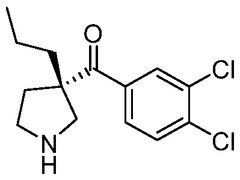
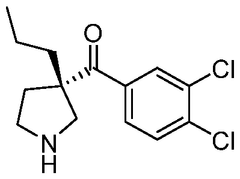
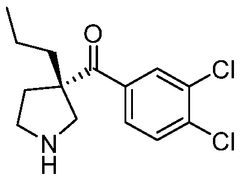
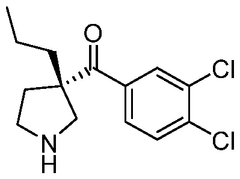
The effectiveness of lithium orotate in menopause-related mood disturbances
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic effects on various neurological and psychiatric conditions. The background of lithium orotate research dates back to the 1970s when it was first synthesized and studied as an alternative to lithium carbonate, the more commonly prescribed form of lithium in psychiatric medicine.
The use of lithium in treating mood disorders has a long history, with its mood-stabilizing properties first discovered in the late 1940s. However, the traditional lithium carbonate formulation often requires high doses to achieve therapeutic effects, which can lead to significant side effects and toxicity concerns. This limitation sparked interest in developing alternative lithium compounds with improved bioavailability and reduced side effects.
Lithium orotate emerged as a promising candidate due to its unique chemical structure, which is believed to enhance lithium's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. This property potentially allows for lower dosages while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. As research progressed, lithium orotate's potential applications expanded beyond bipolar disorder to include other neurological and psychiatric conditions.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in exploring the effectiveness of lithium orotate for managing menopause-related mood disturbances. Menopause is a significant life transition for women, often accompanied by hormonal fluctuations that can lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression. These mood disturbances can significantly impact a woman's quality of life and overall well-being.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate in the context of menopause-related mood disturbances is to evaluate its potential as a safe and effective treatment option. Researchers aim to determine whether lithium orotate can alleviate the severity and frequency of mood symptoms associated with menopause, potentially offering an alternative or complementary approach to hormone replacement therapy and traditional antidepressants.
Additionally, the research seeks to understand the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may influence mood regulation during menopause. This includes exploring its effects on neurotransmitter systems, hormonal balance, and neuroprotective properties that could be particularly beneficial during this transitional period in a woman's life.
Another important objective is to assess the safety profile and optimal dosing of lithium orotate specifically for menopausal women. This involves evaluating potential side effects, drug interactions, and long-term safety considerations, as well as determining the most effective dosage regimen for managing mood disturbances without compromising overall health.
The use of lithium in treating mood disorders has a long history, with its mood-stabilizing properties first discovered in the late 1940s. However, the traditional lithium carbonate formulation often requires high doses to achieve therapeutic effects, which can lead to significant side effects and toxicity concerns. This limitation sparked interest in developing alternative lithium compounds with improved bioavailability and reduced side effects.
Lithium orotate emerged as a promising candidate due to its unique chemical structure, which is believed to enhance lithium's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. This property potentially allows for lower dosages while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. As research progressed, lithium orotate's potential applications expanded beyond bipolar disorder to include other neurological and psychiatric conditions.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in exploring the effectiveness of lithium orotate for managing menopause-related mood disturbances. Menopause is a significant life transition for women, often accompanied by hormonal fluctuations that can lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression. These mood disturbances can significantly impact a woman's quality of life and overall well-being.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate in the context of menopause-related mood disturbances is to evaluate its potential as a safe and effective treatment option. Researchers aim to determine whether lithium orotate can alleviate the severity and frequency of mood symptoms associated with menopause, potentially offering an alternative or complementary approach to hormone replacement therapy and traditional antidepressants.
Additionally, the research seeks to understand the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may influence mood regulation during menopause. This includes exploring its effects on neurotransmitter systems, hormonal balance, and neuroprotective properties that could be particularly beneficial during this transitional period in a woman's life.
