Evaluation of lithium orotate in augmenting psychotherapy outcomes
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Research Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic applications in mental health. This organic salt form of lithium has been the subject of increasing research due to its purported ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than traditional lithium carbonate, potentially offering enhanced neurological benefits with fewer side effects.
The historical context of lithium in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. Since then, lithium has become a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other mood disorders. However, the conventional lithium carbonate formulation has been associated with various side effects and requires careful monitoring of blood levels, limiting its widespread use.
Lithium orotate emerged as an alternative form, with proponents claiming it could deliver therapeutic benefits at lower doses. This has sparked interest in its potential to augment psychotherapy outcomes, particularly in cases where traditional lithium treatment may be contraindicated or poorly tolerated.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate as an adjunct to psychotherapy in improving mental health outcomes. Specifically, this investigation aims to:
1. Assess the impact of lithium orotate on the effectiveness of various psychotherapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, interpersonal therapy, and dialectical behavior therapy.
2. Examine the potential of lithium orotate to enhance mood stability, cognitive function, and overall well-being in patients undergoing psychotherapy for mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and other mental health conditions.
3. Compare the side effect profile and tolerability of lithium orotate to traditional lithium formulations when used in conjunction with psychotherapy.
4. Investigate the optimal dosing regimens and duration of lithium orotate supplementation to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential risks.
5. Explore the neurobiological mechanisms through which lithium orotate may exert its effects on brain function and mental health, particularly in the context of psychotherapy.
By addressing these objectives, this research aims to contribute to the growing body of knowledge on alternative lithium formulations and their potential role in enhancing the outcomes of psychotherapeutic interventions. The findings could have significant implications for the future of mental health treatment, potentially offering a more accessible and tolerable option for lithium supplementation in psychotherapy.
The historical context of lithium in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. Since then, lithium has become a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other mood disorders. However, the conventional lithium carbonate formulation has been associated with various side effects and requires careful monitoring of blood levels, limiting its widespread use.
Lithium orotate emerged as an alternative form, with proponents claiming it could deliver therapeutic benefits at lower doses. This has sparked interest in its potential to augment psychotherapy outcomes, particularly in cases where traditional lithium treatment may be contraindicated or poorly tolerated.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate as an adjunct to psychotherapy in improving mental health outcomes. Specifically, this investigation aims to:
1. Assess the impact of lithium orotate on the effectiveness of various psychotherapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, interpersonal therapy, and dialectical behavior therapy.
2. Examine the potential of lithium orotate to enhance mood stability, cognitive function, and overall well-being in patients undergoing psychotherapy for mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and other mental health conditions.
3. Compare the side effect profile and tolerability of lithium orotate to traditional lithium formulations when used in conjunction with psychotherapy.
4. Investigate the optimal dosing regimens and duration of lithium orotate supplementation to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential risks.
5. Explore the neurobiological mechanisms through which lithium orotate may exert its effects on brain function and mental health, particularly in the context of psychotherapy.
By addressing these objectives, this research aims to contribute to the growing body of knowledge on alternative lithium formulations and their potential role in enhancing the outcomes of psychotherapeutic interventions. The findings could have significant implications for the future of mental health treatment, potentially offering a more accessible and tolerable option for lithium supplementation in psychotherapy.
Market Analysis for Psychotherapy Augmentation
The market for psychotherapy augmentation, particularly focusing on the use of lithium orotate, is experiencing significant growth and transformation. This expansion is driven by the increasing prevalence of mental health disorders globally and the growing recognition of the limitations of traditional psychotherapy approaches. The demand for more effective and efficient treatment options has created a fertile ground for innovative solutions that can enhance therapeutic outcomes.
Lithium orotate, as a potential augmentation strategy for psychotherapy, is garnering attention due to its purported benefits in mood stabilization and cognitive enhancement. The market for this compound is still in its nascent stages, but it shows promise for substantial growth in the coming years. Current estimates suggest that the global market for psychotherapy augmentation techniques, including pharmacological interventions, could reach several billion dollars by 2025.
