How Dipropylene Glycol Drives Perfume Industry Innovations?
JUL 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DPG in Perfumery: Evolution and Objectives
Dipropylene glycol (DPG) has played a pivotal role in the evolution of the perfume industry, driving innovations and shaping the landscape of fragrance creation. The journey of DPG in perfumery began in the mid-20th century when it was first introduced as a solvent and fixative in fragrance formulations. Its unique properties, including low odor, high solvency, and excellent stability, quickly made it an indispensable ingredient in the perfumer's palette.
The evolution of DPG's use in perfumery has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, it was primarily employed as a diluent for essential oils and fragrance concentrates, allowing for more precise control over scent intensity and diffusion. As the industry progressed, perfumers discovered DPG's ability to enhance the longevity of fragrances on the skin, leading to its widespread adoption as a fixative.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the increasing demand for longer-lasting fragrances drove further innovations in DPG applications. Perfumers began experimenting with higher concentrations of DPG in their formulations, resulting in the development of new fragrance categories such as eau de parfum and parfum extraits. This period also saw the emergence of DPG as a carrier for other fragrance ingredients, particularly those that were difficult to incorporate using traditional methods.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed a shift towards more complex and nuanced fragrances, with DPG playing a crucial role in achieving these olfactory goals. Its ability to harmonize different fragrance notes and create smoother transitions between top, middle, and base notes became increasingly valued by perfumers. This led to the development of more sophisticated fragrance structures and the ability to create scents that were previously unattainable.
In recent years, the objectives for DPG in perfumery have expanded beyond its traditional roles. With the growing emphasis on sustainability and natural ingredients, perfumers are exploring ways to use DPG to enhance the performance of natural and organic fragrances. Additionally, there is a focus on developing DPG-based delivery systems that can improve the longevity and projection of fragrances while reducing overall fragrance concentrations.
Looking ahead, the perfume industry is setting ambitious goals for DPG utilization. These include developing more environmentally friendly production methods, exploring novel applications in microencapsulation technologies, and leveraging DPG's properties to create innovative fragrance experiences. The industry is also investigating the potential of DPG in smart fragrance systems that can adapt to environmental conditions or user preferences.
The evolution of DPG's use in perfumery has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, it was primarily employed as a diluent for essential oils and fragrance concentrates, allowing for more precise control over scent intensity and diffusion. As the industry progressed, perfumers discovered DPG's ability to enhance the longevity of fragrances on the skin, leading to its widespread adoption as a fixative.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the increasing demand for longer-lasting fragrances drove further innovations in DPG applications. Perfumers began experimenting with higher concentrations of DPG in their formulations, resulting in the development of new fragrance categories such as eau de parfum and parfum extraits. This period also saw the emergence of DPG as a carrier for other fragrance ingredients, particularly those that were difficult to incorporate using traditional methods.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed a shift towards more complex and nuanced fragrances, with DPG playing a crucial role in achieving these olfactory goals. Its ability to harmonize different fragrance notes and create smoother transitions between top, middle, and base notes became increasingly valued by perfumers. This led to the development of more sophisticated fragrance structures and the ability to create scents that were previously unattainable.
In recent years, the objectives for DPG in perfumery have expanded beyond its traditional roles. With the growing emphasis on sustainability and natural ingredients, perfumers are exploring ways to use DPG to enhance the performance of natural and organic fragrances. Additionally, there is a focus on developing DPG-based delivery systems that can improve the longevity and projection of fragrances while reducing overall fragrance concentrations.
Looking ahead, the perfume industry is setting ambitious goals for DPG utilization. These include developing more environmentally friendly production methods, exploring novel applications in microencapsulation technologies, and leveraging DPG's properties to create innovative fragrance experiences. The industry is also investigating the potential of DPG in smart fragrance systems that can adapt to environmental conditions or user preferences.
Market Demand Analysis for DPG-based Fragrances
The global fragrance market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, with a particular surge in demand for DPG-based fragrances. Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) has emerged as a key ingredient driving innovations in the perfume industry, primarily due to its versatile properties and compatibility with a wide range of fragrance compounds.
