Biochemical interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Neurotransmitter Interaction Background
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic effects on neurological and psychiatric disorders. The interaction between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters represents a crucial area of research in neuropharmacology, with implications for the treatment of various mental health conditions.
The history of lithium in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. However, the use of lithium orotate as a specific form of lithium supplementation is a more recent development. Unlike lithium carbonate, which has been widely used in clinical settings, lithium orotate is believed to have enhanced bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects.
Neurotransmitter transporters play a vital role in regulating the concentration of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, thereby influencing neural signaling and brain function. These transporters are responsible for the reuptake of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are implicated in mood regulation, cognitive function, and various psychiatric disorders.
The interaction between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters is of particular interest due to its potential to modulate neurotransmitter levels and activity. This interaction may contribute to the therapeutic effects observed in conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety. Understanding the biochemical mechanisms underlying these interactions is crucial for developing more effective and targeted treatments.
Research in this field has evolved from initial observations of lithium's effects on mood to more detailed investigations of its molecular targets and mechanisms of action. The focus on lithium orotate specifically has emerged as scientists seek to optimize the therapeutic benefits of lithium while minimizing adverse effects.
Current research aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with neurotransmitter transporters. This includes studying its effects on transporter expression, function, and regulation. Additionally, researchers are investigating how these interactions may differ from those of other lithium compounds and how they contribute to the overall therapeutic profile of lithium orotate.
The exploration of lithium orotate's interactions with neurotransmitter transporters intersects with broader research trends in neuroscience and psychopharmacology. This includes the growing emphasis on personalized medicine approaches in psychiatry and the search for novel therapeutic targets in the treatment of mood disorders and other mental health conditions.
The history of lithium in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. However, the use of lithium orotate as a specific form of lithium supplementation is a more recent development. Unlike lithium carbonate, which has been widely used in clinical settings, lithium orotate is believed to have enhanced bioavailability and potentially fewer side effects.
Neurotransmitter transporters play a vital role in regulating the concentration of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, thereby influencing neural signaling and brain function. These transporters are responsible for the reuptake of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are implicated in mood regulation, cognitive function, and various psychiatric disorders.
The interaction between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters is of particular interest due to its potential to modulate neurotransmitter levels and activity. This interaction may contribute to the therapeutic effects observed in conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety. Understanding the biochemical mechanisms underlying these interactions is crucial for developing more effective and targeted treatments.
Research in this field has evolved from initial observations of lithium's effects on mood to more detailed investigations of its molecular targets and mechanisms of action. The focus on lithium orotate specifically has emerged as scientists seek to optimize the therapeutic benefits of lithium while minimizing adverse effects.
Current research aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with neurotransmitter transporters. This includes studying its effects on transporter expression, function, and regulation. Additionally, researchers are investigating how these interactions may differ from those of other lithium compounds and how they contribute to the overall therapeutic profile of lithium orotate.
The exploration of lithium orotate's interactions with neurotransmitter transporters intersects with broader research trends in neuroscience and psychopharmacology. This includes the growing emphasis on personalized medicine approaches in psychiatry and the search for novel therapeutic targets in the treatment of mood disorders and other mental health conditions.
Market Analysis for Lithium-Based Neuropsychiatric Treatments
The market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of mental health disorders and the growing recognition of lithium's therapeutic potential. Lithium compounds, particularly lithium carbonate and lithium orotate, have shown efficacy in treating bipolar disorder, depression, and other mood disorders. The global market for these treatments is expected to continue expanding, with a compound annual growth rate projected to remain strong over the next five years.
Demand for lithium-based treatments is primarily fueled by the rising incidence of mental health conditions worldwide. The World Health Organization estimates that over 280 million people suffer from depression globally, while bipolar disorder affects approximately 45 million individuals. These numbers are likely to increase due to factors such as population growth, increased awareness, and improved diagnostic capabilities.