The target demographic for lithium orotate as a psychotherapy augmentation tool primarily includes individuals with treatment-resistant depression, bipolar disorder, and other mood disorders. Additionally, there is growing interest in its potential applications for anxiety disorders and cognitive decline. This broad spectrum of potential applications significantly expands the market potential for lithium orotate.
Key market drivers include the rising awareness of mental health issues, the increasing acceptance of complementary and alternative medicine approaches, and the growing body of research supporting the efficacy of lithium compounds in psychiatric treatment. Furthermore, the shift towards personalized medicine in psychiatry is creating opportunities for tailored augmentation strategies, potentially boosting the demand for novel compounds like lithium orotate.
However, the market also faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles are significant barriers to widespread adoption. Additionally, competition from established pharmaceutical interventions and other emerging augmentation techniques could impact market penetration.
Geographically, North America and Europe are expected to dominate the market for psychotherapy augmentation, including lithium orotate, due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher awareness of mental health treatments. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific regions, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups focusing on novel psychotherapy augmentation techniques. Collaborations between research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and mental health providers are becoming increasingly common, driving innovation and market expansion.
Lithium orotate, as a potential augmentation strategy for psychotherapy, is garnering attention due to its purported benefits in mood stabilization and cognitive enhancement. The market for this compound is still in its nascent stages, but it shows promise for substantial growth in the coming years. Current estimates suggest that the global market for psychotherapy augmentation techniques, including pharmacological interventions, could reach several billion dollars by 2025.
The target demographic for lithium orotate as a psychotherapy augmentation tool primarily includes individuals with treatment-resistant depression, bipolar disorder, and other mood disorders. Additionally, there is growing interest in its potential applications for anxiety disorders and cognitive decline. This broad spectrum of potential applications significantly expands the market potential for lithium orotate.
Key market drivers include the rising awareness of mental health issues, the increasing acceptance of complementary and alternative medicine approaches, and the growing body of research supporting the efficacy of lithium compounds in psychiatric treatment. Furthermore, the shift towards personalized medicine in psychiatry is creating opportunities for tailored augmentation strategies, potentially boosting the demand for novel compounds like lithium orotate.
However, the market also faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles are significant barriers to widespread adoption. Additionally, competition from established pharmaceutical interventions and other emerging augmentation techniques could impact market penetration.
Geographically, North America and Europe are expected to dominate the market for psychotherapy augmentation, including lithium orotate, due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher awareness of mental health treatments. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific regions, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups focusing on novel psychotherapy augmentation techniques. Collaborations between research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and mental health providers are becoming increasingly common, driving innovation and market expansion.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium Orotate Research
The current status of lithium orotate research in augmenting psychotherapy outcomes is characterized by a mix of promising preliminary findings and significant challenges. While lithium has long been established as an effective treatment for bipolar disorder, the specific use of lithium orotate in psychotherapy contexts is still in its early stages of investigation.
Recent studies have shown potential benefits of lithium orotate in enhancing cognitive function and mood stability, which could theoretically improve psychotherapy outcomes. However, the research is limited in scope and scale, with most studies involving small sample sizes and short durations. This lack of large-scale, long-term clinical trials presents a significant challenge in establishing the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate as an adjunct to psychotherapy.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the regulatory landscape. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is FDA-approved for bipolar disorder, lithium orotate is classified as a dietary supplement in many countries, including the United States. This classification has led to less rigorous oversight and standardization in its production and use, making it difficult to conduct controlled studies and draw definitive conclusions about its effects.