Market research indicates that the demand for DPG-based fragrances is expected to continue its upward trajectory, fueled by changing consumer preferences and the increasing popularity of long-lasting, skin-friendly perfumes. The rise of clean beauty and natural fragrance trends has further bolstered the demand for DPG as a safer alternative to traditional solvents.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, DPG-based fragrances have gained substantial traction. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that offer both pleasant scents and skin benefits, driving manufacturers to incorporate DPG into their formulations. This trend is particularly evident in the growing market for body mists, hair perfumes, and scented lotions.
The home fragrance segment has also experienced a notable uptick in demand for DPG-based products. With more people spending time at home due to changing work patterns, there has been a surge in interest for long-lasting room sprays, reed diffusers, and scented candles that utilize DPG as a carrier for fragrance oils.
Geographically, North America and Europe remain the largest markets for DPG-based fragrances, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate. The increasing disposable income and changing lifestyle preferences in emerging economies like China and India are driving the adoption of premium fragrances, many of which incorporate DPG in their formulations.
The automotive industry has emerged as an unexpected growth area for DPG-based fragrances. Car manufacturers are increasingly focusing on enhancing the in-car experience, leading to a rise in demand for long-lasting car fresheners and scent diffusers that utilize DPG as a base.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have also played a role in shaping market demand. As stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) come into effect, perfume manufacturers are turning to DPG as a low-VOC alternative, aligning with sustainability goals and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products.
In conclusion, the market demand for DPG-based fragrances is robust and multifaceted, spanning various industries and geographical regions. The versatility, safety profile, and performance characteristics of DPG position it as a crucial component in driving future innovations in the fragrance industry, with sustained growth expected in the coming years.
Market research indicates that the demand for DPG-based fragrances is expected to continue its upward trajectory, fueled by changing consumer preferences and the increasing popularity of long-lasting, skin-friendly perfumes. The rise of clean beauty and natural fragrance trends has further bolstered the demand for DPG as a safer alternative to traditional solvents.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, DPG-based fragrances have gained substantial traction. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that offer both pleasant scents and skin benefits, driving manufacturers to incorporate DPG into their formulations. This trend is particularly evident in the growing market for body mists, hair perfumes, and scented lotions.
The home fragrance segment has also experienced a notable uptick in demand for DPG-based products. With more people spending time at home due to changing work patterns, there has been a surge in interest for long-lasting room sprays, reed diffusers, and scented candles that utilize DPG as a carrier for fragrance oils.
Geographically, North America and Europe remain the largest markets for DPG-based fragrances, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate. The increasing disposable income and changing lifestyle preferences in emerging economies like China and India are driving the adoption of premium fragrances, many of which incorporate DPG in their formulations.
The automotive industry has emerged as an unexpected growth area for DPG-based fragrances. Car manufacturers are increasingly focusing on enhancing the in-car experience, leading to a rise in demand for long-lasting car fresheners and scent diffusers that utilize DPG as a base.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have also played a role in shaping market demand. As stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) come into effect, perfume manufacturers are turning to DPG as a low-VOC alternative, aligning with sustainability goals and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products.
In conclusion, the market demand for DPG-based fragrances is robust and multifaceted, spanning various industries and geographical regions. The versatility, safety profile, and performance characteristics of DPG position it as a crucial component in driving future innovations in the fragrance industry, with sustained growth expected in the coming years.
Current State and Challenges in DPG Application
Dipropylene glycol (DPG) has become a cornerstone in the perfume industry, driving significant innovations and advancements. Currently, DPG is widely used as a solvent and fixative in fragrance formulations, offering excellent stability and compatibility with a wide range of perfume ingredients. Its low odor profile and ability to enhance the longevity of fragrances have made it an indispensable component in modern perfumery.
The current state of DPG application in the perfume industry is characterized by its versatility and efficiency. Perfumers utilize DPG to create complex fragrance compositions, leveraging its ability to dissolve both oil-soluble and water-soluble ingredients. This property allows for the development of more sophisticated and nuanced scent profiles, expanding the creative possibilities for fragrance designers.
