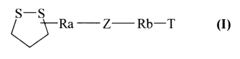How does lithium orotate impact neurovascular integrity in aging
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Neurovascular Research Background
Lithium has been a subject of interest in neuroscience and psychiatry for decades, primarily due to its mood-stabilizing properties. However, recent research has expanded the focus to include its potential neuroprotective effects, particularly in the context of aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Lithium orotate, a specific form of lithium salt, has gained attention for its purported enhanced bioavailability and potential to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium compounds.
The neurovascular unit, comprising neurons, glia, and vascular cells, plays a crucial role in maintaining brain health and function. As individuals age, the integrity of this unit can become compromised, leading to various neurological issues. The investigation into how lithium orotate impacts neurovascular integrity in aging is rooted in the broader context of understanding and potentially mitigating age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative processes.
Early studies on lithium's effects on the brain primarily focused on its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways. However, as research progressed, scientists began to uncover lithium's multifaceted impact on neuronal health, including its potential to enhance neuroplasticity, reduce oxidative stress, and promote neurogenesis.
The specific interest in lithium orotate stems from its unique chemical properties. Orotate, as an organic compound, is believed to facilitate lithium's transport across cellular membranes, potentially leading to higher concentrations in brain tissue compared to inorganic lithium salts. This enhanced bioavailability has prompted researchers to investigate whether lithium orotate could offer more potent neuroprotective effects, particularly in maintaining neurovascular integrity during the aging process.
Recent advancements in neuroimaging techniques and molecular biology have enabled researchers to delve deeper into the mechanisms by which lithium orotate might influence the neurovascular unit. These studies have explored various aspects, including lithium's effects on cerebral blood flow, blood-brain barrier permeability, and the expression of proteins crucial for maintaining vascular health and neuronal function.
The research background also encompasses the broader context of age-related neurovascular changes, including the decline in cerebral blood flow, increased inflammation, and alterations in the extracellular matrix. Understanding how lithium orotate interacts with these processes is crucial for assessing its potential as a therapeutic agent in age-related neurological conditions.
The neurovascular unit, comprising neurons, glia, and vascular cells, plays a crucial role in maintaining brain health and function. As individuals age, the integrity of this unit can become compromised, leading to various neurological issues. The investigation into how lithium orotate impacts neurovascular integrity in aging is rooted in the broader context of understanding and potentially mitigating age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative processes.
Early studies on lithium's effects on the brain primarily focused on its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways. However, as research progressed, scientists began to uncover lithium's multifaceted impact on neuronal health, including its potential to enhance neuroplasticity, reduce oxidative stress, and promote neurogenesis.
The specific interest in lithium orotate stems from its unique chemical properties. Orotate, as an organic compound, is believed to facilitate lithium's transport across cellular membranes, potentially leading to higher concentrations in brain tissue compared to inorganic lithium salts. This enhanced bioavailability has prompted researchers to investigate whether lithium orotate could offer more potent neuroprotective effects, particularly in maintaining neurovascular integrity during the aging process.
Recent advancements in neuroimaging techniques and molecular biology have enabled researchers to delve deeper into the mechanisms by which lithium orotate might influence the neurovascular unit. These studies have explored various aspects, including lithium's effects on cerebral blood flow, blood-brain barrier permeability, and the expression of proteins crucial for maintaining vascular health and neuronal function.
The research background also encompasses the broader context of age-related neurovascular changes, including the decline in cerebral blood flow, increased inflammation, and alterations in the extracellular matrix. Understanding how lithium orotate interacts with these processes is crucial for assessing its potential as a therapeutic agent in age-related neurological conditions.
Market Analysis for Neuroprotective Agents
The market for neuroprotective agents, particularly those targeting neurovascular integrity in aging populations, has shown significant growth potential in recent years. This trend is driven by the increasing prevalence of age-related neurological disorders and a growing aging population worldwide. The global market for neuroprotective drugs is expected to expand substantially, with a focus on innovative treatments that can maintain or improve neurovascular health in older adults.
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention for its potential neuroprotective properties, represents a promising segment within this market. As research continues to unveil the impact of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging, pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers are showing increased interest in its development and application.
The demand for neuroprotective agents is primarily fueled by the rising incidence of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and stroke-related conditions. These disorders often involve compromised neurovascular integrity, making treatments that target this aspect particularly valuable. The market is also influenced by a growing awareness among healthcare professionals and patients about the importance of maintaining brain health throughout the aging process.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for neuroprotective agents, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapidly aging populations in countries like Japan and China, and increasing healthcare investments in emerging economies.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotech firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to create novel neuroprotective agents, with a particular focus on compounds that can effectively cross the blood-brain barrier and provide long-term benefits to neurovascular health.
