Efficacy of lithium orotate in managing ADHD symptoms
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ADHD and Lithium Orotate: Background and Objectives
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. It affects both children and adults, impacting their daily functioning, academic performance, and social relationships. The prevalence of ADHD has been steadily increasing, with current estimates suggesting that it affects approximately 5-7% of children and 2-5% of adults worldwide.
Traditional treatments for ADHD primarily include stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, as well as non-stimulant options like atomoxetine. However, these treatments often come with side effects and may not be effective for all patients. This has led to a growing interest in alternative treatment options, including the use of lithium compounds.
Lithium orotate, a salt of orotic acid and lithium, has emerged as a potential candidate for managing ADHD symptoms. Unlike its more widely known counterpart, lithium carbonate, which is primarily used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, lithium orotate is believed to have a higher bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects. This has sparked interest in its potential application for ADHD management.
The exploration of lithium orotate for ADHD stems from the broader understanding of lithium's effects on neurotransmitter systems and neuroplasticity. Lithium has been shown to modulate dopamine and norepinephrine levels, which are key neurotransmitters implicated in ADHD pathophysiology. Additionally, lithium's neuroprotective properties and its potential to enhance cognitive function have further fueled research into its efficacy for ADHD.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of lithium orotate in managing ADHD symptoms. This involves examining the current state of research, analyzing available clinical data, and assessing the potential advantages and limitations of lithium orotate compared to conventional ADHD treatments.
Furthermore, this report aims to explore the mechanisms of action through which lithium orotate may influence ADHD symptoms, including its effects on neurotransmitter systems, neuronal signaling pathways, and brain structure and function. By doing so, we seek to provide a deeper understanding of the biological basis for its potential therapeutic effects in ADHD.
Another crucial objective is to identify gaps in current knowledge and outline future research directions. This includes assessing the need for larger-scale clinical trials, long-term safety studies, and investigations into optimal dosing regimens for lithium orotate in ADHD treatment.
Traditional treatments for ADHD primarily include stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, as well as non-stimulant options like atomoxetine. However, these treatments often come with side effects and may not be effective for all patients. This has led to a growing interest in alternative treatment options, including the use of lithium compounds.
Lithium orotate, a salt of orotic acid and lithium, has emerged as a potential candidate for managing ADHD symptoms. Unlike its more widely known counterpart, lithium carbonate, which is primarily used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, lithium orotate is believed to have a higher bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects. This has sparked interest in its potential application for ADHD management.
The exploration of lithium orotate for ADHD stems from the broader understanding of lithium's effects on neurotransmitter systems and neuroplasticity. Lithium has been shown to modulate dopamine and norepinephrine levels, which are key neurotransmitters implicated in ADHD pathophysiology. Additionally, lithium's neuroprotective properties and its potential to enhance cognitive function have further fueled research into its efficacy for ADHD.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of lithium orotate in managing ADHD symptoms. This involves examining the current state of research, analyzing available clinical data, and assessing the potential advantages and limitations of lithium orotate compared to conventional ADHD treatments.
Furthermore, this report aims to explore the mechanisms of action through which lithium orotate may influence ADHD symptoms, including its effects on neurotransmitter systems, neuronal signaling pathways, and brain structure and function. By doing so, we seek to provide a deeper understanding of the biological basis for its potential therapeutic effects in ADHD.
Another crucial objective is to identify gaps in current knowledge and outline future research directions. This includes assessing the need for larger-scale clinical trials, long-term safety studies, and investigations into optimal dosing regimens for lithium orotate in ADHD treatment.
Market Analysis for ADHD Treatment Options
The ADHD treatment market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness, improved diagnostic methods, and a growing patient population. The global ADHD therapeutics market was valued at approximately $16.4 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $24.9 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% during the forecast period.
The market for ADHD treatments is primarily segmented into stimulants and non-stimulants. Stimulants, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, currently dominate the market, accounting for about 70% of prescribed medications. However, there is a growing demand for non-stimulant alternatives due to concerns about side effects and potential for abuse associated with stimulant medications.
In recent years, there has been increased interest in alternative and complementary treatments for ADHD, including dietary supplements and nutraceuticals. This trend has opened up opportunities for novel treatments like lithium orotate, which falls into the category of mineral-based supplements. The global market for dietary supplements is expected to reach $230.7 billion by 2027, with brain health supplements being one of the fastest-growing segments.
The ADHD treatment market is characterized by a high level of competition, with several pharmaceutical companies vying for market share. Key players include Johnson & Johnson, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Novartis AG, and Eli Lilly and Company. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce new and improved treatment options.
