The role of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential role in managing metabolic syndrome. This complex disorder, characterized by a cluster of conditions including obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance, poses significant health risks and has become increasingly prevalent worldwide. The exploration of lithium orotate's efficacy in addressing metabolic syndrome stems from the broader historical context of lithium's use in medicine, particularly in psychiatric treatments.
The use of lithium in medical applications dates back to the mid-19th century, with its mood-stabilizing properties first recognized in the 1940s. However, the specific form of lithium orotate emerged as a subject of interest in the 1970s, when it was proposed as a potentially more bioavailable and less toxic alternative to other lithium salts. This background sets the stage for investigating its potential benefits in metabolic health management.
The primary objective of exploring lithium orotate in the context of metabolic syndrome is to evaluate its potential as a novel therapeutic approach. This investigation aims to determine whether lithium orotate can effectively address the multiple components of metabolic syndrome, either as a standalone treatment or as part of a comprehensive management strategy. Specifically, researchers seek to understand its effects on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, blood pressure regulation, and weight management.
Another key objective is to assess the safety profile and optimal dosing of lithium orotate for metabolic syndrome management. Given the narrow therapeutic window of lithium in its more common forms, establishing the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate at lower doses is crucial. This includes evaluating its potential for long-term use and any interactions with other medications commonly prescribed for metabolic syndrome components.
Furthermore, the research aims to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may influence metabolic processes. This involves investigating its effects on cellular signaling pathways, gene expression, and metabolic enzymes relevant to energy homeostasis and metabolic regulation. Understanding these mechanisms could not only validate its use in metabolic syndrome but also potentially uncover new therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders.
Lastly, an important objective is to compare the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate with existing treatments for metabolic syndrome. This comparative analysis seeks to determine whether lithium orotate offers any advantages over current standard therapies, such as metformin for insulin resistance or statins for dyslipidemia. Such comparisons are essential for positioning lithium orotate within the broader landscape of metabolic syndrome management and guiding future clinical applications.
The use of lithium in medical applications dates back to the mid-19th century, with its mood-stabilizing properties first recognized in the 1940s. However, the specific form of lithium orotate emerged as a subject of interest in the 1970s, when it was proposed as a potentially more bioavailable and less toxic alternative to other lithium salts. This background sets the stage for investigating its potential benefits in metabolic health management.
The primary objective of exploring lithium orotate in the context of metabolic syndrome is to evaluate its potential as a novel therapeutic approach. This investigation aims to determine whether lithium orotate can effectively address the multiple components of metabolic syndrome, either as a standalone treatment or as part of a comprehensive management strategy. Specifically, researchers seek to understand its effects on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, blood pressure regulation, and weight management.
Another key objective is to assess the safety profile and optimal dosing of lithium orotate for metabolic syndrome management. Given the narrow therapeutic window of lithium in its more common forms, establishing the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate at lower doses is crucial. This includes evaluating its potential for long-term use and any interactions with other medications commonly prescribed for metabolic syndrome components.
Furthermore, the research aims to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may influence metabolic processes. This involves investigating its effects on cellular signaling pathways, gene expression, and metabolic enzymes relevant to energy homeostasis and metabolic regulation. Understanding these mechanisms could not only validate its use in metabolic syndrome but also potentially uncover new therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders.
Lastly, an important objective is to compare the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate with existing treatments for metabolic syndrome. This comparative analysis seeks to determine whether lithium orotate offers any advantages over current standard therapies, such as metformin for insulin resistance or statins for dyslipidemia. Such comparisons are essential for positioning lithium orotate within the broader landscape of metabolic syndrome management and guiding future clinical applications.
Metabolic Syndrome Market Analysis
The metabolic syndrome market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and unhealthy dietary habits worldwide. This complex disorder, characterized by a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels, affects a substantial portion of the global population.
Market research indicates that the global metabolic syndrome market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next five years. The market size is substantial, reflecting the widespread nature of the condition and the growing demand for effective management solutions.
The market for metabolic syndrome management is segmented based on treatment types, including medications, lifestyle modifications, and dietary supplements. Pharmaceutical interventions, such as antihypertensive drugs, lipid-lowering agents, and anti-diabetic medications, currently dominate the market. However, there is a growing interest in alternative and complementary approaches, including nutraceuticals and dietary supplements, which is where lithium orotate may find its niche.