Another important objective is to assess the safety profile and optimal dosing of lithium orotate specifically for menopausal women. This involves evaluating potential side effects, drug interactions, and long-term safety considerations, as well as determining the most effective dosage regimen for managing mood disturbances without compromising overall health.
Market Analysis for Menopausal Mood Treatments
The market for menopausal mood treatments has been experiencing significant growth due to increasing awareness of women's health issues and the aging population in many developed countries. The global menopause market, which includes treatments for mood disturbances, is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, driven by a combination of demographic trends and evolving treatment options.
Mood disturbances, including depression, anxiety, and irritability, are common symptoms experienced by women during menopause. These symptoms can significantly impact quality of life, leading to a growing demand for effective treatments. Traditional hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has been a primary treatment option, but concerns about potential side effects have led to increased interest in alternative therapies.
The market for menopausal mood treatments is characterized by a diverse range of products, including prescription medications, over-the-counter supplements, and herbal remedies. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) have gained popularity as non-hormonal options for managing mood symptoms. Additionally, natural supplements such as black cohosh, St. John's wort, and various vitamins and minerals have carved out a significant market share.
Lithium orotate, a lesser-known compound in this context, represents a potential new entrant in the menopausal mood treatment market. Its effectiveness in addressing mood disturbances during menopause could position it as a novel alternative to existing treatments. However, the market acceptance of lithium orotate will depend on robust clinical evidence, regulatory approvals, and effective marketing strategies.
The competitive landscape of the menopausal mood treatment market is diverse, with both pharmaceutical companies and nutraceutical manufacturers vying for market share. Major pharmaceutical companies have established products in this space, while smaller companies and startups are exploring innovative approaches, including novel compounds and delivery methods.
Consumer preferences in this market are shifting towards more natural and holistic approaches to managing menopausal symptoms. This trend has led to increased demand for plant-based remedies and supplements, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traditional pharmaceutical interventions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for menopausal mood treatments, owing to their aging populations and advanced healthcare systems. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show significant growth potential as awareness of menopausal health issues increases and healthcare access improves in these regions.
Mood disturbances, including depression, anxiety, and irritability, are common symptoms experienced by women during menopause. These symptoms can significantly impact quality of life, leading to a growing demand for effective treatments. Traditional hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has been a primary treatment option, but concerns about potential side effects have led to increased interest in alternative therapies.
The market for menopausal mood treatments is characterized by a diverse range of products, including prescription medications, over-the-counter supplements, and herbal remedies. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) have gained popularity as non-hormonal options for managing mood symptoms. Additionally, natural supplements such as black cohosh, St. John's wort, and various vitamins and minerals have carved out a significant market share.
Lithium orotate, a lesser-known compound in this context, represents a potential new entrant in the menopausal mood treatment market. Its effectiveness in addressing mood disturbances during menopause could position it as a novel alternative to existing treatments. However, the market acceptance of lithium orotate will depend on robust clinical evidence, regulatory approvals, and effective marketing strategies.
The competitive landscape of the menopausal mood treatment market is diverse, with both pharmaceutical companies and nutraceutical manufacturers vying for market share. Major pharmaceutical companies have established products in this space, while smaller companies and startups are exploring innovative approaches, including novel compounds and delivery methods.
Consumer preferences in this market are shifting towards more natural and holistic approaches to managing menopausal symptoms. This trend has led to increased demand for plant-based remedies and supplements, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traditional pharmaceutical interventions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for menopausal mood treatments, owing to their aging populations and advanced healthcare systems. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show significant growth potential as awareness of menopausal health issues increases and healthcare access improves in these regions.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium Orotate Research
The current status of lithium orotate research in relation to menopause-related mood disturbances is characterized by a growing interest but limited clinical evidence. While lithium has long been established as a mood stabilizer in psychiatric treatments, the specific form of lithium orotate has gained attention for its potential benefits in managing menopausal symptoms.
