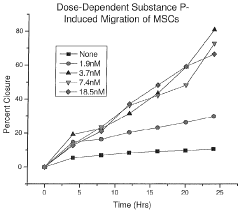
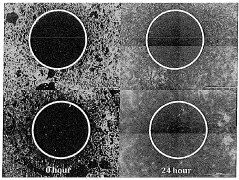
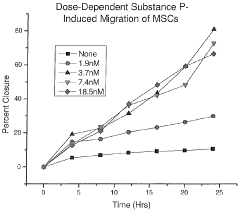
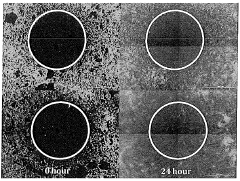
How does lithium orotate modulate neuroimmune interactions
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential neuromodulatory effects. This organic salt form of lithium differs from the more commonly prescribed lithium carbonate used in psychiatric treatments. The background of lithium orotate's interaction with neuroimmune systems traces back to the broader understanding of lithium's role in neuropsychiatry, which began in the mid-20th century.
Initially, lithium's therapeutic potential was discovered serendipitously in the treatment of bipolar disorder. As research progressed, scientists began to explore various forms of lithium, including lithium orotate, which was hypothesized to have enhanced bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects compared to inorganic lithium salts. The interest in lithium orotate stemmed from the idea that the orotate ion could act as a carrier, facilitating lithium's passage across the blood-brain barrier.
The exploration of lithium orotate's effects on neuroimmune interactions is rooted in the growing recognition of the intricate relationship between the nervous and immune systems. This interplay, known as neuroimmune communication, has been a subject of intense study in recent decades. Researchers have identified various pathways through which the brain and immune system influence each other, including cytokine signaling, neurotransmitter interactions, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Lithium's potential to modulate these neuroimmune interactions became a focal point of research due to its established neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties. Studies began to investigate how lithium, particularly in its orotate form, might influence neuroinflammation, microglial activation, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The unique chemical structure of lithium orotate prompted scientists to examine whether it could offer distinct advantages in targeting neuroimmune pathways.
As the field of psychoneuroimmunology expanded, the potential applications of lithium orotate in conditions characterized by neuroimmune dysregulation, such as depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative disorders, garnered increased attention. Researchers began to explore the compound's effects on specific immune markers, neurotrophic factors, and oxidative stress parameters within the central nervous system.
The background of lithium orotate's role in neuroimmune modulation is thus characterized by a convergence of multiple scientific disciplines, including neuropharmacology, immunology, and psychiatry. This interdisciplinary approach has led to a more comprehensive understanding of how lithium orotate might influence the complex interplay between neural and immune processes, paving the way for further investigation into its therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action.
Initially, lithium's therapeutic potential was discovered serendipitously in the treatment of bipolar disorder. As research progressed, scientists began to explore various forms of lithium, including lithium orotate, which was hypothesized to have enhanced bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects compared to inorganic lithium salts. The interest in lithium orotate stemmed from the idea that the orotate ion could act as a carrier, facilitating lithium's passage across the blood-brain barrier.
The exploration of lithium orotate's effects on neuroimmune interactions is rooted in the growing recognition of the intricate relationship between the nervous and immune systems. This interplay, known as neuroimmune communication, has been a subject of intense study in recent decades. Researchers have identified various pathways through which the brain and immune system influence each other, including cytokine signaling, neurotransmitter interactions, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Lithium's potential to modulate these neuroimmune interactions became a focal point of research due to its established neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties. Studies began to investigate how lithium, particularly in its orotate form, might influence neuroinflammation, microglial activation, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The unique chemical structure of lithium orotate prompted scientists to examine whether it could offer distinct advantages in targeting neuroimmune pathways.
As the field of psychoneuroimmunology expanded, the potential applications of lithium orotate in conditions characterized by neuroimmune dysregulation, such as depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative disorders, garnered increased attention. Researchers began to explore the compound's effects on specific immune markers, neurotrophic factors, and oxidative stress parameters within the central nervous system.