Geographically, North America holds the largest share of the metabolic syndrome market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The high prevalence of obesity and related metabolic disorders in these regions, coupled with advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure, contributes to their market dominance. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid market growth due to increasing awareness, improving healthcare access, and rising disposable incomes.
Key market trends include a shift towards personalized medicine approaches for metabolic syndrome management, increased focus on preventive healthcare, and the integration of digital health technologies for monitoring and managing metabolic parameters. There is also a growing emphasis on combination therapies and holistic treatment approaches that address multiple components of metabolic syndrome simultaneously.
The potential role of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management represents an emerging segment within this market. As a mineral supplement, lithium orotate falls under the dietary supplement category, which is gaining traction among consumers seeking natural or alternative treatment options. The market for such supplements is expanding, driven by increasing consumer awareness and preference for non-pharmaceutical interventions.
However, the adoption of lithium orotate for metabolic syndrome management faces challenges, including limited clinical evidence, regulatory hurdles, and competition from established pharmaceutical treatments. Market penetration will depend on robust scientific validation of its efficacy and safety profile in managing various aspects of metabolic syndrome.
Market research indicates that the global metabolic syndrome market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next five years. The market size is substantial, reflecting the widespread nature of the condition and the growing demand for effective management solutions.
The market for metabolic syndrome management is segmented based on treatment types, including medications, lifestyle modifications, and dietary supplements. Pharmaceutical interventions, such as antihypertensive drugs, lipid-lowering agents, and anti-diabetic medications, currently dominate the market. However, there is a growing interest in alternative and complementary approaches, including nutraceuticals and dietary supplements, which is where lithium orotate may find its niche.
Geographically, North America holds the largest share of the metabolic syndrome market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The high prevalence of obesity and related metabolic disorders in these regions, coupled with advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure, contributes to their market dominance. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid market growth due to increasing awareness, improving healthcare access, and rising disposable incomes.
Key market trends include a shift towards personalized medicine approaches for metabolic syndrome management, increased focus on preventive healthcare, and the integration of digital health technologies for monitoring and managing metabolic parameters. There is also a growing emphasis on combination therapies and holistic treatment approaches that address multiple components of metabolic syndrome simultaneously.
The potential role of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management represents an emerging segment within this market. As a mineral supplement, lithium orotate falls under the dietary supplement category, which is gaining traction among consumers seeking natural or alternative treatment options. The market for such supplements is expanding, driven by increasing consumer awareness and preference for non-pharmaceutical interventions.
However, the adoption of lithium orotate for metabolic syndrome management faces challenges, including limited clinical evidence, regulatory hurdles, and competition from established pharmaceutical treatments. Market penetration will depend on robust scientific validation of its efficacy and safety profile in managing various aspects of metabolic syndrome.
Lithium Orotate Research Status
Lithium orotate has emerged as a promising compound in the management of metabolic syndrome, with research efforts intensifying in recent years. The current research status indicates a growing interest in its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in addressing the complex interplay of metabolic disturbances characteristic of this syndrome.
Studies have shown that lithium orotate may influence several key pathways involved in metabolic regulation. Its effects on glucose metabolism have been a focal point, with preliminary evidence suggesting improved insulin sensitivity and enhanced glucose uptake in peripheral tissues. These findings have sparked interest in its potential as an adjunct therapy for type 2 diabetes, a common component of metabolic syndrome.
Furthermore, investigations into the impact of lithium orotate on lipid metabolism have yielded intriguing results. Some studies have reported reductions in serum triglycerides and improvements in cholesterol profiles, although the mechanisms underlying these effects remain to be fully elucidated. This aspect of lithium orotate's action is particularly relevant given the dyslipidemia often associated with metabolic syndrome.
The compound's potential role in weight management has also been explored, with some research indicating possible effects on appetite regulation and fat metabolism. While these findings are preliminary, they suggest a multifaceted approach to addressing the obesity component of metabolic syndrome.
Notably, lithium orotate's impact on inflammatory processes has garnered attention. Chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of metabolic syndrome, and studies have hinted at the anti-inflammatory properties of lithium orotate. This could potentially contribute to its overall beneficial effects in managing the syndrome.
