Harnessing ULED for Educational Display Solutions
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED in Education: Background and Objectives
Ultra-Light Emitting Diode (ULED) technology has emerged as a promising solution for educational display systems, offering significant advancements over traditional display technologies. The evolution of ULED can be traced back to the development of LED technology, which has undergone rapid improvements in efficiency, brightness, and color reproduction over the past decades. ULED represents the latest iteration in this technological progression, characterized by its ultra-thin profile, high energy efficiency, and superior image quality.
The primary objective of harnessing ULED for educational display solutions is to enhance the learning experience through improved visual presentation. This technology aims to address several key challenges in educational environments, including the need for large, high-resolution displays that can be easily viewed from various angles in classrooms, lecture halls, and collaborative spaces. Additionally, ULED displays are designed to reduce eye strain during prolonged viewing, a crucial factor in educational settings where students and educators spend significant time interacting with visual content.
The trend towards digitalization in education has accelerated the demand for advanced display technologies. ULED is positioned to meet this growing need by offering displays that can render complex graphics, high-definition video, and interactive content with exceptional clarity and color accuracy. This is particularly important in subjects such as science, engineering, and visual arts, where precise color reproduction and fine detail visualization are critical for effective learning.
Another key objective of ULED technology in education is to improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of display systems. As educational institutions increasingly focus on sustainability, ULED offers a solution that consumes less power compared to traditional LCD or older LED displays, while maintaining or even surpassing their performance capabilities. This aligns with the broader goals of creating more environmentally friendly and cost-effective educational facilities.
The development of ULED for educational applications also aims to address the challenge of flexibility in display deployment. With its ultra-thin profile and potential for modular design, ULED technology opens up new possibilities for creating adaptable learning spaces. This includes the ability to easily install large displays in various configurations, potentially transforming any surface into an interactive learning tool.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of ULED technology in education is expected to focus on further improvements in image quality, energy efficiency, and integration with other emerging technologies such as touch interfaces and augmented reality. The ultimate goal is to create immersive, interactive learning environments that can adapt to diverse educational needs and teaching methodologies, fostering engagement and enhancing knowledge retention among students.
The primary objective of harnessing ULED for educational display solutions is to enhance the learning experience through improved visual presentation. This technology aims to address several key challenges in educational environments, including the need for large, high-resolution displays that can be easily viewed from various angles in classrooms, lecture halls, and collaborative spaces. Additionally, ULED displays are designed to reduce eye strain during prolonged viewing, a crucial factor in educational settings where students and educators spend significant time interacting with visual content.
The trend towards digitalization in education has accelerated the demand for advanced display technologies. ULED is positioned to meet this growing need by offering displays that can render complex graphics, high-definition video, and interactive content with exceptional clarity and color accuracy. This is particularly important in subjects such as science, engineering, and visual arts, where precise color reproduction and fine detail visualization are critical for effective learning.
Another key objective of ULED technology in education is to improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of display systems. As educational institutions increasingly focus on sustainability, ULED offers a solution that consumes less power compared to traditional LCD or older LED displays, while maintaining or even surpassing their performance capabilities. This aligns with the broader goals of creating more environmentally friendly and cost-effective educational facilities.
The development of ULED for educational applications also aims to address the challenge of flexibility in display deployment. With its ultra-thin profile and potential for modular design, ULED technology opens up new possibilities for creating adaptable learning spaces. This includes the ability to easily install large displays in various configurations, potentially transforming any surface into an interactive learning tool.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of ULED technology in education is expected to focus on further improvements in image quality, energy efficiency, and integration with other emerging technologies such as touch interfaces and augmented reality. The ultimate goal is to create immersive, interactive learning environments that can adapt to diverse educational needs and teaching methodologies, fostering engagement and enhancing knowledge retention among students.
Educational Display Market Analysis
The educational display market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of digital learning technologies and the growing emphasis on interactive and engaging educational experiences. The global educational display market size was valued at $11.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $27.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period.