The market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments can be segmented by compound type, with lithium carbonate currently dominating due to its long-standing use and extensive clinical data. However, lithium orotate is gaining traction as an alternative form, with proponents claiming improved bioavailability and reduced side effects. This shift in preference is creating new opportunities for market players and driving research into the biochemical interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market due to well-established healthcare infrastructure, high awareness levels, and substantial research and development investments. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The competitive landscape of the lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatment market is characterized by a mix of large pharmaceutical companies and specialized mental health-focused firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the efficacy of lithium-based treatments and explore novel delivery mechanisms. Additionally, there is growing interest in combination therapies that leverage lithium's mood-stabilizing properties alongside other psychiatric medications.
Market challenges include the need for careful dosing and monitoring of lithium levels, potential side effects, and competition from alternative mood stabilizers. However, ongoing research into the biochemical mechanisms of lithium, particularly its interactions with neurotransmitter transporters, is expected to lead to more targeted and effective treatments, potentially expanding the market further.
Demand for lithium-based treatments is primarily fueled by the rising incidence of mental health conditions worldwide. The World Health Organization estimates that over 280 million people suffer from depression globally, while bipolar disorder affects approximately 45 million individuals. These numbers are likely to increase due to factors such as population growth, increased awareness, and improved diagnostic capabilities.
The market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments can be segmented by compound type, with lithium carbonate currently dominating due to its long-standing use and extensive clinical data. However, lithium orotate is gaining traction as an alternative form, with proponents claiming improved bioavailability and reduced side effects. This shift in preference is creating new opportunities for market players and driving research into the biochemical interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market due to well-established healthcare infrastructure, high awareness levels, and substantial research and development investments. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The competitive landscape of the lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatment market is characterized by a mix of large pharmaceutical companies and specialized mental health-focused firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the efficacy of lithium-based treatments and explore novel delivery mechanisms. Additionally, there is growing interest in combination therapies that leverage lithium's mood-stabilizing properties alongside other psychiatric medications.
Market challenges include the need for careful dosing and monitoring of lithium levels, potential side effects, and competition from alternative mood stabilizers. However, ongoing research into the biochemical mechanisms of lithium, particularly its interactions with neurotransmitter transporters, is expected to lead to more targeted and effective treatments, potentially expanding the market further.
Current Understanding and Challenges in Lithium Orotate Research
The current understanding of lithium orotate's interactions with neurotransmitter transporters is still evolving, with several key findings and challenges shaping the research landscape. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention for its potential neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties. However, its precise mechanisms of action, particularly in relation to neurotransmitter transporters, remain incompletely understood.
Recent studies have suggested that lithium orotate may influence the function of various neurotransmitter transporters, including those for serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. These interactions are thought to contribute to its therapeutic effects in mood disorders and neurodegenerative conditions. However, the exact nature and extent of these interactions are still subjects of ongoing investigation.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the limited number of comprehensive studies directly comparing its effects to those of more established lithium compounds, such as lithium carbonate. This gap in comparative data makes it difficult to fully assess the potential advantages or unique properties of lithium orotate in terms of its interactions with neurotransmitter systems.
Another significant challenge lies in understanding the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of lithium orotate. While some researchers propose that the orotate form may allow for better penetration of the blood-brain barrier, leading to potentially enhanced effects on neurotransmitter systems, conclusive evidence supporting this claim is still lacking. This uncertainty complicates the interpretation of observed effects on neurotransmitter transporters.
The molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with neurotransmitter transporters also remain unclear. While lithium ions are known to affect various signaling pathways and enzyme systems, the specific role of the orotate moiety in these interactions is not well-defined. This lack of mechanistic clarity presents a significant challenge in fully elucidating the compound's effects on neurotransmitter transport and signaling.
Furthermore, the long-term effects of lithium orotate on neurotransmitter systems and overall brain function are not yet well-established. Given the critical role of neurotransmitter balance in mental health and cognitive function, understanding these long-term impacts is crucial for assessing the compound's therapeutic potential and safety profile.