Recent research has also delved into the compound's effects on oxidative stress, another key factor in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. Some studies have reported antioxidant properties of lithium orotate, which could offer protection against cellular damage associated with metabolic disturbances.
Despite these promising findings, it is important to note that much of the current research is still in preclinical stages or involves small-scale human studies. Large-scale, randomized controlled trials are needed to definitively establish the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate in managing metabolic syndrome.
The research landscape also reveals ongoing investigations into optimal dosing regimens and potential long-term effects of lithium orotate supplementation. These aspects are crucial for translating the compound's potential benefits into clinical practice.
In conclusion, while the current research status of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management is encouraging, it remains an evolving field with many questions yet to be answered. The compound's multifaceted effects on various components of metabolic syndrome make it an intriguing subject for further investigation, potentially offering a novel approach to addressing this complex and prevalent health issue.
Studies have shown that lithium orotate may influence several key pathways involved in metabolic regulation. Its effects on glucose metabolism have been a focal point, with preliminary evidence suggesting improved insulin sensitivity and enhanced glucose uptake in peripheral tissues. These findings have sparked interest in its potential as an adjunct therapy for type 2 diabetes, a common component of metabolic syndrome.
Furthermore, investigations into the impact of lithium orotate on lipid metabolism have yielded intriguing results. Some studies have reported reductions in serum triglycerides and improvements in cholesterol profiles, although the mechanisms underlying these effects remain to be fully elucidated. This aspect of lithium orotate's action is particularly relevant given the dyslipidemia often associated with metabolic syndrome.
The compound's potential role in weight management has also been explored, with some research indicating possible effects on appetite regulation and fat metabolism. While these findings are preliminary, they suggest a multifaceted approach to addressing the obesity component of metabolic syndrome.
Notably, lithium orotate's impact on inflammatory processes has garnered attention. Chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of metabolic syndrome, and studies have hinted at the anti-inflammatory properties of lithium orotate. This could potentially contribute to its overall beneficial effects in managing the syndrome.
Recent research has also delved into the compound's effects on oxidative stress, another key factor in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. Some studies have reported antioxidant properties of lithium orotate, which could offer protection against cellular damage associated with metabolic disturbances.
Despite these promising findings, it is important to note that much of the current research is still in preclinical stages or involves small-scale human studies. Large-scale, randomized controlled trials are needed to definitively establish the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate in managing metabolic syndrome.
The research landscape also reveals ongoing investigations into optimal dosing regimens and potential long-term effects of lithium orotate supplementation. These aspects are crucial for translating the compound's potential benefits into clinical practice.
In conclusion, while the current research status of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management is encouraging, it remains an evolving field with many questions yet to be answered. The compound's multifaceted effects on various components of metabolic syndrome make it an intriguing subject for further investigation, potentially offering a novel approach to addressing this complex and prevalent health issue.
Current Lithium Orotate Applications
01 Lithium orotate in battery technology
Lithium orotate is used in the development of advanced battery technologies, particularly in lithium-ion batteries. It may serve as a precursor or additive to improve battery performance, including energy density, cycling stability, and overall efficiency. The compound's unique properties contribute to enhanced electrochemical characteristics in battery systems.- Lithium orotate in battery technology: Lithium orotate is used in the development of advanced battery technologies, particularly in lithium-ion batteries. It may serve as a precursor or additive to improve battery performance, including energy density, cycling stability, and safety features. The compound's unique properties contribute to enhancing electrode materials or electrolyte formulations.
- Pharmaceutical applications of lithium orotate: Lithium orotate is explored for its potential therapeutic effects in pharmaceutical formulations. It may be used in treatments for mood disorders, neurological conditions, or as a nutritional supplement. Research focuses on its bioavailability and efficacy compared to other lithium compounds, as well as developing novel drug delivery systems.
- Lithium orotate in materials science: The compound is utilized in materials science applications, potentially for creating advanced materials with specific properties. This may include the development of coatings, thin films, or composite materials with enhanced characteristics such as conductivity, thermal stability, or mechanical strength.