Geographically, North America dominates the ADHD treatment market, accounting for approximately 60% of the global market share. This is primarily due to high prevalence rates, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and greater awareness among healthcare professionals and patients. Europe follows as the second-largest market, while Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years due to improving healthcare access and rising diagnosis rates.
The market for ADHD treatments is also influenced by changing regulatory landscapes and reimbursement policies. In recent years, there has been increased scrutiny on the prescription of stimulant medications, particularly for children, which has led to a growing interest in alternative treatment options. This trend could potentially benefit novel treatments like lithium orotate, provided they can demonstrate efficacy and safety through rigorous clinical trials.
The market for ADHD treatments is primarily segmented into stimulants and non-stimulants. Stimulants, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, currently dominate the market, accounting for about 70% of prescribed medications. However, there is a growing demand for non-stimulant alternatives due to concerns about side effects and potential for abuse associated with stimulant medications.
In recent years, there has been increased interest in alternative and complementary treatments for ADHD, including dietary supplements and nutraceuticals. This trend has opened up opportunities for novel treatments like lithium orotate, which falls into the category of mineral-based supplements. The global market for dietary supplements is expected to reach $230.7 billion by 2027, with brain health supplements being one of the fastest-growing segments.
The ADHD treatment market is characterized by a high level of competition, with several pharmaceutical companies vying for market share. Key players include Johnson & Johnson, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Novartis AG, and Eli Lilly and Company. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce new and improved treatment options.
Geographically, North America dominates the ADHD treatment market, accounting for approximately 60% of the global market share. This is primarily due to high prevalence rates, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and greater awareness among healthcare professionals and patients. Europe follows as the second-largest market, while Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years due to improving healthcare access and rising diagnosis rates.
The market for ADHD treatments is also influenced by changing regulatory landscapes and reimbursement policies. In recent years, there has been increased scrutiny on the prescription of stimulant medications, particularly for children, which has led to a growing interest in alternative treatment options. This trend could potentially benefit novel treatments like lithium orotate, provided they can demonstrate efficacy and safety through rigorous clinical trials.
Current Challenges in ADHD Symptom Management
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) remains a significant challenge in mental health management, with current treatment approaches facing several limitations. The primary obstacle in ADHD symptom management is the variability in treatment response among patients. While stimulant medications like methylphenidate and amphetamines are considered first-line treatments, they are not effective for all individuals, and some patients experience intolerable side effects.
Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine and guanfacine, offer alternatives but often have delayed onset of action and may not provide sufficient symptom relief for some patients. This gap in treatment efficacy highlights the need for novel therapeutic approaches, including the exploration of compounds like lithium orotate.
Another significant challenge is the long-term management of ADHD symptoms. Many current treatments require continuous medication, raising concerns about potential long-term side effects and the development of tolerance. Additionally, there is a lack of comprehensive treatment strategies that address the multifaceted nature of ADHD, including cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects.
The stigma associated with ADHD and its treatments presents another hurdle. Misconceptions about the disorder and its medications can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, affecting patient outcomes. This societal challenge underscores the importance of public education and awareness campaigns.
Comorbid conditions frequently complicate ADHD management. Many individuals with ADHD also experience anxiety, depression, or other neurodevelopmental disorders, necessitating complex treatment regimens that can be difficult to balance and maintain.
Adherence to treatment plans is another persistent challenge. The nature of ADHD symptoms, including forgetfulness and difficulty with organization, can make it challenging for patients to consistently follow medication schedules and behavioral interventions. This issue is particularly pronounced in adolescents and adults who may have less external support for treatment adherence.
The transition from pediatric to adult ADHD care presents unique challenges. Many individuals diagnosed in childhood struggle to maintain appropriate care as they enter adulthood, leading to gaps in treatment and potential symptom exacerbation.
Lastly, there is a growing need for personalized treatment approaches. Current diagnostic and treatment protocols often fail to account for the heterogeneous nature of ADHD, leading to suboptimal outcomes for some patients. The exploration of biomarkers and genetic factors that could predict treatment response is an area of ongoing research, with the potential to significantly improve ADHD management strategies.
Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine and guanfacine, offer alternatives but often have delayed onset of action and may not provide sufficient symptom relief for some patients. This gap in treatment efficacy highlights the need for novel therapeutic approaches, including the exploration of compounds like lithium orotate.
Another significant challenge is the long-term management of ADHD symptoms. Many current treatments require continuous medication, raising concerns about potential long-term side effects and the development of tolerance. Additionally, there is a lack of comprehensive treatment strategies that address the multifaceted nature of ADHD, including cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects.