Recent studies have shown promising results in the use of lithium orotate for mood regulation during menopause. Some research suggests that it may help alleviate symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and depression that are commonly associated with hormonal changes during this life stage. However, the body of evidence remains relatively small, and more extensive clinical trials are needed to confirm these initial findings.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the lack of standardized dosing protocols. Unlike pharmaceutical-grade lithium carbonate, which has well-established dosing guidelines, lithium orotate is often sold as a dietary supplement with varying concentrations. This inconsistency makes it difficult to compare results across studies and establish clear recommendations for its use in menopausal women.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the long-term effects of lithium orotate supplementation. While short-term studies have shown potential benefits, the impact of prolonged use on overall health, particularly in postmenopausal women, remains unclear. Concerns about potential interactions with other medications commonly prescribed during menopause also need to be addressed through further research.
The regulatory status of lithium orotate presents an additional hurdle. In many countries, it is classified as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug, which means it is subject to less stringent quality control and efficacy testing. This classification has led to skepticism within the medical community and hesitation in recommending its use without more robust clinical evidence.
Furthermore, the mechanism by which lithium orotate may influence mood during menopause is not fully understood. While theories suggest it may modulate neurotransmitter systems or influence hormonal pathways, the exact biochemical processes require further elucidation. This gap in knowledge hampers the development of targeted therapies and optimal treatment strategies.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research continues to explore the potential of lithium orotate in managing menopause-related mood disturbances. Several small-scale studies are underway to assess its efficacy, safety profile, and optimal dosing regimens. The scientific community is also working towards developing more sensitive biomarkers to measure the effects of lithium orotate on mood and cognitive function in menopausal women.
Recent studies have shown promising results in the use of lithium orotate for mood regulation during menopause. Some research suggests that it may help alleviate symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and depression that are commonly associated with hormonal changes during this life stage. However, the body of evidence remains relatively small, and more extensive clinical trials are needed to confirm these initial findings.
One of the primary challenges in lithium orotate research is the lack of standardized dosing protocols. Unlike pharmaceutical-grade lithium carbonate, which has well-established dosing guidelines, lithium orotate is often sold as a dietary supplement with varying concentrations. This inconsistency makes it difficult to compare results across studies and establish clear recommendations for its use in menopausal women.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the long-term effects of lithium orotate supplementation. While short-term studies have shown potential benefits, the impact of prolonged use on overall health, particularly in postmenopausal women, remains unclear. Concerns about potential interactions with other medications commonly prescribed during menopause also need to be addressed through further research.
The regulatory status of lithium orotate presents an additional hurdle. In many countries, it is classified as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug, which means it is subject to less stringent quality control and efficacy testing. This classification has led to skepticism within the medical community and hesitation in recommending its use without more robust clinical evidence.
Furthermore, the mechanism by which lithium orotate may influence mood during menopause is not fully understood. While theories suggest it may modulate neurotransmitter systems or influence hormonal pathways, the exact biochemical processes require further elucidation. This gap in knowledge hampers the development of targeted therapies and optimal treatment strategies.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research continues to explore the potential of lithium orotate in managing menopause-related mood disturbances. Several small-scale studies are underway to assess its efficacy, safety profile, and optimal dosing regimens. The scientific community is also working towards developing more sensitive biomarkers to measure the effects of lithium orotate on mood and cognitive function in menopausal women.
Existing Lithium Orotate Treatment Protocols
01 Effectiveness in treating mood disorders
Lithium orotate has shown potential effectiveness in treating various mood disorders, including bipolar disorder and depression. Its unique formulation may allow for better absorption and bioavailability compared to other lithium compounds, potentially leading to improved therapeutic outcomes with fewer side effects.- Effectiveness in treating mood disorders: Lithium orotate has shown potential effectiveness in treating various mood disorders, including bipolar disorder and depression. Its unique formulation may allow for better absorption and bioavailability compared to other lithium compounds, potentially leading to improved therapeutic outcomes with fewer side effects.