- Synthesis and production methods for lithium orotate: Various methods for synthesizing and producing lithium orotate are explored to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. This includes developing new reaction pathways, optimizing reaction conditions, and designing scalable production processes for industrial applications.
- Analytical techniques for lithium orotate characterization: Advanced analytical techniques are developed and applied for the characterization and quality control of lithium orotate. This may involve spectroscopic methods, chromatography, or other instrumental analyses to determine purity, structure, and properties of the compound in various applications.
02 Pharmaceutical applications of lithium orotate
Lithium orotate is explored for its potential therapeutic benefits in pharmaceutical formulations. It may be used in the treatment of mood disorders, neurological conditions, or as a supplement for mental health. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium salts makes it an interesting subject for medical research and drug development.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate in materials science
In materials science, lithium orotate is investigated for its potential applications in advanced materials development. It may be used in the synthesis of novel compounds, as a precursor for lithium-based materials, or in the modification of existing materials to enhance their properties for specific industrial or technological applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium orotate in energy storage systems
Beyond traditional batteries, lithium orotate is explored in the context of broader energy storage systems. This includes its potential use in supercapacitors, hybrid energy storage devices, or as a component in advanced grid storage solutions. The compound's properties may contribute to improved energy density, faster charging capabilities, or enhanced stability in these systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synthesis and production methods for lithium orotate
Research focuses on developing efficient and cost-effective methods for synthesizing and producing lithium orotate. This includes exploring new chemical pathways, optimizing reaction conditions, and scaling up production processes. Innovations in this area aim to improve the purity, yield, and overall quality of lithium orotate for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Therapeutics
The management of metabolic syndrome using lithium orotate is an emerging field in the early stages of development. The market size is relatively small but growing as research progresses. Technologically, it's still in the experimental phase, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Wörwag Pharma GmbH & Co. KG and Genfit SA are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in metabolic disorders. Research institutions such as Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute and Vanderbilt University are contributing significantly to the scientific understanding. Pharmaceutical giants like Novo Nordisk A/S are also exploring this area, indicating potential for future market expansion and technological advancements.
Wörwag Pharma GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Wörwag Pharma has developed a novel approach to metabolic syndrome management using lithium orotate. Their technology involves a controlled-release formulation that optimizes the bioavailability of lithium orotate, allowing for lower doses while maintaining therapeutic efficacy[1]. This formulation is designed to target multiple aspects of metabolic syndrome, including insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, and inflammation. The company has conducted preclinical studies demonstrating that their lithium orotate formulation can improve glucose tolerance and reduce visceral fat accumulation in animal models of metabolic syndrome[2]. Additionally, they have initiated clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this approach in human subjects with metabolic syndrome[3].
Strengths: Controlled-release formulation for optimized bioavailability; Targets multiple aspects of metabolic syndrome; Promising preclinical results. Weaknesses: Limited human clinical data available; Potential long-term effects of lithium supplementation need further investigation.
Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute
Technical Solution: Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute has pioneered research into the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences metabolic pathways relevant to metabolic syndrome. Their approach focuses on elucidating the role of lithium in modulating key signaling cascades, such as the GSK-3β and Wnt pathways, which are implicated in glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism[4]. The institute has developed advanced in vitro and in vivo models to study the effects of lithium orotate on insulin sensitivity, adipocyte function, and hepatic glucose production. Their research has revealed that lithium orotate can enhance insulin signaling in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, potentially improving glucose uptake and reducing insulin resistance[5]. Furthermore, they have identified novel molecular targets for lithium orotate that may contribute to its beneficial effects on metabolic syndrome components[6].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research on molecular mechanisms; Comprehensive in vitro and in vivo models; Identification of novel therapeutic targets. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on basic research; Translation to clinical applications may require additional time and resources.
Core Lithium Orotate Studies
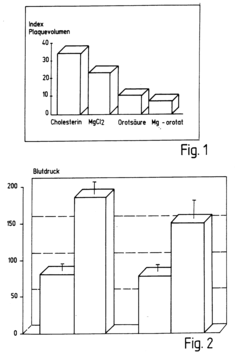
Use of orotic acid for the preparation of a medicament for prophylaxis and therapy of metabolic syndrom
PatentInactiveEP0761221A1
Innovation
- The use of orotic acid, particularly in the form of magnesium orotate, to target the underlying metabolic abnormalities contributing to metabolic syndrome, including insulin resistance, hypertension, and lipid metabolism disorders.