Moreover, DPG's role in extending the shelf life of perfumes has significantly impacted product formulation and packaging strategies. Its stability and resistance to oxidation contribute to maintaining the integrity of fragrances over time, addressing a long-standing challenge in the industry.
Despite its widespread adoption, the application of DPG in perfumery faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential for skin sensitization in a small percentage of consumers. While DPG is generally considered safe for use in cosmetics, ongoing research is necessary to fully understand and mitigate any potential adverse reactions.
Another challenge lies in balancing the use of DPG with the growing demand for natural and sustainable fragrance ingredients. As consumers increasingly seek eco-friendly products, perfume manufacturers must innovate to incorporate DPG in formulations that align with these preferences without compromising on performance or scent quality.
The regulatory landscape also presents challenges for DPG application. Varying global regulations on the use of synthetic ingredients in cosmetics require manufacturers to navigate complex compliance requirements, potentially limiting the use of DPG in certain markets or product categories.
Furthermore, the perfume industry faces the challenge of optimizing DPG usage to achieve desired fragrance performance while managing production costs. As raw material prices fluctuate, finding the right balance between DPG concentration and other ingredients becomes crucial for maintaining product quality and profitability.
Lastly, the industry must address the technical challenge of enhancing DPG's compatibility with an ever-expanding range of fragrance molecules. As new aroma chemicals are developed, ensuring seamless integration with DPG-based formulations remains an ongoing area of research and development.
The current state of DPG application in the perfume industry is characterized by its versatility and efficiency. Perfumers utilize DPG to create complex fragrance compositions, leveraging its ability to dissolve both oil-soluble and water-soluble ingredients. This property allows for the development of more sophisticated and nuanced scent profiles, expanding the creative possibilities for fragrance designers.
Moreover, DPG's role in extending the shelf life of perfumes has significantly impacted product formulation and packaging strategies. Its stability and resistance to oxidation contribute to maintaining the integrity of fragrances over time, addressing a long-standing challenge in the industry.
Despite its widespread adoption, the application of DPG in perfumery faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential for skin sensitization in a small percentage of consumers. While DPG is generally considered safe for use in cosmetics, ongoing research is necessary to fully understand and mitigate any potential adverse reactions.
Another challenge lies in balancing the use of DPG with the growing demand for natural and sustainable fragrance ingredients. As consumers increasingly seek eco-friendly products, perfume manufacturers must innovate to incorporate DPG in formulations that align with these preferences without compromising on performance or scent quality.
The regulatory landscape also presents challenges for DPG application. Varying global regulations on the use of synthetic ingredients in cosmetics require manufacturers to navigate complex compliance requirements, potentially limiting the use of DPG in certain markets or product categories.
Furthermore, the perfume industry faces the challenge of optimizing DPG usage to achieve desired fragrance performance while managing production costs. As raw material prices fluctuate, finding the right balance between DPG concentration and other ingredients becomes crucial for maintaining product quality and profitability.
Lastly, the industry must address the technical challenge of enhancing DPG's compatibility with an ever-expanding range of fragrance molecules. As new aroma chemicals are developed, ensuring seamless integration with DPG-based formulations remains an ongoing area of research and development.
Existing DPG-based Fragrance Solutions
01 Use as a solvent in cosmetic formulations
Dipropylene glycol is commonly used as a solvent in various cosmetic and personal care products. It helps to dissolve and blend different ingredients, improving the overall stability and consistency of the formulation. This versatile solvent is particularly useful in products such as fragrances, skin care items, and hair care products.- Use as a solvent in cosmetic formulations: Dipropylene glycol is commonly used as a solvent in various cosmetic and personal care products. It helps to dissolve and blend different ingredients, improving the overall stability and consistency of the formulation. This versatile compound can be found in a wide range of products, including skincare, haircare, and fragrances.