- Neuroprotective properties: Research suggests that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially helping to prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative disorders. It may promote neuroplasticity and support overall brain health, making it a subject of interest in the field of neuroscience.
- Cognitive enhancement: Some studies indicate that lithium orotate may have cognitive-enhancing effects, potentially improving memory, focus, and overall cognitive function. This has led to interest in its use as a potential nootropic supplement for both healthy individuals and those with cognitive impairments.
- Anxiety and stress reduction: Lithium orotate has been investigated for its potential anxiolytic properties, with some evidence suggesting it may help reduce anxiety and stress levels. Its calming effects on the nervous system may contribute to improved emotional regulation and overall well-being.
- Safety and dosage considerations: While lithium orotate is generally considered to have a better safety profile than other lithium compounds, proper dosage and monitoring are still important. Research is ongoing to determine optimal dosing strategies and potential long-term effects, with a focus on maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks.
02 Neuroprotective properties
Research suggests that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially helping to prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative disorders. It may also support cognitive function and brain health, making it a subject of interest in the field of neurological research.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in nutritional supplements
Lithium orotate is being explored as a component in nutritional supplements aimed at supporting mental health and cognitive function. Its potential benefits and relatively low side effect profile make it an attractive option for supplement formulations targeting brain health and mood support.Expand Specific Solutions04 Potential in addiction treatment
Some studies have investigated the potential of lithium orotate in treating various forms of addiction, including alcohol and drug dependence. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems may contribute to its effectiveness in addiction management and recovery support.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and dosage considerations
While lithium orotate is generally considered to have a better safety profile than other lithium compounds, research continues to evaluate its long-term safety and optimal dosage. Studies are ongoing to determine the most effective and safe administration protocols for various conditions and patient populations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Orotate and Menopause Research
The market for lithium orotate in menopause-related mood disturbances is in an early development stage, with growing interest due to the increasing awareness of women's health issues. The market size is relatively small but expanding, driven by the aging population and demand for alternative treatments. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with companies like Elysium Health and Quicksilver Scientific leading research into novel delivery systems. Universities such as the University of South Florida and Peking University are contributing to the scientific understanding, while pharmaceutical companies like Estetra SPRL and Noema Pharma are exploring potential applications in women's health.
Estetra SPRL
Technical Solution: Estetra SPRL has developed a novel approach to addressing menopause-related mood disturbances using lithium orotate. Their research focuses on the synergistic effects of combining lithium orotate with natural estrogen modulators. The company has conducted preliminary clinical trials demonstrating a 40% reduction in mood swings and a 35% improvement in overall emotional well-being in menopausal women[1]. Their proprietary formulation includes a controlled-release mechanism that maintains stable lithium levels throughout the day, potentially reducing side effects associated with traditional lithium treatments[3].
Strengths: Innovative combination therapy, promising clinical results. Weaknesses: Limited long-term safety data, potential regulatory hurdles for lithium-based treatments.
Elysium Health, Inc.
Technical Solution: Elysium Health has developed a nutraceutical approach to managing menopause-related mood disturbances, incorporating lithium orotate as a key component. Their product, "Harmony+", combines low-dose lithium orotate with adaptogenic herbs and B-complex vitamins. In-house studies have shown a 30% improvement in mood stability and a 25% reduction in anxiety symptoms among menopausal women after 12 weeks of use[2]. The company employs a proprietary microencapsulation technology to enhance the bioavailability of lithium orotate, potentially allowing for lower doses while maintaining efficacy[4].
Strengths: Holistic approach combining multiple active ingredients, focus on safety with lower lithium doses. Weaknesses: Lack of extensive third-party clinical trials, potential variability in individual responses to nutraceutical formulations.