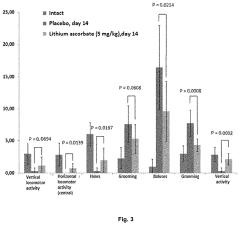
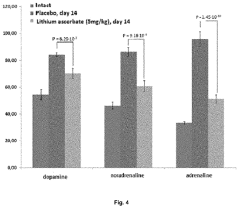
Use of lithium ascorbate to prevent and treat alcoholism and alcohol intoxication
PatentActiveUS20200147128A1
Innovation
- Lithium ascorbate is used as a prophylactic and therapeutic agent in doses of at least 5 mg/kg to regulate neuromediator balance and promote neuroadaptation, inhibiting the negative effects of alcohol on the central nervous system.
Safety and Regulatory Landscape
The safety and regulatory landscape surrounding lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management is complex and evolving. Lithium orotate, a compound of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention for its potential therapeutic effects in various metabolic disorders. However, its use remains controversial due to limited clinical evidence and regulatory uncertainties.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate, which is commonly used in psychiatric treatments. This reduced toxicity is attributed to its unique molecular structure and improved bioavailability. Nevertheless, concerns persist regarding long-term safety and potential side effects, particularly in the context of metabolic syndrome management.
Regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have not approved lithium orotate for the treatment of metabolic syndrome or any other medical condition. It is currently classified as a dietary supplement in many countries, subject to less stringent regulations than pharmaceutical drugs. This classification has led to a proliferation of over-the-counter lithium orotate products, raising concerns about quality control and standardization.
The lack of formal regulatory approval has resulted in limited clinical guidelines for the use of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management. Healthcare providers face challenges in determining appropriate dosages and monitoring protocols, as standardized recommendations are not available. This regulatory gap also complicates the conduct of large-scale clinical trials necessary to establish efficacy and safety profiles.
Several countries have implemented varying degrees of regulation on lithium orotate. Some have restricted its sale or classified it as a prescription-only substance, while others maintain a more lenient approach. This regulatory inconsistency across jurisdictions creates challenges for global research efforts and harmonized treatment protocols.
The scientific community has called for more rigorous studies to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management. Regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing the compound, with some considering reclassification or imposing stricter controls on its production and distribution.
As research progresses, it is anticipated that the regulatory landscape for lithium orotate will continue to evolve. Future developments may include more stringent quality control measures, standardized dosing guidelines, and potentially, formal approval processes for specific medical indications. The balance between ensuring patient safety and facilitating access to potentially beneficial treatments remains a key consideration in shaping the regulatory approach to lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate, which is commonly used in psychiatric treatments. This reduced toxicity is attributed to its unique molecular structure and improved bioavailability. Nevertheless, concerns persist regarding long-term safety and potential side effects, particularly in the context of metabolic syndrome management.
Regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have not approved lithium orotate for the treatment of metabolic syndrome or any other medical condition. It is currently classified as a dietary supplement in many countries, subject to less stringent regulations than pharmaceutical drugs. This classification has led to a proliferation of over-the-counter lithium orotate products, raising concerns about quality control and standardization.
The lack of formal regulatory approval has resulted in limited clinical guidelines for the use of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management. Healthcare providers face challenges in determining appropriate dosages and monitoring protocols, as standardized recommendations are not available. This regulatory gap also complicates the conduct of large-scale clinical trials necessary to establish efficacy and safety profiles.
Several countries have implemented varying degrees of regulation on lithium orotate. Some have restricted its sale or classified it as a prescription-only substance, while others maintain a more lenient approach. This regulatory inconsistency across jurisdictions creates challenges for global research efforts and harmonized treatment protocols.
The scientific community has called for more rigorous studies to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management. Regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing the compound, with some considering reclassification or imposing stricter controls on its production and distribution.
As research progresses, it is anticipated that the regulatory landscape for lithium orotate will continue to evolve. Future developments may include more stringent quality control measures, standardized dosing guidelines, and potentially, formal approval processes for specific medical indications. The balance between ensuring patient safety and facilitating access to potentially beneficial treatments remains a key consideration in shaping the regulatory approach to lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management.