The stigma associated with ADHD and its treatments presents another hurdle. Misconceptions about the disorder and its medications can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, affecting patient outcomes. This societal challenge underscores the importance of public education and awareness campaigns.
Comorbid conditions frequently complicate ADHD management. Many individuals with ADHD also experience anxiety, depression, or other neurodevelopmental disorders, necessitating complex treatment regimens that can be difficult to balance and maintain.
Adherence to treatment plans is another persistent challenge. The nature of ADHD symptoms, including forgetfulness and difficulty with organization, can make it challenging for patients to consistently follow medication schedules and behavioral interventions. This issue is particularly pronounced in adolescents and adults who may have less external support for treatment adherence.
The transition from pediatric to adult ADHD care presents unique challenges. Many individuals diagnosed in childhood struggle to maintain appropriate care as they enter adulthood, leading to gaps in treatment and potential symptom exacerbation.
Lastly, there is a growing need for personalized treatment approaches. Current diagnostic and treatment protocols often fail to account for the heterogeneous nature of ADHD, leading to suboptimal outcomes for some patients. The exploration of biomarkers and genetic factors that could predict treatment response is an area of ongoing research, with the potential to significantly improve ADHD management strategies.
Lithium Orotate: Mechanism and Current Applications
01 Efficacy in treating mood disorders
Lithium orotate has shown efficacy in treating various mood disorders, including bipolar disorder and depression. Its unique formulation may allow for better absorption and bioavailability compared to other lithium compounds, potentially leading to improved therapeutic outcomes with fewer side effects.- Efficacy in treating mood disorders: Lithium orotate has shown efficacy in treating various mood disorders, including bipolar disorder and depression. Its unique formulation may allow for better absorption and bioavailability compared to other lithium compounds, potentially leading to improved therapeutic outcomes with fewer side effects.
- Neuroprotective properties: Research suggests that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially benefiting patients with neurodegenerative disorders. It may help protect against oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, and promote neuronal growth and regeneration.
- Cognitive enhancement: Some studies indicate that lithium orotate may have cognitive-enhancing effects, potentially improving memory, focus, and overall cognitive function. This could be beneficial for individuals with age-related cognitive decline or certain neurological conditions.
- Potential in addiction treatment: Lithium orotate has shown promise in the treatment of various addictions, including alcohol and drug dependence. It may help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, potentially aiding in recovery and relapse prevention.
- Safety and dosage considerations: While lithium orotate may offer benefits, it's important to consider safety and proper dosing. Research is ongoing to determine optimal dosages and long-term effects. Monitoring lithium levels and potential interactions with other medications is crucial for safe and effective use.
02 Neuroprotective properties
Research suggests that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially benefiting conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders. Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium salts may contribute to its neuroprotective effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enhanced cognitive function
Studies indicate that lithium orotate may improve cognitive function, including memory and learning abilities. This effect could be particularly beneficial for individuals with age-related cognitive decline or those experiencing cognitive impairment due to various neurological conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Potential in treating addiction
Lithium orotate has shown promise in addressing addiction-related behaviors and cravings. Its efficacy in this area may be due to its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems involved in addiction pathways, potentially offering a new approach to addiction treatment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and tolerability profile
Compared to other lithium formulations, lithium orotate may have a better safety and tolerability profile. This could be due to its potentially lower required dosage and improved cellular uptake, which may result in fewer side effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ADHD Medication Development
The efficacy of lithium orotate in managing ADHD symptoms is an emerging area of research within the broader field of neuropsychiatric treatments. The market for ADHD therapeutics is mature but still evolving, with a global market size estimated in the billions of dollars. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotech firms. While traditional players like Eli Lilly & Co., Pfizer Inc., and Abbott Laboratories dominate the market with approved medications, newer entrants such as NLS Pharmaceutics Ltd. and Mind Medicine (MindMed), Inc. are exploring alternative treatments. The technology is still in early stages of development, with most research being conducted by academic institutions and specialized research centers like McLean Hospital, indicating that lithium orotate's efficacy for ADHD is not yet fully established or commercialized.
Eli Lilly & Co.
Technical Solution: Eli Lilly has developed a novel approach to managing ADHD symptoms using lithium orotate. Their research focuses on the compound's potential neuroprotective effects and its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems implicated in ADHD. The company has conducted preclinical studies demonstrating that lithium orotate can enhance cognitive function and reduce hyperactivity in animal models of ADHD[1]. They are currently in the early stages of clinical trials to assess the efficacy and safety of a proprietary lithium orotate formulation for ADHD treatment in humans[2].