- Application in pharmaceutical compositions: Dipropylene glycol is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations as a solvent and carrier for active ingredients. It can enhance the solubility and absorption of certain drugs, making it valuable in various medicinal preparations. This compound is particularly useful in topical and oral medications.
- Role in fragrance and perfume industry: In the fragrance industry, dipropylene glycol serves as a diluent and fixative for perfumes and colognes. It helps to stabilize volatile fragrance compounds, extend their longevity, and improve their overall performance. This makes it an essential component in many perfumery formulations.
- Use in industrial and household products: Dipropylene glycol finds applications in various industrial and household products due to its solvent properties and low toxicity. It is used in cleaning solutions, paints, lubricants, and antifreeze formulations. The compound's ability to mix with both water and oil makes it versatile for different product types.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Dipropylene glycol is generally considered to have low toxicity and environmental impact compared to some other solvents. It is biodegradable and has a relatively low vapor pressure, which reduces its potential for air pollution. These properties make it a preferred choice in many applications where safety and environmental concerns are important.
02 Application in pharmaceutical compositions
Dipropylene glycol finds applications in pharmaceutical formulations as a solvent and carrier for active ingredients. It can enhance the solubility and stability of certain drugs, improving their bioavailability. This compound is used in various dosage forms, including oral, topical, and injectable preparations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Role in industrial processes and products
In industrial applications, dipropylene glycol serves as a key component in the production of polyurethanes, resins, and plasticizers. It is also used as a heat transfer fluid and in the formulation of hydraulic fluids. The compound's properties make it suitable for use in various manufacturing processes and end products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in cleaning and degreasing agents
Dipropylene glycol is utilized in the formulation of cleaning and degreasing agents due to its excellent solvency properties. It can effectively dissolve oils, greases, and other organic compounds, making it useful in industrial cleaners, household cleaning products, and automotive degreasers.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application in personal care and hygiene products
In personal care and hygiene products, dipropylene glycol is used as a humectant and moisturizer. It helps to attract and retain moisture, improving the texture and feel of products such as lotions, creams, and deodorants. The compound also acts as a carrier for fragrances and other active ingredients in these formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in DPG and Fragrance Industry
The perfume industry's innovation driven by dipropylene glycol is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated at $50 billion. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread adoption by major players like Symrise, Firmenich, IFF, and Givaudan. These companies leverage dipropylene glycol's versatility as a solvent and fixative to enhance fragrance longevity and stability. The competitive landscape is characterized by continuous R&D efforts to develop novel applications and improve existing formulations, with a focus on sustainability and natural alternatives. Emerging trends include the use of dipropylene glycol in microencapsulation technologies and the development of hypoallergenic fragrances, indicating ongoing innovation potential in this established market.
Firmenich SA
Technical Solution: Firmenich has developed innovative applications of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) in perfumery, focusing on its role as a solvent and fixative. Their approach involves using DPG to enhance the longevity and diffusion of fragrances. They have created proprietary blends that optimize the interaction between DPG and various fragrance molecules, resulting in improved performance and stability of perfumes[1]. Firmenich has also explored the use of DPG in combination with other solvents to create unique olfactory experiences and improve the overall fragrance profile[3].
Strengths: Extensive research in DPG applications, proprietary blending techniques, and improved fragrance performance. Weaknesses: Potential overreliance on DPG, which may limit exploration of alternative solvents.
International Flavors & Fragrances, Inc.
Technical Solution: IFF has leveraged DPG in developing advanced encapsulation technologies for fragrance delivery. Their approach involves using DPG as a carrier for microencapsulated fragrance oils, allowing for controlled release and extended wear time of perfumes[2]. IFF has also explored the use of DPG in creating water-based fragrance systems, addressing the growing demand for more sustainable and environmentally friendly perfume formulations[4]. Additionally, they have invested in research to understand the interaction between DPG and various fragrance molecules, optimizing formulations for different product applications[5].
Strengths: Advanced encapsulation technologies, focus on sustainable formulations, and extensive research into DPG-fragrance interactions. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in balancing performance with sustainability goals.