The demand for educational displays is primarily fueled by the digitization of classrooms, the rise of e-learning platforms, and the need for advanced visual aids in educational institutions. Schools, colleges, and universities are increasingly investing in interactive displays, smart boards, and digital signage to enhance the learning experience and improve student engagement.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of educational display technologies, as remote and hybrid learning models have become more prevalent. This shift has created a surge in demand for displays that can facilitate seamless virtual collaboration and content sharing.
In terms of product types, interactive flat panel displays (IFPDs) dominate the market, accounting for the largest share due to their versatility and interactive capabilities. However, there is a growing interest in emerging technologies such as ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays, which offer superior image quality, energy efficiency, and longer lifespan compared to traditional LED displays.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by increasing investments in education technology and the rapid digitization of classrooms in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the educational display sector include BenQ Corporation, Promethean World Ltd., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., and Smart Technologies Inc. These companies are focusing on product innovations, partnerships with educational institutions, and strategic acquisitions to strengthen their market position.
The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and cloud computing into educational displays is expected to create new growth opportunities in the market. These technologies can enable personalized learning experiences, real-time analytics, and improved content delivery, further enhancing the value proposition of educational displays.
The demand for educational displays is primarily fueled by the digitization of classrooms, the rise of e-learning platforms, and the need for advanced visual aids in educational institutions. Schools, colleges, and universities are increasingly investing in interactive displays, smart boards, and digital signage to enhance the learning experience and improve student engagement.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of educational display technologies, as remote and hybrid learning models have become more prevalent. This shift has created a surge in demand for displays that can facilitate seamless virtual collaboration and content sharing.
In terms of product types, interactive flat panel displays (IFPDs) dominate the market, accounting for the largest share due to their versatility and interactive capabilities. However, there is a growing interest in emerging technologies such as ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays, which offer superior image quality, energy efficiency, and longer lifespan compared to traditional LED displays.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by increasing investments in education technology and the rapid digitization of classrooms in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the educational display sector include BenQ Corporation, Promethean World Ltd., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., and Smart Technologies Inc. These companies are focusing on product innovations, partnerships with educational institutions, and strategic acquisitions to strengthen their market position.
The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and cloud computing into educational displays is expected to create new growth opportunities in the market. These technologies can enable personalized learning experiences, real-time analytics, and improved content delivery, further enhancing the value proposition of educational displays.
ULED Technology: Current State and Challenges
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in recent years, particularly in the realm of educational display solutions. The current state of ULED technology showcases impressive advancements in image quality, energy efficiency, and durability, making it an attractive option for educational environments.
One of the primary strengths of ULED displays is their superior brightness and contrast ratio. These displays can achieve peak brightness levels of up to 1,500 nits, significantly outperforming traditional LED and LCD screens. This enhanced brightness allows for clear visibility even in well-lit classrooms or outdoor learning spaces, addressing a common challenge in educational settings.
Color accuracy and gamut coverage have also seen substantial improvements in ULED technology. Many ULED displays now offer support for wide color gamuts such as DCI-P3 and Rec. 2020, providing more vibrant and lifelike images. This feature is particularly beneficial for subjects like art, design, and science, where accurate color representation is crucial for learning.
Energy efficiency is another area where ULED technology excels. Compared to conventional display technologies, ULED consumes significantly less power while maintaining high brightness levels. This not only reduces operational costs for educational institutions but also aligns with sustainability goals, an increasingly important consideration in modern education.
Despite these advancements, ULED technology still faces several challenges in the educational sector. One of the primary hurdles is the cost of implementation. While prices have decreased over time, ULED displays remain more expensive than traditional LED or LCD alternatives, potentially limiting widespread adoption in budget-constrained educational environments.
Durability and longevity are areas that require further improvement. While ULED displays generally offer good lifespan, the demanding nature of educational settings – with frequent use and potential physical impacts – necessitates even more robust solutions. Manufacturers are working on enhancing the durability of ULED panels to withstand the rigors of classroom use.
Another challenge lies in the integration of touch functionality with ULED displays. While touch-enabled ULED screens exist, the technology still lags behind some competing display technologies in terms of responsiveness and multi-touch capabilities. This is a critical area for improvement, given the increasing emphasis on interactive learning in modern education.