The background of lithium orotate's role in neuroimmune modulation is thus characterized by a convergence of multiple scientific disciplines, including neuropharmacology, immunology, and psychiatry. This interdisciplinary approach has led to a more comprehensive understanding of how lithium orotate might influence the complex interplay between neural and immune processes, paving the way for further investigation into its therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action.
Neuroimmune Market Analysis
The neuroimmune market, encompassing products and therapies targeting the interaction between the nervous and immune systems, has witnessed significant growth in recent years. This expansion is driven by the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and mental health conditions. The market for neuroimmune modulators, including lithium orotate, is expected to continue its upward trajectory due to the rising awareness of the intricate relationship between neural and immune functions.
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention in the neuroimmune space, represents a niche segment within the broader lithium market. While traditional lithium carbonate and lithium citrate dominate the pharmaceutical landscape for mood disorders, lithium orotate is carving out its own space in the nutraceutical and alternative medicine sectors. The compound's potential to modulate neuroimmune interactions has sparked interest among researchers and clinicians alike, contributing to its market growth.
The global neuroimmune market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including pharmaceuticals, biologics, and dietary supplements. Lithium orotate falls into the latter category, appealing to consumers seeking natural or alternative approaches to managing neurological and immune-related conditions. This positioning aligns with the growing trend towards personalized medicine and holistic health approaches, further driving market demand.
Key factors influencing the neuroimmune market include the aging population, increasing stress levels in modern society, and the growing body of research linking neuroinflammation to various health conditions. These trends create a favorable environment for products like lithium orotate, which may offer neuroprotective and immunomodulatory benefits. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened public awareness of the importance of immune health, potentially expanding the market for neuroimmune modulators.
The market for lithium orotate and similar neuroimmune modulators faces both opportunities and challenges. On the opportunity side, there is a growing consumer base seeking alternative treatments for mood disorders, cognitive decline, and autoimmune conditions. However, challenges include regulatory hurdles, as many of these compounds straddle the line between supplements and pharmaceuticals. Moreover, the need for more extensive clinical research to validate efficacy and safety claims presents both a challenge and an opportunity for market players.
Looking ahead, the neuroimmune market is poised for continued expansion, with lithium orotate and similar compounds likely to play an increasingly significant role. As research advances our understanding of neuroimmune interactions, new therapeutic targets and innovative products are expected to emerge, further shaping the market landscape and offering potential solutions for a wide range of neurological and immune-related disorders.
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention in the neuroimmune space, represents a niche segment within the broader lithium market. While traditional lithium carbonate and lithium citrate dominate the pharmaceutical landscape for mood disorders, lithium orotate is carving out its own space in the nutraceutical and alternative medicine sectors. The compound's potential to modulate neuroimmune interactions has sparked interest among researchers and clinicians alike, contributing to its market growth.
The global neuroimmune market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including pharmaceuticals, biologics, and dietary supplements. Lithium orotate falls into the latter category, appealing to consumers seeking natural or alternative approaches to managing neurological and immune-related conditions. This positioning aligns with the growing trend towards personalized medicine and holistic health approaches, further driving market demand.
Key factors influencing the neuroimmune market include the aging population, increasing stress levels in modern society, and the growing body of research linking neuroinflammation to various health conditions. These trends create a favorable environment for products like lithium orotate, which may offer neuroprotective and immunomodulatory benefits. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened public awareness of the importance of immune health, potentially expanding the market for neuroimmune modulators.
The market for lithium orotate and similar neuroimmune modulators faces both opportunities and challenges. On the opportunity side, there is a growing consumer base seeking alternative treatments for mood disorders, cognitive decline, and autoimmune conditions. However, challenges include regulatory hurdles, as many of these compounds straddle the line between supplements and pharmaceuticals. Moreover, the need for more extensive clinical research to validate efficacy and safety claims presents both a challenge and an opportunity for market players.