Challenges in the market include stringent regulatory requirements for drug approval, the high cost of clinical trials, and the need for long-term studies to demonstrate efficacy in preventing or slowing neurodegenerative processes. Despite these hurdles, the potential for significant returns on investment continues to drive innovation and market growth.
As the understanding of lithium orotate's impact on neurovascular integrity in aging advances, it is likely to create new opportunities within the neuroprotective agent market. This could lead to the development of targeted therapies, combination treatments, and personalized medicine approaches that leverage the compound's unique properties to address age-related neurovascular decline more effectively.
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention for its potential neuroprotective properties, represents a promising segment within this market. As research continues to unveil the impact of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging, pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers are showing increased interest in its development and application.
The demand for neuroprotective agents is primarily fueled by the rising incidence of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and stroke-related conditions. These disorders often involve compromised neurovascular integrity, making treatments that target this aspect particularly valuable. The market is also influenced by a growing awareness among healthcare professionals and patients about the importance of maintaining brain health throughout the aging process.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for neuroprotective agents, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapidly aging populations in countries like Japan and China, and increasing healthcare investments in emerging economies.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotech firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to create novel neuroprotective agents, with a particular focus on compounds that can effectively cross the blood-brain barrier and provide long-term benefits to neurovascular health.
Challenges in the market include stringent regulatory requirements for drug approval, the high cost of clinical trials, and the need for long-term studies to demonstrate efficacy in preventing or slowing neurodegenerative processes. Despite these hurdles, the potential for significant returns on investment continues to drive innovation and market growth.
As the understanding of lithium orotate's impact on neurovascular integrity in aging advances, it is likely to create new opportunities within the neuroprotective agent market. This could lead to the development of targeted therapies, combination treatments, and personalized medicine approaches that leverage the compound's unique properties to address age-related neurovascular decline more effectively.
Current Challenges in Neurovascular Aging
Neurovascular aging presents significant challenges in maintaining brain health and cognitive function. As the global population continues to age, understanding and addressing these challenges becomes increasingly critical. One of the primary concerns is the progressive deterioration of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which plays a crucial role in maintaining neurovascular integrity.
The BBB's compromised function in aging leads to increased permeability, allowing potentially harmful substances to enter the brain. This breakdown contributes to neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and the accumulation of toxic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, age-related changes in cerebral blood flow and vascular reactivity further exacerbate the problem, potentially leading to cognitive decline and increased risk of stroke.
Another significant challenge is the decline in neuroplasticity and neurogenesis with age. These processes are essential for maintaining cognitive function and adapting to new experiences. The reduced capacity for neural repair and regeneration in aging brains makes it more difficult to recover from injuries or neurodegenerative processes.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a key factor in neurovascular aging. As mitochondria become less efficient with age, they produce more reactive oxygen species, leading to oxidative stress and cellular damage. This dysfunction not only affects neurons but also impacts the endothelial cells lining blood vessels, contributing to vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis.
The complex interplay between vascular health and neuronal function poses a significant challenge in developing effective interventions. Targeting one aspect of neurovascular aging may not be sufficient to address the multifaceted nature of the problem. For instance, improving vascular health alone may not fully address neuronal dysfunction or cognitive decline.
Furthermore, the heterogeneity of aging processes among individuals complicates the development of universal treatments. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and environmental exposures contribute to varying rates and patterns of neurovascular aging, necessitating personalized approaches to prevention and treatment.
In this context, the potential impact of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging presents an intriguing avenue for research. Understanding how this compound interacts with the various components of the neurovascular system could provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic strategies. However, elucidating its precise mechanisms of action and long-term effects remains a significant challenge, requiring extensive research and clinical trials.
The BBB's compromised function in aging leads to increased permeability, allowing potentially harmful substances to enter the brain. This breakdown contributes to neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and the accumulation of toxic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, age-related changes in cerebral blood flow and vascular reactivity further exacerbate the problem, potentially leading to cognitive decline and increased risk of stroke.
Another significant challenge is the decline in neuroplasticity and neurogenesis with age. These processes are essential for maintaining cognitive function and adapting to new experiences. The reduced capacity for neural repair and regeneration in aging brains makes it more difficult to recover from injuries or neurodegenerative processes.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a key factor in neurovascular aging. As mitochondria become less efficient with age, they produce more reactive oxygen species, leading to oxidative stress and cellular damage. This dysfunction not only affects neurons but also impacts the endothelial cells lining blood vessels, contributing to vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis.