In conclusion, while initial research suggests promising interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters, significant challenges remain in fully characterizing and understanding these biochemical processes. Addressing these challenges will require more targeted studies, improved analytical techniques, and a comprehensive approach to unraveling the complex interplay between lithium orotate and the brain's neurotransmitter systems.
Recent studies have suggested that lithium orotate may influence the function of various neurotransmitter transporters, including those for serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. These interactions are thought to contribute to its therapeutic effects in mood disorders and neurodegenerative conditions. However, the exact nature and extent of these interactions are still subjects of ongoing investigation.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the limited number of comprehensive studies directly comparing its effects to those of more established lithium compounds, such as lithium carbonate. This gap in comparative data makes it difficult to fully assess the potential advantages or unique properties of lithium orotate in terms of its interactions with neurotransmitter systems.
Another significant challenge lies in understanding the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of lithium orotate. While some researchers propose that the orotate form may allow for better penetration of the blood-brain barrier, leading to potentially enhanced effects on neurotransmitter systems, conclusive evidence supporting this claim is still lacking. This uncertainty complicates the interpretation of observed effects on neurotransmitter transporters.
The molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with neurotransmitter transporters also remain unclear. While lithium ions are known to affect various signaling pathways and enzyme systems, the specific role of the orotate moiety in these interactions is not well-defined. This lack of mechanistic clarity presents a significant challenge in fully elucidating the compound's effects on neurotransmitter transport and signaling.
Furthermore, the long-term effects of lithium orotate on neurotransmitter systems and overall brain function are not yet well-established. Given the critical role of neurotransmitter balance in mental health and cognitive function, understanding these long-term impacts is crucial for assessing the compound's therapeutic potential and safety profile.
In conclusion, while initial research suggests promising interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters, significant challenges remain in fully characterizing and understanding these biochemical processes. Addressing these challenges will require more targeted studies, improved analytical techniques, and a comprehensive approach to unraveling the complex interplay between lithium orotate and the brain's neurotransmitter systems.
Existing Mechanisms of Lithium Orotate-Neurotransmitter Interaction
01 Effects of lithium orotate on neurotransmitter transporters
Lithium orotate may influence the function and regulation of neurotransmitter transporters in the brain. This compound could potentially modulate the reuptake of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, affecting their availability in the synaptic cleft and potentially impacting mood and cognitive function.- Effects of lithium orotate on neurotransmitter transporters: Lithium orotate has been found to influence neurotransmitter transporters, potentially affecting the regulation of neurotransmitters in the brain. This interaction may contribute to its therapeutic effects in various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Research suggests that lithium orotate may modulate the activity of transporters for serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are crucial for maintaining proper neurotransmitter balance.
- Genetic factors influencing neurotransmitter transporter response to lithium orotate: Studies have investigated the genetic variations that may affect an individual's response to lithium orotate treatment, particularly in relation to neurotransmitter transporters. Certain genetic polymorphisms in transporter genes may influence the efficacy of lithium orotate in modulating neurotransmitter levels. This research aims to develop personalized treatment approaches based on genetic profiles.
- Lithium orotate's impact on synaptic plasticity and neurotransmitter release: Research has explored how lithium orotate affects synaptic plasticity and neurotransmitter release mechanisms. The compound may influence the expression and function of proteins involved in synaptic vesicle trafficking and neurotransmitter release. These effects could contribute to its potential neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties.
- Combination therapies involving lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporter modulators: Investigations have been conducted on the potential synergistic effects of combining lithium orotate with other compounds that modulate neurotransmitter transporters. These combination therapies aim to enhance the therapeutic benefits while potentially reducing side effects. The research focuses on identifying optimal drug combinations for treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Novel delivery methods for lithium orotate targeting neurotransmitter transporters: Innovative delivery methods have been developed to enhance the targeted delivery of lithium orotate to neurotransmitter transporters in the brain. These approaches aim to improve the compound's bioavailability and efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. Research in this area includes the development of nanoparticle-based delivery systems and other advanced drug delivery technologies.