Another critical challenge is the lack of standardized dosing protocols for lithium orotate in psychotherapy settings. The optimal dosage for augmenting psychotherapy outcomes may differ from its use in other contexts, and determining this requires extensive research that has yet to be conducted. Additionally, the potential interactions between lithium orotate and other medications commonly used in mental health treatment remain largely unexplored.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate in the context of psychotherapy is another area requiring further investigation. While the general effects of lithium on neurotransmitter systems and neuroplasticity are well-documented, the specific impact of the orotate form on these processes in relation to psychotherapy outcomes is not fully understood. This gap in knowledge hinders the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
Ethical considerations also pose challenges in lithium orotate research. The use of a supplement to enhance psychotherapy outcomes raises questions about the nature of therapeutic change and the potential for creating dependency on chemical augmentation. Balancing the potential benefits with these ethical concerns requires careful consideration and robust ethical frameworks for research and clinical practice.
Despite these challenges, there is growing interest in the potential of lithium orotate to enhance psychotherapy outcomes. Preliminary research suggests it may offer benefits with fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium formulations. However, overcoming the current challenges will require a concerted effort from researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies to establish a solid evidence base and clear guidelines for its use in psychotherapy contexts.
Recent studies have shown potential benefits of lithium orotate in enhancing cognitive function and mood stability, which could theoretically improve psychotherapy outcomes. However, the research is limited in scope and scale, with most studies involving small sample sizes and short durations. This lack of large-scale, long-term clinical trials presents a significant challenge in establishing the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate as an adjunct to psychotherapy.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the regulatory landscape. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is FDA-approved for bipolar disorder, lithium orotate is classified as a dietary supplement in many countries, including the United States. This classification has led to less rigorous oversight and standardization in its production and use, making it difficult to conduct controlled studies and draw definitive conclusions about its effects.
Another critical challenge is the lack of standardized dosing protocols for lithium orotate in psychotherapy settings. The optimal dosage for augmenting psychotherapy outcomes may differ from its use in other contexts, and determining this requires extensive research that has yet to be conducted. Additionally, the potential interactions between lithium orotate and other medications commonly used in mental health treatment remain largely unexplored.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate in the context of psychotherapy is another area requiring further investigation. While the general effects of lithium on neurotransmitter systems and neuroplasticity are well-documented, the specific impact of the orotate form on these processes in relation to psychotherapy outcomes is not fully understood. This gap in knowledge hinders the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
Ethical considerations also pose challenges in lithium orotate research. The use of a supplement to enhance psychotherapy outcomes raises questions about the nature of therapeutic change and the potential for creating dependency on chemical augmentation. Balancing the potential benefits with these ethical concerns requires careful consideration and robust ethical frameworks for research and clinical practice.
Despite these challenges, there is growing interest in the potential of lithium orotate to enhance psychotherapy outcomes. Preliminary research suggests it may offer benefits with fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium formulations. However, overcoming the current challenges will require a concerted effort from researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies to establish a solid evidence base and clear guidelines for its use in psychotherapy contexts.
Existing Protocols for Lithium Orotate in Psychotherapy
01 Use of lithium orotate in psychotherapy
Lithium orotate is being investigated for its potential benefits in psychotherapy outcomes. This compound may have mood-stabilizing properties and could be used as an adjunct to traditional psychotherapy methods. Research suggests it may help improve treatment outcomes for various mental health conditions.- Lithium orotate in psychiatric treatment: Lithium orotate is being investigated for its potential in treating various psychiatric conditions. It may offer improved bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. Research suggests it could be effective in managing mood disorders, depression, and anxiety, potentially leading to better psychotherapy outcomes.
- Combination therapy with lithium orotate: Combining lithium orotate with other therapeutic approaches may enhance psychotherapy outcomes. This could include pairing it with cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness practices, or other pharmacological interventions. The synergistic effect may lead to improved treatment efficacy and patient response rates.
- Monitoring and assessment of lithium orotate therapy: Effective use of lithium orotate in psychotherapy requires careful monitoring and assessment. This includes tracking patient progress, adjusting dosages, and evaluating potential side effects. Advanced monitoring techniques and assessment tools may be developed to optimize treatment outcomes and ensure patient safety.