Looking ahead, the neuroimmune market is poised for continued expansion, with lithium orotate and similar compounds likely to play an increasingly significant role. As research advances our understanding of neuroimmune interactions, new therapeutic targets and innovative products are expected to emerge, further shaping the market landscape and offering potential solutions for a wide range of neurological and immune-related disorders.
Current Challenges in Neuroimmune Modulation
The field of neuroimmune modulation faces several significant challenges in understanding and harnessing the potential of lithium orotate. One primary obstacle is the complexity of neuroimmune interactions, which involve intricate communication between the nervous and immune systems. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate and study the specific effects of lithium orotate on these interactions.
Another challenge lies in the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences neuroimmune pathways. While research has shown promising results in terms of its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, the exact molecular targets and signaling cascades involved remain unclear. This lack of mechanistic insight hinders the development of targeted therapies and optimal dosing strategies.
The heterogeneity of neurological and psychiatric disorders further complicates the study of lithium orotate's neuroimmune modulatory effects. Different conditions may involve distinct neuroimmune dysregulations, making it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all approach to treatment. Researchers must navigate this complexity to identify which specific disorders or patient subgroups may benefit most from lithium orotate intervention.
Additionally, the field faces methodological challenges in designing and conducting robust clinical trials. The long-term effects of lithium orotate on neuroimmune function require extended study periods, which can be costly and logistically challenging. Moreover, the selection of appropriate biomarkers to measure neuroimmune modulation in human subjects remains a significant hurdle.
The potential for side effects and drug interactions also presents a challenge in the clinical application of lithium orotate for neuroimmune modulation. While generally considered safer than other lithium formulations, concerns about long-term safety and optimal dosing regimens persist. Researchers must carefully balance the therapeutic benefits against potential risks, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding lithium orotate as a neuroimmune modulator poses challenges for its widespread adoption in clinical practice. The compound's classification as a dietary supplement in some regions complicates the process of conducting rigorous clinical trials and obtaining regulatory approval for specific therapeutic indications. This regulatory ambiguity may hinder investment in large-scale studies and limit the availability of standardized, pharmaceutical-grade formulations for research and clinical use.
Another challenge lies in the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences neuroimmune pathways. While research has shown promising results in terms of its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, the exact molecular targets and signaling cascades involved remain unclear. This lack of mechanistic insight hinders the development of targeted therapies and optimal dosing strategies.
The heterogeneity of neurological and psychiatric disorders further complicates the study of lithium orotate's neuroimmune modulatory effects. Different conditions may involve distinct neuroimmune dysregulations, making it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all approach to treatment. Researchers must navigate this complexity to identify which specific disorders or patient subgroups may benefit most from lithium orotate intervention.
Additionally, the field faces methodological challenges in designing and conducting robust clinical trials. The long-term effects of lithium orotate on neuroimmune function require extended study periods, which can be costly and logistically challenging. Moreover, the selection of appropriate biomarkers to measure neuroimmune modulation in human subjects remains a significant hurdle.
The potential for side effects and drug interactions also presents a challenge in the clinical application of lithium orotate for neuroimmune modulation. While generally considered safer than other lithium formulations, concerns about long-term safety and optimal dosing regimens persist. Researchers must carefully balance the therapeutic benefits against potential risks, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding lithium orotate as a neuroimmune modulator poses challenges for its widespread adoption in clinical practice. The compound's classification as a dietary supplement in some regions complicates the process of conducting rigorous clinical trials and obtaining regulatory approval for specific therapeutic indications. This regulatory ambiguity may hinder investment in large-scale studies and limit the availability of standardized, pharmaceutical-grade formulations for research and clinical use.
Lithium Orotate Mechanisms
01 Lithium orotate's effects on neuroimmune signaling
Lithium orotate has been found to modulate neuroimmune signaling pathways, potentially influencing neuroinflammation and immune responses in the central nervous system. This interaction may have implications for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders with an inflammatory component.- Lithium orotate's effects on neuroimmune signaling: Lithium orotate has been found to modulate neuroimmune signaling pathways, potentially influencing neuroinflammation and immune responses in the central nervous system. This compound may affect the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and neurotrophic factors, contributing to its neuroprotective properties.