02 Lithium orotate in neurological disorder treatments
Lithium orotate may be used in the treatment of various neurological disorders, potentially by interacting with neurotransmitter systems. Its effects on neurotransmitter transporters could make it a candidate for treating conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety, possibly offering advantages over other lithium formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mechanisms of lithium orotate on cellular signaling
Lithium orotate may affect cellular signaling pathways related to neurotransmitter transport. This could involve modulation of gene expression, protein synthesis, or post-translational modifications of neurotransmitter transporters, potentially altering their function or expression levels in neurons.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium orotate in combination therapies
The use of lithium orotate in combination with other compounds or therapies may enhance its effects on neurotransmitter transporters. Such combinations could potentially lead to more effective treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders, possibly with reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium therapies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Bioavailability and safety of lithium orotate
The bioavailability and safety profile of lithium orotate may differ from other lithium formulations, potentially affecting its interaction with neurotransmitter transporters. This could influence its efficacy and side effect profile in neurological treatments, possibly making it a more attractive option for certain patient populations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Orotate and Neurotransmitter Research
The biochemical interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters represent an emerging field of study with significant potential for therapeutic applications. The market is in its early stages, characterized by limited commercial products and ongoing research. Key players like F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen Pharmaceutica, and Incyte Corp. are investing in neurotransmitter research, although specific focus on lithium orotate interactions is not widespread. The technology's maturity is still developing, with academic institutions such as Johns Hopkins University and Columbia University leading fundamental research efforts. As the understanding of these interactions grows, we can expect increased interest from pharmaceutical companies and potential market expansion in the coming years.
Glaxo Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Glaxo Group Ltd. has developed a novel approach to study the biochemical interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters. Their research focuses on the use of advanced imaging techniques, such as fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), to visualize the real-time interactions between lithium orotate and various neurotransmitter transporters in living cells[1]. This method allows for the precise measurement of binding affinities and kinetics, providing valuable insights into the mechanism of action of lithium orotate on neurotransmitter systems. Additionally, they have employed molecular dynamics simulations to predict potential binding sites and conformational changes induced by lithium orotate on transporter proteins[3].
Strengths: High-resolution imaging techniques provide detailed insights into molecular interactions. The combination of experimental and computational approaches offers a comprehensive understanding of the biochemical processes. Weaknesses: The complexity of the cellular environment may limit the accuracy of in vitro studies, and the computational models may not fully capture all aspects of the biological system.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. has developed a multi-omics approach to investigate the biochemical interactions between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters. Their method integrates proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics data to provide a comprehensive view of the cellular response to lithium orotate treatment[2]. By using stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) combined with mass spectrometry, they have identified specific protein-protein interactions and post-translational modifications associated with lithium orotate's effects on neurotransmitter transporters[4]. Furthermore, they have employed RNA sequencing to elucidate the transcriptional changes induced by lithium orotate, revealing potential regulatory mechanisms governing neurotransmitter transporter expression and function.
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-omics approach provides a holistic view of cellular responses. High-throughput techniques allow for the identification of novel molecular targets and pathways. Weaknesses: The complexity of data integration and interpretation may lead to challenges in distinguishing direct effects from secondary responses. The approach may be less sensitive to subtle or transient interactions.
Innovative Studies on Lithium Orotate Biochemical Pathways
Enhancing CNS drug transport through surface-modified oleuropein nanostructured lipid carriers via nasal delivery
PatentPendingIN202341085391A
Innovation
- Surface modification of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) loaded with oleuropein, specifically optimized through a melt-emulsification and ultrasonication process, to enhance nasal delivery and CNS transport, using chitosan coating to improve penetration and stability.