- Personalized treatment approaches with lithium orotate: Tailoring lithium orotate treatment to individual patient needs may improve psychotherapy outcomes. This could involve genetic testing, biomarker analysis, or other personalized medicine approaches to determine optimal dosing and treatment strategies for each patient.
- Integration of lithium orotate in digital mental health platforms: Incorporating lithium orotate treatment into digital mental health platforms and telemedicine services may enhance accessibility and effectiveness of psychotherapy. This could include remote monitoring, virtual therapy sessions, and AI-assisted treatment planning to optimize outcomes for patients using lithium orotate as part of their mental health care.
02 Combination of lithium orotate with other therapeutic approaches
Studies are exploring the synergistic effects of combining lithium orotate with other therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or mindfulness-based interventions. This combination may enhance overall treatment efficacy and lead to improved psychotherapy outcomes for patients with mood disorders or anxiety.Expand Specific Solutions03 Monitoring and assessment of lithium orotate effects
Researchers are developing methods to monitor and assess the effects of lithium orotate on psychotherapy outcomes. This includes the use of biomarkers, neuroimaging techniques, and standardized psychological assessments to measure changes in mood, cognitive function, and overall mental health status during treatment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Personalized dosing and administration of lithium orotate
Efforts are being made to develop personalized dosing and administration protocols for lithium orotate in psychotherapy. This involves considering individual patient factors such as genetics, metabolism, and specific mental health conditions to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize potential side effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of lithium orotate in digital mental health interventions
Researchers are exploring the integration of lithium orotate treatment with digital mental health interventions, such as mobile apps or teletherapy platforms. This combination aims to enhance psychotherapy outcomes by providing comprehensive, accessible, and personalized mental health support to patients.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Psychopharmacology and Psychotherapy
The evaluation of lithium orotate in augmenting psychotherapy outcomes is an emerging field in the intersection of psychiatry and pharmacology. The competitive landscape is characterized by early-stage research and development, with limited market penetration. The global market for lithium-based treatments in mental health is growing, driven by increasing awareness and demand for novel therapies. Key players in this space include established pharmaceutical companies like H. Lundbeck A/S and Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, as well as research institutions such as the University of South Florida and Emory University. The technology is still in its infancy, with ongoing clinical trials and studies to determine efficacy and safety profiles, indicating a low to moderate level of technological maturity.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S is exploring the potential of lithium orotate as a novel mood stabilizer in combination with psychotherapy. Their approach involves developing a proprietary formulation of lithium orotate designed to enhance bioavailability and reduce side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate[4]. The company is conducting preclinical studies to evaluate the neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate and its potential synergistic effects with various psychotherapeutic modalities[5]. Lundbeck is also investigating the use of pharmacogenomic markers to identify patients most likely to benefit from lithium orotate augmentation in psychotherapy[6].
Strengths: Strong pharmaceutical development capabilities and global distribution network. Established presence in the psychiatric medication market. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory hurdles in bringing a new lithium formulation to market.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV is investigating the use of lithium orotate as part of a combination therapy approach to enhance psychotherapy outcomes. Their research focuses on developing a novel drug delivery system for lithium orotate that allows for controlled release and targeted action in specific brain regions[7]. The company is conducting phase II clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of their lithium orotate formulation when used in conjunction with cognitive-behavioral therapy for treatment-resistant depression[8]. Janssen is also exploring the potential of lithium orotate in modulating neuroplasticity and enhancing the effects of psychotherapy in patients with bipolar disorder[9].
Strengths: Extensive experience in psychiatric drug development and clinical trials. Robust research and development infrastructure. Weaknesses: Potential competition from existing mood stabilizers in their product portfolio.
