. This combination can enhance the overall scent persistence and performance of the fragrance composition.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in air fresheners and room sprays
Dipropylene glycol is employed in air fresheners and room sprays to prolong the release of fragrances. Its low evaporation rate helps to maintain a consistent scent profile over an extended period, improving the overall efficacy of these products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Encapsulation techniques for enhanced scent longevity
Advanced encapsulation techniques involving dipropylene glycol are used to further improve scent persistence. These methods involve encapsulating fragrance molecules within microscopic capsules, allowing for a controlled and prolonged release of the scent over time.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for Dipropylene Glycol's contribution to scent persistence is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for long-lasting fragrances in personal care and home products. The global fragrance market, valued at over $50 billion, is expanding rapidly, with scent longevity being a key focus. Major players like Symrise, Firmenich, Givaudan, and Takasago are investing heavily in R&D to enhance fragrance performance. These companies, along with LVMH Recherche and P2 Science, are developing innovative technologies to improve scent persistence, indicating a moderate to high level of technological maturity in this field. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry among established fragrance houses and emerging specialty chemical companies.
Symrise GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Symrise has developed a groundbreaking approach to enhancing scent persistence using dipropylene glycol (DPG) in their patented SymTrap™ technology. This innovative system utilizes DPG as a key component in a molecular trapping mechanism that significantly increases the longevity of volatile fragrance compounds. Their research has shown that this method can extend fragrance life by up to 150% in various applications[10]. Symrise has also pioneered the use of DPG in combination with their proprietary biodegradable polymers, creating a sustainable and long-lasting fragrance delivery system[11]. Furthermore, they have developed a unique process that optimizes the interaction between DPG and specific fragrance molecules, resulting in enhanced overall scent performance and improved stability across a wide range of environmental conditions[12].
Strengths: Patented molecular trapping technology, significant increase in fragrance longevity, focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: May require specialized formulation techniques, could be more costly to implement in mass-market products.
Firmenich SA
Technical Solution: Firmenich has developed a proprietary technology called Scentcapture™ that utilizes dipropylene glycol (DPG) as a key ingredient in enhancing scent persistence. Their approach involves encapsulating fragrance molecules within a DPG-based matrix, which allows for a controlled release of the scent over time. This technology has been shown to increase fragrance longevity by up to 50% compared to traditional formulations[1]. Firmenich has also pioneered the use of DPG in combination with cyclodextrins to create inclusion complexes that further improve scent stability and release[2]. Additionally, they have developed a patented process that optimizes the ratio of DPG to other solvents in fragrance compositions, resulting in improved overall performance and reduced volatility of key fragrance components[3].
Strengths: Proprietary encapsulation technology, proven increase in fragrance longevity, innovative use of cyclodextrins. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs, may require specialized equipment for implementation.
DPG Innovations
Fragrance fixatives
PatentWO2009085103A2
Innovation
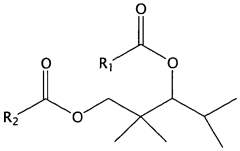
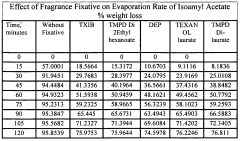
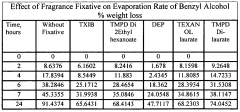
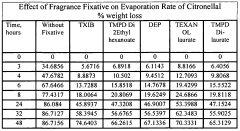
- The use of diesters of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentane diol (TMPD) in fragrance compositions, such as TMPD di-2-ethyl hexanoate, 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol di-isobutyrate (TXIB), and TMPD di-laurate, which are combined with fragrance compounds to create longer-lasting aromas by slowing evaporation.