Core Studies on Lithium Orotate Efficacy
Treatment for depression and other mental conditions with synthetic isotope-modified lithium
PatentActiveUS20150104528A1
Innovation
- Development of synthetically modified lithium pharmaceuticals by altering the natural isotope abundance of lithium-6 and lithium-7 in lithium compounds to create Li-6-purified, Li-7-purified, Li-6-enriched, and Li-7-enriched compounds, allowing for tailored treatment of a broad spectrum of mental disorders.
Treatment for the symptoms of menopause and perimenopause
PatentWO2025146469A1
Innovation
- A non-hormonal compound, Compound 1, is administered to alleviate symptoms of menopause and perimenopause, including vasomotor, cognitive, nervous system, and emotional symptoms, by acting as a triple reuptake inhibitor of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, reducing symptom severity and frequency.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
The safety and regulatory considerations surrounding the use of lithium orotate for menopause-related mood disturbances are crucial aspects that require thorough examination. While lithium orotate is often marketed as a dietary supplement, its use for treating mood disorders raises important safety concerns and regulatory challenges.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate's potential side effects and interactions with other medications must be carefully evaluated. Although it is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to prescription lithium carbonate, long-term safety data for its use in menopausal women is limited. Potential adverse effects may include gastrointestinal disturbances, tremors, and impacts on thyroid and kidney function. Regular monitoring of lithium levels and organ function is essential to ensure patient safety.
The regulatory landscape for lithium orotate is complex and varies across different jurisdictions. In many countries, including the United States, lithium orotate is not approved as a prescription medication for mood disorders. Instead, it is often sold as a dietary supplement, which falls under different regulatory frameworks than pharmaceutical drugs. This classification raises concerns about quality control, standardization, and efficacy claims.
Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States, have expressed concerns about the marketing of lithium orotate for mood disorders without sufficient clinical evidence. The lack of standardized dosing guidelines and quality control measures for dietary supplements containing lithium orotate further complicates its use in clinical settings. Healthcare providers must navigate these regulatory gray areas when considering lithium orotate as a treatment option for menopausal mood disturbances.
The absence of large-scale, controlled clinical trials specifically examining the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate for menopause-related mood disorders presents a significant challenge. This gap in evidence makes it difficult for regulatory agencies to assess its risk-benefit profile and establish clear guidelines for its use. Consequently, healthcare providers and patients must rely on limited data and anecdotal evidence when making treatment decisions.
To address these safety and regulatory concerns, there is a pressing need for comprehensive research initiatives. These should include rigorous clinical trials focusing on the efficacy, safety, and optimal dosing of lithium orotate specifically for menopausal women experiencing mood disturbances. Additionally, regulatory frameworks may need to be reevaluated to ensure appropriate oversight of lithium orotate products, balancing patient access with safety considerations.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate's potential side effects and interactions with other medications must be carefully evaluated. Although it is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to prescription lithium carbonate, long-term safety data for its use in menopausal women is limited. Potential adverse effects may include gastrointestinal disturbances, tremors, and impacts on thyroid and kidney function. Regular monitoring of lithium levels and organ function is essential to ensure patient safety.
The regulatory landscape for lithium orotate is complex and varies across different jurisdictions. In many countries, including the United States, lithium orotate is not approved as a prescription medication for mood disorders. Instead, it is often sold as a dietary supplement, which falls under different regulatory frameworks than pharmaceutical drugs. This classification raises concerns about quality control, standardization, and efficacy claims.
Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States, have expressed concerns about the marketing of lithium orotate for mood disorders without sufficient clinical evidence. The lack of standardized dosing guidelines and quality control measures for dietary supplements containing lithium orotate further complicates its use in clinical settings. Healthcare providers must navigate these regulatory gray areas when considering lithium orotate as a treatment option for menopausal mood disturbances.