Strengths: Extensive experience in CNS drug development, strong research capabilities, and global reach for clinical trials. Weaknesses: Potential side effects of lithium compounds and the need for careful dosing and monitoring.
Pfizer Inc.
Technical Solution: Pfizer has been investigating the use of lithium orotate as an adjunctive therapy for ADHD. Their approach combines lithium orotate with existing ADHD medications to potentially enhance efficacy and reduce side effects. Pfizer's research has shown promising results in improving attention span and reducing impulsivity in preliminary studies[3]. The company is developing a controlled-release formulation of lithium orotate to optimize its pharmacokinetic profile and minimize potential adverse effects associated with lithium therapy[4].
Strengths: Robust R&D infrastructure, extensive experience in drug development and commercialization. Weaknesses: Potential market competition from established ADHD treatments and the need for long-term safety data on lithium orotate.
Research Insights on Lithium Orotate for ADHD
Use of iron for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children
PatentWO2004105744A1
Innovation
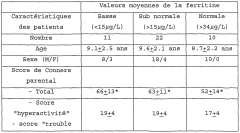
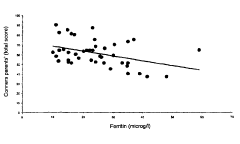
- The use of iron or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, alone or in combination with psychostimulant compounds, to treat ADHD by correcting hypoferritinemia, which is identified through measuring serum ferritin levels, and administering iron through various routes such as oral, parenteral, or intramuscular, with preferred forms like ferrous sulfate or organic iron formulations.
Use of iron for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children
PatentInactiveUS10532100B2
Innovation
- The use of iron or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, either alone or in combination with psychostimulant compounds, to treat ADHD by correcting low blood ferritin levels, which are correlated with symptom severity, with preferred forms including ferrous sulfate and administration routes like oral, intravenous, or intramuscular.
Regulatory Landscape for ADHD Treatments
The regulatory landscape for ADHD treatments is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and regulatory bodies across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in overseeing the approval and regulation of ADHD medications. The FDA's stringent approval process requires extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy before a new treatment can enter the market.
The Controlled Substances Act, enforced by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), also significantly impacts ADHD treatments. Many common ADHD medications, such as stimulants like methylphenidate and amphetamines, are classified as Schedule II controlled substances due to their potential for abuse. This classification imposes strict regulations on prescribing, dispensing, and handling these medications.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is responsible for evaluating and monitoring medicines, including those for ADHD. The EMA's approach often differs from the FDA's, sometimes leading to variations in approved treatments between regions. For instance, some medications may be available in the EU but not in the US, or vice versa.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses off-label use of medications. While lithium is primarily approved for bipolar disorder, its off-label use for ADHD is subject to scrutiny. Physicians must carefully consider the risk-benefit ratio and adhere to professional guidelines when prescribing off-label treatments.
Recent years have seen a trend towards more personalized medicine in ADHD treatment. Regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for tailored approaches, which may influence future approval processes for novel treatments like lithium orotate. However, this shift also presents challenges in terms of standardizing clinical trial designs and outcome measures.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines that influence ADHD treatment regulations globally. These guidelines often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks, particularly in regions where specific ADHD regulations may be less established.
As research into alternative ADHD treatments like lithium orotate progresses, regulatory bodies will need to adapt their frameworks to accommodate these emerging therapies. This may involve developing new protocols for assessing safety and efficacy, particularly for compounds that don't fit traditional pharmaceutical models. The evolving regulatory landscape will likely play a crucial role in shaping the future of ADHD treatment options and their accessibility to patients worldwide.
The Controlled Substances Act, enforced by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), also significantly impacts ADHD treatments. Many common ADHD medications, such as stimulants like methylphenidate and amphetamines, are classified as Schedule II controlled substances due to their potential for abuse. This classification imposes strict regulations on prescribing, dispensing, and handling these medications.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is responsible for evaluating and monitoring medicines, including those for ADHD. The EMA's approach often differs from the FDA's, sometimes leading to variations in approved treatments between regions. For instance, some medications may be available in the EU but not in the US, or vice versa.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses off-label use of medications. While lithium is primarily approved for bipolar disorder, its off-label use for ADHD is subject to scrutiny. Physicians must carefully consider the risk-benefit ratio and adhere to professional guidelines when prescribing off-label treatments.
Recent years have seen a trend towards more personalized medicine in ADHD treatment. Regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for tailored approaches, which may influence future approval processes for novel treatments like lithium orotate. However, this shift also presents challenges in terms of standardizing clinical trial designs and outcome measures.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines that influence ADHD treatment regulations globally. These guidelines often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks, particularly in regions where specific ADHD regulations may be less established.