- Lithium orotate in neuropsychiatric disorders with immune components: Research suggests that lithium orotate may have therapeutic potential in neuropsychiatric disorders with immune system involvement. Its ability to modulate both neuronal and immune functions could be beneficial in conditions such as depression, bipolar disorder, and neurodegenerative diseases where neuroimmune interactions play a role.
- Mechanisms of lithium orotate's neuroimmune effects: The mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences neuroimmune interactions may involve regulation of intracellular signaling pathways, modulation of neurotransmitter systems, and alteration of gene expression related to immune function. These effects could contribute to its potential neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties.
- Lithium orotate's impact on microglial activation: Studies indicate that lithium orotate may affect microglial activation, a key process in neuroinflammation. By modulating microglial function, lithium orotate could influence the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses in the brain, potentially offering therapeutic benefits in neurological disorders.
- Combination therapies involving lithium orotate for neuroimmune modulation: Research is exploring the potential of combining lithium orotate with other compounds to enhance its neuroimmune modulatory effects. These combination therapies may offer synergistic benefits in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders with immune system involvement, potentially improving efficacy and reducing side effects.
02 Neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate
Research suggests that lithium orotate may possess neuroprotective properties, potentially reducing neuronal damage and promoting neuroplasticity. These effects could be mediated through its interaction with various neuroimmune mechanisms, offering potential therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate's impact on neuroinflammatory markers
Studies have investigated the effects of lithium orotate on neuroinflammatory markers, suggesting its potential to modulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other immune mediators in the brain. This could have implications for managing neuroinflammatory conditions and related disorders.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synergistic effects of lithium orotate with other compounds
Research has explored the potential synergistic effects of combining lithium orotate with other compounds to enhance its neuroimmune modulatory properties. These combinations may offer improved therapeutic outcomes in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders with an immune component.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery methods for lithium orotate in neuroimmune applications
Innovative delivery methods have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and targeted delivery of lithium orotate for neuroimmune applications. These approaches aim to improve the compound's efficacy and reduce potential side effects in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neuroimmune Research
The field of neuroimmune interactions modulated by lithium orotate is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market driven by increasing interest in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. The global market for neuroimmune modulators is expanding, though precise figures for lithium orotate are limited. Technologically, research is progressing but still nascent, with key players like Harvard University, Eli Lilly & Co., and New York University leading academic and pharmaceutical investigations. Janssen Pharmaceutica and Merck Sharp & Dohme are also active in this space, leveraging their expertise in neuroscience and immunology to explore lithium orotate's potential. The technology's maturity is evolving, with ongoing studies focusing on mechanism elucidation and clinical applications.
President & Fellows of Harvard College
Technical Solution: Harvard College has been at the forefront of research on lithium orotate and its effects on neuroimmune interactions. Their approach involves studying the modulation of microglial activation and neuroinflammation by lithium orotate. Researchers have found that lithium orotate can cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium salts, potentially leading to enhanced neuroprotective effects[1]. The college's studies have shown that lithium orotate may reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production and promote anti-inflammatory responses in the central nervous system[2]. Additionally, they have investigated its potential in modulating the gut-brain axis, which plays a crucial role in neuroimmune interactions[3].
Strengths: Access to cutting-edge research facilities and interdisciplinary collaboration. Weaknesses: Limited focus on clinical applications compared to pharmaceutical companies.
Eli Lilly & Co.
Technical Solution: Eli Lilly & Co. has been exploring the potential of lithium orotate in modulating neuroimmune interactions, particularly in the context of mood disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Their research focuses on the compound's ability to regulate neuroinflammation and microglial activation. Eli Lilly's approach involves investigating the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences key signaling pathways, such as glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)[4]. They have conducted preclinical studies demonstrating that lithium orotate can attenuate neuroinflammation by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine production and enhancing neuroprotective factors[5]. The company is also exploring the potential synergistic effects of combining lithium orotate with other compounds to enhance its neuroimmune modulatory properties.