Core Studies on Lithium Orotate Efficacy
System and Method of Reducing Impairment of Alertness, Concentration, Motivation, and Creativity Caused by Medication
PatentInactiveUS20130337052A1
Innovation
- Administering a therapeutically effective dose of lithium ions, either alone or in combination with cannabinoids, to mitigate these side effects, potentially through various delivery vehicles like pills, gelcaps, or food, to enhance alertness, concentration, and motivation.
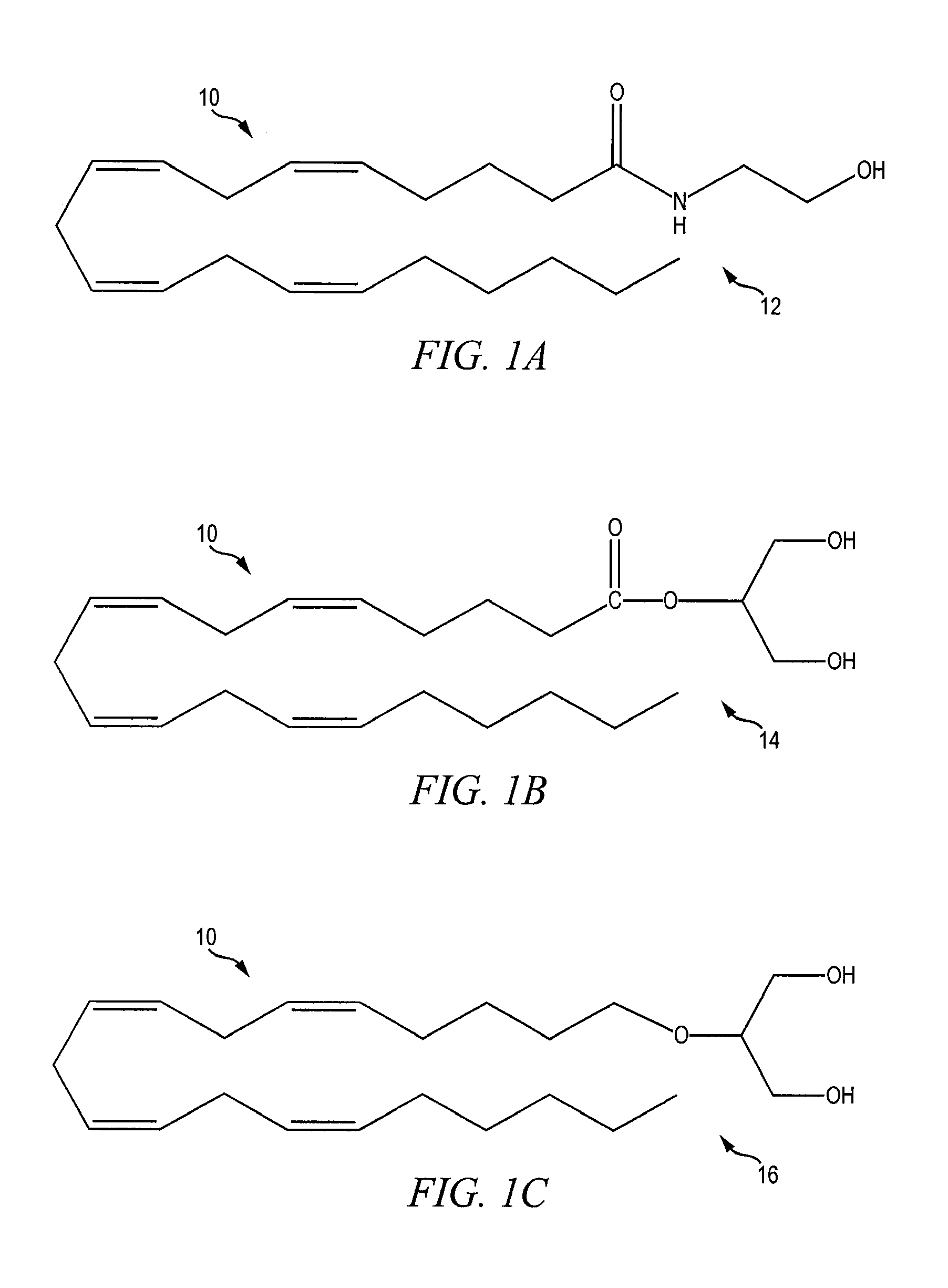
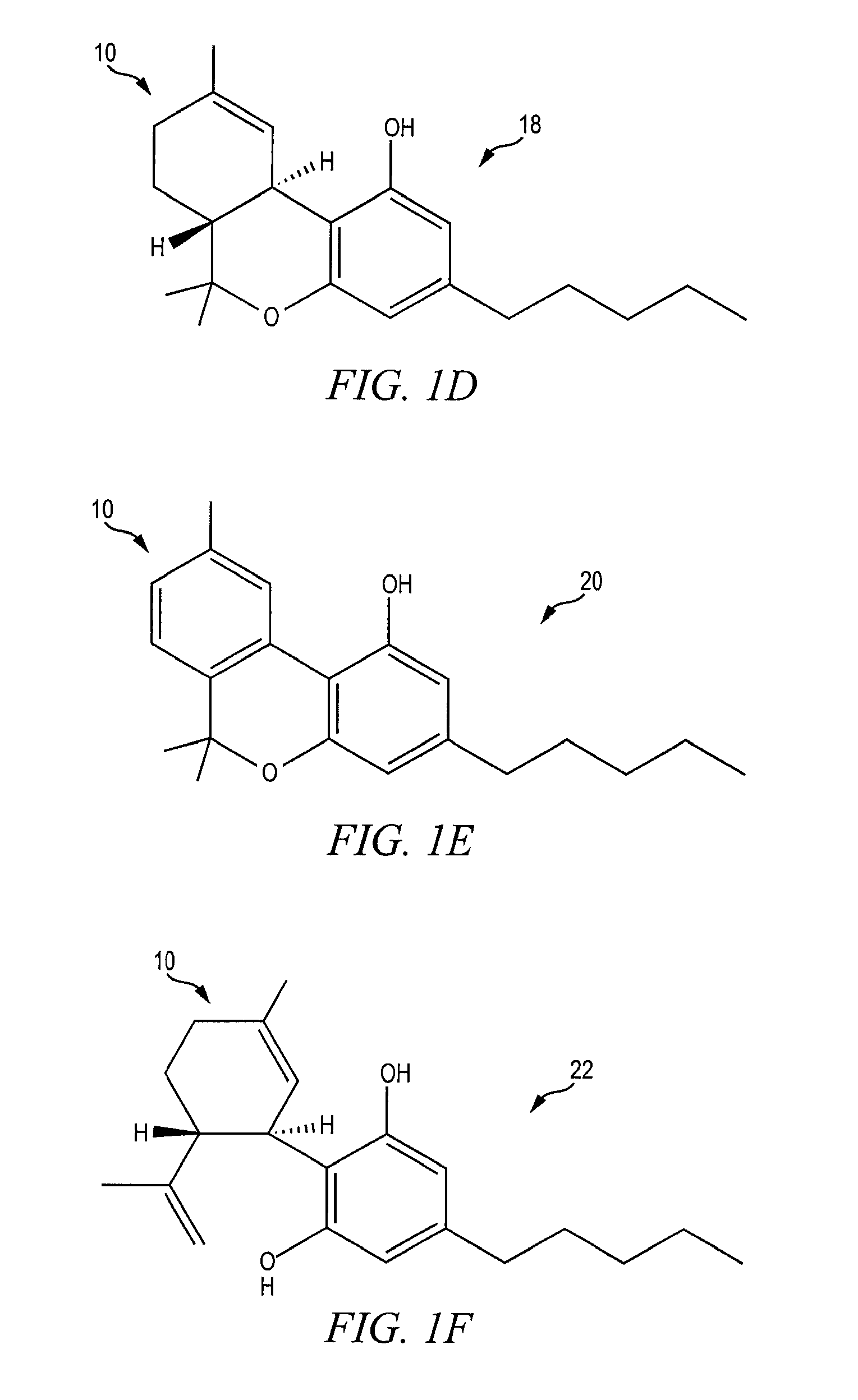
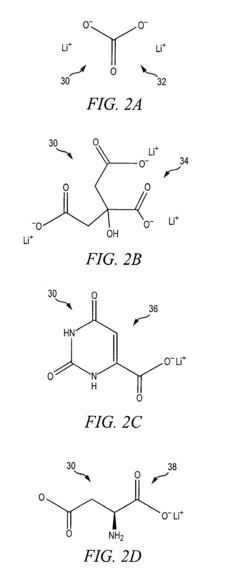
Compositions and methods and uses relating thereto
PatentActiveUS20230234972A1
Innovation
- Development of stable crystalline forms of lithium as anhydrous coordination polymers with organic acid conjugate bases, which provide improved stability, reduced toxicity, and enhanced brain bioavailability, allowing for a more controlled release and improved therapeutic window.
Regulatory Framework for Nutraceuticals in Psychotherapy
The regulatory framework for nutraceuticals in psychotherapy is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful consideration. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the regulation of nutraceuticals, including lithium orotate, when used in conjunction with psychotherapy. The FDA classifies most nutraceuticals as dietary supplements, which fall under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before they are marketed. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before selling dietary supplements. This regulatory approach allows for greater market access but also places a significant burden on manufacturers to maintain product safety and quality.