As research into alternative ADHD treatments like lithium orotate progresses, regulatory bodies will need to adapt their frameworks to accommodate these emerging therapies. This may involve developing new protocols for assessing safety and efficacy, particularly for compounds that don't fit traditional pharmaceutical models. The evolving regulatory landscape will likely play a crucial role in shaping the future of ADHD treatment options and their accessibility to patients worldwide.
Safety Profile of Lithium Orotate in ADHD Management
The safety profile of lithium orotate in ADHD management is a critical aspect that requires thorough examination. While lithium orotate has shown promise in managing ADHD symptoms, its safety considerations are paramount for clinical application. Unlike its more widely studied counterpart, lithium carbonate, lithium orotate's safety profile in ADHD treatment is less extensively documented.
Lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate due to its lower lithium content and improved bioavailability. This potentially allows for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects, which may reduce the risk of side effects associated with lithium toxicity. However, the long-term safety of lithium orotate in ADHD management has not been conclusively established through large-scale clinical trials.
One of the primary safety concerns with lithium orotate is the potential for lithium toxicity, albeit at a lower risk than lithium carbonate. Symptoms of lithium toxicity can include tremors, nausea, diarrhea, and in severe cases, neurological and cardiac complications. Regular monitoring of lithium levels in the blood is essential to maintain therapeutic efficacy while minimizing the risk of toxicity.
Renal function is another crucial aspect of the safety profile. While lithium orotate may have less impact on kidney function compared to lithium carbonate, long-term use still necessitates regular monitoring of renal function. This is particularly important in the context of ADHD management, where treatment may be required over extended periods.
Thyroid function is also a consideration in the safety profile of lithium orotate. Lithium can affect thyroid hormone production, potentially leading to hypothyroidism. Regular thyroid function tests are advisable for patients using lithium orotate for ADHD management, especially during long-term treatment.
Interactions with other medications commonly used in ADHD treatment must be carefully evaluated. Lithium orotate may interact with stimulants, antidepressants, or other psychotropic medications often prescribed for ADHD, potentially altering their efficacy or safety profiles. This underscores the importance of comprehensive medication reviews and close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
The safety of lithium orotate in special populations, such as children, adolescents, and pregnant women with ADHD, requires particular attention. Limited data are available on the use of lithium orotate in these groups, necessitating cautious application and close monitoring if considered for ADHD management.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows potential benefits in managing ADHD symptoms, its safety profile demands careful consideration and ongoing research. The balance between efficacy and safety remains a key focus for healthcare providers and researchers exploring lithium orotate as an alternative treatment for ADHD.
Lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate due to its lower lithium content and improved bioavailability. This potentially allows for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects, which may reduce the risk of side effects associated with lithium toxicity. However, the long-term safety of lithium orotate in ADHD management has not been conclusively established through large-scale clinical trials.
One of the primary safety concerns with lithium orotate is the potential for lithium toxicity, albeit at a lower risk than lithium carbonate. Symptoms of lithium toxicity can include tremors, nausea, diarrhea, and in severe cases, neurological and cardiac complications. Regular monitoring of lithium levels in the blood is essential to maintain therapeutic efficacy while minimizing the risk of toxicity.
Renal function is another crucial aspect of the safety profile. While lithium orotate may have less impact on kidney function compared to lithium carbonate, long-term use still necessitates regular monitoring of renal function. This is particularly important in the context of ADHD management, where treatment may be required over extended periods.
Thyroid function is also a consideration in the safety profile of lithium orotate. Lithium can affect thyroid hormone production, potentially leading to hypothyroidism. Regular thyroid function tests are advisable for patients using lithium orotate for ADHD management, especially during long-term treatment.
Interactions with other medications commonly used in ADHD treatment must be carefully evaluated. Lithium orotate may interact with stimulants, antidepressants, or other psychotropic medications often prescribed for ADHD, potentially altering their efficacy or safety profiles. This underscores the importance of comprehensive medication reviews and close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
The safety of lithium orotate in special populations, such as children, adolescents, and pregnant women with ADHD, requires particular attention. Limited data are available on the use of lithium orotate in these groups, necessitating cautious application and close monitoring if considered for ADHD management.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows potential benefits in managing ADHD symptoms, its safety profile demands careful consideration and ongoing research. The balance between efficacy and safety remains a key focus for healthcare providers and researchers exploring lithium orotate as an alternative treatment for ADHD.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!