Strengths: Extensive experience in drug development and clinical trials. Weaknesses: Potential conflicts of interest due to commercial interests.
Core Neuroimmune Interactions
Lithium for use in the treatment of antibody drug conjugate (ADC)-induced neuropathy
PatentWO2025165975A1
Innovation
- Administering lithium, either before, during, or after ADC treatment, to prevent or treat ADC-induced neuropathy and cognitive impairment, as lithium modulates intracellular calcium signaling and protects neuronal cells from toxicity without interfering with the antitumor effect of ADCs.
Treatment of neurological conditions by activation of neural stem cells
PatentInactiveAU2015230790A1
Innovation
- The use of specific dosages of lithium and valproic acid to activate endogenous neural stem cells, inducing proliferation, migration, and epigenetic reprogramming, which can be administered through various routes and formulations to treat neurological conditions by promoting tissue regeneration and neuroprotection.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
When considering the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate in modulating neuroimmune interactions, several key factors must be carefully evaluated. The bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate differ from more commonly used lithium salts, potentially affecting its safety profile and therapeutic efficacy.
Lithium orotate has been reported to have a lower risk of side effects compared to lithium carbonate, which is widely used in psychiatric treatments. This reduced toxicity may be attributed to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, allowing for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects. However, long-term safety data for lithium orotate is limited, necessitating cautious interpretation of its risk-benefit profile.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in neuroimmune modulation are multifaceted. Preliminary studies suggest that it may have neuroprotective properties and could potentially influence inflammatory processes in the central nervous system. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and impact glial cell function may contribute to its effects on neuroimmune interactions.
The optimal dosage for lithium orotate in this context remains unclear, as most research has focused on other lithium compounds. Establishing appropriate dosing regimens that balance efficacy with safety is crucial for its potential therapeutic application in neuroimmune disorders.
Monitoring lithium levels in patients using lithium orotate presents challenges due to its unique pharmacokinetics. Traditional methods for measuring serum lithium concentrations may not accurately reflect brain lithium levels when using this formulation, potentially complicating treatment management and safety assessments.
Interactions between lithium orotate and other medications or supplements must be carefully considered. Its impact on thyroid and kidney function, although potentially less severe than other lithium salts, still requires vigilant monitoring, especially in long-term use scenarios.
The potential for lithium orotate to modulate neuroimmune interactions in specific patient populations, such as those with autoimmune disorders or neurodegenerative diseases, warrants further investigation. Age-related differences in response and tolerability should also be examined to ensure safe and effective use across diverse patient groups.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in modulating neuroimmune interactions, comprehensive safety and efficacy studies are essential to establish its role in clinical practice. Rigorous clinical trials comparing lithium orotate to established treatments are needed to fully elucidate its therapeutic potential and long-term safety profile in the context of neuroimmune modulation.
Lithium orotate has been reported to have a lower risk of side effects compared to lithium carbonate, which is widely used in psychiatric treatments. This reduced toxicity may be attributed to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, allowing for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects. However, long-term safety data for lithium orotate is limited, necessitating cautious interpretation of its risk-benefit profile.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in neuroimmune modulation are multifaceted. Preliminary studies suggest that it may have neuroprotective properties and could potentially influence inflammatory processes in the central nervous system. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and impact glial cell function may contribute to its effects on neuroimmune interactions.
The optimal dosage for lithium orotate in this context remains unclear, as most research has focused on other lithium compounds. Establishing appropriate dosing regimens that balance efficacy with safety is crucial for its potential therapeutic application in neuroimmune disorders.
Monitoring lithium levels in patients using lithium orotate presents challenges due to its unique pharmacokinetics. Traditional methods for measuring serum lithium concentrations may not accurately reflect brain lithium levels when using this formulation, potentially complicating treatment management and safety assessments.