Core Innovations in DPG Formulation
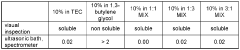
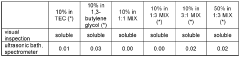
Solvent mixtures comprising 1,3-butylene glycol and triethyl- citrate
PatentWO2023144363A1
Innovation
- A solvent mixture comprising 1,3-butylene glycol and triethyl citrate, which is derived from renewable resources, is nearly odorless, colorless, and biodegradable, offering excellent solubility properties for a broad range of fragrance compounds and compositions, and is stable under various conditions, making it a suitable replacement for existing solvents like dipropylene glycol.
Solubilizing system for volatile ingredients
PatentWO2008110995A2
Innovation
- A solubilizing system based on DL-panthenol and glycols, particularly dipropylene glycol, which allows for higher fragrance concentrations (up to 5% w/w) without affecting product appearance, stability, or viscosity, and enables effective solubilization of hydrophobic fragrances through a synergistic mechanism with the surfactant system.
Environmental Impact of DPG in Fragrances
The environmental impact of Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) in fragrances is a critical consideration for the perfume industry as it strives to balance innovation with sustainability. DPG, a synthetic compound widely used as a solvent and fixative in perfumes, has both positive and negative environmental implications that warrant careful examination.
From a positive perspective, DPG's low volatility contributes to the longevity of fragrances, potentially reducing the frequency of application and, consequently, the overall consumption of perfume products. This characteristic may lead to a decrease in packaging waste and transportation-related emissions associated with fragrance distribution.
However, the production of DPG involves petrochemical processes that can have significant environmental footprints. The synthesis of DPG typically requires propylene oxide as a precursor, which is derived from fossil fuels. This reliance on non-renewable resources raises concerns about long-term sustainability and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing.
When released into the environment, DPG demonstrates relatively low toxicity to aquatic life and undergoes biodegradation in both water and soil. Nevertheless, its widespread use in personal care products means that substantial quantities may enter wastewater systems. While most modern treatment facilities can effectively remove DPG, there is still potential for environmental accumulation in areas with inadequate wastewater management.
The perfume industry has been exploring alternatives to DPG, including bio-based solvents derived from renewable resources. These alternatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of fragrance production while maintaining the desired performance characteristics. However, the transition to more environmentally friendly options faces challenges in terms of cost, scalability, and consumer acceptance.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of fragrance ingredients. The European Union's REACH regulation, for instance, requires comprehensive safety assessments for chemicals, including their environmental fate. This regulatory pressure is driving the industry to invest in research and development of greener alternatives and more sustainable production methods for DPG.
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is growing demand for eco-friendly fragrances. This shift in consumer preferences is prompting perfume manufacturers to reassess their formulations and consider the entire lifecycle impact of their products, including the role of solvents like DPG.
In response to these challenges, some companies are implementing closed-loop systems for DPG recovery and reuse, minimizing waste and reducing the need for new production. Additionally, advancements in green chemistry are paving the way for more sustainable synthesis methods for DPG, potentially mitigating its environmental impact without compromising its functionality in fragrances.
From a positive perspective, DPG's low volatility contributes to the longevity of fragrances, potentially reducing the frequency of application and, consequently, the overall consumption of perfume products. This characteristic may lead to a decrease in packaging waste and transportation-related emissions associated with fragrance distribution.
However, the production of DPG involves petrochemical processes that can have significant environmental footprints. The synthesis of DPG typically requires propylene oxide as a precursor, which is derived from fossil fuels. This reliance on non-renewable resources raises concerns about long-term sustainability and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing.
When released into the environment, DPG demonstrates relatively low toxicity to aquatic life and undergoes biodegradation in both water and soil. Nevertheless, its widespread use in personal care products means that substantial quantities may enter wastewater systems. While most modern treatment facilities can effectively remove DPG, there is still potential for environmental accumulation in areas with inadequate wastewater management.