Lastly, the issue of blue light emission and its potential impact on eye health remains a concern, particularly in educational settings where students may spend extended periods in front of displays. While ULED technology has made progress in reducing harmful blue light emissions, further research and development are needed to fully address this issue and ensure the long-term well-being of students and educators alike.
One of the primary strengths of ULED displays is their superior brightness and contrast ratio. These displays can achieve peak brightness levels of up to 1,500 nits, significantly outperforming traditional LED and LCD screens. This enhanced brightness allows for clear visibility even in well-lit classrooms or outdoor learning spaces, addressing a common challenge in educational settings.
Color accuracy and gamut coverage have also seen substantial improvements in ULED technology. Many ULED displays now offer support for wide color gamuts such as DCI-P3 and Rec. 2020, providing more vibrant and lifelike images. This feature is particularly beneficial for subjects like art, design, and science, where accurate color representation is crucial for learning.
Energy efficiency is another area where ULED technology excels. Compared to conventional display technologies, ULED consumes significantly less power while maintaining high brightness levels. This not only reduces operational costs for educational institutions but also aligns with sustainability goals, an increasingly important consideration in modern education.
Despite these advancements, ULED technology still faces several challenges in the educational sector. One of the primary hurdles is the cost of implementation. While prices have decreased over time, ULED displays remain more expensive than traditional LED or LCD alternatives, potentially limiting widespread adoption in budget-constrained educational environments.
Durability and longevity are areas that require further improvement. While ULED displays generally offer good lifespan, the demanding nature of educational settings – with frequent use and potential physical impacts – necessitates even more robust solutions. Manufacturers are working on enhancing the durability of ULED panels to withstand the rigors of classroom use.
Another challenge lies in the integration of touch functionality with ULED displays. While touch-enabled ULED screens exist, the technology still lags behind some competing display technologies in terms of responsiveness and multi-touch capabilities. This is a critical area for improvement, given the increasing emphasis on interactive learning in modern education.
Lastly, the issue of blue light emission and its potential impact on eye health remains a concern, particularly in educational settings where students may spend extended periods in front of displays. While ULED technology has made progress in reducing harmful blue light emissions, further research and development are needed to fully address this issue and ensure the long-term well-being of students and educators alike.
ULED Implementation in Educational Settings
01 ULED structure and fabrication
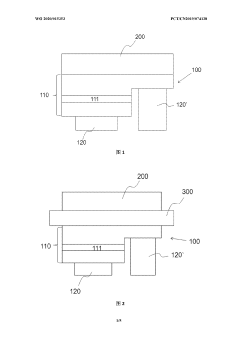
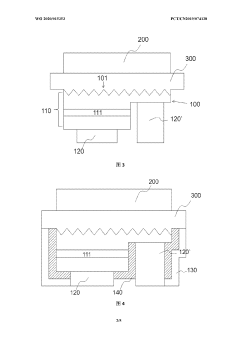
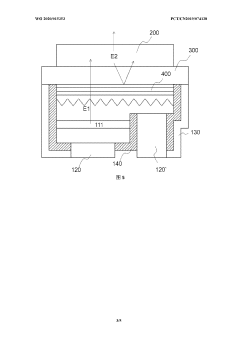
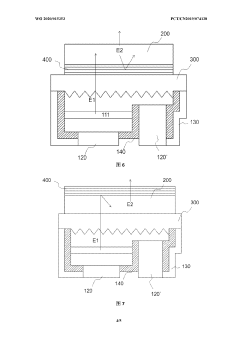
Ultra Light Emitting Diode (ULED) displays utilize advanced semiconductor structures and fabrication techniques to achieve ultra-high brightness and efficiency. These displays incorporate novel materials and layer compositions to enhance light emission and reduce power consumption. The manufacturing process may involve specialized deposition methods and patterning techniques to create precise ULED structures.- ULED structure and fabrication: Ultra Light Emitting Diode (ULED) displays utilize advanced semiconductor structures and fabrication techniques to achieve ultra-high brightness and efficiency. These displays incorporate novel materials and layer compositions to enhance light emission and reduce power consumption. The manufacturing process may involve specialized deposition methods and patterning techniques to create precise ULED structures.