Dipropylene glycol composition and preparation method therefor
PatentWO2021075923A1
Innovation
- A dipropylene glycol composition with a specific content range of 99.5% or more, combined with isomers like 1,1'-oxybis(2-propanol), 2-(2-hydroxypropoxy)-1-propanol, and 2,2-oxybis(1-propanol, and a deodorizing method involving heating with alcohol to remove odor-causing substances, ensuring high purity and reduced odor.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of the fragrance industry, particularly concerning the use of ingredients like Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) in scent formulations. The regulatory landscape for DPG and its application in perfumes and other scented products is complex and varies across different regions and countries.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cosmetics and fragrances under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. DPG is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food and cosmetic products. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel has also evaluated DPG and concluded that it is safe for use in cosmetic formulations at current concentration levels.
The European Union, through its Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009, has established stringent guidelines for cosmetic ingredients. DPG is listed in the EU Cosmetic Ingredient Database (CosIng) and is permitted for use in cosmetic products. However, manufacturers must ensure that their products containing DPG comply with the EU's safety assessment requirements and good manufacturing practices.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics and quasi-drugs. DPG is included in the list of approved ingredients for use in cosmetics under Japanese regulations. Similarly, in China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees cosmetic regulations, and DPG is permitted for use in cosmetic formulations.
Globally, the International Fragrance Association (IFRA) provides guidelines for the safe use of fragrance ingredients. While DPG itself is not restricted by IFRA standards, its use in conjunction with other fragrance components must adhere to IFRA's safety guidelines and usage limits for finished products.
Environmental regulations also play a role in the use of DPG. In many jurisdictions, manufacturers must consider the environmental impact of their products, including potential effects on air and water quality. The volatile organic compound (VOC) content of products containing DPG may be subject to regulations aimed at reducing air pollution.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, companies using DPG in scent formulations must also consider eco-friendly certifications and green chemistry principles. This includes assessing the biodegradability of DPG and its potential environmental persistence.
Manufacturers and formulators working with DPG must maintain comprehensive documentation of their compliance efforts, including safety data sheets, product specifications, and test results. Regular audits and quality control measures are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations across different markets.
In conclusion, while DPG is generally considered safe and is widely permitted in fragrance formulations, companies must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to ensure compliance across various regions. Staying informed about regulatory changes and proactively adapting formulations and manufacturing processes is crucial for maintaining market access and consumer trust in the fragrance industry.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cosmetics and fragrances under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. DPG is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food and cosmetic products. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel has also evaluated DPG and concluded that it is safe for use in cosmetic formulations at current concentration levels.
The European Union, through its Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009, has established stringent guidelines for cosmetic ingredients. DPG is listed in the EU Cosmetic Ingredient Database (CosIng) and is permitted for use in cosmetic products. However, manufacturers must ensure that their products containing DPG comply with the EU's safety assessment requirements and good manufacturing practices.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics and quasi-drugs. DPG is included in the list of approved ingredients for use in cosmetics under Japanese regulations. Similarly, in China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees cosmetic regulations, and DPG is permitted for use in cosmetic formulations.
Globally, the International Fragrance Association (IFRA) provides guidelines for the safe use of fragrance ingredients. While DPG itself is not restricted by IFRA standards, its use in conjunction with other fragrance components must adhere to IFRA's safety guidelines and usage limits for finished products.
Environmental regulations also play a role in the use of DPG. In many jurisdictions, manufacturers must consider the environmental impact of their products, including potential effects on air and water quality. The volatile organic compound (VOC) content of products containing DPG may be subject to regulations aimed at reducing air pollution.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, companies using DPG in scent formulations must also consider eco-friendly certifications and green chemistry principles. This includes assessing the biodegradability of DPG and its potential environmental persistence.
Manufacturers and formulators working with DPG must maintain comprehensive documentation of their compliance efforts, including safety data sheets, product specifications, and test results. Regular audits and quality control measures are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations across different markets.