Interactions between lithium orotate and other medications or supplements must be carefully considered. Its impact on thyroid and kidney function, although potentially less severe than other lithium salts, still requires vigilant monitoring, especially in long-term use scenarios.
The potential for lithium orotate to modulate neuroimmune interactions in specific patient populations, such as those with autoimmune disorders or neurodegenerative diseases, warrants further investigation. Age-related differences in response and tolerability should also be examined to ensure safe and effective use across diverse patient groups.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in modulating neuroimmune interactions, comprehensive safety and efficacy studies are essential to establish its role in clinical practice. Rigorous clinical trials comparing lithium orotate to established treatments are needed to fully elucidate its therapeutic potential and long-term safety profile in the context of neuroimmune modulation.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium Orotate
The regulatory framework for lithium orotate is complex and evolving, reflecting the unique position of this compound at the intersection of dietary supplements and pharmaceutical products. In the United States, lithium orotate is primarily regulated as a dietary supplement under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This classification allows for its sale without prior FDA approval, provided manufacturers comply with good manufacturing practices and avoid making specific disease claims.
However, the regulatory landscape becomes more intricate when considering the pharmacological effects of lithium. The FDA has approved lithium carbonate and lithium citrate as prescription medications for bipolar disorder, but lithium orotate remains in a regulatory gray area. This ambiguity stems from its potential therapeutic effects, which may blur the line between supplement and drug.
Internationally, regulations vary significantly. In some European countries, lithium orotate is classified as a prescription medication, subject to stricter controls. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not established a tolerable upper intake level for lithium, citing insufficient data, which further complicates its regulatory status in the EU.
Safety concerns have prompted regulatory scrutiny. The FDA has issued warnings about potential risks associated with lithium-containing supplements, emphasizing the need for consumer awareness and medical supervision. These concerns are particularly relevant given lithium's narrow therapeutic index and potential for toxicity.
Labeling requirements for lithium orotate products also fall under regulatory purview. Manufacturers must adhere to specific guidelines regarding content claims, dosage information, and safety warnings. The lack of standardized dosing recommendations for lithium orotate as a supplement presents additional regulatory challenges.
Research into lithium orotate's neuroimmune modulation effects may influence future regulatory decisions. As scientific understanding advances, regulatory bodies may reassess the compound's classification, potentially leading to more stringent oversight or expanded therapeutic applications.
The regulatory framework must also address quality control and standardization issues. Unlike pharmaceutical-grade lithium compounds, the purity and consistency of lithium orotate supplements can vary, necessitating robust quality assurance measures to ensure consumer safety.
However, the regulatory landscape becomes more intricate when considering the pharmacological effects of lithium. The FDA has approved lithium carbonate and lithium citrate as prescription medications for bipolar disorder, but lithium orotate remains in a regulatory gray area. This ambiguity stems from its potential therapeutic effects, which may blur the line between supplement and drug.
Internationally, regulations vary significantly. In some European countries, lithium orotate is classified as a prescription medication, subject to stricter controls. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not established a tolerable upper intake level for lithium, citing insufficient data, which further complicates its regulatory status in the EU.
Safety concerns have prompted regulatory scrutiny. The FDA has issued warnings about potential risks associated with lithium-containing supplements, emphasizing the need for consumer awareness and medical supervision. These concerns are particularly relevant given lithium's narrow therapeutic index and potential for toxicity.
Labeling requirements for lithium orotate products also fall under regulatory purview. Manufacturers must adhere to specific guidelines regarding content claims, dosage information, and safety warnings. The lack of standardized dosing recommendations for lithium orotate as a supplement presents additional regulatory challenges.
Research into lithium orotate's neuroimmune modulation effects may influence future regulatory decisions. As scientific understanding advances, regulatory bodies may reassess the compound's classification, potentially leading to more stringent oversight or expanded therapeutic applications.
The regulatory framework must also address quality control and standardization issues. Unlike pharmaceutical-grade lithium compounds, the purity and consistency of lithium orotate supplements can vary, necessitating robust quality assurance measures to ensure consumer safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!