- Pixel design and arrangement: ULED displays employ innovative pixel designs and arrangements to optimize light output and color reproduction. This may include sub-pixel configurations, pixel density optimization, and novel addressing schemes. The pixel architecture is crucial for achieving high resolution and improved image quality in ULED displays.
- Color conversion and enhancement: ULED technology incorporates advanced color conversion and enhancement techniques to achieve a wide color gamut and improved color accuracy. This may involve the use of quantum dots, phosphors, or other color conversion materials integrated into the display structure. Color management algorithms and hardware implementations are also crucial for optimizing the display's color performance.
- Driving and control circuits: ULED displays require sophisticated driving and control circuits to manage power delivery, brightness control, and image processing. These circuits may include advanced thin-film transistor (TFT) backplanes, voltage regulation systems, and timing controllers. The driving scheme is optimized to ensure uniform brightness and prevent degradation of the ULED elements over time.
- Encapsulation and packaging: ULED displays employ advanced encapsulation and packaging techniques to protect the sensitive ULED elements from environmental factors and ensure long-term reliability. This may include the use of thin-film encapsulation, moisture barriers, and specialized packaging materials. The encapsulation process is critical for maintaining the display's performance and extending its lifespan.
02 Pixel design and arrangement
ULED displays employ innovative pixel designs and arrangements to optimize light output and color reproduction. This may include sub-pixel configurations, pixel density optimization, and novel addressing schemes. Advanced pixel architectures are implemented to improve contrast ratios, viewing angles, and overall display performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Driving and control circuits
Specialized driving and control circuits are developed for ULED displays to manage power delivery, brightness control, and color accuracy. These circuits may incorporate advanced algorithms for image processing, motion compensation, and dynamic range enhancement. The integration of these circuits with the ULED array is crucial for achieving optimal display performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Encapsulation and packaging
ULED displays require advanced encapsulation and packaging techniques to protect the sensitive components and ensure long-term reliability. This may involve the use of specialized materials and structures to prevent moisture ingress, manage heat dissipation, and enhance optical properties. Novel packaging designs are implemented to achieve thin and flexible display configurations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with other display technologies
ULED technology can be integrated with other display technologies to create hybrid solutions with enhanced performance characteristics. This may include combinations with quantum dot technology, micro-LED arrays, or traditional LCD backplanes. Such integrations aim to leverage the strengths of multiple technologies to achieve superior display quality and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key ULED Manufacturers and Competitors
The ULED technology for educational display solutions is in its growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring established players like Samsung Display Co., Ltd. and BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd., alongside emerging companies such as eLux, Inc. and Micledi Microdisplays BV. The market is characterized by ongoing innovation, with companies like Lumileds LLC and Appotronics Corp. Ltd. pushing the boundaries of ULED technology. The involvement of research institutions like Ghent University and Industrial Technology Research Institute indicates a focus on continuous improvement and application development, suggesting that while the technology is advancing, there is still room for significant growth and refinement in educational applications.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology for educational display solutions. Their ULED panels offer high brightness, wide color gamut, and energy efficiency. BOE's ULED displays incorporate quantum dot technology and mini-LED backlighting, providing superior image quality with deep blacks and vibrant colors. For educational applications, BOE has implemented eye-care features such as low blue light emission and flicker-free operation to reduce eye strain during extended viewing periods. Additionally, BOE's ULED displays offer touch functionality and support for interactive learning experiences.
Strengths: Superior image quality, energy efficiency, and eye-care features. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to traditional LCD displays, and limited market penetration in the education sector.
Samsung Display Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Display has developed ULED technology for educational displays, focusing on enhancing visual performance and energy efficiency. Their ULED panels utilize quantum dot technology and advanced local dimming techniques to achieve high contrast ratios and wide color gamut. Samsung's educational ULED displays feature anti-glare coatings and low reflection properties to improve visibility in various lighting conditions. They have also implemented a smart dimming algorithm that adjusts brightness based on ambient light and content, optimizing both image quality and power consumption. Samsung's ULED displays for education come with built-in collaboration tools and wireless connectivity options to facilitate interactive learning environments.
Strengths: Advanced visual technologies, smart features for educational use, and established brand reputation. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial costs and the need for ecosystem integration in educational settings.
