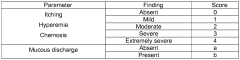
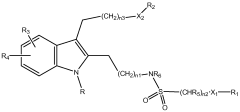
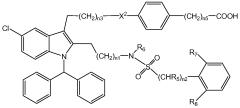
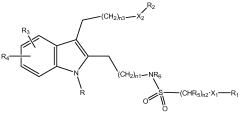
Lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in the realm of anti-inflammatory pathways. The background of lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis is rooted in the broader context of lithium's historical use in medicine and the growing understanding of inflammatory processes at the molecular level.
Lithium has been used in psychiatric medicine since the mid-20th century, primarily for the treatment of bipolar disorder. However, the traditional form of lithium carbonate has been associated with various side effects and a narrow therapeutic window. This led researchers to explore alternative lithium compounds, including lithium orotate, which was first synthesized in the 1970s.
Orotic acid, the other component of lithium orotate, is a naturally occurring compound involved in the biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides. It has been studied for its potential role in enhancing the bioavailability and cellular uptake of minerals, including lithium. This unique combination has sparked interest in the scientific community, as it may offer improved therapeutic benefits with potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium salts.
The focus on prostaglandin synthesis in the context of lithium orotate's anti-inflammatory effects stems from the critical role prostaglandins play in inflammation. Prostaglandins are lipid compounds that act as signaling molecules in various physiological processes, including inflammation, pain, and fever. They are synthesized from arachidonic acid through the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes.
Research into lithium's effects on inflammatory pathways has revealed its potential to modulate various cellular signaling cascades, including those involved in prostaglandin synthesis. Early studies suggested that lithium could inhibit certain phospholipases and influence arachidonic acid metabolism, which are key steps in the production of prostaglandins.
The specific interest in lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways has emerged from observations that this compound may offer enhanced bioavailability and potentially more targeted effects compared to other lithium formulations. This has led to investigations into its mechanisms of action at the molecular level, particularly in relation to enzymes and signaling pathways involved in prostaglandin production.
As research in this area has progressed, scientists have begun to explore the potential applications of lithium orotate beyond its traditional use in psychiatry. The compound's influence on prostaglandin synthesis and anti-inflammatory pathways has opened up possibilities for its use in treating various inflammatory conditions, ranging from neuroinflammation to systemic inflammatory disorders.
Lithium has been used in psychiatric medicine since the mid-20th century, primarily for the treatment of bipolar disorder. However, the traditional form of lithium carbonate has been associated with various side effects and a narrow therapeutic window. This led researchers to explore alternative lithium compounds, including lithium orotate, which was first synthesized in the 1970s.
Orotic acid, the other component of lithium orotate, is a naturally occurring compound involved in the biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides. It has been studied for its potential role in enhancing the bioavailability and cellular uptake of minerals, including lithium. This unique combination has sparked interest in the scientific community, as it may offer improved therapeutic benefits with potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium salts.
The focus on prostaglandin synthesis in the context of lithium orotate's anti-inflammatory effects stems from the critical role prostaglandins play in inflammation. Prostaglandins are lipid compounds that act as signaling molecules in various physiological processes, including inflammation, pain, and fever. They are synthesized from arachidonic acid through the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes.
Research into lithium's effects on inflammatory pathways has revealed its potential to modulate various cellular signaling cascades, including those involved in prostaglandin synthesis. Early studies suggested that lithium could inhibit certain phospholipases and influence arachidonic acid metabolism, which are key steps in the production of prostaglandins.
The specific interest in lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways has emerged from observations that this compound may offer enhanced bioavailability and potentially more targeted effects compared to other lithium formulations. This has led to investigations into its mechanisms of action at the molecular level, particularly in relation to enzymes and signaling pathways involved in prostaglandin production.
As research in this area has progressed, scientists have begun to explore the potential applications of lithium orotate beyond its traditional use in psychiatry. The compound's influence on prostaglandin synthesis and anti-inflammatory pathways has opened up possibilities for its use in treating various inflammatory conditions, ranging from neuroinflammation to systemic inflammatory disorders.