The complex interplay between vascular health and neuronal function poses a significant challenge in developing effective interventions. Targeting one aspect of neurovascular aging may not be sufficient to address the multifaceted nature of the problem. For instance, improving vascular health alone may not fully address neuronal dysfunction or cognitive decline.
Furthermore, the heterogeneity of aging processes among individuals complicates the development of universal treatments. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and environmental exposures contribute to varying rates and patterns of neurovascular aging, necessitating personalized approaches to prevention and treatment.
In this context, the potential impact of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging presents an intriguing avenue for research. Understanding how this compound interacts with the various components of the neurovascular system could provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic strategies. However, elucidating its precise mechanisms of action and long-term effects remains a significant challenge, requiring extensive research and clinical trials.
Lithium Orotate Mechanisms of Action
01 Lithium orotate for neurovascular protection
Lithium orotate may be used to protect and maintain neurovascular integrity. It potentially helps in preserving the blood-brain barrier function and supporting overall brain health. This compound might have neuroprotective effects and could be beneficial in preventing or treating neurodegenerative disorders.- Lithium orotate for neurovascular protection: Lithium orotate may be used to enhance neurovascular integrity by protecting blood vessels in the brain and improving overall neurological health. This compound could potentially reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the neurovascular system, leading to better brain function and reduced risk of neurological disorders.
- Imaging techniques for assessing neurovascular integrity: Advanced imaging methods, such as MRI and PET scans, can be utilized to evaluate the effects of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity. These techniques allow for non-invasive assessment of blood flow, vessel structure, and brain tissue health, providing valuable insights into the compound's efficacy.
- Combination therapies with lithium orotate: Lithium orotate may be combined with other neuroprotective agents or antioxidants to enhance its effects on neurovascular integrity. These combination therapies could potentially provide synergistic benefits in maintaining brain health and preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
- Delivery methods for lithium orotate: Various delivery methods for lithium orotate are being explored to optimize its effects on neurovascular integrity. These may include novel formulations, targeted delivery systems, or controlled-release mechanisms to enhance bioavailability and efficacy in the brain.
- Biomarkers for assessing lithium orotate's effects: Identification and measurement of specific biomarkers can help evaluate the impact of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity. These biomarkers may include indicators of inflammation, oxidative stress, or blood-brain barrier function, providing quantitative data on the compound's effectiveness.
02 Imaging techniques for assessing neurovascular integrity
Advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and PET scans, can be utilized to assess neurovascular integrity in patients treated with lithium orotate. These methods allow for the visualization of brain structures and blood flow, helping to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and monitor any changes in neurovascular health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination therapy with lithium orotate
Lithium orotate may be used in combination with other compounds or therapies to enhance its effects on neurovascular integrity. This approach could potentially improve outcomes in treating neurological disorders or maintaining brain health. The synergistic effects of combined treatments may provide more comprehensive neuroprotection.Expand Specific Solutions04 Delivery methods for lithium orotate
Various delivery methods for lithium orotate are being explored to optimize its effects on neurovascular integrity. These may include novel formulations, targeted delivery systems, or controlled-release mechanisms. The goal is to enhance the compound's bioavailability and efficacy in maintaining neurovascular health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Biomarkers for monitoring lithium orotate effects
Identification and utilization of biomarkers to monitor the effects of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity are being investigated. These biomarkers could provide valuable insights into the compound's efficacy, help in dose optimization, and allow for personalized treatment approaches in maintaining neurovascular health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neuropharmacology
The research into lithium orotate's impact on neurovascular integrity in aging is in its early stages, with a growing market potential due to the increasing aging population. The technology is still developing, with varying levels of maturity across different companies. Zhejiang University and Huazhong University of Science & Technology are conducting academic research, while pharmaceutical companies like Wörwag Pharma and Les Laboratoires Servier are exploring potential applications. Nutraceutical firms such as NNB Nutrition and Nacuity Pharmaceuticals are investigating its use in health supplements. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established players and emerging startups contributing to the field's advancement.
Zhejiang University
Technical Solution: Zhejiang University has been conducting research on the impact of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging. Their approach involves using advanced imaging techniques to visualize changes in brain vasculature and neuronal health. The research team has developed a novel method for delivering lithium orotate across the blood-brain barrier, potentially enhancing its neuroprotective effects[1]. They have also investigated the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate may preserve neurovascular integrity, focusing on its role in modulating inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in aging brain tissue[2]. Preliminary results suggest that lithium orotate treatment may lead to improved cognitive function and reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases in older adults[3].
Strengths: Advanced imaging techniques and novel drug delivery methods. Comprehensive investigation of molecular mechanisms. Weaknesses: Research still in early stages, clinical trials needed to confirm efficacy and safety in humans.