Selective potentiation of serotonin receptor subtypes
PatentInactiveUS6858649B1
Innovation
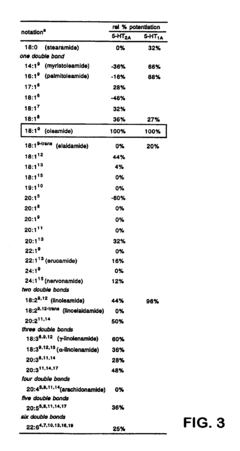
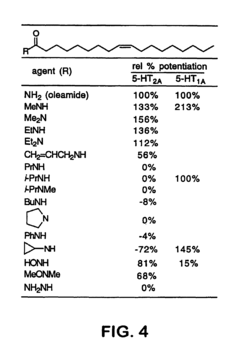
- Development of oleamide-based analogs that act as selective agonists or antagonists for specific serotonin receptor subtypes, such as 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A, with structures optimized to enhance or inhibit serotonergic signal transduction responses, allowing for tailored modulation of serotonin receptor activities.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Lithium Orotate Use
The safety and efficacy of lithium orotate use are critical considerations in the context of its biochemical interactions with neurotransmitter transporters. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention as an alternative to traditional lithium carbonate in the treatment of mood disorders and other neurological conditions.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate's interaction with neurotransmitter transporters may lead to altered neurotransmitter levels in the brain. This could potentially affect mood, cognition, and behavior. However, the precise mechanisms and extent of these interactions are not fully understood, necessitating careful monitoring and further research to establish safe dosage ranges and potential side effects.
One key safety concern is the potential for lithium accumulation in the body, which could lead to toxicity. Unlike lithium carbonate, lithium orotate's pharmacokinetics and bioavailability are less well-established, making it challenging to predict its long-term effects on neurotransmitter systems and overall brain function.
Regarding efficacy, the interaction between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters may contribute to its therapeutic effects. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may modulate the activity of transporters for serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, potentially influencing mood regulation and cognitive function. However, the extent to which these interactions translate to clinical efficacy remains a subject of ongoing research.
The lower dosage typically used with lithium orotate compared to lithium carbonate may offer a more favorable side effect profile. This could potentially improve patient compliance and long-term adherence to treatment. However, the lack of standardized dosing guidelines and limited clinical trials comparing lithium orotate to established treatments make it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about its relative efficacy.
Another consideration is the potential for lithium orotate to interact with other medications that affect neurotransmitter systems. These interactions could either enhance or diminish the therapeutic effects of lithium orotate or lead to unexpected side effects. Healthcare providers must be aware of these potential interactions when considering lithium orotate as a treatment option.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in its interactions with neurotransmitter transporters, more rigorous clinical studies are needed to fully elucidate its safety profile and establish its efficacy in various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Until such data are available, caution should be exercised in its use, and close monitoring of patients is essential to ensure both safety and optimal therapeutic outcomes.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate's interaction with neurotransmitter transporters may lead to altered neurotransmitter levels in the brain. This could potentially affect mood, cognition, and behavior. However, the precise mechanisms and extent of these interactions are not fully understood, necessitating careful monitoring and further research to establish safe dosage ranges and potential side effects.
One key safety concern is the potential for lithium accumulation in the body, which could lead to toxicity. Unlike lithium carbonate, lithium orotate's pharmacokinetics and bioavailability are less well-established, making it challenging to predict its long-term effects on neurotransmitter systems and overall brain function.
Regarding efficacy, the interaction between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters may contribute to its therapeutic effects. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may modulate the activity of transporters for serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, potentially influencing mood regulation and cognitive function. However, the extent to which these interactions translate to clinical efficacy remains a subject of ongoing research.
The lower dosage typically used with lithium orotate compared to lithium carbonate may offer a more favorable side effect profile. This could potentially improve patient compliance and long-term adherence to treatment. However, the lack of standardized dosing guidelines and limited clinical trials comparing lithium orotate to established treatments make it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about its relative efficacy.