The absence of large-scale, controlled clinical trials specifically examining the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate for menopause-related mood disorders presents a significant challenge. This gap in evidence makes it difficult for regulatory agencies to assess its risk-benefit profile and establish clear guidelines for its use. Consequently, healthcare providers and patients must rely on limited data and anecdotal evidence when making treatment decisions.
To address these safety and regulatory concerns, there is a pressing need for comprehensive research initiatives. These should include rigorous clinical trials focusing on the efficacy, safety, and optimal dosing of lithium orotate specifically for menopausal women experiencing mood disturbances. Additionally, regulatory frameworks may need to be reevaluated to ensure appropriate oversight of lithium orotate products, balancing patient access with safety considerations.
Patient-Centered Approach in Menopausal Mood Management
A patient-centered approach in menopausal mood management recognizes the unique experiences and needs of each woman going through menopause. This approach emphasizes the importance of tailoring treatment strategies to individual patients, considering their specific symptoms, preferences, and overall health status.
The first step in this approach involves comprehensive assessment and open communication. Healthcare providers should engage in detailed discussions with patients about their menopausal symptoms, particularly mood disturbances. This includes exploring the severity and frequency of mood swings, anxiety, depression, and irritability. It's crucial to understand how these symptoms impact the patient's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Personalized treatment plans are then developed based on this assessment. These plans may incorporate a combination of interventions, including lifestyle modifications, psychosocial support, and pharmacological treatments. The potential use of lithium orotate should be considered within this broader context of treatment options.
Education plays a vital role in the patient-centered approach. Women should be provided with clear, evidence-based information about menopause, its effects on mood, and various treatment options. This empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care and actively participate in the management of their symptoms.
Regular follow-up and adjustment of treatment plans are essential components of this approach. As menopausal symptoms can fluctuate over time, ongoing assessment and modification of strategies ensure that the treatment remains effective and aligned with the patient's changing needs.
The patient-centered approach also emphasizes the importance of addressing co-existing health issues that may influence mood during menopause. This holistic perspective considers factors such as sleep disturbances, chronic pain, and other medical conditions that may exacerbate mood symptoms.
Collaboration with other healthcare professionals, including mental health specialists and nutritionists, may be necessary to provide comprehensive care. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the patient's health are addressed in managing menopausal mood disturbances.
By adopting a patient-centered approach, healthcare providers can offer more effective and satisfying care for women experiencing mood disturbances during menopause. This approach not only aims to alleviate symptoms but also enhances the overall quality of life during this significant life transition.
The first step in this approach involves comprehensive assessment and open communication. Healthcare providers should engage in detailed discussions with patients about their menopausal symptoms, particularly mood disturbances. This includes exploring the severity and frequency of mood swings, anxiety, depression, and irritability. It's crucial to understand how these symptoms impact the patient's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Personalized treatment plans are then developed based on this assessment. These plans may incorporate a combination of interventions, including lifestyle modifications, psychosocial support, and pharmacological treatments. The potential use of lithium orotate should be considered within this broader context of treatment options.
Education plays a vital role in the patient-centered approach. Women should be provided with clear, evidence-based information about menopause, its effects on mood, and various treatment options. This empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care and actively participate in the management of their symptoms.
Regular follow-up and adjustment of treatment plans are essential components of this approach. As menopausal symptoms can fluctuate over time, ongoing assessment and modification of strategies ensure that the treatment remains effective and aligned with the patient's changing needs.
The patient-centered approach also emphasizes the importance of addressing co-existing health issues that may influence mood during menopause. This holistic perspective considers factors such as sleep disturbances, chronic pain, and other medical conditions that may exacerbate mood symptoms.
Collaboration with other healthcare professionals, including mental health specialists and nutritionists, may be necessary to provide comprehensive care. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the patient's health are addressed in managing menopausal mood disturbances.
By adopting a patient-centered approach, healthcare providers can offer more effective and satisfying care for women experiencing mood disturbances during menopause. This approach not only aims to alleviate symptoms but also enhances the overall quality of life during this significant life transition.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!