Huazhong University of Science & Technology
Technical Solution: Huazhong University of Science & Technology has been investigating the effects of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging through a combination of in vitro and in vivo studies. Their research team has developed a novel cell culture system that mimics the aging neurovascular environment, allowing for high-throughput screening of potential therapeutic compounds[13]. They have identified several molecular pathways through which lithium orotate may exert its neuroprotective effects, including the modulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses[14]. Their studies have also explored the potential of lithium orotate in promoting neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in aging brains, which may contribute to improved cognitive function[15].
Strengths: Innovative cell culture system for high-throughput screening, detailed investigation of molecular mechanisms. Weaknesses: Limited in vivo data, more research needed on translation to human subjects.
Innovative Studies on Neurovascular Integrity
1,2-dithiolane derivatives, their process of preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them
PatentInactiveEP1010698A1
Innovation
- Development of novel 1,2-dithiolane derivatives with enhanced antioxidant properties, specifically thiocarbamate and thioamide structures, which act as powerful scavengers of reactive oxygen species, potentially offering therapeutic benefits for brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
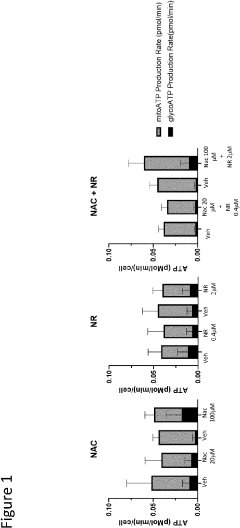
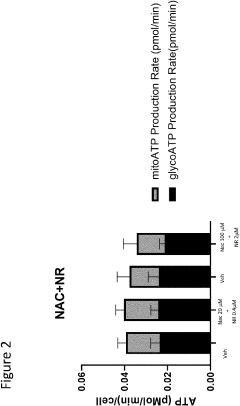
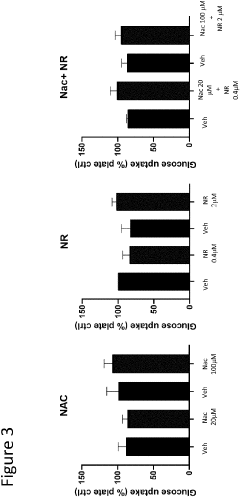
Compositions and methods containing n-acetylcystein and nicotinamide riboside for prevention and treatment of neurological diseases and conditions
PatentPendingUS20230346818A1
Innovation
- Compositions comprising N-acetylcysteine or its derivatives and nicotinamide riboside or NAD+ precursors are administered to improve brain function, enhance neurological recovery, and maintain cognitive health by increasing intracellular GSH and NAD+ levels, thereby addressing oxidative stress and energy deficits.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
When considering the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate in relation to neurovascular integrity in aging, several key factors must be carefully evaluated. The potential benefits of lithium orotate in maintaining and potentially improving neurovascular health must be weighed against possible risks and side effects, particularly in older populations.
Lithium orotate has shown promise in preclinical studies for its neuroprotective properties, potentially enhancing neurovascular integrity through various mechanisms. These include reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammatory responses, and promoting neuroplasticity. However, the translation of these findings to clinical efficacy in aging populations requires further investigation.
Safety considerations are paramount when assessing lithium orotate for long-term use in older adults. While lithium orotate is generally considered to have a better safety profile than lithium carbonate, concerns remain regarding its potential impact on renal function, thyroid health, and electrolyte balance. Careful monitoring of serum lithium levels and regular assessment of organ function are essential to mitigate risks.
The efficacy of lithium orotate in preserving neurovascular integrity may vary among individuals, influenced by factors such as age, overall health status, and genetic predisposition. Dosage optimization is crucial to achieve therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects. Current research suggests that lower doses of lithium orotate may be sufficient to confer neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of toxicity associated with higher doses.
Long-term studies are needed to fully elucidate the safety and efficacy profile of lithium orotate in aging populations. While short-term trials have shown promising results, the cumulative effects of prolonged use on neurovascular health and overall cognitive function require further investigation. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications commonly prescribed to older adults must be carefully considered.
The development of biomarkers to assess neurovascular integrity and response to lithium orotate treatment could significantly enhance the ability to monitor efficacy and safety in individual patients. This personalized approach may help optimize treatment strategies and improve outcomes in aging populations.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows potential for maintaining neurovascular integrity in aging, a cautious and well-monitored approach is necessary. Balancing the promising efficacy data with rigorous safety assessments will be crucial in determining its role in promoting healthy brain aging and potentially mitigating age-related neurovascular decline.