ULED Display Patents and Technical Literature
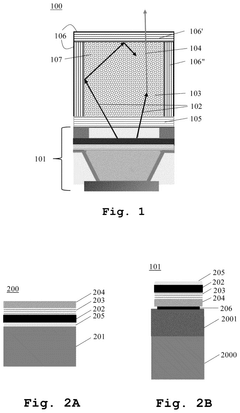
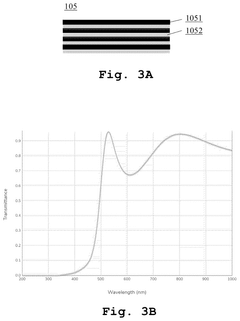
An optoelectronic device with color conversion and with conformal DBR and an associated fabrication method
PatentPendingUS20250151479A1
Innovation
- The proposed optoelectronic device incorporates a semiconductor light-emitting component with a cavity filled with wavelength conversion material, surrounded by multilayer interference reflectors that enhance light conversion and isolation, allowing for improved light emission efficiency and longer device lifetime.
Micro light emitting device and display thereof
PatentWO2020015353A1
Innovation
- Using a micro-light-emitting diode structure with a transparent adhesive layer, the blue/green light is converted into red light through photon conversion technology, the AlInGaP-based quantum well layer is used to achieve efficient photon conversion, and anti-reflection and anti-reflection are set on the micro-light-emitting diode. The film layer and light reflective layer optimize the light emission efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability of ULED Displays
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a promising solution for energy-efficient and sustainable display systems in educational settings. The energy efficiency of ULED displays is significantly higher compared to traditional LCD and LED technologies, offering substantial power savings and reduced environmental impact.
ULED displays consume up to 40% less energy than conventional LED displays, primarily due to their advanced light management and pixel structure. This reduction in energy consumption translates to lower operational costs for educational institutions and decreased carbon emissions. The improved energy efficiency is achieved through innovative backlight control systems and enhanced light transmission capabilities, allowing for brighter displays with less power input.
The sustainability aspects of ULED technology extend beyond energy efficiency. These displays have a longer lifespan, typically lasting up to 100,000 hours, which is significantly higher than traditional display technologies. This longevity reduces the frequency of replacements, minimizing electronic waste and the associated environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal.
ULED displays also incorporate eco-friendly materials in their construction, with reduced use of harmful substances such as mercury and lead. The manufacturing process for ULED panels has been optimized to minimize resource consumption and waste generation, further enhancing their sustainability credentials.
In educational environments, the energy efficiency of ULED displays contributes to reduced electricity bills, allowing institutions to allocate more resources to other critical areas. The lower heat generation of ULED technology also reduces the need for cooling systems, further decreasing overall energy consumption in classrooms and lecture halls.
The sustainability benefits of ULED displays align well with the growing emphasis on environmental responsibility in educational institutions. By adopting this technology, schools and universities can demonstrate their commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and promoting sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, ongoing research and development in ULED technology promise even greater energy efficiency and sustainability improvements. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes are expected to further reduce power consumption while enhancing display performance. These advancements will likely include more efficient light-emitting compounds, improved color filters, and optimized backlight systems.
ULED displays consume up to 40% less energy than conventional LED displays, primarily due to their advanced light management and pixel structure. This reduction in energy consumption translates to lower operational costs for educational institutions and decreased carbon emissions. The improved energy efficiency is achieved through innovative backlight control systems and enhanced light transmission capabilities, allowing for brighter displays with less power input.
The sustainability aspects of ULED technology extend beyond energy efficiency. These displays have a longer lifespan, typically lasting up to 100,000 hours, which is significantly higher than traditional display technologies. This longevity reduces the frequency of replacements, minimizing electronic waste and the associated environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal.
ULED displays also incorporate eco-friendly materials in their construction, with reduced use of harmful substances such as mercury and lead. The manufacturing process for ULED panels has been optimized to minimize resource consumption and waste generation, further enhancing their sustainability credentials.