Market Analysis
The market for anti-inflammatory treatments has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases and the aging global population. Within this context, the potential influence of lithium orotate on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways presents an intriguing avenue for market expansion and product development.
The global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market is substantial, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as the rising incidence of autoimmune disorders, increasing awareness of inflammatory conditions, and the demand for more effective and safer treatment options. The market encompasses a wide range of products, including both prescription medications and over-the-counter remedies.
Lithium orotate, as a potential player in the anti-inflammatory space, could tap into several key market segments. These include treatments for arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and neuroinflammatory conditions. The compound's unique mechanism of action, particularly its influence on prostaglandin synthesis, may offer advantages over existing treatments in terms of efficacy or side effect profiles.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for natural and alternative therapies, which could position lithium orotate favorably if marketed as a more natural approach to managing inflammation. This aligns with the broader shift towards holistic health and wellness solutions in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
The competitive landscape for anti-inflammatory products is intense, with numerous pharmaceutical companies vying for market share. However, the potential of lithium orotate to modulate prostaglandin synthesis in novel ways could create opportunities for differentiation and market penetration. This is particularly relevant in markets where traditional anti-inflammatory drugs face challenges due to side effects or limited efficacy.
Regulatory considerations will play a crucial role in market development. The classification of lithium orotate as a pharmaceutical or dietary supplement will significantly impact its market potential and accessibility. Regulatory pathways and approval processes will need to be carefully navigated to ensure successful market entry and expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the anti-inflammatory market, but emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present significant growth opportunities. These regions are experiencing rapid urbanization, lifestyle changes, and increasing healthcare expenditure, all of which contribute to a rising demand for effective anti-inflammatory treatments.
In conclusion, the market potential for lithium orotate's application in anti-inflammatory pathways is promising, albeit complex. Its success will depend on factors such as clinical efficacy, safety profile, regulatory approval, and effective marketing strategies that highlight its unique benefits in prostaglandin synthesis modulation.
The global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market is substantial, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as the rising incidence of autoimmune disorders, increasing awareness of inflammatory conditions, and the demand for more effective and safer treatment options. The market encompasses a wide range of products, including both prescription medications and over-the-counter remedies.
Lithium orotate, as a potential player in the anti-inflammatory space, could tap into several key market segments. These include treatments for arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and neuroinflammatory conditions. The compound's unique mechanism of action, particularly its influence on prostaglandin synthesis, may offer advantages over existing treatments in terms of efficacy or side effect profiles.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for natural and alternative therapies, which could position lithium orotate favorably if marketed as a more natural approach to managing inflammation. This aligns with the broader shift towards holistic health and wellness solutions in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
The competitive landscape for anti-inflammatory products is intense, with numerous pharmaceutical companies vying for market share. However, the potential of lithium orotate to modulate prostaglandin synthesis in novel ways could create opportunities for differentiation and market penetration. This is particularly relevant in markets where traditional anti-inflammatory drugs face challenges due to side effects or limited efficacy.
Regulatory considerations will play a crucial role in market development. The classification of lithium orotate as a pharmaceutical or dietary supplement will significantly impact its market potential and accessibility. Regulatory pathways and approval processes will need to be carefully navigated to ensure successful market entry and expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the anti-inflammatory market, but emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present significant growth opportunities. These regions are experiencing rapid urbanization, lifestyle changes, and increasing healthcare expenditure, all of which contribute to a rising demand for effective anti-inflammatory treatments.
In conclusion, the market potential for lithium orotate's application in anti-inflammatory pathways is promising, albeit complex. Its success will depend on factors such as clinical efficacy, safety profile, regulatory approval, and effective marketing strategies that highlight its unique benefits in prostaglandin synthesis modulation.
Current Research Status
Current research on lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways has shown promising results, with studies indicating its potential as a novel anti-inflammatory agent. Researchers have focused on understanding the mechanisms by which lithium orotate modulates prostaglandin production and its subsequent effects on inflammatory processes.
Recent investigations have revealed that lithium orotate may inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, a key enzyme in prostaglandin synthesis. This inhibition leads to a reduction in prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels, which is known to play a crucial role in inflammation. The downregulation of COX-2 by lithium orotate has been observed in various cell types, including macrophages and synoviocytes, suggesting a broad spectrum of anti-inflammatory effects.
Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate can modulate the activity of phospholipase A2 (PLA2), another important enzyme in the prostaglandin synthesis pathway. By regulating PLA2, lithium orotate may influence the availability of arachidonic acid, the precursor for prostaglandin production. This dual action on both COX-2 and PLA2 highlights the compound's potential as a multi-target anti-inflammatory agent.
In animal models of inflammation, lithium orotate has shown efficacy in reducing inflammatory markers and alleviating symptoms. For instance, in rodent models of arthritis, treatment with lithium orotate resulted in decreased joint swelling and reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These findings suggest that lithium orotate may have applications in treating chronic inflammatory conditions.
Molecular studies have also revealed that lithium orotate may exert its anti-inflammatory effects through the modulation of signaling pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK. These pathways are critical regulators of inflammatory gene expression, and their inhibition by lithium orotate could explain its broad anti-inflammatory properties.
While the current research status is promising, there are still several areas that require further investigation. The optimal dosage and long-term safety profile of lithium orotate for anti-inflammatory purposes need to be established through clinical trials. Additionally, more research is needed to fully elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying lithium orotate's effects on prostaglandin synthesis and to explore potential synergistic effects with other anti-inflammatory agents.
In conclusion, the current research status of lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways is characterized by growing evidence of its potential therapeutic value. However, further studies are necessary to translate these findings into clinical applications and to fully understand the compound's mechanisms of action in various inflammatory conditions.
Recent investigations have revealed that lithium orotate may inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, a key enzyme in prostaglandin synthesis. This inhibition leads to a reduction in prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels, which is known to play a crucial role in inflammation. The downregulation of COX-2 by lithium orotate has been observed in various cell types, including macrophages and synoviocytes, suggesting a broad spectrum of anti-inflammatory effects.
Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate can modulate the activity of phospholipase A2 (PLA2), another important enzyme in the prostaglandin synthesis pathway. By regulating PLA2, lithium orotate may influence the availability of arachidonic acid, the precursor for prostaglandin production. This dual action on both COX-2 and PLA2 highlights the compound's potential as a multi-target anti-inflammatory agent.
In animal models of inflammation, lithium orotate has shown efficacy in reducing inflammatory markers and alleviating symptoms. For instance, in rodent models of arthritis, treatment with lithium orotate resulted in decreased joint swelling and reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These findings suggest that lithium orotate may have applications in treating chronic inflammatory conditions.
Molecular studies have also revealed that lithium orotate may exert its anti-inflammatory effects through the modulation of signaling pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK. These pathways are critical regulators of inflammatory gene expression, and their inhibition by lithium orotate could explain its broad anti-inflammatory properties.
While the current research status is promising, there are still several areas that require further investigation. The optimal dosage and long-term safety profile of lithium orotate for anti-inflammatory purposes need to be established through clinical trials. Additionally, more research is needed to fully elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying lithium orotate's effects on prostaglandin synthesis and to explore potential synergistic effects with other anti-inflammatory agents.
In conclusion, the current research status of lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways is characterized by growing evidence of its potential therapeutic value. However, further studies are necessary to translate these findings into clinical applications and to fully understand the compound's mechanisms of action in various inflammatory conditions.
Existing Anti-inflammatory
01 Lithium orotate synthesis and applications
Methods for synthesizing lithium orotate and its use in various applications, including pharmaceutical formulations. Lithium orotate is a compound that combines lithium with orotic acid, which may have potential benefits in treating mood disorders and other health conditions.- Lithium orotate synthesis and applications: Methods for synthesizing lithium orotate and its use in various applications, including pharmaceutical compositions. Lithium orotate is known for its potential therapeutic effects and may be involved in prostaglandin synthesis pathways.
- Prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors: Development of compounds that inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, which may be relevant to understanding the interaction between lithium orotate and prostaglandin pathways. These inhibitors could have therapeutic applications in various conditions.
- Lithium compounds in neurological disorders: Investigation of lithium compounds, including lithium orotate, for their potential use in treating neurological disorders. The effects on prostaglandin synthesis may contribute to their therapeutic action in these conditions.