In conclusion, while DPG is generally considered safe and is widely permitted in fragrance formulations, companies must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to ensure compliance across various regions. Staying informed about regulatory changes and proactively adapting formulations and manufacturing processes is crucial for maintaining market access and consumer trust in the fragrance industry.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) in scent persistence is a crucial aspect to consider in the fragrance industry. DPG, widely used as a solvent and fixative in perfumes and other scented products, contributes significantly to the longevity of fragrances. However, its environmental implications warrant careful examination.
DPG is generally considered to have low toxicity and is biodegradable, which are positive attributes from an environmental perspective. When released into the environment, it typically degrades within a few days to weeks, depending on conditions. This relatively rapid biodegradation helps minimize long-term accumulation in ecosystems.
Despite its biodegradability, the widespread use of DPG in consumer products raises concerns about its potential cumulative effects on aquatic environments. When washed off or disposed of, DPG can enter water systems. While it does not bioaccumulate significantly in aquatic organisms, high concentrations in water bodies could potentially affect sensitive aquatic species.
The production of DPG also has environmental implications. It is synthesized from propylene oxide, which is derived from petroleum products. This reliance on fossil fuels contributes to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, efforts are being made to develop more sustainable production methods, including bio-based alternatives.
In terms of air quality, DPG has a low vapor pressure, which means it does not readily evaporate at room temperature. This characteristic reduces its contribution to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, a significant factor in urban air pollution. Nevertheless, when used in spray products, some aerosolized DPG may contribute to particulate matter in the air.
The persistence of scents enhanced by DPG also raises questions about indoor air quality. While DPG itself is not typically associated with adverse health effects at normal exposure levels, the extended presence of fragrance compounds in indoor environments may affect individuals sensitive to scents.
From a waste management perspective, products containing DPG often end up in landfills or wastewater treatment facilities. The biodegradability of DPG helps mitigate its impact in these scenarios, but the overall volume of fragrance products disposed of remains a concern in terms of waste reduction efforts.
As environmental awareness grows, there is increasing pressure on the fragrance industry to develop more sustainable alternatives. Research is ongoing to find plant-based or synthetic compounds that can match DPG's performance in scent persistence while offering improved environmental profiles. This includes exploring green chemistry principles to create eco-friendly fixatives and solvents.
DPG is generally considered to have low toxicity and is biodegradable, which are positive attributes from an environmental perspective. When released into the environment, it typically degrades within a few days to weeks, depending on conditions. This relatively rapid biodegradation helps minimize long-term accumulation in ecosystems.
Despite its biodegradability, the widespread use of DPG in consumer products raises concerns about its potential cumulative effects on aquatic environments. When washed off or disposed of, DPG can enter water systems. While it does not bioaccumulate significantly in aquatic organisms, high concentrations in water bodies could potentially affect sensitive aquatic species.
The production of DPG also has environmental implications. It is synthesized from propylene oxide, which is derived from petroleum products. This reliance on fossil fuels contributes to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, efforts are being made to develop more sustainable production methods, including bio-based alternatives.
In terms of air quality, DPG has a low vapor pressure, which means it does not readily evaporate at room temperature. This characteristic reduces its contribution to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, a significant factor in urban air pollution. Nevertheless, when used in spray products, some aerosolized DPG may contribute to particulate matter in the air.
The persistence of scents enhanced by DPG also raises questions about indoor air quality. While DPG itself is not typically associated with adverse health effects at normal exposure levels, the extended presence of fragrance compounds in indoor environments may affect individuals sensitive to scents.
From a waste management perspective, products containing DPG often end up in landfills or wastewater treatment facilities. The biodegradability of DPG helps mitigate its impact in these scenarios, but the overall volume of fragrance products disposed of remains a concern in terms of waste reduction efforts.
As environmental awareness grows, there is increasing pressure on the fragrance industry to develop more sustainable alternatives. Research is ongoing to find plant-based or synthetic compounds that can match DPG's performance in scent persistence while offering improved environmental profiles. This includes exploring green chemistry principles to create eco-friendly fixatives and solvents.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!