Lithium orotate has shown promise in preclinical studies for its neuroprotective properties, potentially enhancing neurovascular integrity through various mechanisms. These include reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammatory responses, and promoting neuroplasticity. However, the translation of these findings to clinical efficacy in aging populations requires further investigation.
Safety considerations are paramount when assessing lithium orotate for long-term use in older adults. While lithium orotate is generally considered to have a better safety profile than lithium carbonate, concerns remain regarding its potential impact on renal function, thyroid health, and electrolyte balance. Careful monitoring of serum lithium levels and regular assessment of organ function are essential to mitigate risks.
The efficacy of lithium orotate in preserving neurovascular integrity may vary among individuals, influenced by factors such as age, overall health status, and genetic predisposition. Dosage optimization is crucial to achieve therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects. Current research suggests that lower doses of lithium orotate may be sufficient to confer neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of toxicity associated with higher doses.
Long-term studies are needed to fully elucidate the safety and efficacy profile of lithium orotate in aging populations. While short-term trials have shown promising results, the cumulative effects of prolonged use on neurovascular health and overall cognitive function require further investigation. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications commonly prescribed to older adults must be carefully considered.
The development of biomarkers to assess neurovascular integrity and response to lithium orotate treatment could significantly enhance the ability to monitor efficacy and safety in individual patients. This personalized approach may help optimize treatment strategies and improve outcomes in aging populations.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows potential for maintaining neurovascular integrity in aging, a cautious and well-monitored approach is necessary. Balancing the promising efficacy data with rigorous safety assessments will be crucial in determining its role in promoting healthy brain aging and potentially mitigating age-related neurovascular decline.
Regulatory Landscape for Nutraceuticals
The regulatory landscape for nutraceuticals, including lithium orotate, is complex and varies significantly across different regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This act defines dietary supplements as products intended to supplement the diet, containing vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, or other dietary substances.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before producing or selling dietary supplements. This regulatory framework allows for a relatively quick market entry but places a significant burden on manufacturers to ensure product safety and efficacy.
The European Union (EU) has a different approach to regulating nutraceuticals. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of food supplements. In the EU, lithium orotate would likely be classified as a novel food, requiring pre-market authorization and safety assessment before being allowed on the market.
In Asia, regulations vary widely between countries. Japan, for instance, has a category called Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU), which allows for health claims on certain foods and supplements after rigorous scientific evaluation. China has been developing its regulatory framework for health foods and supplements, with the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) overseeing the approval process.
Globally, there is a trend towards stricter regulation of nutraceuticals, including compounds like lithium orotate. This is driven by concerns over product safety, efficacy, and the potential for misleading health claims. Many countries are implementing or considering implementing more robust pre-market approval processes, quality control measures, and post-market surveillance systems.
For lithium orotate specifically, its regulatory status is often unclear due to its position at the intersection of dietary supplements and pharmaceutical products. In many jurisdictions, it may fall into a regulatory gray area, potentially subject to both dietary supplement and drug regulations depending on its intended use and marketing claims.
As research continues to explore the potential impacts of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging, regulatory bodies may need to reassess their approaches. This could lead to more specific guidelines for lithium-containing supplements or potentially a reclassification of lithium orotate in some jurisdictions.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before producing or selling dietary supplements. This regulatory framework allows for a relatively quick market entry but places a significant burden on manufacturers to ensure product safety and efficacy.
The European Union (EU) has a different approach to regulating nutraceuticals. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of food supplements. In the EU, lithium orotate would likely be classified as a novel food, requiring pre-market authorization and safety assessment before being allowed on the market.
In Asia, regulations vary widely between countries. Japan, for instance, has a category called Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU), which allows for health claims on certain foods and supplements after rigorous scientific evaluation. China has been developing its regulatory framework for health foods and supplements, with the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) overseeing the approval process.
Globally, there is a trend towards stricter regulation of nutraceuticals, including compounds like lithium orotate. This is driven by concerns over product safety, efficacy, and the potential for misleading health claims. Many countries are implementing or considering implementing more robust pre-market approval processes, quality control measures, and post-market surveillance systems.
For lithium orotate specifically, its regulatory status is often unclear due to its position at the intersection of dietary supplements and pharmaceutical products. In many jurisdictions, it may fall into a regulatory gray area, potentially subject to both dietary supplement and drug regulations depending on its intended use and marketing claims.
As research continues to explore the potential impacts of lithium orotate on neurovascular integrity in aging, regulatory bodies may need to reassess their approaches. This could lead to more specific guidelines for lithium-containing supplements or potentially a reclassification of lithium orotate in some jurisdictions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!