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) also plays a role in regulating nutraceuticals by monitoring advertising claims. The FTC requires that all health claims made about nutraceuticals be substantiated by scientific evidence. This is particularly relevant when considering the use of lithium orotate in augmenting psychotherapy outcomes, as any claims regarding its efficacy must be supported by robust clinical data.
In the context of psychotherapy, the use of nutraceuticals like lithium orotate falls into a regulatory gray area. While psychotherapy itself is regulated by state licensing boards and professional organizations, the integration of nutraceuticals into treatment protocols is not as clearly defined. Mental health professionals must navigate the ethical and legal implications of recommending or prescribing nutraceuticals as part of their practice.
The European Union (EU) has a different regulatory approach to nutraceuticals. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of food supplements, including those used in conjunction with psychotherapy. The EU's regulatory framework is generally more stringent, requiring pre-market authorization for certain health claims and novel food ingredients.
In both the US and EU, there is growing recognition of the need for more specific regulations regarding the use of nutraceuticals in mental health treatment. This has led to calls for increased research and the development of guidelines for the integration of nutraceuticals into psychotherapy practices. As the field evolves, it is likely that regulatory bodies will need to adapt their frameworks to address the unique challenges posed by the intersection of nutraceuticals and mental health treatment.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before they are marketed. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before selling dietary supplements. This regulatory approach allows for greater market access but also places a significant burden on manufacturers to maintain product safety and quality.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) also plays a role in regulating nutraceuticals by monitoring advertising claims. The FTC requires that all health claims made about nutraceuticals be substantiated by scientific evidence. This is particularly relevant when considering the use of lithium orotate in augmenting psychotherapy outcomes, as any claims regarding its efficacy must be supported by robust clinical data.
In the context of psychotherapy, the use of nutraceuticals like lithium orotate falls into a regulatory gray area. While psychotherapy itself is regulated by state licensing boards and professional organizations, the integration of nutraceuticals into treatment protocols is not as clearly defined. Mental health professionals must navigate the ethical and legal implications of recommending or prescribing nutraceuticals as part of their practice.
The European Union (EU) has a different regulatory approach to nutraceuticals. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of food supplements, including those used in conjunction with psychotherapy. The EU's regulatory framework is generally more stringent, requiring pre-market authorization for certain health claims and novel food ingredients.