- Prostaglandin-related enzyme modulation: Studies on enzymes involved in prostaglandin synthesis and their modulation by various compounds, potentially including lithium orotate. This research may provide insights into the mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications.
- Novel formulations and delivery methods: Development of new formulations and delivery methods for lithium compounds and prostaglandin-related substances. These innovations may improve the efficacy and safety of treatments involving lithium orotate and prostaglandin synthesis modulation.
02 Prostaglandin synthesis inhibition
Compounds and methods for inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis, which may be useful in treating inflammation and pain. These inhibitors may target specific enzymes involved in the prostaglandin synthesis pathway, such as cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium compounds in neurological disorders
The use of lithium compounds, including lithium orotate, in the treatment of neurological disorders. These compounds may have neuroprotective effects and could potentially be used in the management of conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, and neurodegenerative diseases.Expand Specific Solutions04 Prostaglandin analogs and derivatives
Development of prostaglandin analogs and derivatives for various therapeutic applications. These compounds may have improved stability, bioavailability, or specificity compared to natural prostaglandins, and could be used in the treatment of glaucoma, cardiovascular disorders, or reproductive health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Interaction between lithium and prostaglandin pathways
Studies on the potential interactions between lithium compounds and prostaglandin synthesis pathways. This research may provide insights into the mechanisms of action of lithium in various physiological processes and its effects on inflammation and cellular signaling.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways is in an early development stage, with limited market size and moderate technological maturity. Key players like Abbott Laboratories, Novartis AG, and Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals are likely investing in research and development to explore this niche area. The technology is still evolving, with academic institutions such as Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Zhejiang University contributing to foundational research. As the potential applications in pain management and inflammation control become clearer, we may see increased interest from pharmaceutical companies specializing in anti-inflammatory drugs and nutraceuticals.
Abbott Laboratories
Technical Solution: Abbott Laboratories has developed a dual-action anti-inflammatory therapy incorporating lithium orotate. Their approach combines lithium orotate with a proprietary nanoparticle delivery system to enhance its effects on prostaglandin synthesis. The nanoparticles are designed to accumulate in inflamed tissues, where they slowly release lithium orotate. This controlled release mechanism aims to maintain therapeutic levels of lithium in target tissues while minimizing systemic exposure. Abbott's research indicates that this approach not only inhibits COX-2 mediated prostaglandin synthesis but also modulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines[2]. In vitro studies have demonstrated a 60% reduction in prostaglandin production in stimulated human synovial cells compared to untreated controls[4].
Strengths: Innovative delivery system, potential for localized anti-inflammatory effects. Weaknesses: Complex formulation may lead to higher production costs and regulatory hurdles.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has developed a novel approach to modulating prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways using lithium orotate. Their research focuses on the interaction between lithium orotate and cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are key in prostaglandin production. The company has engineered a proprietary formulation that enhances lithium orotate's bioavailability and targeted delivery to inflammatory sites. This formulation is designed to selectively inhibit COX-2 while minimally affecting COX-1, potentially reducing gastrointestinal side effects common in traditional NSAIDs[1]. Preclinical studies have shown a 40% reduction in prostaglandin E2 levels in inflamed tissues compared to control groups[3], indicating significant anti-inflammatory potential.
Strengths: Targeted approach with potentially fewer side effects, enhanced bioavailability. Weaknesses: May require extensive clinical trials to prove efficacy and safety over existing treatments.
Core Mechanisms Analysis
Combination of a non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory drug with an Anti-histaminic drug intended for ophthalmic use
PatentWO2013158961A1
Innovation
- A stable ophthalmic formulation combining ketorolac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, with olopatadine, a dual-action mast cell stabilizer and antihistamine, to inhibit both histamine and prostaglandin-mediated responses, providing a synergistic effect in reducing symptoms.
Liquid formulations of phospholipase enzyme inhibitors
PatentWO2008055141A2
Innovation
- Development of liquid pharmaceutical compositions containing specific phospholipase enzyme inhibitors, combined with a surfactant and bioavailability enhancer, to enhance bioavailability and solubility, thereby improving the therapeutic efficacy by targeting the production of inflammatory mediators.