In educational environments, the energy efficiency of ULED displays contributes to reduced electricity bills, allowing institutions to allocate more resources to other critical areas. The lower heat generation of ULED technology also reduces the need for cooling systems, further decreasing overall energy consumption in classrooms and lecture halls.
The sustainability benefits of ULED displays align well with the growing emphasis on environmental responsibility in educational institutions. By adopting this technology, schools and universities can demonstrate their commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and promoting sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, ongoing research and development in ULED technology promise even greater energy efficiency and sustainability improvements. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes are expected to further reduce power consumption while enhancing display performance. These advancements will likely include more efficient light-emitting compounds, improved color filters, and optimized backlight systems.
ULED Integration with Educational Software
The integration of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology with educational software represents a significant advancement in creating immersive and interactive learning environments. This convergence of cutting-edge display technology and pedagogical software offers numerous benefits for both educators and students.
ULED displays, known for their superior brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency, provide an ideal canvas for educational content. When paired with specialized educational software, these displays can render high-fidelity images, videos, and interactive simulations that enhance the learning experience. The exceptional contrast ratios and wide color gamut of ULED screens ensure that complex visual information, such as scientific diagrams or historical artifacts, is presented with utmost clarity and detail.
One of the key advantages of integrating ULED with educational software is the ability to create dynamic, responsive learning environments. Touch-enabled ULED displays allow for direct interaction with digital content, enabling students to manipulate objects, solve problems, and explore concepts in real-time. This hands-on approach to learning can significantly improve engagement and knowledge retention.
Educational software developers are leveraging ULED's capabilities to create more immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences. These applications can transport students to historical events, inside the human body, or to distant planets, providing a level of visual fidelity that was previously unattainable in classroom settings.
The integration also supports collaborative learning environments. Large-format ULED displays can accommodate multiple touch inputs, allowing groups of students to work together on shared projects or problem-solving tasks. This fosters teamwork and communication skills while providing educators with new tools for facilitating group activities.
Adaptive learning algorithms within educational software can take full advantage of ULED's rapid refresh rates and low latency. This allows for seamless transitions between different types of content and instantaneous feedback, creating a more responsive and personalized learning experience tailored to each student's pace and style of learning.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency of ULED technology aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainability in education. Schools and institutions can benefit from reduced power consumption and longer display lifespans, making ULED an economically viable and environmentally responsible choice for long-term educational investments.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in educational settings. Future developments may include holographic ULED displays for 3D visualization of complex concepts or ultra-high-resolution walls that can transform entire classrooms into interactive learning spaces.
ULED displays, known for their superior brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency, provide an ideal canvas for educational content. When paired with specialized educational software, these displays can render high-fidelity images, videos, and interactive simulations that enhance the learning experience. The exceptional contrast ratios and wide color gamut of ULED screens ensure that complex visual information, such as scientific diagrams or historical artifacts, is presented with utmost clarity and detail.
One of the key advantages of integrating ULED with educational software is the ability to create dynamic, responsive learning environments. Touch-enabled ULED displays allow for direct interaction with digital content, enabling students to manipulate objects, solve problems, and explore concepts in real-time. This hands-on approach to learning can significantly improve engagement and knowledge retention.
Educational software developers are leveraging ULED's capabilities to create more immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences. These applications can transport students to historical events, inside the human body, or to distant planets, providing a level of visual fidelity that was previously unattainable in classroom settings.
The integration also supports collaborative learning environments. Large-format ULED displays can accommodate multiple touch inputs, allowing groups of students to work together on shared projects or problem-solving tasks. This fosters teamwork and communication skills while providing educators with new tools for facilitating group activities.
Adaptive learning algorithms within educational software can take full advantage of ULED's rapid refresh rates and low latency. This allows for seamless transitions between different types of content and instantaneous feedback, creating a more responsive and personalized learning experience tailored to each student's pace and style of learning.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency of ULED technology aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainability in education. Schools and institutions can benefit from reduced power consumption and longer display lifespans, making ULED an economically viable and environmentally responsible choice for long-term educational investments.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in educational settings. Future developments may include holographic ULED displays for 3D visualization of complex concepts or ultra-high-resolution walls that can transform entire classrooms into interactive learning spaces.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!