In both the US and EU, there is growing recognition of the need for more specific regulations regarding the use of nutraceuticals in mental health treatment. This has led to calls for increased research and the development of guidelines for the integration of nutraceuticals into psychotherapy practices. As the field evolves, it is likely that regulatory bodies will need to adapt their frameworks to address the unique challenges posed by the intersection of nutraceuticals and mental health treatment.
Ethical Considerations in Psychotherapy Augmentation
The ethical considerations surrounding the use of lithium orotate to augment psychotherapy outcomes are complex and multifaceted. One primary concern is the potential for coercion or undue influence on patients to participate in such augmentation. Therapists must ensure that patients have full autonomy in decision-making and are not pressured to use lithium orotate as part of their treatment.
Another critical ethical issue is informed consent. Patients must be thoroughly educated about the potential risks, benefits, and alternatives to using lithium orotate. This includes discussing the current state of research, known side effects, and any uncertainties regarding long-term use. Therapists have an ethical obligation to provide accurate, up-to-date information to enable patients to make informed choices about their treatment.
Privacy and confidentiality are also paramount ethical considerations. The use of lithium orotate in psychotherapy may involve additional medical monitoring and data collection. Therapists must ensure that patient information is protected and that any data sharing for research purposes is done with explicit consent and in compliance with relevant privacy laws and regulations.
The principle of non-maleficence, or "do no harm," is particularly relevant when considering the use of lithium orotate. Given that this compound is not as well-studied as other forms of lithium, therapists must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of adverse effects or interactions with other medications. Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential to minimize potential harm to patients.
Equity and access are important ethical considerations as well. If lithium orotate proves to be an effective augmentation to psychotherapy, there may be concerns about its availability and affordability. Therapists and healthcare systems must consider how to ensure fair access to this treatment option across different socioeconomic groups.
The ethical implications of off-label use must also be addressed. As lithium orotate is not FDA-approved for mental health treatment, therapists must carefully consider the ethical justification for its use and ensure that patients understand its status as an experimental or alternative treatment.
Lastly, there are ethical considerations related to professional boundaries and competence. Therapists recommending or administering lithium orotate must have adequate training and knowledge about its use. They should also be prepared to collaborate with other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive care and monitoring for patients using this augmentation strategy.
Another critical ethical issue is informed consent. Patients must be thoroughly educated about the potential risks, benefits, and alternatives to using lithium orotate. This includes discussing the current state of research, known side effects, and any uncertainties regarding long-term use. Therapists have an ethical obligation to provide accurate, up-to-date information to enable patients to make informed choices about their treatment.
Privacy and confidentiality are also paramount ethical considerations. The use of lithium orotate in psychotherapy may involve additional medical monitoring and data collection. Therapists must ensure that patient information is protected and that any data sharing for research purposes is done with explicit consent and in compliance with relevant privacy laws and regulations.
The principle of non-maleficence, or "do no harm," is particularly relevant when considering the use of lithium orotate. Given that this compound is not as well-studied as other forms of lithium, therapists must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of adverse effects or interactions with other medications. Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential to minimize potential harm to patients.
Equity and access are important ethical considerations as well. If lithium orotate proves to be an effective augmentation to psychotherapy, there may be concerns about its availability and affordability. Therapists and healthcare systems must consider how to ensure fair access to this treatment option across different socioeconomic groups.
The ethical implications of off-label use must also be addressed. As lithium orotate is not FDA-approved for mental health treatment, therapists must carefully consider the ethical justification for its use and ensure that patients understand its status as an experimental or alternative treatment.
Lastly, there are ethical considerations related to professional boundaries and competence. Therapists recommending or administering lithium orotate must have adequate training and knowledge about its use. They should also be prepared to collaborate with other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive care and monitoring for patients using this augmentation strategy.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!