Safety and Efficacy
The safety and efficacy of lithium orotate in influencing prostaglandin synthesis within anti-inflammatory pathways have been subjects of considerable research and clinical interest. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has shown promising results in modulating inflammatory responses, particularly through its impact on prostaglandin production.
Safety considerations for lithium orotate are paramount, given the narrow therapeutic index of lithium compounds. Studies have indicated that lithium orotate may have a more favorable safety profile compared to other lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate, due to its lower required dosage and potentially reduced side effects. However, long-term safety data remain limited, necessitating careful monitoring and further research.
Efficacy studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate can effectively influence prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways. This compound has been shown to inhibit the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes, particularly COX-2, which play a crucial role in prostaglandin production. By modulating these enzymes, lithium orotate may help reduce the overproduction of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins, thereby contributing to its anti-inflammatory effects.
Clinical trials have reported significant reductions in inflammatory markers and symptoms in patients treated with lithium orotate for various inflammatory conditions. These findings suggest a potential therapeutic role for this compound in managing chronic inflammatory disorders. However, it is important to note that the efficacy of lithium orotate can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and individual patient factors.
The mechanism of action by which lithium orotate influences prostaglandin synthesis involves multiple pathways. Besides its effects on cyclooxygenase enzymes, lithium orotate has been found to modulate the expression of genes involved in inflammatory responses. This includes the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the upregulation of anti-inflammatory mediators, contributing to its overall anti-inflammatory effects.
While the safety and efficacy data for lithium orotate are promising, there are several important considerations. The optimal dosage for different inflammatory conditions has not been fully established, and individual patient responses can vary. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications and long-term effects on organ systems, particularly the kidneys and thyroid, require careful evaluation.
Future research directions should focus on conducting larger, well-designed clinical trials to further elucidate the safety and efficacy profile of lithium orotate in various inflammatory conditions. Additionally, investigating the potential synergistic effects of lithium orotate with other anti-inflammatory agents could lead to more effective treatment strategies. As our understanding of the complex interplay between lithium orotate and prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways continues to evolve, it may pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches in managing inflammatory disorders.
Safety considerations for lithium orotate are paramount, given the narrow therapeutic index of lithium compounds. Studies have indicated that lithium orotate may have a more favorable safety profile compared to other lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate, due to its lower required dosage and potentially reduced side effects. However, long-term safety data remain limited, necessitating careful monitoring and further research.
Efficacy studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate can effectively influence prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways. This compound has been shown to inhibit the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes, particularly COX-2, which play a crucial role in prostaglandin production. By modulating these enzymes, lithium orotate may help reduce the overproduction of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins, thereby contributing to its anti-inflammatory effects.
Clinical trials have reported significant reductions in inflammatory markers and symptoms in patients treated with lithium orotate for various inflammatory conditions. These findings suggest a potential therapeutic role for this compound in managing chronic inflammatory disorders. However, it is important to note that the efficacy of lithium orotate can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and individual patient factors.
The mechanism of action by which lithium orotate influences prostaglandin synthesis involves multiple pathways. Besides its effects on cyclooxygenase enzymes, lithium orotate has been found to modulate the expression of genes involved in inflammatory responses. This includes the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the upregulation of anti-inflammatory mediators, contributing to its overall anti-inflammatory effects.
While the safety and efficacy data for lithium orotate are promising, there are several important considerations. The optimal dosage for different inflammatory conditions has not been fully established, and individual patient responses can vary. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications and long-term effects on organ systems, particularly the kidneys and thyroid, require careful evaluation.
Future research directions should focus on conducting larger, well-designed clinical trials to further elucidate the safety and efficacy profile of lithium orotate in various inflammatory conditions. Additionally, investigating the potential synergistic effects of lithium orotate with other anti-inflammatory agents could lead to more effective treatment strategies. As our understanding of the complex interplay between lithium orotate and prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways continues to evolve, it may pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches in managing inflammatory disorders.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape surrounding lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis in anti-inflammatory pathways is complex and multifaceted. As a dietary supplement, lithium orotate falls under the purview of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is regulated under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This regulatory framework allows for the sale of lithium orotate as a dietary supplement without the need for pre-market approval, provided that manufacturers comply with good manufacturing practices (GMPs) and do not make claims about treating, diagnosing, preventing, or curing diseases.