Another consideration is the potential for lithium orotate to interact with other medications that affect neurotransmitter systems. These interactions could either enhance or diminish the therapeutic effects of lithium orotate or lead to unexpected side effects. Healthcare providers must be aware of these potential interactions when considering lithium orotate as a treatment option.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in its interactions with neurotransmitter transporters, more rigorous clinical studies are needed to fully elucidate its safety profile and establish its efficacy in various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Until such data are available, caution should be exercised in its use, and close monitoring of patients is essential to ensure both safety and optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Potential Clinical Applications of Lithium Orotate Interactions
The potential clinical applications of lithium orotate interactions with neurotransmitter transporters are diverse and promising. These interactions may offer new therapeutic avenues for various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
One of the most significant potential applications is in the treatment of mood disorders, particularly bipolar disorder and depression. The modulation of neurotransmitter transporters by lithium orotate could lead to more effective mood stabilization and antidepressant effects. This interaction may provide a more targeted approach compared to traditional lithium carbonate treatments, potentially reducing side effects and improving patient compliance.
Anxiety disorders represent another area where lithium orotate interactions could prove beneficial. By influencing neurotransmitter transport, particularly serotonin and norepinephrine, lithium orotate may help regulate anxiety responses and provide a novel treatment option for patients who do not respond well to current anxiolytic medications.
Neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, might also benefit from lithium orotate's interactions with neurotransmitter transporters. The neuroprotective properties of lithium, combined with its potential to modulate neurotransmitter levels, could slow disease progression and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
In the field of addiction medicine, lithium orotate's interactions may offer new strategies for treating substance use disorders. By influencing dopamine and serotonin transport, it could help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, potentially aiding in addiction recovery and relapse prevention.
Cognitive enhancement is another area of interest. The interaction between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters may lead to improved cognitive function, potentially benefiting patients with cognitive impairments or even healthy individuals seeking to optimize their mental performance.
Sleep disorders could also be addressed through these interactions. By modulating neurotransmitter levels involved in sleep-wake cycles, lithium orotate might offer a novel approach to treating insomnia and other sleep-related disorders.
Lastly, the potential applications extend to pain management. The influence on neurotransmitter transport could provide new avenues for treating chronic pain conditions, offering an alternative to opioid-based pain medications.
As research in this area progresses, it is likely that additional clinical applications will emerge, further expanding the therapeutic potential of lithium orotate's interactions with neurotransmitter transporters.
One of the most significant potential applications is in the treatment of mood disorders, particularly bipolar disorder and depression. The modulation of neurotransmitter transporters by lithium orotate could lead to more effective mood stabilization and antidepressant effects. This interaction may provide a more targeted approach compared to traditional lithium carbonate treatments, potentially reducing side effects and improving patient compliance.
Anxiety disorders represent another area where lithium orotate interactions could prove beneficial. By influencing neurotransmitter transport, particularly serotonin and norepinephrine, lithium orotate may help regulate anxiety responses and provide a novel treatment option for patients who do not respond well to current anxiolytic medications.
Neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, might also benefit from lithium orotate's interactions with neurotransmitter transporters. The neuroprotective properties of lithium, combined with its potential to modulate neurotransmitter levels, could slow disease progression and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
In the field of addiction medicine, lithium orotate's interactions may offer new strategies for treating substance use disorders. By influencing dopamine and serotonin transport, it could help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, potentially aiding in addiction recovery and relapse prevention.
Cognitive enhancement is another area of interest. The interaction between lithium orotate and neurotransmitter transporters may lead to improved cognitive function, potentially benefiting patients with cognitive impairments or even healthy individuals seeking to optimize their mental performance.
Sleep disorders could also be addressed through these interactions. By modulating neurotransmitter levels involved in sleep-wake cycles, lithium orotate might offer a novel approach to treating insomnia and other sleep-related disorders.
Lastly, the potential applications extend to pain management. The influence on neurotransmitter transport could provide new avenues for treating chronic pain conditions, offering an alternative to opioid-based pain medications.
As research in this area progresses, it is likely that additional clinical applications will emerge, further expanding the therapeutic potential of lithium orotate's interactions with neurotransmitter transporters.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!