The perfume industry has been exploring alternatives to DPG, including bio-based solvents derived from renewable resources. These alternatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of fragrance production while maintaining the desired performance characteristics. However, the transition to more environmentally friendly options faces challenges in terms of cost, scalability, and consumer acceptance.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of fragrance ingredients. The European Union's REACH regulation, for instance, requires comprehensive safety assessments for chemicals, including their environmental fate. This regulatory pressure is driving the industry to invest in research and development of greener alternatives and more sustainable production methods for DPG.
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is growing demand for eco-friendly fragrances. This shift in consumer preferences is prompting perfume manufacturers to reassess their formulations and consider the entire lifecycle impact of their products, including the role of solvents like DPG.
In response to these challenges, some companies are implementing closed-loop systems for DPG recovery and reuse, minimizing waste and reducing the need for new production. Additionally, advancements in green chemistry are paving the way for more sustainable synthesis methods for DPG, potentially mitigating its environmental impact without compromising its functionality in fragrances.
Regulatory Framework for DPG in Cosmetics
The regulatory framework for Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) in cosmetics is a critical aspect of its use in the perfume industry. Governed by various international and regional bodies, these regulations ensure the safe and appropriate use of DPG in cosmetic products, including fragrances.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of DPG in cosmetics under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA classifies DPG as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance, allowing its use in cosmetic formulations. However, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products and must comply with labeling requirements.
The European Union regulates DPG through the European Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009. This comprehensive legislation sets safety standards and restrictions for cosmetic ingredients. DPG is listed in Annex V of the regulation as a permitted preservative, with a maximum concentration of 1.0% in leave-on products and rinse-off products.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. DPG is approved for use in cosmetics and is listed in the Japanese Standards of Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI) with specific purity requirements.
The International Fragrance Association (IFRA) provides global guidelines for the safe use of fragrance ingredients. While DPG itself is not restricted by IFRA, the association's standards indirectly impact its use in perfume formulations by regulating other ingredients that may be used in conjunction with DPG.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which affects the labeling and safety data sheet requirements for DPG when used in cosmetic products. This system ensures consistent communication of hazard information across different regions.
Regulatory bodies often require manufacturers to conduct safety assessments and provide documentation on the use of DPG in their products. This includes toxicological data, exposure assessments, and stability studies to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of DPG in cosmetic formulations.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to address environmental concerns. Some regions are implementing stricter guidelines on the biodegradability and environmental impact of cosmetic ingredients, which may influence future regulations on DPG use.
The regulatory landscape for DPG in cosmetics continues to evolve, with ongoing research and risk assessments informing policy decisions. Manufacturers and formulators must stay abreast of these changes to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust in their products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of DPG in cosmetics under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA classifies DPG as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance, allowing its use in cosmetic formulations. However, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products and must comply with labeling requirements.
The European Union regulates DPG through the European Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009. This comprehensive legislation sets safety standards and restrictions for cosmetic ingredients. DPG is listed in Annex V of the regulation as a permitted preservative, with a maximum concentration of 1.0% in leave-on products and rinse-off products.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. DPG is approved for use in cosmetics and is listed in the Japanese Standards of Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI) with specific purity requirements.
The International Fragrance Association (IFRA) provides global guidelines for the safe use of fragrance ingredients. While DPG itself is not restricted by IFRA, the association's standards indirectly impact its use in perfume formulations by regulating other ingredients that may be used in conjunction with DPG.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which affects the labeling and safety data sheet requirements for DPG when used in cosmetic products. This system ensures consistent communication of hazard information across different regions.
Regulatory bodies often require manufacturers to conduct safety assessments and provide documentation on the use of DPG in their products. This includes toxicological data, exposure assessments, and stability studies to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of DPG in cosmetic formulations.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to address environmental concerns. Some regions are implementing stricter guidelines on the biodegradability and environmental impact of cosmetic ingredients, which may influence future regulations on DPG use.
The regulatory landscape for DPG in cosmetics continues to evolve, with ongoing research and risk assessments informing policy decisions. Manufacturers and formulators must stay abreast of these changes to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust in their products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!