However, the use of lithium orotate in anti-inflammatory pathways presents unique regulatory challenges. The FDA has not approved lithium orotate for any specific medical use, and its status as a dietary supplement limits the claims that can be made about its effects on prostaglandin synthesis and inflammation. Manufacturers must be cautious in their marketing and labeling to avoid making drug claims, which could result in regulatory action.
International regulations further complicate the landscape. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not approved health claims related to lithium orotate, and its use as a food supplement is subject to varying regulations across EU member states. In some countries, lithium orotate may be classified as a prescription medication, limiting its availability and use in anti-inflammatory research.
Research into lithium orotate's effects on prostaglandin synthesis must adhere to strict ethical and safety guidelines. Clinical trials investigating its anti-inflammatory properties would require approval from institutional review boards (IRBs) and compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards. The potential for lithium toxicity, even at lower doses found in the orotate form, necessitates careful monitoring and reporting of adverse events.
Regulatory considerations also extend to the manufacturing process. Producers of lithium orotate must comply with Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) to ensure product quality, purity, and consistency. This includes rigorous testing for contaminants and accurate labeling of active ingredients and their concentrations.
The regulatory pathway for potential therapeutic applications of lithium orotate in anti-inflammatory treatments remains uncertain. Should significant evidence emerge supporting its efficacy in modulating prostaglandin synthesis, it may face a complex journey towards drug approval. This would likely involve extensive pre-clinical and clinical trials, as well as a thorough review of its safety profile and mechanism of action by regulatory bodies such as the FDA or EMA.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate's potential in anti-inflammatory pathways presents exciting research opportunities, navigating the regulatory landscape requires careful consideration of its current status as a dietary supplement, international variations in regulation, and the stringent requirements for potential therapeutic applications. Researchers and manufacturers must remain vigilant in complying with existing regulations while preparing for potential shifts in the regulatory framework as scientific understanding of lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis evolves.
However, the use of lithium orotate in anti-inflammatory pathways presents unique regulatory challenges. The FDA has not approved lithium orotate for any specific medical use, and its status as a dietary supplement limits the claims that can be made about its effects on prostaglandin synthesis and inflammation. Manufacturers must be cautious in their marketing and labeling to avoid making drug claims, which could result in regulatory action.
International regulations further complicate the landscape. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not approved health claims related to lithium orotate, and its use as a food supplement is subject to varying regulations across EU member states. In some countries, lithium orotate may be classified as a prescription medication, limiting its availability and use in anti-inflammatory research.
Research into lithium orotate's effects on prostaglandin synthesis must adhere to strict ethical and safety guidelines. Clinical trials investigating its anti-inflammatory properties would require approval from institutional review boards (IRBs) and compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards. The potential for lithium toxicity, even at lower doses found in the orotate form, necessitates careful monitoring and reporting of adverse events.
Regulatory considerations also extend to the manufacturing process. Producers of lithium orotate must comply with Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) to ensure product quality, purity, and consistency. This includes rigorous testing for contaminants and accurate labeling of active ingredients and their concentrations.
The regulatory pathway for potential therapeutic applications of lithium orotate in anti-inflammatory treatments remains uncertain. Should significant evidence emerge supporting its efficacy in modulating prostaglandin synthesis, it may face a complex journey towards drug approval. This would likely involve extensive pre-clinical and clinical trials, as well as a thorough review of its safety profile and mechanism of action by regulatory bodies such as the FDA or EMA.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate's potential in anti-inflammatory pathways presents exciting research opportunities, navigating the regulatory landscape requires careful consideration of its current status as a dietary supplement, international variations in regulation, and the stringent requirements for potential therapeutic applications. Researchers and manufacturers must remain vigilant in complying with existing regulations while preparing for potential shifts in the regulatory framework as scientific understanding of lithium orotate's influence on prostaglandin synthesis evolves.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!