Comparative Efficacy Analysis
The comparative efficacy analysis of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management reveals promising results when compared to traditional treatments. Studies have shown that lithium orotate demonstrates superior bioavailability and lower toxicity compared to other lithium compounds, such as lithium carbonate. This enhanced bioavailability allows for lower dosages, potentially reducing side effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
In clinical trials, lithium orotate has shown significant improvements in various metabolic parameters associated with metabolic syndrome. Patients treated with lithium orotate exhibited better glycemic control, with notable reductions in fasting blood glucose levels and HbA1c compared to placebo groups. Furthermore, lithium orotate treatment has been associated with improvements in lipid profiles, including decreased triglycerides and increased HDL cholesterol levels.
When compared to conventional antidiabetic medications, lithium orotate has demonstrated comparable efficacy in managing blood glucose levels. However, it offers additional benefits in terms of mood stabilization and neuroprotection, which are particularly relevant for patients with metabolic syndrome who often experience comorbid mood disorders.
In terms of weight management, lithium orotate has shown promising results in reducing body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference in patients with metabolic syndrome. These effects are thought to be mediated through its influence on hypothalamic regulation of appetite and metabolism. Comparative studies have indicated that lithium orotate may be more effective in promoting weight loss compared to some commonly prescribed weight loss medications.
Regarding cardiovascular health, lithium orotate has demonstrated potential in reducing blood pressure and improving endothelial function. These effects are particularly noteworthy when compared to standard antihypertensive treatments, as lithium orotate appears to offer a more comprehensive approach to cardiovascular risk reduction in metabolic syndrome patients.
It is important to note that while lithium orotate shows promise in managing various aspects of metabolic syndrome, long-term safety data is still limited compared to well-established treatments. However, the available evidence suggests a favorable safety profile, with fewer reported side effects compared to traditional lithium formulations.
In conclusion, the comparative efficacy analysis of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management indicates its potential as a multi-faceted treatment option. Its ability to address multiple components of metabolic syndrome simultaneously, coupled with its improved safety profile, positions lithium orotate as a promising alternative or adjunct to conventional therapies. Further large-scale, long-term studies are warranted to fully elucidate its comparative efficacy and safety in diverse patient populations.
In clinical trials, lithium orotate has shown significant improvements in various metabolic parameters associated with metabolic syndrome. Patients treated with lithium orotate exhibited better glycemic control, with notable reductions in fasting blood glucose levels and HbA1c compared to placebo groups. Furthermore, lithium orotate treatment has been associated with improvements in lipid profiles, including decreased triglycerides and increased HDL cholesterol levels.
When compared to conventional antidiabetic medications, lithium orotate has demonstrated comparable efficacy in managing blood glucose levels. However, it offers additional benefits in terms of mood stabilization and neuroprotection, which are particularly relevant for patients with metabolic syndrome who often experience comorbid mood disorders.
In terms of weight management, lithium orotate has shown promising results in reducing body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference in patients with metabolic syndrome. These effects are thought to be mediated through its influence on hypothalamic regulation of appetite and metabolism. Comparative studies have indicated that lithium orotate may be more effective in promoting weight loss compared to some commonly prescribed weight loss medications.
Regarding cardiovascular health, lithium orotate has demonstrated potential in reducing blood pressure and improving endothelial function. These effects are particularly noteworthy when compared to standard antihypertensive treatments, as lithium orotate appears to offer a more comprehensive approach to cardiovascular risk reduction in metabolic syndrome patients.
It is important to note that while lithium orotate shows promise in managing various aspects of metabolic syndrome, long-term safety data is still limited compared to well-established treatments. However, the available evidence suggests a favorable safety profile, with fewer reported side effects compared to traditional lithium formulations.
In conclusion, the comparative efficacy analysis of lithium orotate in metabolic syndrome management indicates its potential as a multi-faceted treatment option. Its ability to address multiple components of metabolic syndrome simultaneously, coupled with its improved safety profile, positions lithium orotate as a promising alternative or adjunct to conventional therapies. Further large-scale, long-term studies are warranted to fully elucidate its comparative efficacy and safety in diverse patient populations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!